Medicine Prescription to Treat a Disease- ANOVA in Excel
Overview
Medicine prescription is a critical aspect of treating any disease. However, with multiple options available, it is challenging to determine which medication provides the best outcome. In this article, we will explore how ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) in Excel can help analyze the effectiveness of various medications used to treat a particular disease. By analyzing data on medication outcomes, we can identify which medication has a statistically significant difference in treatment effectiveness. The insights gained through ANOVA analysis can help healthcare providers make data-driven decisions in prescribing medication and improving patient outcomes.
What are we Building?
In this project, we will be building an ANOVA analysis in Excel to determine the effectiveness of medications in treating a particular disease. ANOVA analysis is a statistical technique used to compare means between multiple groups and identify any significant differences.
a. Pre-Requisites
Before diving into the project, it is essential to have a good understanding of the following topics:
- Data analysis fundamentals
- Data Analysis Toolpak
- Basic statistics concepts
- Excel functions and formulas
- Hypothesis testing
b. How are We Going to Build This?
To build the ANOVA analysis in Excel, we will follow these steps:
- Collect the medication data for the disease treatment.
- Organize the data into groups and calculate the means.
- Determine the sum of squares for each group and the total sum of squares.
- Calculate the degrees of freedom and mean square for each group and the error.
- Calculate the F-statistic and determine the p-value.
- Interpret the results and conclusions.
c. Final Output
After following the above steps, we will get an ANOVA table that summarizes the results of our analysis. The table will include the sum of squares, degrees of freedom, mean square, F-statistic, p-value for each group, and the error. The final output will look something like this:
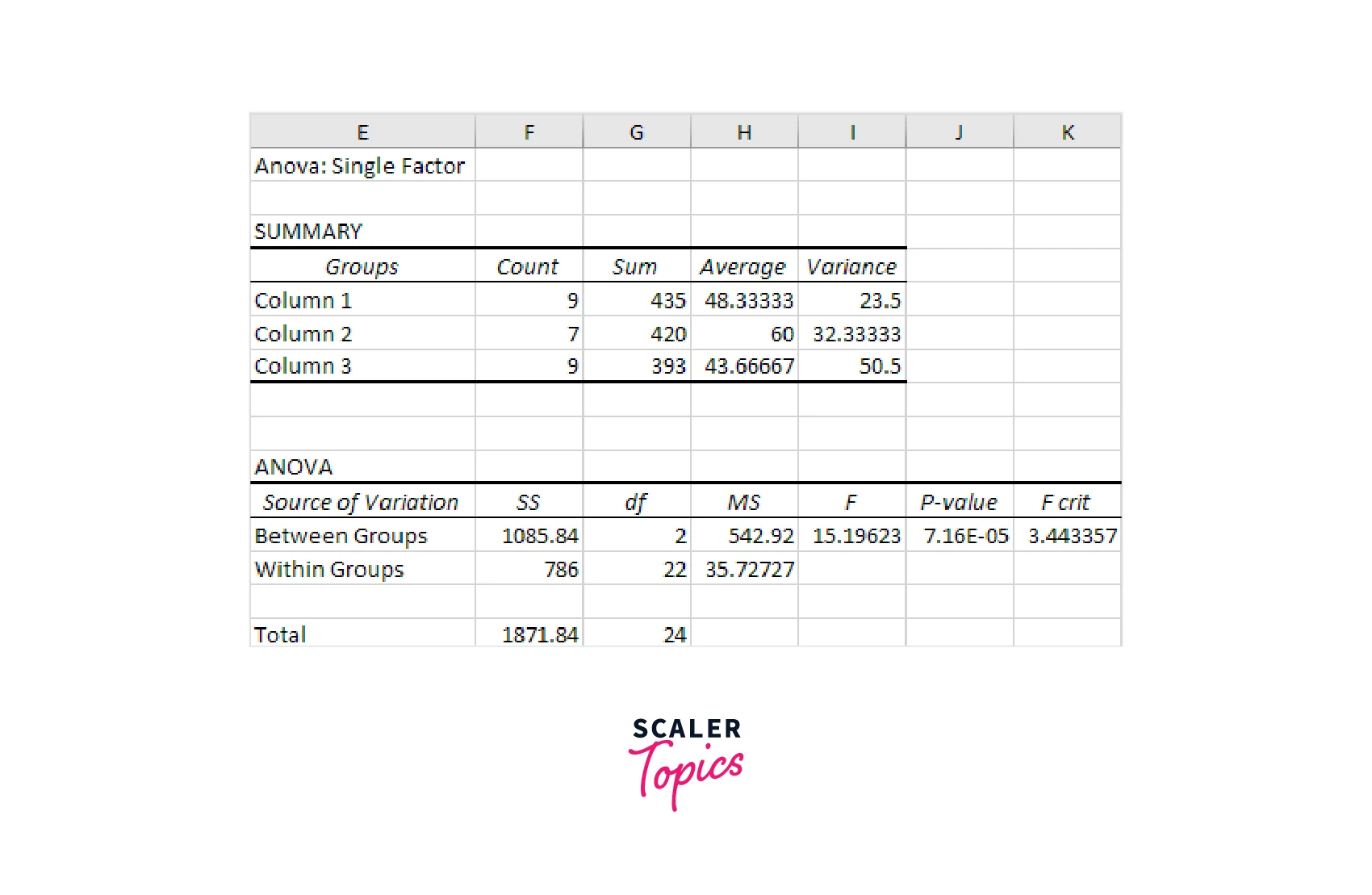
Requirements
Since we will be building this project in Excel, we do not require any libraries or modules. However, we do need to ensure that we have access to the following:
- Microsoft Excel (2016 or later)
- Data Analysis Toolpak
- Dataset containing medication data for disease treatment
Medicine Prescription to Treat a Disease With ANOVA
"Medicine Prescription to treat a disease with ANOVA in Excel":
Step 1: Collect Your Data
Collect the data related to the medical prescription to treat a particular disease. The data should include the medicine name, dose, and the response of patients to that medicine.
Step 2: Create a New Worksheet
Open a new worksheet in Excel and enter the collected data in columns. Give appropriate column headings to the data.
Step 3: Calculate the Mean and Standard Deviation
Calculate the mean and standard deviation for each medicine in the dataset using the AVERAGE and STDEV.S functions, respectively. Place the mean and standard deviation values in separate columns beside the data columns.
Step 4: Calculate the Total Sum of Squares
To calculate the total sum of squares, find the difference between each data point and the overall mean (grand mean) of the entire dataset, square the differences, and add them up using the SUM function. The formula for calculating the total sum of squares is:
Step 5: Calculate the Sum of Squares Within Groups
To calculate the sum of squares within groups, find the difference between each data point and the mean of its respective group (medicine), square the differences, and add them up using the SUM function. The formula for calculating the sum of squares within groups is: =SSW(S) = SUM((B2:B16-A2:A16)^2)
Step 6: Calculate the sum of squares between groups
To calculate the sum of squares between groups, find the difference between the mean of each group (medicine) and the overall mean (grand mean) of the entire dataset, square the differences, and multiply them by the number of observations in each group, and add them up using the SUM function. The formula for calculating the sum of squares between groups is:
Step 7: Calculate the Degrees of Freedom
To calculate the degrees of freedom, subtract one from the number of observations for each medicine to get the within-group degrees of freedom (dfw), and subtract one from the total number of observations to get the total degrees of freedom (DFT). The degrees of freedom between groups (dfb) can be calculated as the difference between DFT and dfw. The formulas for calculating the degrees of freedom are:
Step 8: Calculate the F-value
To calculate the F-value, divide the mean sum of squares between groups by the mean sum of squares within groups. The formula for calculating the F-value is: =F = MSB/MSW
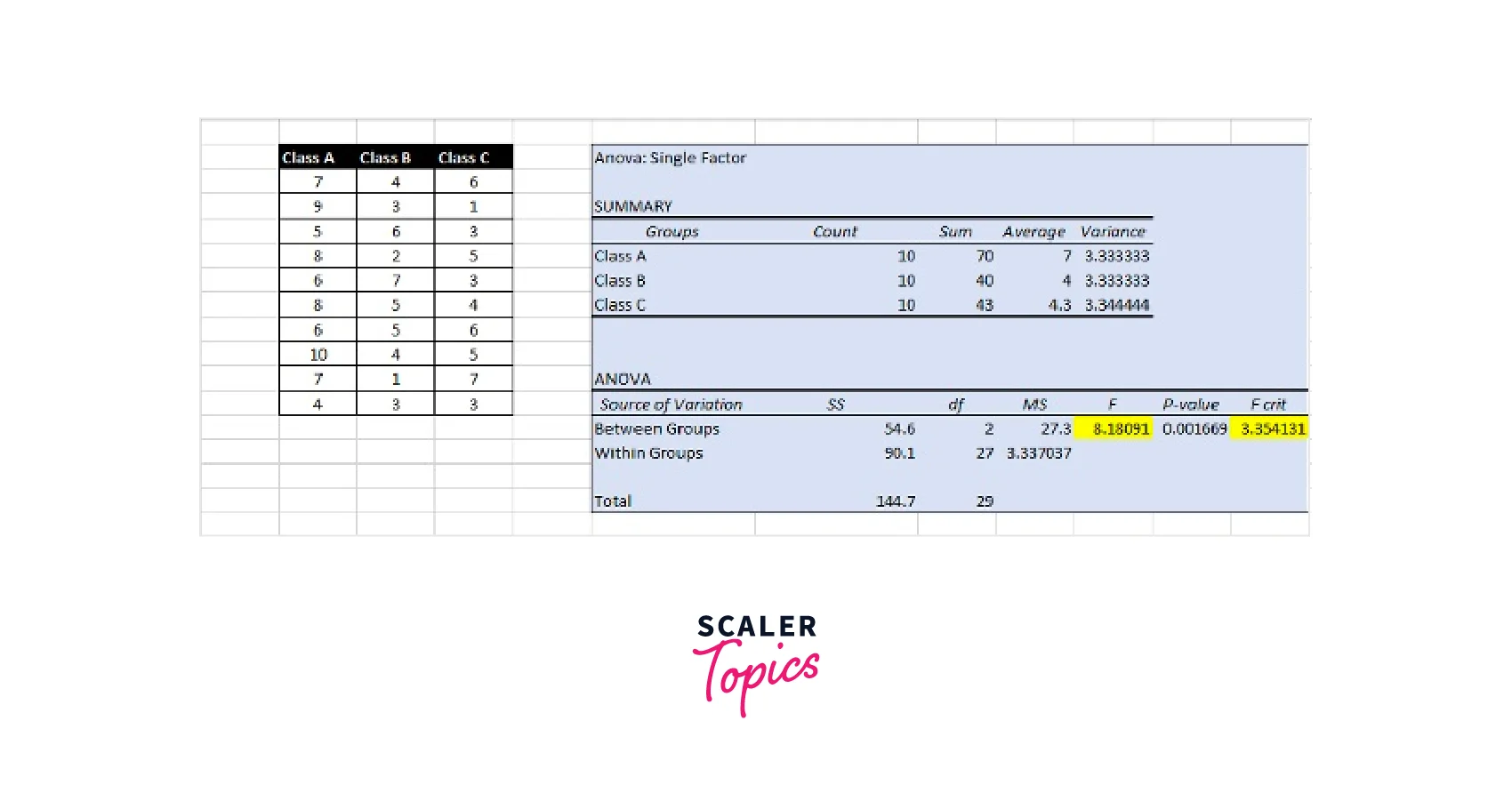
Step 9: Interpret the Results
Interpret the results by comparing the calculated F-value with the critical F-value from the F-distribution table. If the calculated F-value is greater than the critical F-value, we can reject the null hypothesis that there is no significant difference between the means of the groups (medicines). If the calculated F-value is less than the critical F-value, we fail to reject the null hypothesis.
- "n" represents the number of observations, "k" represents the number of groups (medicines), "AVERAGE" represents the Excel function to calculate the mean, and "STDEV.S" represents the Excel function to calculate the standard deviation.
More Monthly Sales Report Templates
- Restaurant Monthly Sales Report Template
This template is designed specifically for restaurants to track their monthly sales, including food and beverage sales, tips, and discounts. It also includes a section for tracking monthly expenses, such as labor costs, food costs, and other overhead expenses. - End-of-Month Sales Report Template
This template provides a summary of all sales made during the month, including the total revenue generated, number of sales, and average sale amount. It also includes a breakdown of sales by product category, sales channel, and customer type. - Monthly Retail Sales Summary Report Template
This template is ideal for retail businesses looking to track their monthly sales performance. It includes sections for tracking sales by product category, location, and customer type, as well as total revenue generated, number of transactions, and average sale amount. - Monthly Sales Activity Report Template
This template is useful for sales teams to track their monthly sales activity, including the number of sales calls made, meetings held, and proposals sent out. It also includes a section for tracking sales performance by individual sales reps. - Monthly Sales Call Report Template
This template is designed for sales reps to track their monthly sales calls, including the name of the prospect, date of the call, and outcome of the call (e.g., closed sale, follow-up needed, etc.). It also includes a section for tracking sales performance by territory or product line. - Simple Monthly Sales Report Template
This template provides a basic overview of monthly sales performance, including total revenue generated, number of sales, and average sale amount. It is ideal for small businesses or startups that are just getting started with sales tracking. - Hotel Monthly Sales Report Template
This template is designed specifically for hotels to track their monthly room sales, banquet sales, and other revenue streams. It includes sections for tracking sales by market segment, sales channel, and booking source. - Small Business Monthly Sales Forecast Report
This template is designed for small businesses to track their monthly sales forecasts, including projected revenue, sales volume, and sales growth. It also includes a section for tracking actual sales performance against the forecast.
Conclusion
- ANOVA is a statistical tool that helps to compare the means of multiple groups simultaneously.
- Excel's built-in Data Analysis Toolpak includes ANOVA as one of its statistical functions, which makes it easier to perform ANOVA calculations in Excel.
- Collecting and organizing data in Excel is an essential step before performing ANOVA.
- Calculating various statistical values such as mean, standard deviation, the total sum of squares, the sum of squares within groups, and a sum of squares between groups can help to identify differences between treatment groups and assess the effectiveness of different treatments.
- The degrees of freedom and F-value can provide insights into whether the differences between treatment groups are statistically significant.
- Interpreting the results of ANOVA can help to make informed decisions about the effectiveness of different treatment options.
- Excel is a powerful tool for data analysis, and learning how to use ANOVA in Excel can be a valuable skill for medical professionals and researchers alike.
