Applications of Neural Networks

The Applications of Neural Networks span from enhancing computational capabilities in data analysis and prediction to revolutionizing fields such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous driving, demonstrating their versatility and transformative potential in various industries.
What is Artificial Neural Networks?
Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are a cornerstone in the Applications of Neural Networks, serving as computational models inspired by the human brain. These networks consist of interconnected units or nodes, mimicking biological neurons, which collectively learn to perform tasks by considering examples, generally without being programmed with any task-specific rules. ANNs are particularly powerful in pattern recognition, classification, and prediction tasks, making them instrumental across a wide range of applications.
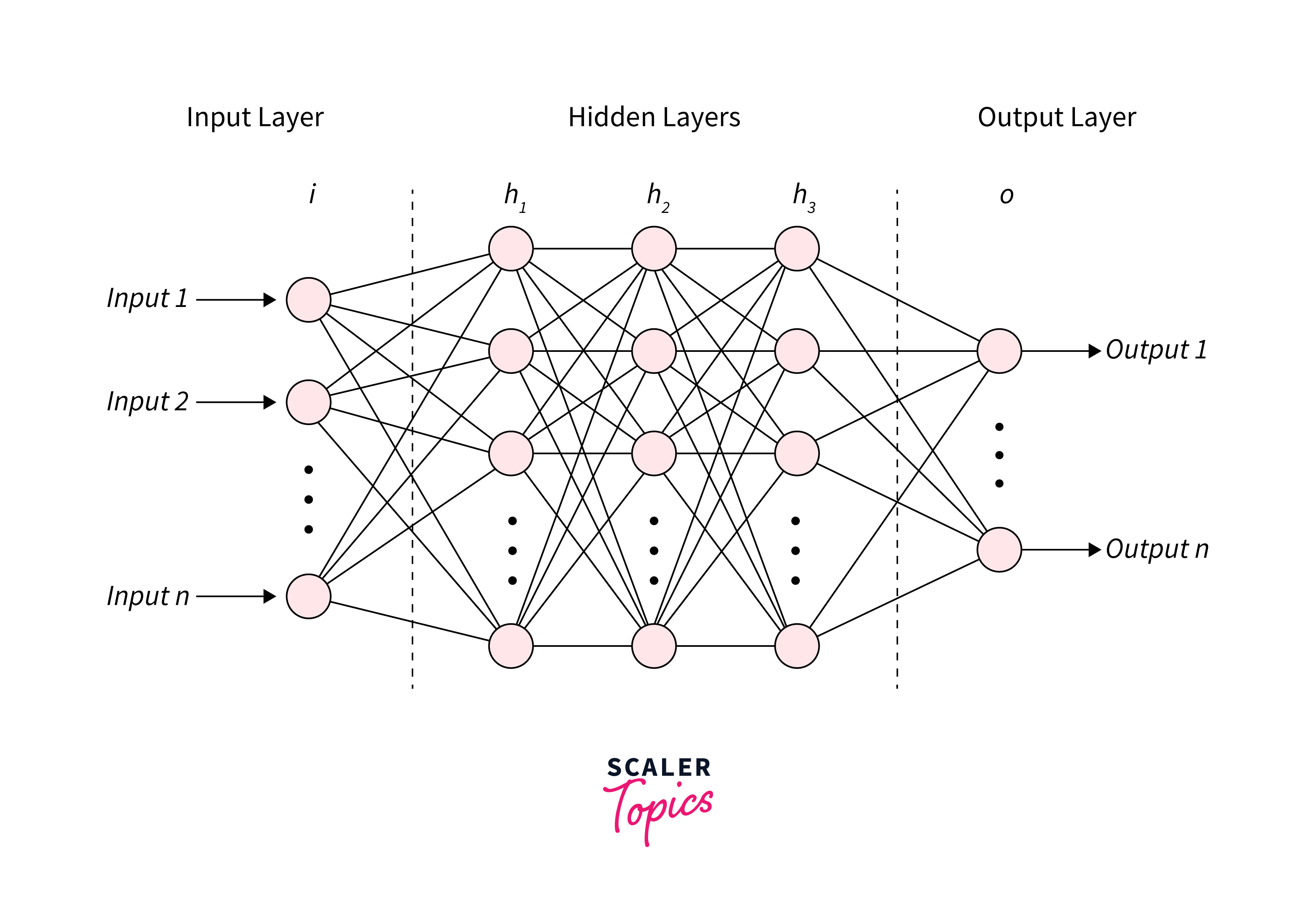
Types
There are several types of ANNs, each designed for specific Applications of Neural Networks:
- Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs):
The simplest type of ANN architecture where connections between the nodes do not form a cycle. This type is widely used in straightforward prediction and classification problems. - Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs):
Designed for sequential data processing, RNNs have connections that form cycles, allowing information to persist. This makes RNNs ideal for time series analysis, natural language processing, and more. - Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs):
Particularly known for their use in processing grid-like data such as images, CNNs employ a mathematical operation called convolution. CNNs are dominant in image and video recognition, image classification, and medical image analysis. - Deep Belief Networks (DBNs):
They are a form of deep neural network known as a generative graphical model. They consist of several layers of hidden variables, with each layer connected to the next but without any connections between the units within the same layer. - Autoencoders:
A type of neural network used for unsupervised learning of efficient codings, typically for the purpose of dimensionality reduction or feature learning.
Bio Neurons Vs Artificial Neurons
The comparison between Biological Neurons and Artificial Neurons provides fascinating insights into how scientists have drawn inspiration from the human brain to design computational models for the Applications of Neural Networks. Biological neurons are the fundamental units of the brain and nervous system, responsible for processing and transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals.
| Feature | Biological Neuron | Artificial Neuron |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Complex organic cell | Simple mathematical model |
| Processing Mechanism | Electrochemical signals | Weighted sum of inputs |
| Learning | Through synaptic strength changes | Adjusting weights via algorithms |
| Communication | Neurotransmitters across synapses | Numerical data through connections |
| Speed | Milliseconds to seconds | Can process millions of operations per second |
How do Artificial Neurons Learn?
The learning process of artificial neurons is a fascinating aspect of the Applications of Neural Networks, underpinning their ability to make predictions, classify data, and recognize patterns. This process hinges on the network's capacity to adjust and optimize the weights of the connections between neurons based on the input data it receives. Here's a closer look at how artificial neurons learn, simplified into key stages:
-
Initialization:
Initially, the weights and biases in the network are set to small random values. This randomness breaks the symmetry, ensuring that the neurons can learn diverse features as training progresses. -
Forward Propagation:
In this phase, input data is fed into the network, passing through each layer sequentially. Each neuron in a layer receives inputs from the previous layer, applies a weighted sum followed by an activation function to introduce non-linearity, enabling the network to learn complex patterns. -
Loss Calculation:
After forward propagation, the network produces an output. The accuracy of this output is measured using a loss function (also known as a cost function), which calculates the difference between the network's prediction and the actual target values. This loss provides a quantitative measure of the network's performance.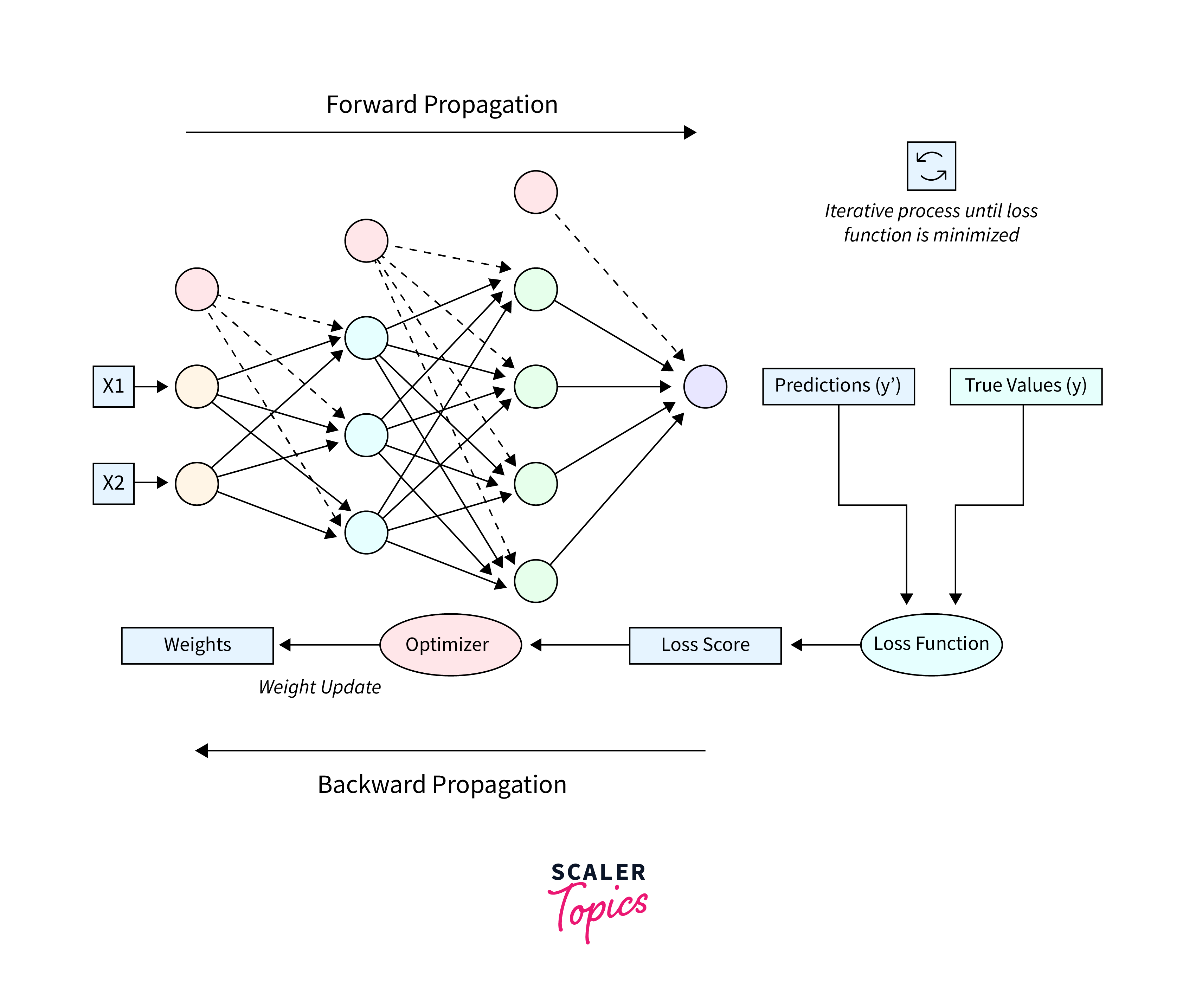
-
Backpropagation:
It is the cornerstone of learning in artificial neural networks. It involves calculating the gradient of the loss function with respect to each weight in the network, essentially determining how changes to weights affect the overall error. By understanding this relationship, the network can adjust its weights in a way that minimizes the loss. -
Weight Update:
Using the gradients calculated during backpropagation, the network updates its weights. This is typically done using an optimization algorithm like Gradient Descent or its variants (e.g., Stochastic Gradient Descent, Adam). The weight update is crucial—it's the step where learning actually happens, as the network adjusts its weights to reduce the error.
Iteration
The entire process, from forward propagation to weight update, is repeated across many iterations (or epochs) over the training dataset. With each iteration, the network weights are fine-tuned, reducing the loss and improving the network's ability to predict or classify accurately.
This iterative learning process enables artificial neurons and, by extension, entire neural networks, to "learn" from the data. It's a process of continual adjustment and optimization, mirroring, albeit in a very simplified form, the way biological neurons adapt and strengthen their connections in response to stimuli. Through this method, neural networks achieve remarkable capabilities in various Applications of Neural Networks, solving problems that were once thought to be the exclusive domain of human intelligence.
Important Applications of Neural Networks
The versatility and power of artificial neural networks have led to significant advancements across various fields. Here are some of the most important applications of neural networks:
- Image Recognition and Processing:
Neural networks, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), have revolutionized image recognition, enabling computers to identify and classify objects within images with high accuracy. This technology underpins various applications, from facial recognition systems for security purposes to medical imaging analysis, helping in the early detection of diseases like cancer.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):
Applications of neural networks in NLP have transformed how machines understand human language, enabling functionalities such as translation services, sentiment analysis, and voice-activated assistants. These systems can process, understand, and generate human languages in a way that is both contextual and nuanced. - Autonomous Vehicles:
Neural networks play a critical role in the development of autonomous vehicles. They enable cars to recognize traffic signs, detect pedestrians, and make intelligent navigation decisions in real-time, enhancing safety and efficiency on the roads.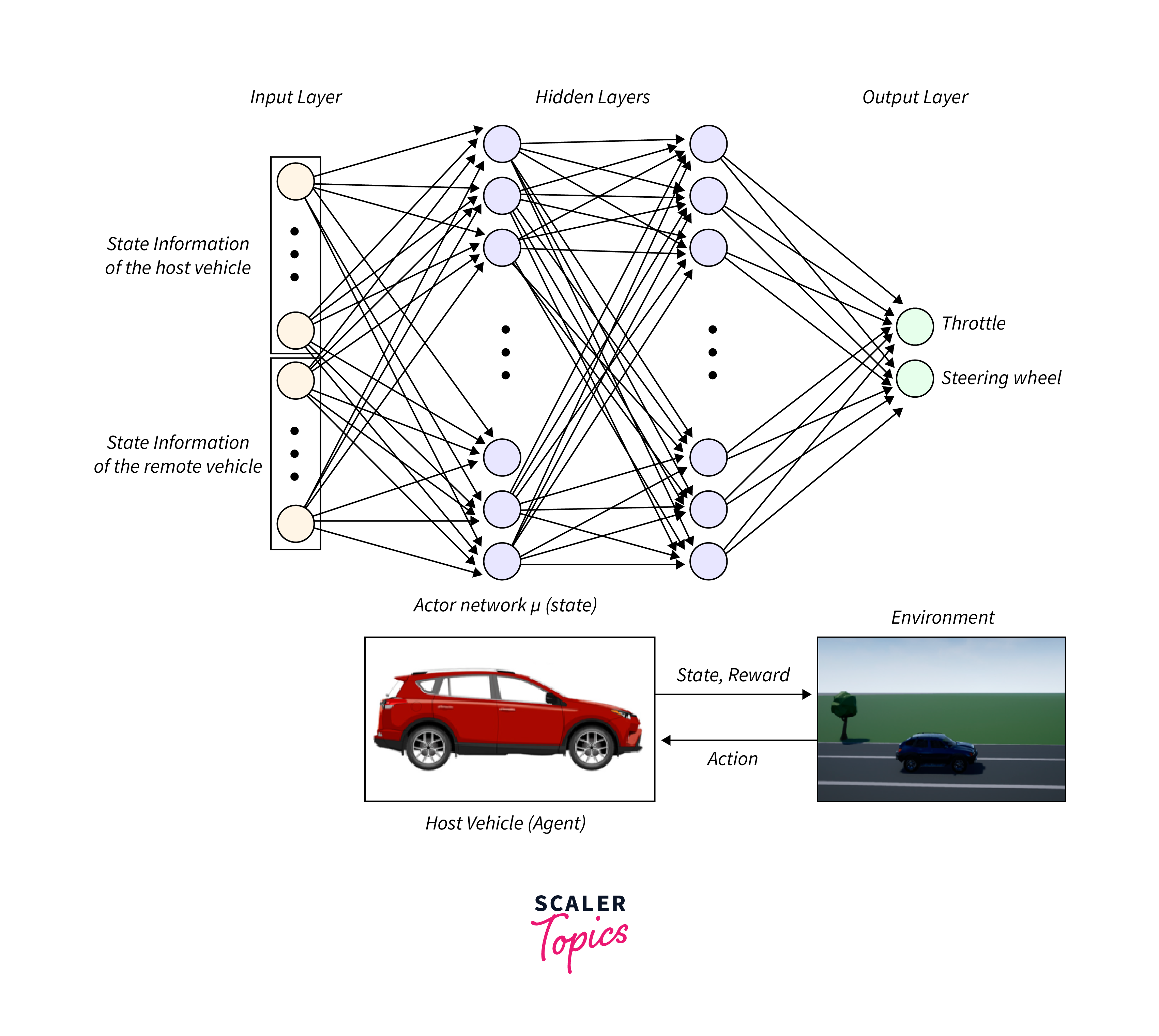
- Financial Services:
In finance, neural networks are used for algorithmic trading, fraud detection, and risk assessment. These applications allow financial institutions to make faster and more accurate decisions by analyzing vast amounts of market data and identifying patterns that might indicate fraudulent activity or market trends. - Healthcare:
Neural networks have made significant contributions to healthcare, from disease diagnosis to drug discovery and personalized medicine. They can analyze medical records, imaging data, and genetic information to assist in diagnosing illnesses earlier and more accurately, potentially saving lives. - Recommender Systems:
Used extensively in e-commerce and streaming services, neural networks improve the accuracy of recommender systems. By analyzing user behavior, preferences, and interaction data, these systems can provide personalized recommendations, enhancing user experience and engagement.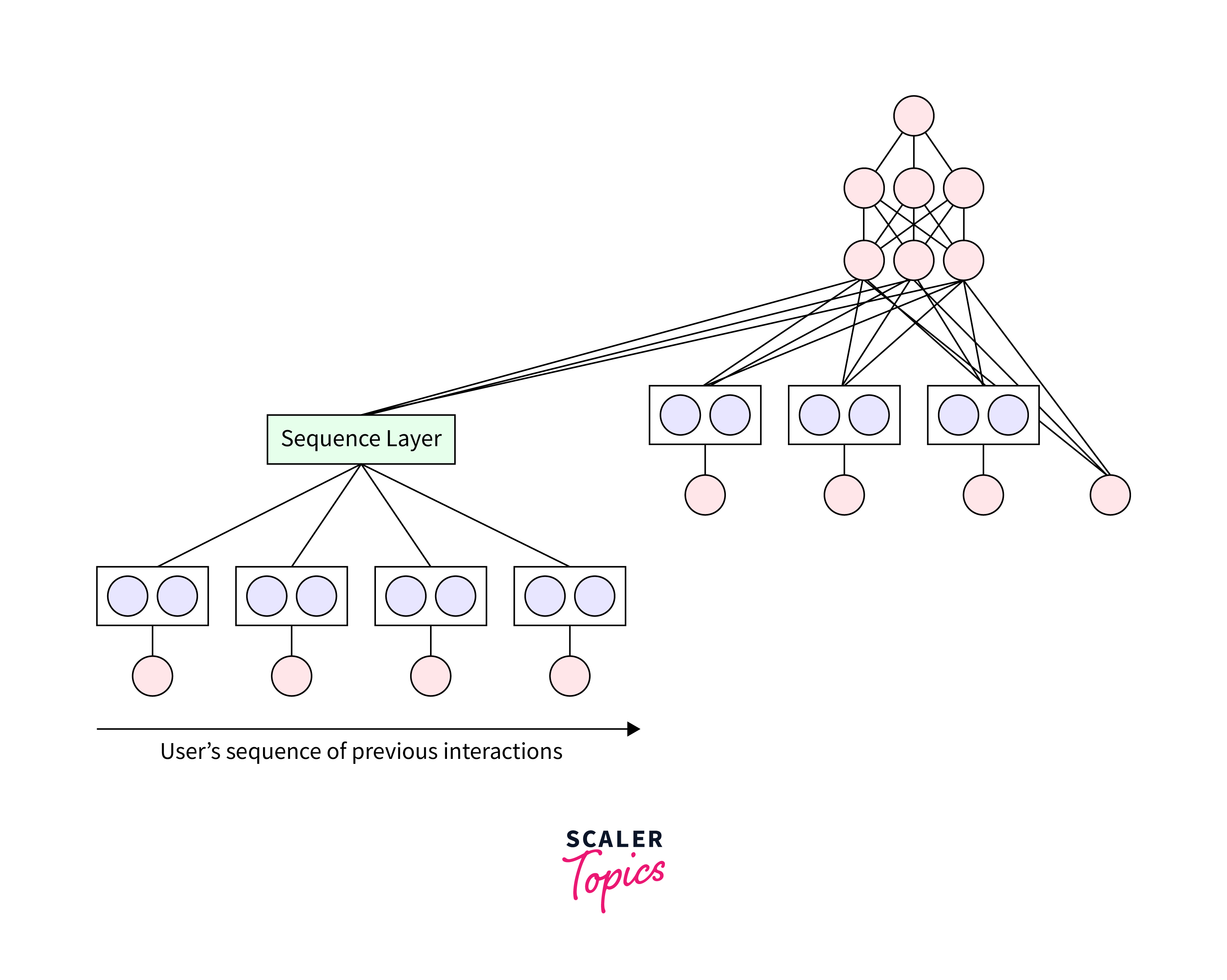
- Gaming and Entertainment:
Neural networks have also impacted the gaming and entertainment industry, enabling more realistic and interactive gaming environments. AI characters powered by neural networks can learn from players' actions to become more challenging and engaging, providing a richer gaming experience. - Speech Recognition:
The improvement in speech recognition is another significant application of neural networks. Systems can accurately transcribe human speech into text and understand spoken commands, which is foundational for voice-controlled gadgets, accessibility features, and efficient customer service automation.
FAQs
Q. Can neural networks work with any type of data?
A. Yes, neural networks can process a wide range of data types, such as images, text, audio, and numerical data. However, each type of data must be converted into a suitable format that the neural network can accept, as they cannot directly process raw video or audio inputs.
Q. Are neural networks the same as artificial intelligence?
A. Neural networks are a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) focused on mimicking the learning process of the human brain to solve complex tasks.
Q. How much data is needed to train a neural network?
A. The amount of data needed can vary widely depending on the complexity of the task and the specific type of neural network, but generally, larger datasets lead to more accurate models.
Q. Can neural networks predict future events?
A. While neural networks can't predict the future with certainty, they can analyze patterns in historical data to make educated predictions about future trends or outcomes, especially in fields like finance, weather forecasting, and demand planning.
Conclusion
- The Applications of Neural Networks showcase their versatility and transformative impact across various sectors, including healthcare, finance, autonomous vehicles, and more, underlining their critical role in advancing technology and improving lives.
- Drawing inspiration from the human brain, artificial neural networks demonstrate the power of bio-inspired computational models to solve complex problems and perform tasks that were once considered exclusive to human intelligence.
- As technology evolves, so do the capabilities and applications of neural networks, promising even more innovative solutions and enhancements in efficiency, accuracy, and automation across industries.
- The effectiveness of neural networks is largely dependent on the quality and quantity of data available for training, highlighting the importance of robust datasets in achieving high-performing models.
- The ongoing research and development in neural network technologies signal a future where their applications could expand even further, potentially uncovering new ways to address global challenges and drive progress in the digital age.
