In the tech world, you’ve probably noticed plenty of job openings specifically for full stack developers, and that is surely for good reason. A full stack developer builds the foundation of a website or application from start to finish. In simple terms, they work on both the front-end, which is what users see and interact with, and the back-end, which is the server, database, and logic that keep everything running.
This versatility makes them one of the most in-demand roles in 2025. Companies choose to hire full-stack developers because they are fit to conduct both design and functionality, making projects more efficient. This means you can have better job opportunities, greater flexibility, and the ability to build complete products on your own.
We understand that with so many languages, frameworks, and tools out there, it’s easy to feel lost. That’s exactly why we have made a beginner-friendly roadmap for you. This will help you focus on what to learn first, how to grow your skills step by step, and how to eventually land the kind of projects or jobs you’re aiming for.
Who is a Full Stack Developer?
A full stack developer is someone who can work on both sides of a website or app: the front-end, which users interact with, and the back-end, which handles the logic, servers, and databases. This means they’re capable of taking an idea and turning it into a working product without depending entirely on others for each layer of development.
To be effective, full stack developers usually learn a mix of languages, frameworks, and database tools. This broader skill set allows them to step into different kinds of roles depending on the project.
What responsibilities do they mainly fulfill?
- In startups, they are often hired to build and launch products quickly.
- In larger companies, they contribute by working across teams and making sure features are complete from design to functionality.
- In freelance work, they have the flexibility to take on projects that need both design and development.
If you’re wondering whether this career path is suitable for you, then do read along for a better understanding of full-stack development.



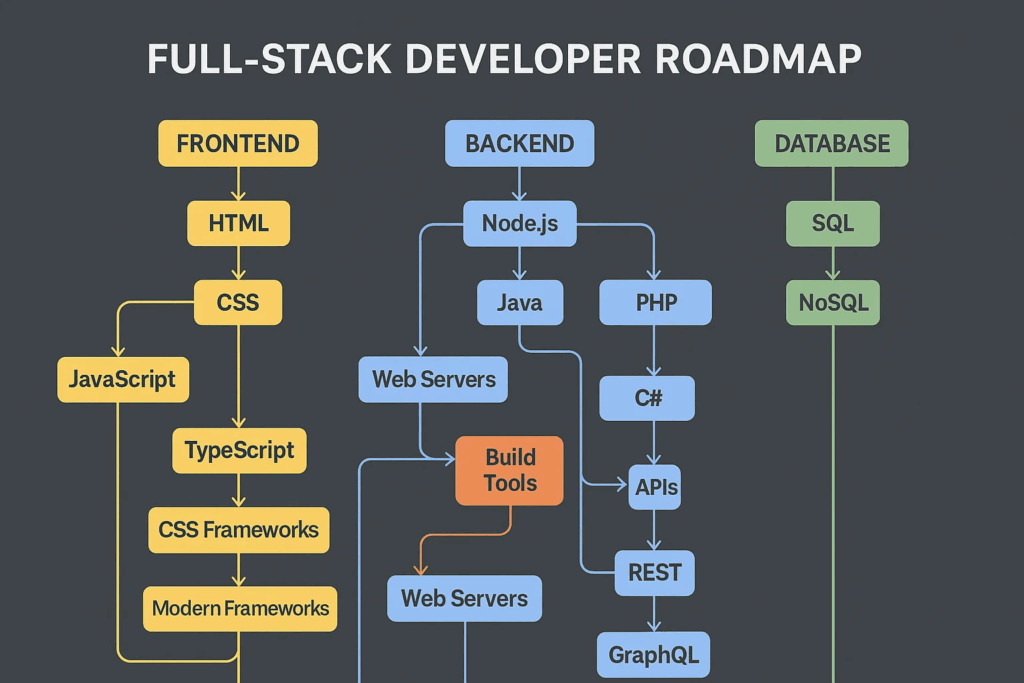
Step-by-Step Full Stack Developer Roadmap (2025 Edition)
1. Choose a Technology Stack
Before starting your journey, it’s important to understand what a tech stack is. Simply put, it’s the combination of programming languages, frameworks, and tools you’ll use to build applications. As a full stack developer, your stack defines how you handle both the front-end and back-end of a project.
Some of the well-known stacks include:
- MERN (MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js): It is popular for modern web apps and startups.
- MEAN (MongoDB, Express, Angular, Node.js): Great for enterprise-grade applications.
- LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP): You can say it’s a traditional option still used for server-heavy apps.
- JAMStack (JavaScript, APIs, Markup): Modern “headless” stack, known for speed and scalability.
How do you decide?
Think about your career goals here. If you’re aiming for startups, MERN or JAMStack can be helpful. For enterprise work, MEAN or LAMP might be more suitable. The key is to pick one and go deep before branching out.
2. Begin with Front-End Development
Front-end development focuses on building the user interface of websites and applications, which makes it an essential skill for every full-stack developer to learn. Here’s what you can do:

Kick off your full-stack path — join a free live masterclass and learn from the makers.
Scaler Masterclasses
Learn from industry experts and accelerate your career with hands-on, interactive sessions.
Clear Your Foundations
Start with the basics like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Here is how much time each can take:
- HTML: Learn to structure pages with headings, links, forms, and tables.
- CSS: Focus on styling, layouts (Flexbox, Grid), and responsive design so your pages look good across devices.
- JavaScript: Get comfortable with variables, functions, events, and DOM manipulation to add interactivity.
Responsive Design & Accessibility
Modern websites should be mobile-friendly and accessible. And so, you should focus on learning media queries, semantic HTML, and ARIA labels. This not only improves user experience but also boosts SEO.
Enhancing User Experience
Once your coding skills become stronger, try moving on to design principles. A basic understanding of tools like Figma can help you translate design files into code. Experiment with animations, smooth transitions, and interactive elements to make your projects engaging.
Front-End Frameworks
Once you’re confident with vanilla JavaScript, move to frameworks. Start with React, which is widely used, or explore Vue and Angular, which are more enterprise-focused. Don’t rush into these; having solid JS fundamentals will make frameworks much easier.
Projects You Can Try
Apply your learning through small but impactful projects:
- Personal portfolio website
- A responsive landing page
- A simple to-do app or quiz game
Version Control with Git/GitHub
As soon as you begin projects, learn Git basics, i.e, commits, branching,and merging. Push your code to GitHub; it doubles as both a portfolio and a way to network with other developers. Recruiters often check GitHub profiles, so it’s worth investing time here early on.
You should dedicate about 2–3 months to mastering front-end. By then, you’ll have both the confidence and the portfolio pieces to move forward.
3. Move on to Back-End Development
After wrapping up front-end development essentials, it’s time to learn the back-end. This is where you’ll manage logic, databases, and security.

Exploring the full-stack journey? Jump into a free live masterclass with senior engineers.
Scaler Masterclasses
Learn from industry experts and accelerate your career with hands-on, interactive sessions.
Here’s what you can do step-by-step:
Choose a Language
Try to pick one language and stick with it for starters. You choose from languages like:
- Node.js: Great for JavaScript learners and widely used in startups.
- Python: Beginner-friendly, with strong frameworks like Django and Flask.
- Java: Enterprise-grade, especially with Spring Boot.
- Go: Lightweight, fast, and increasingly popular for scalable apps.
Use Frameworks for Speed
Frameworks reduce repetitive coding and provide structure. For example:
- Express.js (Node.js) is minimal and flexible.
- Django (Python) has a batteries-included approach.
- Spring Boot (Java) is robust for enterprise solutions.
Working with APIs
APIs connect your front-end to the back-end. Learn how to build and consume both REST and GraphQL APIs. Start with CRUD operations, understand status codes, and practice with tools like Postman or Swagger for testing.
Database Integration
Every app needs data storage. Use these tools for better functionality:
- SQL databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL): These are structured and relational.
- NoSQL databases (MongoDB): Flexible, document-based.
Learn how to write queries, manage relationships, and optimize performance with indexes.
Authentication & Security
Building security is an absolute must for an App. Explore basics like JWT (JSON Web Tokens) for user sessions, OAuth for third-party logins, and password hashing/validation to protect user data.
Mini Projects to Try
The best kind of practice that you can achieve is by doing real and relevant projects, which can also be a part of your portfoli., Try these for starters:
- A Blog CMS for a content management system
- An Authentication system for login/register
- An Expense tracker with CRUD and reports
By the end of back-end training, you’ll have the skills to build functional, secure applications and connect them seamlessly with your front-end.
4. Prepare Full-Stack Integration Projects
After learning both front-end and back-end, the next step is to combine them into a working application. This is where you see how everything connects from user interactions to database updates.
A great way to practice is by building a full-stack MERN, i.,e MongoDB, Express, React, Node.js application. It could be a task manager, a blog platform, or even a small e-commerce site. The goal is to get comfortable with connecting APIs, handling data flow, and managing user authentication.
Don’t forget hosting and repository management. Use platforms like Vercel, Netlify, or Heroku to deploy your app, and keep your code organized on GitHub. Good commit practices, clear folder structures, and documentation not only help you stay organized but also showcase your work professionally to potential employers.
Thistage willll help youlevel upp your skills as a full-stack developer and overall help you add interesting projects to your portfolio.
Turn the roadmap into results — learn live from engineers, apply your full-stack skills, free to join.
Scaler Masterclasses
Learn from industry experts and accelerate your career with hands-on, interactive sessions.
Build Your Developer Portfolio
Having a strong portfolio is one of the most important tools for a full-stack developer. It’s often the first thing hiring managers see, and your project level can even set you apart from other candidates. A good portfolio demonstrates your problem-solving skills, coding style, and ability to deliver complete projects.

Here’s What to Include:
- Projects of varying complexity: Include beginner projects to show learning progression, intermediate projects to demonstrate practical skills, and at least one advanced project that reflects full-stack integration.
- Links to GitHub repositories and live demos: Allow viewers to explore your code and interact with your applications.
- Documentation: Clear ReadMe files explain your thought process, project setup, and any challenges you overcame.
- Showcasing on GitHub:
- Pin your best repositories to highlight them immediately.
- Maintain consistent activity to reflect ongoing learning.
- Ensure your ReadMe files are detailed yet concise, showcasing your skills and professionalism.
A well-organized portfolio not only boosts your confidence but also makes it easier for recruiters to understand your capabilities. Try to always turn your practice projects into a workable piece to add credibility to your skills.
Other Useful Skills For a Full-Stack Developer
Being a successful full stack developer depends on your technical as well as your soft skills. These soft skills help employers know whether you can handle working in a team, and with what mindset you will be performing your tasks. Trust us when we say these qualities are very important.
Improve Soft Skills Like:
- Communication: Explaining complex ideas in simple terms is much needed when working with clients or teammates who may not be technical.
- Problem-Solving: Bugs, errors, and unexpected challenges are part of the job; your ability to troubleshoot and think logically is just as important as coding.
- Collaboration: Most development happens in teams, so knowing how to share tasks, review code, and give constructive feedback makes you a stronger contributor.
DevOps & Cloud (Advanced Track):
- CI/CD Basics: Understanding continuous integration and delivery pipelines helps you deploy code efficiently and catch errors early.
- Cloud Platforms: Familiarity with AWS, GCP, or Azure can give you an edge since many companies now run their apps on the cloud.
- Linux & Docker: Even basic knowledge of Linux commands or containerization with Docker makes you versatile when handling deployments and server environments.
These additional skills can help boost your resume. Try to inculcate as many as you can and solidify the ones that are commonly asked by companies.
How to Land Your First Full-Stack Developer Job?
Getting your first full-stack role requires various steps after gaining technical and soft skills. It’s a whole process that requires learning about presenting yourself, preparing, and searching for where to apply.

Here are some usual steps:
Build Your Resume & LinkedIn
- Use skill-based bullet points that show what you actually built and the tools you used. “Built REST API with Node.js and Express, improving response time by 30%,” for example.
- Include links to your GitHub repos, live projects, and demos. Employers appreciate seeing your work firsthand.
- On LinkedIn, optimize your headline and summary with full-stack-relevant keywords (React, Node.js, API, etc.), and make sure your most impressive projects are pinned or highlighted. Growth in profile views and recruiter messages often follows from having a well-organized GitHub + LinkedIn profile.
Interview Preparation
Brush up on DSA basics (arrays, strings, sorting, searching) and introductory system design; these are common in full-stack interviews.
Do mock interviews or pair programming.
Be ready to explain your projects, how you built them, what decisions you made, and what you’d do differently if starting again. Interviewers often ask about trade-offs.
Where to Apply for Full-Stack Developer Jobs?
There are various Job portals and platforms where you can find genuine listings and openings for the role. We will mention some platforms below:
| Platform | Openings (approx.) & Salary for Beginners |
| Approx. 4,000+ full-stack/junior full-stack roles in India right now. Entry-level salaries range from ₹3.5-₹6 LPA depending on location. | |
| Indeed | Approx. 8000+ jobs are listed; entry/full-stack engineers commonly start at US $50,000-70,000 or ₹3-6 LPA in India for freshers. |
| Glassdoor | Approx. 8000 + job listings are often available. For entry-level full-stack roles in India, salaries are often ₹3-6 LPA, depending on city and company. |
| AngelList / Wellfound | Frequent startup full-stack role openings; pay varies more (lower base, possibly equity), but beginners can expect ₹3-5 LPA+ in India. Specific salary data, which is less available publicly, is not disclosed. |
| Naukri | Approx. 53,000+ roles available on the portal, and the entry-level salary remains ₹3-6 LPA for freshers. |
Other Platforms to Explore:
- Company Websites: Check career pages of startups such as Zoho, Razorpay, Swiggy, and enterprises such as Microsoft, Accenture, Infosys.
- Referrals: Networking on LinkedIn or through alumni/tech meetups increases your chances significantly.
- Freelance Platforms: Upwork, Fiverr, and Toptal let you gain project-based experience while building your portfolio.
Try to check at least 9-10 requirements of a company with a salary range you desire, and try to upskill yourself in accordance with, while it might take time, so always keep checking the trends of requirements until it’s your turn to apply.
How Scaler Academy Can Help in Your Full-Stack Journey?
Learning Full-stack development can get a bit confusing, we understand this as our students always seem to worry about which tools, projects, or skills to work on. At Scaler Academy, we have included everything a learner requires to become an industry-ready full stack developer, here you will get live classes led by industry experts, 1:1 mentorship to clear roadblocks, and structured projects that showcase your skills to recruiters. The program also emphasizes GitHub readiness and interview preparation so you’re job-ready, not just course-complete.
Explore the Scaler Full Stack Developer Course to see how you can accelerate your journey.
Explore “Startup School: Prompt to Prototype partnered with Google” and check how it can help you build AI-powered prototypes faster.
Conclusion
Becoming a full-stack developer is a step-by-step process, choosing a stack, mastering front-end and back-end, and building projects that tie everything together. The key is consistent practice and real-world application. Start small, refine your skills, and gradually take on bigger projects.
Whether it’s an internship, a freelance gig, or your first full-time role, every project brings you closer to expertise. Start today, to explore a variety of skills to become a full stack developer.
Read These Important Roadmaps: More Paths to Career Success
FAQs: Full Stack Developer Roadmap
What is the path to be a full stack developer?
Start with front-end basics i.e HTML, CSS, JavaScript, then move to back-end languages which are Node.js, Python, or Java, and learn databases SQL/NoSQL. Once you can integrate both, work on full-stack projects and refine your portfolio.
Is 3 months enough to become a full stack developer?
Three months can help you grasp basics, but becoming job-ready usually takes 6-12 months of consistent learning and practice.
Is full stack developer in demand in 2025?
Yes, demand is increasingly growing. With businesses moving online, the versatility of handling both front-end and back-end makes full-stack roles highly valuable.
Is being a full stack developer a tough job?
It’s challenging because you work across multiple layers of development, but the variety also makes it exciting and rewarding. With practice and guidance, it becomes manageable.
Do I need a computer science degree to become a full stack developer?
No, it’s not mandatory. Many developers come from non-CS backgrounds. What matters most is practical skills, projects, and problem-solving ability.