Wumpus World in AI
The Wumpus World problem is one of the most well-known problems in artificial intelligence. It is used to explain how a knowledge-based agent can reason, infer, and make decisions in an uncertain environment using logical reasoning rather than complete information.
This problem is widely taught in AI courses, university exams, and interviews because it clearly demonstrates agent behavior, perception, and logical inference.

What Is the Wumpus World Problem in AI?
The Wumpus World problem in artificial intelligence is a classic AI problem that illustrates how an intelligent agent navigates an unknown environment using percepts and propositional logic to reach a goal safely.
The agent does not know the full layout of the environment and must infer safe and unsafe locations step by step.
Wumpus World Environment
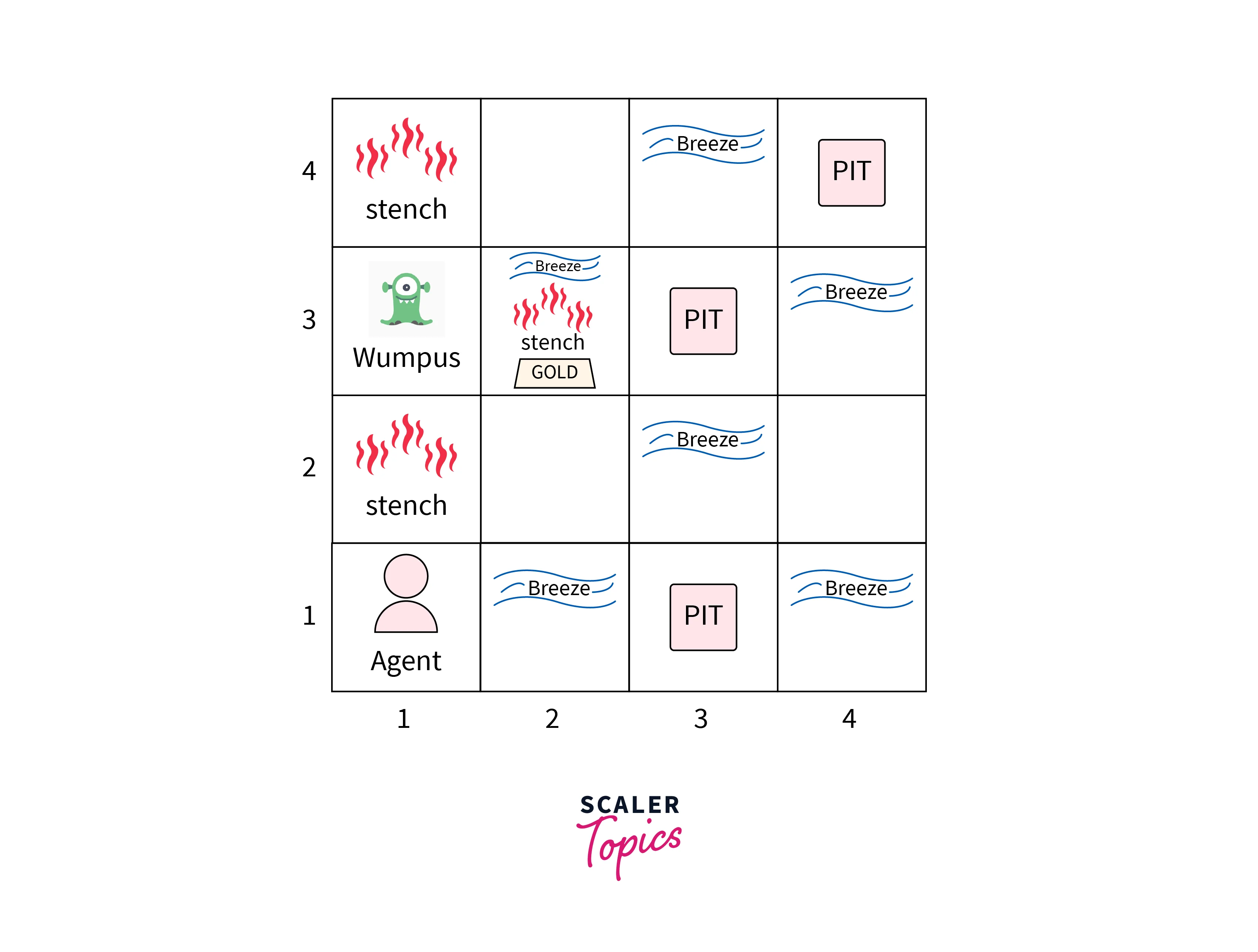
The Wumpus World environment is a grid-based cave represented as a 4×4 grid.
The environment contains:
-
One Wumpus (monster)
-
Several pits
-
One piece of gold
-
An agent starting at position (1,1)
The agent’s objective is to find the gold and exit the cave without falling into pits or being killed by the Wumpus.
Conceptual Grid Representation
[ ] [P] [ ] [ ]
[ ] [ ] [W] [ ]
[A] [ ] [ ] [G]
[ ] [P] [ ] [ ]
The agent cannot see this grid directly and must infer it through percepts.
Stop learning AI in fragments—master a structured AI Engineering Course with hands-on GenAI systems with IIT Roorkee CEC Certification
Percepts in Wumpus World
The agent relies entirely on percepts, which provide indirect information about the environment.
| Percept | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Stench | Wumpus is in an adjacent cell |
| Breeze | A pit is in an adjacent cell |
| Glitter | Gold is in the current cell |
| Bump | Agent hit a wall |
| Scream | Wumpus has been killed |
Percepts are sensed only in the current cell.
Agent Goals
The main objectives of the Wumpus World agent are:
1. Locate and grab the gold
The primary goal of the agent is to find the cell containing the gold. When the agent enters a cell and perceives glitter, it infers that gold is present and performs the Grab action.
2. Avoid pits and the Wumpus
Pits and the Wumpus are deadly hazards. The agent must avoid entering any cell that could contain:
-
A pit, inferred from a breeze
-
The Wumpus, inferred from a stench
Using logical rules, the agent marks certain cells as unsafe and avoids them whenever possible.
3. Exit the cave safely
Once the gold is collected, the agent must return to the starting cell and perform the Climb action to exit the cave. Successfully exiting alive completes the task.
Build Intelligent Systems
Master the logic behind AI agents and build advanced machine learning models with Scaler's Data Science & Machine Learning Course.
Agent Actions
The agent has a limited but well-defined set of actions it can perform:
Move Forward
Moves the agent one cell in the direction it is facing, provided there is no wall.
Turn Left / Turn Right
Changes the agent’s orientation without changing its position. This allows the agent to navigate the grid properly.
Grab
Used when the agent perceives glitter in the current cell to pick up the gold.
Shoot
The agent has one arrow that can be shot in a straight line. If the arrow hits the Wumpus, the agent hears a scream, indicating the Wumpus has been killed and the environment is safer.
Climb
Used in the starting cell to exit the cave after completing the objective.
How the Agent Solves the Wumpus World Problem
The Wumpus World problem is solved using a structured reasoning-based approach rather than trial and error.
1. Receives percepts in the current cell
At each step, the agent senses percepts such as breeze, stench, glitter, bump, or scream. These percepts provide indirect information about nearby hazards or rewards.
2. Updates its knowledge base
The agent stores percepts and inferred facts in its knowledge base, such as:
-
Which cells are visited
-
Which cells are safe
-
Which cells may contain a pit or the Wumpus
This knowledge accumulates over time.
3. Applies logical rules to infer safe or unsafe cells
Using propositional logic, the agent reasons as follows:
-
No breeze → neighboring cells have no pits
-
No stench → neighboring cells have no Wumpus
-
Breeze or stench → danger exists nearby
Through inference, the agent identifies safe paths without directly observing hazards.
4. Chooses actions that minimize risk
Based on its current knowledge, the agent selects actions that:
-
Prefer safe, unexplored cells
-
Avoid known or suspected dangerous cells
-
Use the arrow only when necessary
The goal is to reach the gold with minimum risk.
5. Repeats the process until the goal is achieved
The agent continuously:
-
Moves
-
Perceives
-
Reasons
-
Acts
This cycle continues until the agent successfully grabs the gold and exits the cave or determines that no safe solution exists.
Master structured AI Engineering + GenAI hands-on, earn IIT Roorkee CEC Certification at ₹40,000
Wumpus World Using Propositional Logic
The Wumpus World problem using propositional logic demonstrates how logical rules help infer hidden dangers.
Example rules:
-
If there is a breeze, then at least one neighboring cell has a pit
-
If there is no breeze, neighboring cells are pit-free
-
If there is a stench, the Wumpus is nearby
-
If there is no stench, nearby cells do not contain the Wumpus
Using these rules, the agent deduces which cells are safe to explore.
Example Walkthrough of Wumpus World
-
The agent starts at (1,1)
-
No breeze or stench is detected, so adjacent cells are marked safe
-
The agent moves to a new cell
-
A breeze is perceived, indicating a nearby pit
-
The agent avoids unsafe cells
-
Glitter is eventually detected
-
The agent grabs the gold and exits safely
This step-by-step inference is central to understanding the Wumpus World game.
Characteristics of the Wumpus World Environment
The environment is:
-
Partially observable: The agent only perceives the immediate square.
-
Deterministic: Outcomes are known (e.g., moving forward always moves the agent unless there is a wall).
-
Sequential: Current decisions affect future decisions.
-
Static: The Wumpus and pits do not move.
-
Discrete: The environment is a grid with distinct states.
These properties are commonly tested in exams.
Applications of Wumpus World
Wumpus World is used for:
-
Teaching AI fundamentals
-
Understanding knowledge-based agents
-
Demonstrating propositional logic in AI
-
Explaining reasoning in intelligent systems
FAQs
What is the Wumpus World problem in AI?
It is a classic AI problem that shows how an agent uses percepts and logic to act intelligently in an uncertain environment.
What are percepts in Wumpus World?
Percepts are signals like stench, breeze, and glitter that provide indirect information about hazards and rewards.
What type of agent is used in Wumpus World?
A knowledge-based agent that reasons using propositional logic.
Is Wumpus World deterministic?
Yes, each action leads to a predictable outcome.
Why is Wumpus World important in AI?
It helps learners understand logical reasoning, inference, and intelligent agent design.

