Kafka vs ActiveMQ - What are the Differences?
What is Apache Kafka?
To efficiently manage their expanding data and transition from batch processing to real-time processing, LinkedIn created the open-source stream-processing application Apache Kafka (which was eventually donated to Apache).
Some large enterprises dealing with large amounts of data find this to be the best solution due to its scalability, adaptability, and fault tolerance.
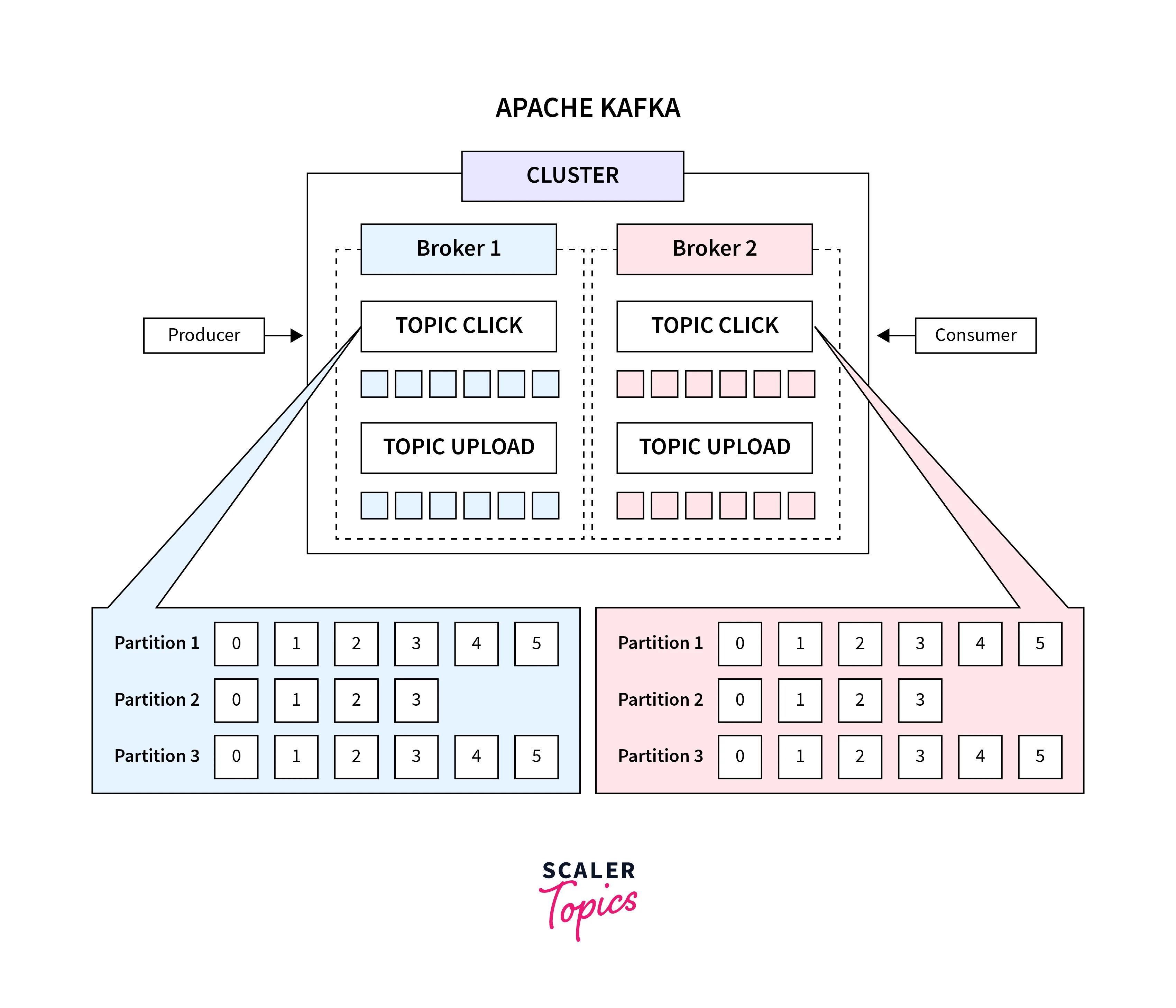
Consists of several components: Brokers, Topics, Producers, Consumers and Partitions.
- The Kafka ecosystem is made up of both producers and consumers. Producers and consumers are considered external players for our purposes.
- Kafka's Zookeeper service and Kafka cluster are part of the internal ecology. Zookeeper is a solution for managing and coordinating Kafka brokers that uses distributed configuration and synchronizing.
- When a broker is added to or fails in the Kafka system, Zookeeper alerts producers and consumers.
- Load balancing is the responsibility of brokers inside a Kafka cluster.
- To handle the increased traffic, Zookeeper launches several Kafka brokers inside the Kafka cluster.
Features of Apache Kafka:
-
Scalability
- Primarily designed to handle large amounts of data, it allows users to grow and expand as their needs grow.
- Basically, it handles scalability in four dimensions which are Event Connectors, Producers, Processors, and Consumers.
- It scales easily to multiple nodes or machines, so it can reliably handle very large amounts of incoming data. Plus, it scales proportionally with no downtime.
-
Fault Tolerance
- Fault tolerance guarantees that responses are not lost in the case of message delivery system node failures or network outages.
- Efficiently handles master and database errors such as Aggregate and join using windows. Perfect for mission-critical applications that require high reliability.
-
Stream processing
- Kafka's built-in stream processing capabilities allow users to quickly access real-time insights from data streams.
- This allows you to apply advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to streaming data to uncover valuable insights.
-
Durability
- Uses the distributed commit protocol to ensure messages are persisted on disk.
- This ensures that your messages are preserved and not lost in the event of a system crash or network disruption.
-
Low latency
- A low-latency messaging feature, Apache Kafka can provide extremely fast messaging.
- It is therefore ideal for applications that require near-real-time performance. It also provides developers with a high-speed messaging system with strong order guarantees.
- Pros of Apache Kafka:
- High-performance server cost-cutting method.
- Effortlessly manages large amounts of data streams.
- It is very scalable as it is connected to many other apps.
- Scales horizontally over numerous servers while preserving data order.
- Cons of Apache Kafka:
- There is no full set of monitoring tools.
- Absence of some Messaging Paradigms and Problems with Message Tweaking
- Wildcard subject selection is not supported.
Use Cases:
-
Sourcing for Events
- Event sourcing is a design style in which state changes are documented as a time-ordered sequence of records.
- Kafka's capacity for very big stored log data makes it a great backend for this type of application.
-
Commit Log
- Kafka can function as an external commit log for a distributed system.
- The log aids in the replication of data across nodes and serves as a way for failing nodes to recover their data.
-
Website Activity Monitoring
- In order to reconstruct a user activity tracking pipeline as a collection of real-time publish-subscribe feeds, Kafka's original use case was created.
- This implies that site activity (page views, searches, or other actions taken by users) is published to core themes, with one topic for each sort of activity.
- Subscriptions are offered for a variety of use cases, include real-time processing, real-time monitoring, and loading into Hadoop or offline data warehousing systems for offline processing and reporting.
- Because multiple activity messages are created for each user page visit, activity tracking is frequently quite high in volume.
What is ActiveMQ?
The Apache Software Foundation built ActiveMQ, a high-performance, open-source messaging system. This messaging proxy is intended to enhance application messaging.
It essentially serves as a message bridge between multiple components located on different servers or written in various languages.
- ActiveMQ transfers messages between client applications, producing messages and submitting them for delivery, and consumers receiving and processing messages.
- Each message is routed by the ActiveMQ broker through a messaging endpoint known as a destination (in ActiveMQ Classic) or an address (in Artemis).
- Both ActiveMQ versions support point-to-point messaging, in which the broker routes each message to one of the available consumers in a round-robin pattern, as well as publish/subscribe (or "pub/sub") messaging, in which the broker delivers each message to every consumer who is subscribed to the topic (in ActiveMQ Classic) or address (in ActiveMQ Express) (in ActiveMQ Artemis).
Features of ActiveMQ
-
Multiple Connection Options
- Supports a variety of connection protocols, including XMPP, UDP, STOMP, HTTP/S, and SSL.
- This gives a variety of connecting choices. Furthermore, it allows different systems to communicate using their chosen protocols.
-
Compatible with JMS
- Developed to meet the JMS 1.1 specifications. In essence, the JMS specification defines a standard method for synchronous and asynchronous message delivery, as well as durability and single message delivery.
-
Multi Platform
- Client APIs are provided for all prominent programming languages, including Python, PHP, Perl,.NET, C, C++, Java, Ruby, and others.
- Runs in the JVM, however clients can be written in any supported language.
-
Architecture with Pluggable Components
- Moreover, ActiveMQ allows users to modify a variety of settings, including security.
- Fundamentally, you tailor permission and authentication methods based on the needs of the application.
-
Security
- It features include authentication, permission, SSL encryption, and so forth. These security mechanisms guarantee that communication between clients and servers is secure and efficient.
- Overall, you have total control over who has access to the message broker and what actions may be performed on it.
- Pros of ActiveMQ:
- For connection, many protocols such as HTTP/HTTPS, STOMP, and UDP are supported.
- Client APIs are available for a variety of languages, including Java,.Net, Python, Ruby, and many more.
- It enables you to customize the permission and verification necessary for your communication to your specific requirements.
- Ensures consistent communication between the producer and the customer.
- Scales easily move up or down to suit varying demands.
- Cons of ActiveMQ:
- Any message that you load, copy, drag & drop, or amend will be added to the queue's end.
- QueueExplorer truly transmits new messages to ActiveMQ whenever you update or copy a message. As a result, several characteristics, including ID and timestamp, could be altered.
- Limited documentation that's difficult to understand for new users.
- Security breaches are possible if not configured correctly.
- ActiveMQ does not offer thorough monitoring features, making it challenging to keep track on message broker activity.
Use Cases:
-
Data Streaming over the Internet
- This use case focuses on ActiveMQ's Ajax functionality.
- People are increasingly requesting real-time data streaming directly into web browsers. For example, streaming financial stock prices, live IM discussions, live auctions, or dynamically updating live information and news are all examples.
- Integrate ActiveMQ within a web container and provide tight web connectivity to enable HTTP POSTs to publish messages and sluggish JavaScript HTTP GET operations to receive messages in this use case.
-
HTTP RESTful API for messaging
- This use case is concerned with connection, as well as cross-language and cross-technology connectivity.
- Offer a simple cross-language and technology agnostic HTTP interface to the message broker for posting and receiving messages.
- To send a message, use HTTP POST to the Message Broker, and to receive one, use HTTP GET. To specify the destination, use the URL and request parameters.
-
Market data distribution with high performance
- This application is concerned with throughput and efficient routing. The goal is to disseminate vast amounts of rapidly changing data as soon as feasible across a wide network.
- Generally, throughput and performance are critical - since the amount of data and rate of change is quite large, persistence is seldom employed, and missing a message is frequently acceptable in times of failure because old data is often not required, and the current prices are what count.
Key Differences Between Kafka and ActiveMQ

| Activemq | Kafka |
|---|---|
| It uses a conventional messaging system to handle a modest quantity of data. | It's a distributed system designed to handle massive amounts of data. |
| It supports transactions.JMS Transactions and XA Transactions are the two tiers of transaction support. Transactions are handled by TransactionStore. TransactionStore will cache all messags and ACKS until commit or rollback occurs. | Initially, Kafka didn't allow transactions, but from the 0.11 version, it has some level of support for transactions. |
| It is a platform for push messaging, where the providers send the messages to the users. | The customers draw the messages from the brokers on this pull-style messaging platform. |
| As the number of users increases, both queue and topic performance suffers. | With more customers, it doesn't become slower. |
| A feature known as JMS API message selector enables a customer to choose the messages in which they are most interested. Thus, the JMS and not the applications must do the task of filtering messages. | Kafka is unclear of any brokers' filters that could guarantee that messages picked up by customers adhere to a specific standard. Either consumers or applications must perform the filtering. |
| It keeps track of every message's delivery status, which reduces throughput. | Producers of Kafka don't wait for Broker acknowledgements. As a result, brokers are able to write messages at a very rapid rate, increasing throughput. |
Conclusion
- The most common message brokers are ActiveMQ and Apache Kafka
- They assist businesses in streamlining their technical infrastructure and easily connecting applications, to start with. Second, they offer smooth data flow between applications without requiring manual intervention or coding by serving as an intermediary.
- The advantages of Apache Kafka are worth manages large amounts of data streams and scalability whereas activemq is worth for scaling up or down easily to handle fluctuating workloads.
- On the one hand, ActiveMQ offers out-of-the-box functionality to make information sharing between client applications extremely quick, while Apache Kafka is a distributed streaming platform that manages massive data streams in real time.
