TestNG Annotations in Selenium Webdriver
Overview
TestNG annotations in Selenium play a vital role in Selenium WebDriver testing, providing a mechanism to structure and control test scripts effectively. TestNG annotations are special markers added to methods or classes, defining their behavior during test execution. They offer features like test configuration, grouping, prioritization, dependency management, and reporting. By leveraging TestNG annotations in Selenium, testers can enhance the reliability, maintainability, and flexibility of their Selenium test scripts.
What are TestNG Annotations?
TestNG annotations are special markers or labels used in TestNG, a testing framework for Java, to define the behavior and characteristics of test methods or classes during test execution. These annotations in Selenium provide instructions and configurations to the TestNG framework, allowing testers to control various aspects of test execution.
TestNG annotations in Selenium can be applied to methods or classes, enabling testers to define the order of test execution, handle dependencies between tests, set up preconditions, perform cleanup tasks, and more. They help in organizing and structuring test scripts effectively.
Some commonly used TestNG annotations in Selenium WebDriver testing include:
- @Test:
Marks a method as a test case, indicating that it should be executed as part of the test suite. - @BeforeSuite:
Specifies a method that should be executed before all test methods in a suite. - @AfterSuite:
Specifies a method that should be executed after all test methods in a suite.
These annotations help testers in structuring and organizing their test cases, defining the setup and teardown operations, and controlling the flow of test execution. By utilizing TestNG annotations in Selenium effectively, testers can create more maintainable and scalable test suites in Selenium WebDriver.
Why Use TestNG with Selenium?
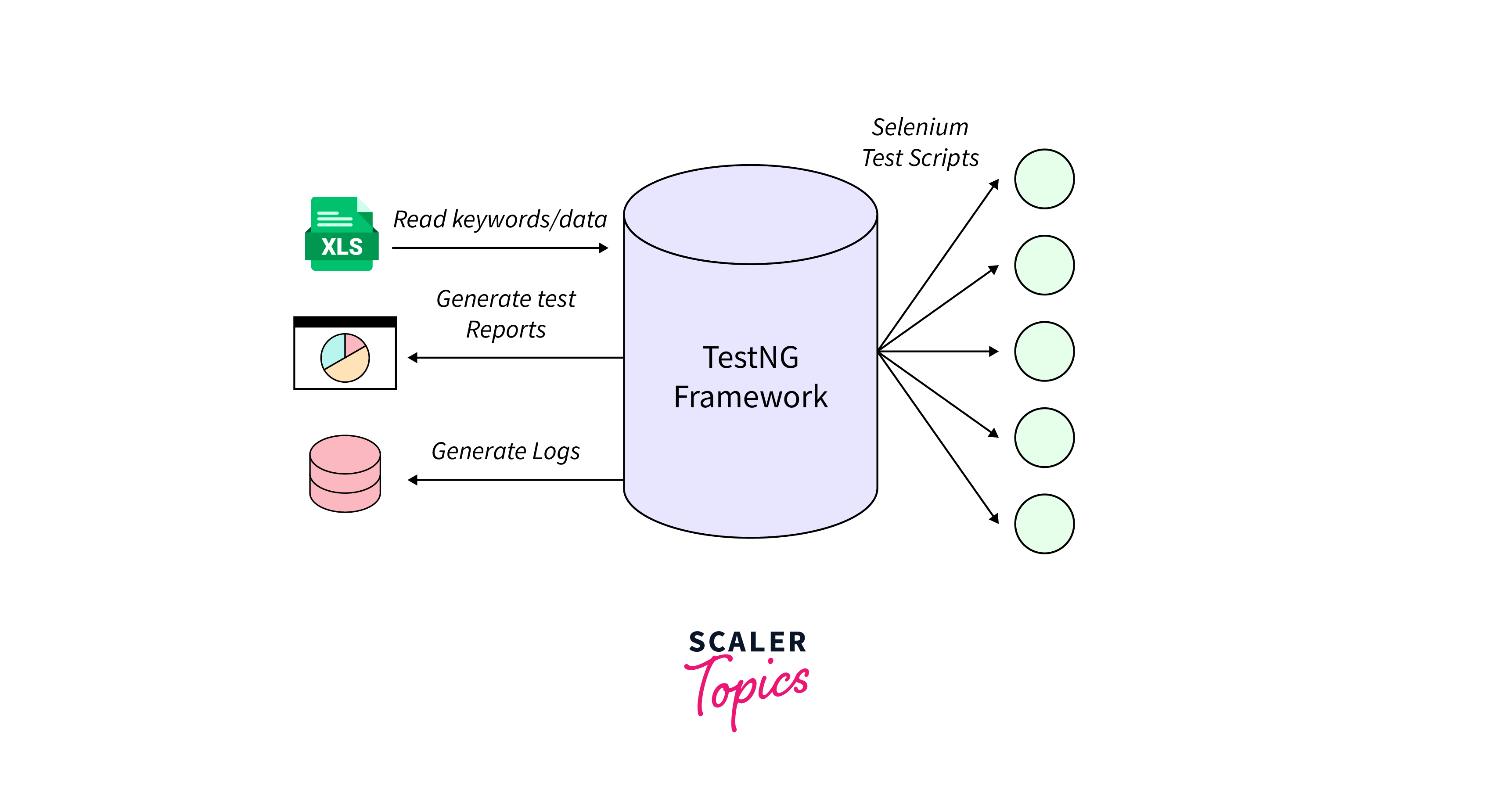
Using TestNG with Selenium WebDriver offers several advantages that makes it a popular choice among automation testers. Let's explore some key reasons for using TestNG in conjunction with Selenium:
- Enhanced Test Configuration:
TestNG allows testers to configure various aspects of test execution, such as defining the test order, parallel execution, data-driven testing, and test reporting. This flexibility helps in creating comprehensive and manageable test suites. - Powerful Test Grouping and Prioritization:
TestNG enables the categorization of test cases into groups based on different criteria, such as functionality, priority, or risk level. It provides mechanisms to prioritize the execution order of test methods, ensuring critical scenarios are tested first. - Flexible Test Dependency Management:
TestNG allows the establishment of dependencies between test methods, ensuring that tests run in a specific order. This feature is particularly useful when one test case relies on the successful execution of another test case. - Rich Reporting and Logging Capabilities:
TestNG provides detailed HTML reports with comprehensive information about test execution, including test status, execution time, and stack traces in case of failures. Additionally, it allows customizing the reports to meet specific project requirements.
Types of TestNG Annotations in Selenium
TestNG provides a wide range of annotations in Selenium to control the execution flow and behavior of test scripts. Let's explore the most commonly used annotations in Selenium WebDriver:
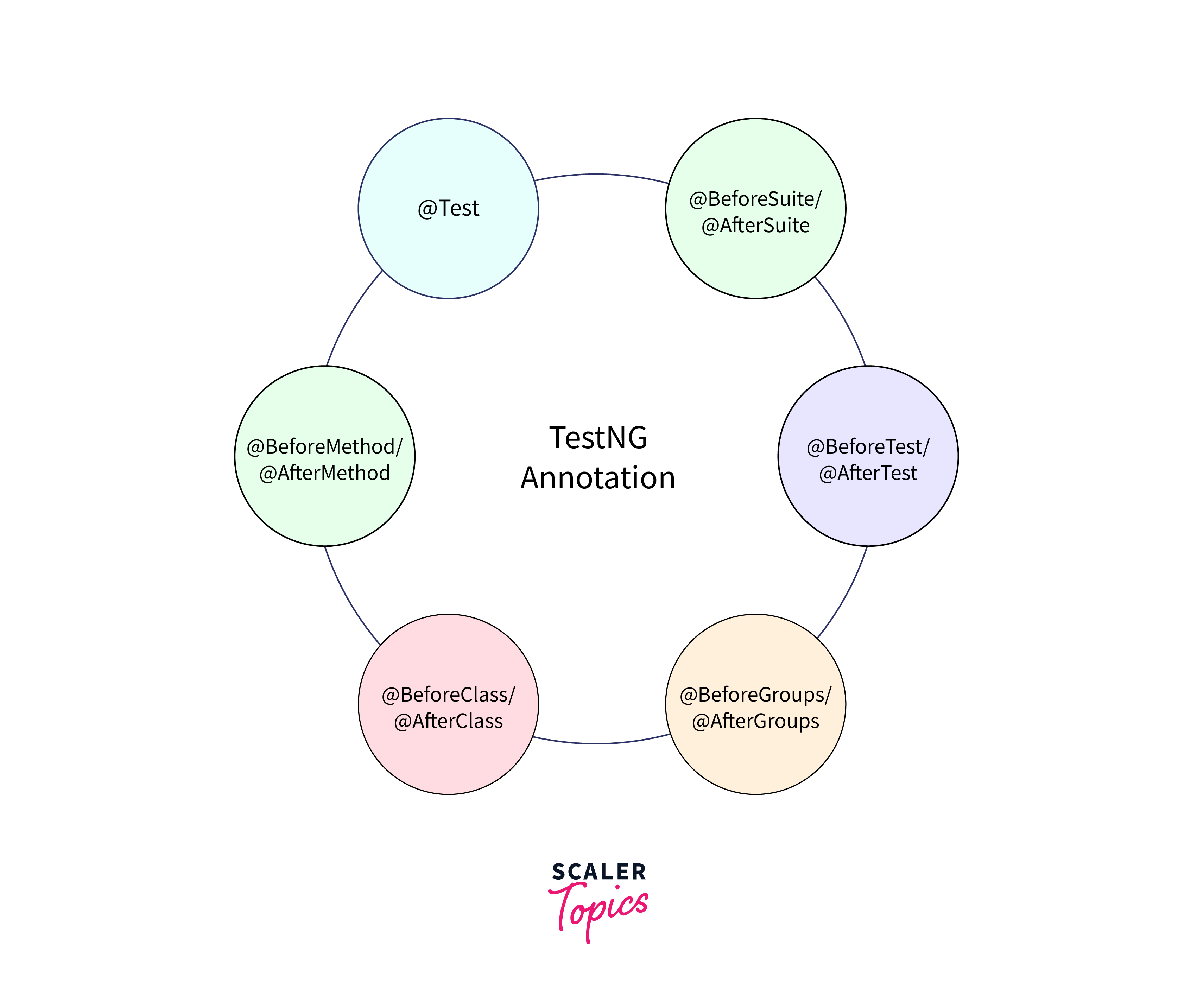
- @BeforeSuite and @AfterSuite:
These annotations mark methods that run before and after the entire suite execution, respectively. It is useful for setting up and tearing down the test environment, such as initializing resources or closing database connections. - @BeforeTest and @AfterTest:
These annotations define methods that run before and after each test tag in the testng.xml file. It helps in preparing the test environment and performing cleanup activities specific to each test tag. - @BeforeClass and @AfterClass:
These annotations mark methods that run before and after the execution of all test methods within a class. It is suitable for performing class-level setup and teardown operations. - @BeforeMethod and @AfterMethod:
These annotations are used to mark methods that run before and after each test method execution. It is useful for activities like launching the browser, initializing variables, or cleaning up after the test. - @Test:
The @Test annotation is used to mark methods as test cases. These methods contain the actual test logic, including the interactions with Selenium WebDriver API. Each @Test method represents an independent test case. - @DataProvider:
The @DataProvider annotation is used to provide data to test methods from a specified data source. It allows testers to create data-driven tests, where the same test logic is executed with different input data.
Creating Test Cases Using TestNG Annotations
Creating test cases using TestNG annotations in Selenium involves the following steps:
1. Set up TestNG:
Ensure that TestNG is properly configured in your Java project. You can add the TestNG dependency to your project's build configuration or use a build management tool like Maven or Gradle to handle dependencies.
2. Import TestNG and Selenium WebDriver:
In your test class, import the necessary TestNG and Selenium WebDriver libraries.
3. Define Test Methods:
Create individual test methods in your test class, and annotate them with the @Test annotation. Each test method represents a separate test case.
4. Set Up Pre-conditions:
Use annotations such as @BeforeSuite, @BeforeTest, @BeforeClass, or @BeforeMethod to define any setup operations that need to be performed before the test case execution. These annotations mark the methods that will be executed before specific test scenarios.
5. Implement Test Logic:
Inside each test method, write the test logic using Selenium WebDriver API to interact with the web application under test. Perform actions like navigating to URLs, interacting with web elements, submitting forms, and validating expected outcomes.
6. Handle Assertions and Verifications:
Use assertions or TestNG's built-in assertions like 'assertEquals' or 'assertTrue' to validate the expected results and compare actual values with the expected values.
7. Handle Post-conditions:
Use annotations such as @AfterMethod, @AfterClass, @AfterTest, or @AfterSuite to define any cleanup or teardown operations that need to be performed after the test case execution.
8. Run TestNG:
Run your test class as a TestNG test. You can execute the tests through an IDE, command-line, or using build automation tools.
9. Analyze Test Results:
TestNG provides detailed test reports that include information about test status, execution time, and any failures or errors encountered during the test execution. Analyze the test reports to identify any issues or failures in your test cases.
Working of TestNG Annotations
The execution flow of TestNG annotations in Selenium follows a specific order defined by the TestNG framework. Understanding this order is crucial for properly structuring and controlling the execution of test cases. Let's delve into the sequence of execution for commonly used TestNG annotations in Selenium:

1. @BeforeSuite and @AfterSuite
These annotations mark methods that are executed before and after the entire test suite, respectively. The methods annotated with @BeforeSuite are typically used for global setup tasks, such as initializing resources or establishing connections to databases or external systems.
On the other hand, methods annotated with @AfterSuite handle teardown activities, such as closing connections or releasing resources. These annotations ensure that the setup and cleanup tasks are performed at the suite level.
2. @BeforeTest and @AfterTest
These annotations define methods that run before and after each test tag defined in the testng.xml file. A test tag represents a group of test methods or a specific test scenario. The methods annotated with @BeforeTest handle setup operations specific to each test tag, such as loading test data or configuring environment settings.
The methods annotated with @AfterTest perform teardown activities specific to each test tag, such as cleaning up data or restoring the environment to its initial state. These annotations provide the flexibility to execute setup and cleanup tasks at the test tag level.
3. @BeforeClass and @AfterClass
These annotations mark methods that run before and after all the test methods within a class. The methods annotated with @BeforeClass are executed once before any test method in the class is executed. They are typically used for class-level setup operations, such as initializing shared resources or opening a browser session.
Similarly, methods annotated with @AfterClass run once after all the test methods in the class have been executed. They are used for performing class-level teardown operations, such as closing the browser or releasing shared resources.
4. @BeforeMethod and @AfterMethod
These annotations are used to mark methods that run before and after each test method execution. The methods annotated with @BeforeMethod are executed before each test method in the class, ensuring that any necessary preparations are made before running the test logic.
Conversely, methods annotated with @AfterMethod run after each test method, allowing for cleanup tasks such as closing browser windows, logging out, or restoring the application to a clean state for the next test. These annotations ensure that each test method starts with a consistent environment and ends with a proper cleanup.
5. @Test
This annotation marks the methods that represent individual test cases. These methods contain the actual test logic and assertions. The execution order of test methods can be defined explicitly in the testng.xml file or inferred based on the dependencies specified using other annotations. Test methods execute after the setup methods (@BeforeSuite, @BeforeTest, @BeforeClass, @BeforeMethod) and before the teardown methods (@AfterMethod, @AfterClass, @AfterTest).
Conclusion
- TestNG annotations in Selenium are a crucial component in Selenium WebDriver testing, offering a powerful way to structure and control test scripts.
- By using TestNG annotations, testers can define the execution flow, dependencies, and setup/teardown operations of test cases.
- TestNG's @Test annotation marks individual test cases, allowing for easy identification and execution.
- TestNG's reporting capabilities provide comprehensive test reports with detailed information on test results.
- TestNG annotations enhance the maintainability and scalability of test scripts by promoting modularity and reusability.
- By utilizing TestNG annotations effectively, testers can create robust, structured, and easily maintainable test suites in Selenium WebDriver.
