ArrayList vs LinkedList in Java

Introduction
ArrayList and LinkedList are two popular data structures in Java. Both are used to store and manage collections of objects, but they have different strengths and weaknesses.
In this section we are going to discuss about ArrayList vs LinkedList in Java.
ArrayList and LinkedList are part of Java's Collections Framework, a system that offers an architecture for storing and manipulating groups of objects. This framework streamlines operations like searching, sorting, inserting, manipulating, and deleting data. It provides faster search, insertion, and deletion capabilities, reducing both human effort and computational time complexity.
While both ArrayList and LinkedList store data linearly and accommodate the same data type, their intricate details and usage significantly distinguish them. Through file handling, these data structures can also store data in file systems, ensuring data recovery in the event of a system crash.
What is ArrayList?
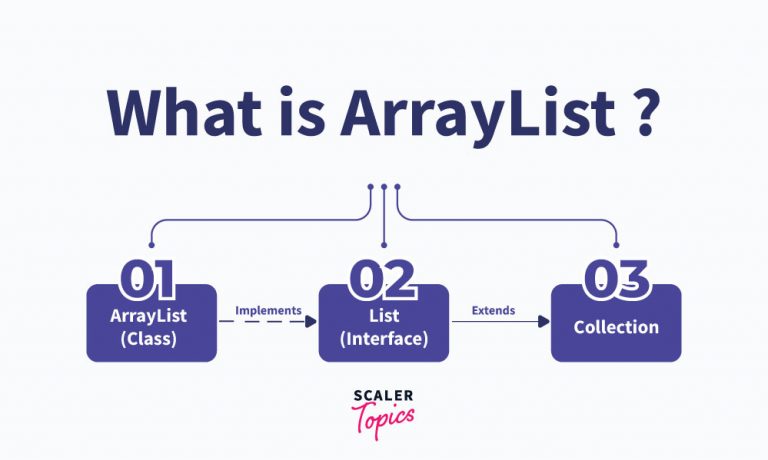
Arraylist is a class which is a part of the Collections Frameworks in java. It implements the List interface hence all the methods of the List class can be used here. We need to import the java.util package for using the Arraylist class.

As the name suggests ArrayList provides us with a dynamic array( resizable array which can change its size whenever required) for storing data items of the same data type. The Arraylist implemented here is different from the fixed sized array in terms of size and speed as well.
What is LinkedList?
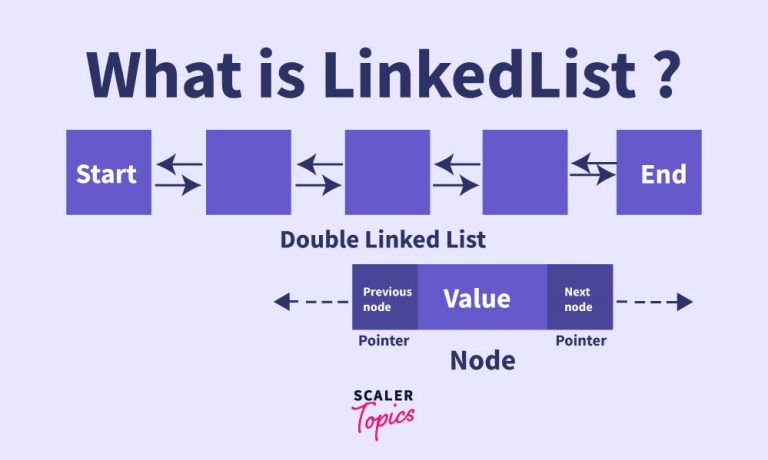
LinkedList are also linear data structures like ArrayList. Here we are not required to specify any size. The objects stored here are not stored in contiguous memory locations like ArrayList. A LinkedList is made up of ‘nodes’. These nodes are the building blocks of the LinkedList just like the cells of an array. A node stores the object data as well as the next node’s address in its p address field.
There are 2 types of Linked List
- Singly Linked List – Here every node stores the address of only the next node in the list. We can traverse the list only in one direction( start to end ).
- Doubly Linked List – Here every node stores the address of the previous as well as next node in the list. We can traverse the list only in both directions( start to end and end to start ).
Key Difference Between ArrayList vs LinkedList
The main difference between ArrayList and LinkedList in Java is the underlying data structure they use and performance characteristics.
ArrayList uses an array, which allows for fast random access but slow insertion and deletion. While LinkedList uses a doubly linked list, which allows for fast insertion and deletion but slow random access.
Also one of the major difference lies in the access time. ArrayList provides O(1) time complexity for index-based access but O(n) for insertions and removals within the list. In contrast, LinkedList offers O(1) time complexity for insertions and removals but O(n) for index-based access, as it requires traversing the list.
Difference Between ArrayList and LinkedList
| Parameters | ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| Underlying Data Structure | Array | Doubly linked list |
| Insertion | Slower compared to LikedListTime Complexity : O(N) | Faster than ArrayListTime Complexity : O(1) |
| Deletion | Slower compared to LikedListTime Complexity : O(N) | Faster than ArrayListTime Complexity : O(1) |
| Traverse | Bidirectional | Bidirectional |
| Searching | Fast searching Time Complexity : O(N) | Fast searching Time Complexity : O(N) |
| Random Access | Fast | Slow |
| Memory Usage | Memory efficient. It only stores the object in the list. | Memory inefficient. It stores the object and the pointers to next and previous nodes. |
| Memory Allocation | Contiguous memory is allocated to all the objects. | Contiguous memory is not allocated. |
Working of an ArrayList
When ArrayList is declared in the program the JVM(Java Virtual Machine) allocates a memory block of contiguous memory locations according to the size given in the declaration. While filling the ArrayList just when 75% of the ArrayList gets filled a new and bigger memory block is allocated and all the previous values are copied to it.
The ArrayList is a part of the collections framework in Java .They are present in the java.util package in Java. They implement the list interface that allows us to work on a dynamic array that increases its size whenever needed. This array is slower than the conventional static size array. This makes ArrayList analogous to vectors in C++.
Syntax:
An arraylist can be dynamically declared using the following syntax
Inserting data in the ArrayList
We can insert new values into the ArrayList either at a specific position in the or at the end of the existing Arraylist just like vectors in C++.
For inserting new elements we have two methods which are both named ‘add’. Furthermore add(object) – It adds the given object at the end of the list
add(int index,object) – It adds the given object at the index specified in the argument. The elements from the given index upto the end are shifted right in order to create space. After this process the element is assigned to the index. This overhead makes the overall process’ time complexity large to O(N) where N is the size of the list.

Accessing and Searching values in the ArrayList
The objects stored in the ArrayList can be accessed by the index where they are stored in the list using the ‘get’ method function.
get(int index) – This function returns the object stored at the given index in the list. This method takes constant time, due to the use of indices this process is very fast.
Modifying the ArrayList
The objects in the ArrayList can be modified using the ‘set’ method function. This function assigns a new value to the index which it refers to.
set(int index,object) – The new object in the argument is assigned to the vector at the given index.
Deleting in the ArrayList
The objects in the ArrayList can be deleted using two functions both named ‘remove’.
- remove(object) – This function deletes the given object in the ArrayList. If the object appears multiple times then the first occurrence of the object is deleted.
- remove(int index) – This function deletes the data value stored at a given index. After doing so all the elements that lie on the right of the deleted element are shifted to left. This overhead makes the overall process’ time complexity large to O(N) where N is the size of the list.

Working of a LinkedList
In Java when used in program the LinkedList implements the doubly linked list in the memory in the background of all the logic of the code.
An LinkedList can be dynamically declared using the following syntax
Inserting values in the LinkedList
We can insert new values into the LinkedList either at a specific position in the vector or at the end of the existing vector.
For inserting new elements we have two methods which are both named ‘add’. Furthermore add(object) – It adds the given object at the end of the list
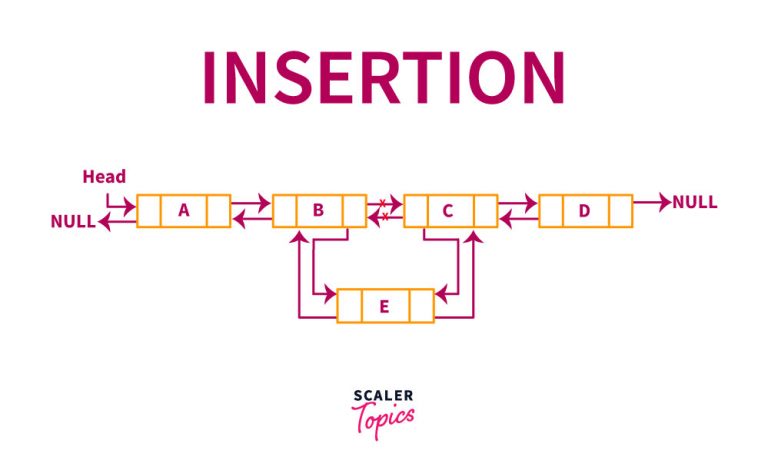
add(int index,object) – It adds the given object at the index specified in the argument. Unlike ArrayLists we do not get an overhead of shifting elements for every insertion. Here the connection between the nodes helps us greatly to insert a new element in constant time.
Accessing and Searching values in the LinkedList
The objects stored in the LinkedList can be accessed by the index where they are stored in the list using the ‘get’ method function.
get(int index) – This function returns the object stored at the given index in the list. This method takes constant time due to the use of indices and is very fast.
Modifying the LinkedList
The objects in the LinkedList can be modified using the ‘set’ method function. This function assigns a new value to the index which it refers to.
set(int index,object) – The new object in the argument is assigned to the vector at the given index.
Deleting in the LinkedList
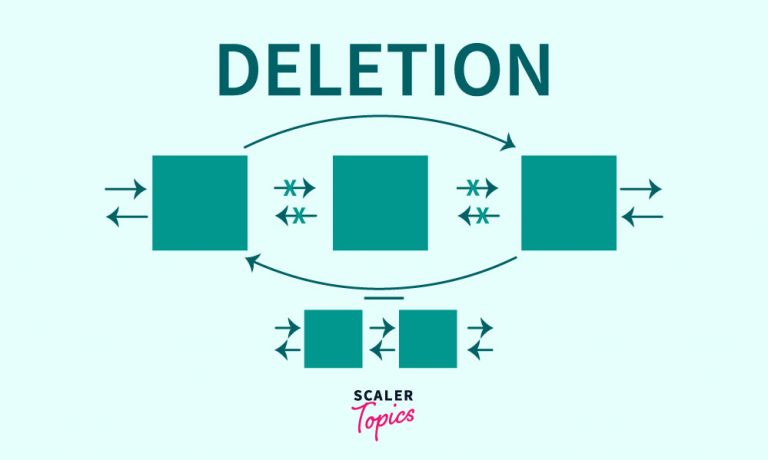
The objects in the LinkedList can be deleted using two functions both named ‘remove’. remove(object) – This function deletes the given object in the LinkedList. If the object appears multiple times then the first occurrence of the object is deleted.
remove(int index) – This function deletes the data value stored at a given index. Unlike ArrayLists we do not get an overhead of shifting elements for every deletion. Here the connection between the nodes helps us greatly to delete a new element in constant time.
When Should We Use ArrayList or LinkedList ?
Several factors help decide between using an ArrayList or LinkedList in Java.
We should choose LinkedList when operations like data addition or deletion occur more frequently than reading the data. Conversely, use ArrayList when data reading scenarios are more common than adding or removing data. This is because ArrayList is better equipped for frequent data retrievals.
The data in an ArrayList is stored more compactly than in LinkedList, making ArrayList more cache-friendly and reducing the likelihood of cache misses. In contrast, LinkedList tends to have poorer cache-locality due to its scattered data storage.
Memory overhead is another critical factor. LinkedList consumes more memory than ArrayList due to the additional links needed to connect nodes. Each node in LinkedList holds the address of both the previous and the next nodes, requiring extra space. This additional link structure is not present in ArrayList, making it more memory-efficient.
Conclusion
- ArrayList and LinkedList are both powerful data structures that can be used to store and manage collections of objects. The best data structure to use depends on the specific needs of your application.
- Use ArrayList when you need fast random access and don’t need to do a lot of insertion and deletion.
- Use LinkedList when you need fast insertion and deletion and don’t need to do a lot of random access.
- Ultimately, the choice should align with your specific use case and performance priorities, striking a balance between access patterns, data modifications, and memory constraints.
