Big Data In Retail
Overview
Big data has changed how retailers do business, enabling them to acquire insights into customer behavior and preferences, optimize processes, and improve overall performance. In retail, big data refers to collecting, storing, and analyzing massive and complex data sets such as customer, inventory, and sales data. By evaluating this data, retailers can obtain significant insights into consumer behavior and preferences, which can help them customize their marketing tactics, optimize pricing, and improve customer experiences. In addition, big data can also be utilized to manage inventories better, eliminate waste, and increase supply chain efficiency.
What are We Building?
In this project, we will develop a Big Data application for the retail business. We will handle and analyze enormous volumes of data using SQL and MySQL and create a web-based dashboard to display our findings. This project will provide learners with hands-on experience dealing with Big Data and a practical grasp of successfully managing and analyzing data using SQL and MySQL.
Pre-requisites
As the retail industry continues to grow, so does the amount of data generated by businesses. Companies require big data tools and frameworks to make sense of this vast amount of data. In this section, we will discuss the prerequisites for big data in retail, including SQL, and several big data frameworks like Spark, Data Link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet.
- SQL : Structured Query Language (SQL) is the foundation of big data analytics. It is a programming language used to manage relational databases, and it allows users to manipulate and extract data. SQL is a vital tool in the retail industry, as it allows retailers to store and manage data on sales, inventory, and customer behaviour.
- Big Data Frameworks : Big data frameworks are essential in processing and analyzing large amounts of data. Here are some of the most popular big data frameworks used in retail:
- Spark : Apache Spark is a powerful open-source big data processing engine. It is used to process large datasets quickly and efficiently and can handle batch and real-time data processing. Spark has a wide range of APIs and libraries that allow developers to build complex data pipelines and machine-learning models.
- Data Link : Data Link is a data integration platform that enables businesses to connect, transform, and stream data from various sources. It simplifies the process of data integration by providing a drag-and-drop interface for creating data pipelines.
- PySpark : PySpark is the Python API for Apache Spark. It provides an interface for developers to work with Spark using Python. PySpark allows developers to write Spark applications in Python, which makes it easier to work with data in a familiar programming language.
- PyFlink : Apache Flink is a distributed processing engine for big data. PyFlink is the Python API for Apache Flink. It enables developers to write Flink applications using Python. PyFlink provides a simple and intuitive API for working with data streams.
- Parquet : Apache Parquet is a columnar file format that provides optimizations to speed up queries. It is a far more efficient file format than CSV or JSON.
Matplotlib is a Python data visualization package. It includes a variety of functions and tools for making graphs, charts, and other data visualizations. Matplotlib is used to explain data insights and trends visually.
In conclusion, big data is becoming increasingly important in the retail industry, and companies need to have the right tools and frameworks in place to make sense of their data. SQL is the foundation of big data analytics, and big data frameworks like Spark, Data Link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet are essential for processing and analyzing large amounts of data. By using these tools and frameworks, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, sales trends, and inventory management.
Overview of Big Data in Retail
Every day, the retail business creates a massive quantity of data, including sales data, customer data, inventory data, and more. Big Data technologies are critical for successfully organizing and analyzing massive data.
We will deal with a dataset including information about a customer's sales and inventory in this project. We aim to load the data with PySpark, then analyze it and create a web-based dashboard that displays critical parameters like sales by product category and inventory levels.
How Are We Going to Build This?
In today's world, businesses are collecting vast amounts of data to make informed decisions about their products, services, and customers. The retail industry is no exception. With the help of big data analytics, retailers can gain insights into their customers' behaviour, preferences, and purchasing habits. To make this possible, we are going to build a big data analytics application using various frameworks like Pyspark, Parquet, and others.
The approach we will use to build this project is a combination of SQL and several big data frameworks like Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet. Our goal is to create an application that can efficiently handle large volumes of data, process it quickly, and provide valuable insights to retailers. Here's how we are going to do it.
Step 1: Understanding the Retail Domain
The first step is to understand the retail domain and the data generated by it. This includes analyzing the data generated by the point-of-sale systems, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management systems. We need to identify the key metrics that retailers need to track, such as sales, inventory levels, customer demographics, and purchase history.
Step 2: Data Collection and Preprocessing
The next step is to collect and preprocess the data. This involves identifying the data sources, extracting the data, and cleaning it up to ensure that it is accurate and consistent. We will use SQL to preprocess the data and prepare it for analysis.
Step 3: Data Storage and Management
Once we have preprocessed the data, the next step is to store and manage it. We will use big data frameworks like Hadoop and Spark to store and manage the data. These frameworks provide scalable and distributed storage solutions that can handle large volumes of data.
Step 4: Data Analysis
The most crucial step is to analyze the data to gain valuable insights. We will use Pyspark, Pyflink, and other big data frameworks to perform data analysis. These frameworks provide advanced analytics capabilities, such as machine learning algorithms, graph processing, and real-time stream processing.
Step 5: Data Visualization and Reporting
The final step is to visualize and report the insights gained from data analysis. We will use tools like Tableau, PowerBI, and QlikView to create interactive dashboards and reports that can be used by retailers to make informed decisions. Now, Machine learning algorithms can also be used to forecast client behaviour and preferences. This involves predicting sales with regression models and grouping customers based on their behaviour with clustering algorithms. The data can also be visualized using matplotlib. For example, we can generate a histogram of our data. We may also use scatter plots to display the relationships between the dataset's variables. The PySpark library can also filter and sort the data as desired.
In conclusion, we are going to build a big data analytics application for the retail industry using various frameworks like Pyspark, Parquet, and others. We will use a combination of SQL and big data frameworks to collect, preprocess, store, manage, analyze, visualize, and report the data. This will help retailers gain valuable insights into their customers' behaviour, preferences, and purchasing habits, which will ultimately help them make better business decisions.
Final Output
One example of the potential final output is a recommendation engine that proposes products to customers based on their previous purchases and browsing behaviour. This can be accomplished by analyzing customer data with machine learning algorithms to uncover patterns and correlations. Personalized product recommendations tailored to each customer's specific interests and habits would be the output of such an engine.
Here's a high-level diagram that shows the different steps involved in implementing big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks:
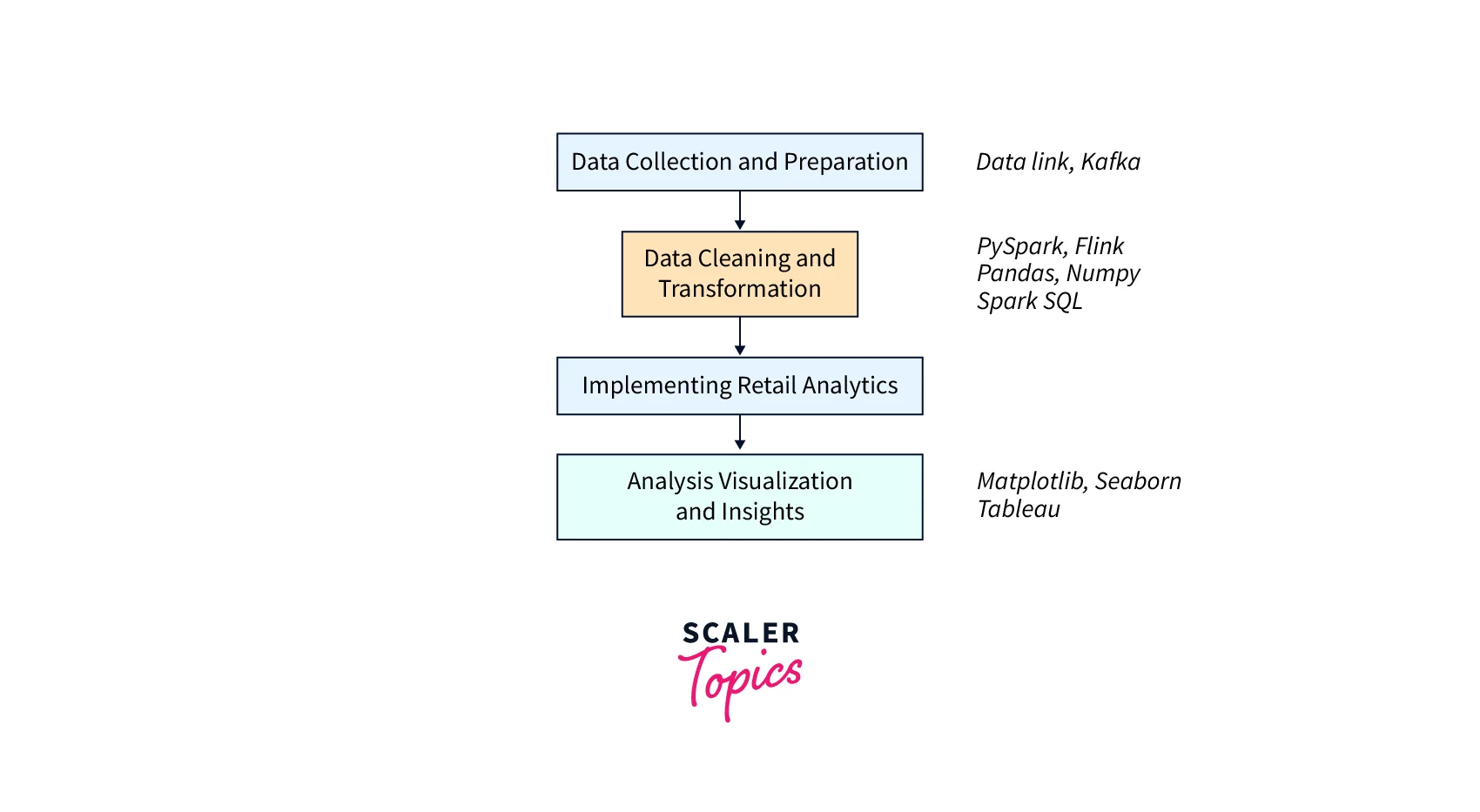
Ultimately, the outcome of big data retail analysis can vary based on the retailer's individual goals and objectives. The potential benefits, however, are numerous and can include higher customer satisfaction, increased sales, and enhanced operations. In addition, retailers may get a competitive advantage in the business by using the potential of big data and machine learning.
Requirements
Here are some of the libraries and frameworks used in the project:
- Spark : Apache Spark is a powerful open-source big data processing engine. It is used to process large datasets quickly and efficiently and can handle batch and real-time data processing. Spark has a wide range of APIs and libraries that allow developers to build complex data pipelines and machine-learning models.
- Data Link : Data Link is a data integration platform that enables businesses to connect, transform, and stream data from various sources. It simplifies the process of data integration by providing a drag-and-drop interface for creating data pipelines.
- PySpark : PySpark is the Python API for Apache Spark. It provides an interface for developers to work with Spark using Python. PySpark allows developers to write Spark applications in Python, which makes it easier to work with data in a familiar programming language.
- PyFlink : Apache Flink is a distributed processing engine for big data. PyFlink is the Python API for Apache Flink. It enables developers to write Flink applications using Python. PyFlink provides a simple and intuitive API for working with data streams.
- Parquet : Apache Parquet is a columnar file format that provides optimizations to speed up queries.
Customer behaviour, supply chain management, and inventory management are all aspects of inventory management. Therefore, many requirements must be met to create a successful big data application for the retail industry:
- Data Sources : Identifying data sources is the first stage in designing a big data application for the retail industry. Sales data, customer data, inventory data, and supply chain data are examples of this. To assist analysis, it is critical to ensure that data is collected and kept structured and organized.
- Scalability : Retail data sets can be massive, and a big data application for the retail industry must be capable of handling massive amounts of data efficiently. The software should be built to scale horizontally, allowing for the inclusion of more features as data grows.
- Real-time Data Processing : (Optional) Because retail data is frequently time-sensitive, a big data application for the retail industry must be able to process data in real-time to deliver correct insights. Retailers can also respond swiftly to changes in customer behaviour or market trends thanks to real-time data processing.
- Data Security : Retail data includes sensitive customer details, sales information, and supply chain information. Data must be safeguarded from illegal access, data breaches, and other security concerns in a big data application for the retail business.
- Analytics Capabilities : A big data application for the retail business should have strong analytics capabilities to extract important insights from data. The application should make possible data mining, predictive analytics, and machine learning.
- User-Friendly Interface : To allow users to access and evaluate data easily, the big data application for the retail business must have a user-friendly interface. The UI should be straightforward, allowing users to create custom reports and visualizations.
- Integration with Existing Systems : The retail industry's big data application should be developed to interact with current systems such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, and point-of-sale (POS) systems.
As a result, creating a successful big data application for the retail business needs careful consideration of data sources, scalability, real-time data processing, data security, analytics capabilities, a user-friendly interface, and connection with current systems. By achieving these requirements, retailers can obtain important insights into customer behaviour, supply chain management, and inventory management, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that improve business outcomes.
Implementation of Big Data in Retail
In today's fast-paced world, retailers are constantly looking for ways to optimize their operations and gain a competitive edge. One way they can do this is by leveraging the power of big data. By analyzing large volumes of data, retailers can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, product performance, and operational efficiency. As a result, developing a successful big data application for the retail industry necessitates careful thought about data sources, scalability, real-time data processing, data security, analytics capabilities, a user-friendly interface, and integration with existing systems. By meeting these requirements, retailers can gain valuable insights into customer behaviour, supply chain management, and inventory management, allowing them to make data-driven decisions that improve business outcomes. So, in this article, we will discuss the implementation of big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks.
Data Collection and Preparation
The first step in implementing big data in retail is data collection and preparation. Retailers need to collect data from various sources such as point-of-sale systems, customer loyalty programs, social media, and website analytics. Once the data is collected, it needs to be prepared for analysis. This involves cleaning the data and transforming it into a format that can be easily analyzed.
To collect and prepare the data, we can use SQL, a language that is widely used for managing and analyzing relational databases. SQL can help us extract data from various sources and transform it into a format that can be easily analyzed.
Example :
Data Cleaning and Transformation
Data cleaning and transformation is the process of identifying and correcting errors in the data and transforming it into a format that can be easily analyzed. This is a critical step in the data analysis process because inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to incorrect conclusions.
To clean and transform the data, we can use several big data frameworks like Spark, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet. These frameworks are designed to handle large volumes of data and can perform complex data transformations.
Example :
Implementing the Analytics in Big Data
Once the data is prepared and cleaned, the next step is to implement analytics in big data. This involves applying various statistical and machine-learning techniques to the data to gain insights into customer behaviour, product performance, and operational efficiency.
To implement healthcare analytics in big data, we can use various big data frameworks like Spark, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet. These frameworks provide tools for statistical analysis, machine learning, and data visualization.
Example :
Analysis Visualization and Insights
The final step in implementing big data in retail is analysis, visualization and insights. Once the data has been analyzed, we need to visualize the results to gain insights into customer behaviour, product performance, and operational efficiency.
To visualize the results, we can use various data visualization tools like Tableau, Power BI, and matplotlib. These tools can help us create visualizations like charts, graphs, and maps that make it easy to understand the data and gain insights.
Example:
Code Implementation
To implement big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks, we need to write code that performs various data analysis tasks. Here's an example of code that extracts data from a database, cleans and transforms it, and applies machine learning techniques to gain insights into customer behaviour:
This code starts by importing the required libraries, including PySpark, the VectorAssemble and KMeans modules, and matplotlib for data visualization.
The code then creates a Spark session and loads data from a database using the read method of the DataFrameReader class. The na.drop() method is used to remove any rows with missing data, and a new column called total_sales is created by multiplying the unit_price and quantity columns.
Next, the data is transformed using the VectorAssembler module to combine the total_sales, customer_age, and customer_gender columns into a single feature vector, which is then passed to the KMeans module for clustering analysis. The resulting model is used to generate predictions for each data point in the dataset.
Finally, the results are visualized using matplotlib by creating a scatter plot of the total sales vs. customer age, with each point coloured based on its predicted cluster. The resulting plot can be used to gain insights into customer behaviour and segment customers based on their purchasing patterns.
Results
Implementing big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet files, and other big data frameworks has numerous benefits for retailers. By collecting and analyzing large amounts of data, retailers can gain insights into customer behaviour, preferences, and purchasing patterns, which can be used to improve the customer experience and increase sales.
The process of implementing big data in retail starts with data collection and preparation. Retailers can collect data from a variety of sources, including point-of-sale systems, customer loyalty programs, social media, and other online sources. This data can be processed and cleaned using PySpark and other big data frameworks to remove any inconsistencies or errors in the data.
Once the data has been cleaned and transformed, retailers can use machine learning techniques to identify patterns and insights within the data. For example, retailers can use clustering analysis to segment customers based on their purchasing patterns or use predictive modelling to forecast future sales. Preprocessing data in big data can take longer than preprocessing data without big data due to the sheer volume and complexity of the data. With big data, the preprocessing stage involves not only cleaning and transforming the data but also distributing and parallelizing the data across multiple nodes in a cluster. This can require additional time and resources to set up the big data infrastructure and optimize the preprocessing algorithms. However, the benefit of using big data is that it enables the processing of much larger and more complex datasets, which would be infeasible or impossible to handle with traditional data processing techniques.
One of the key benefits of using big data in retail is scalability. PySpark and other big data frameworks are designed to handle large amounts of data and can easily scale to meet the needs of growing retailers. This means that retailers can continue to collect and analyze data as they grow and expand, without having to worry about data limitations or processing delays.
Another benefit of using big data in retail is cost-effectiveness. By automating the data collection and analysis process, retailers can save time and money on manual data entry and analysis. Additionally, by gaining insights into customer behaviour and preferences, retailers can make more informed decisions about inventory management and marketing, which can lead to increased sales and revenue.
The amount of cost saving through the use of big data in retail can vary depending on the specific use case and the size of the retailer. It is difficult to provide a precise estimate without knowing the specifics of a given scenario. However, studies have shown that using big data analytics in retail can lead to significant cost savings and revenue growth.
For example, a report by McKinsey & Company estimated that retailers using big data analytics can reduce their operational costs by up to 20% and increase their operating margins by up to 60%. Another study by Accenture found that retailers using big data analytics can increase their return on investment (ROI) by up to 1,000%.
It's important to note that these numbers are estimates and may not apply to all retail situations. The actual cost savings will depend on factors such as the size of the retailer, the complexity of the data, the quality of the data, and the effectiveness of the analytics implementation.
The use cases for big data in retail are numerous. Retailers can use data analysis to improve inventory management, optimize pricing strategies, and identify new sales opportunities. Additionally, retailers can use data to personalize the customer experience by tailoring marketing messages and product recommendations to individual customers.
Overall, the implementation of big data in retail using PySpark and other big data frameworks has the potential to revolutionize the retail industry. By leveraging the power of big data, retailers can gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences that were previously unattainable, which can be used to improve the customer experience and increase sales. With the scalability, cost-effectiveness, and use cases of big data in retail, retailers of all sizes can benefit from implementing these technologies in their operations.
Testing
Testing is an essential step in the implementation of big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks. Testing ensures that the data analysis is accurate and the results are reliable, which is critical in making informed business decisions.
To test the implementation of big data in retail, we can use a variety of testing methods and tools. One of the primary methods is unit testing, which involves testing individual functions and modules of the application to ensure that they are working correctly. Pytest is a popular testing library that can be used to create and run unit tests for Python code.
Another testing method is integration testing, which involves testing the interactions between different modules and components of the application. Integration testing ensures that the other parts of the application are working together as expected. Apache Beam is a popular framework for building scalable, distributed data processing pipelines, which can be used for integration testing.
We can also use performance testing to test the scalability of the application. Performance testing involves simulating high-volume data processing and analyzing the application's performance under heavy loads. Apache JMeter is a popular tool for performance testing, which can be used to simulate high-volume data processing and measure the application's performance under different loads.
Once the testing is complete, we can evaluate the results of the implementation. By analyzing the data, we can gain insights into customer behaviour, preferences, and purchasing patterns, which can be used to improve the customer experience and increase sales. For example, we can use data analysis to identify the most popular products, optimize pricing strategies, and tailor marketing messages to individual customers.
The libraries and big data frameworks used in the implementation of big data in retail play a critical role in testing and evaluating the results. PySpark provides a powerful data processing engine that can handle large amounts of data and is well-suited for data analysis in retail. Parquet is a distributed SQL engine that can be used for processing and querying large datasets, and Apache Beam provides a scalable framework for building data processing pipelines.
In conclusion, testing is a crucial step in the implementation of big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks. By using a variety of testing methods and tools, we can ensure that the data analysis is accurate and the results are reliable. The libraries and big data frameworks used in the implementation play a critical role in testing and evaluating the results, and can help retailers gain insights into customer behaviour and preferences, which can be used to improve the customer experience and increase sales.
Conclusion
- The implementation of big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks is a powerful tool for retailers to gain insights into customer behaviour, preferences, and purchasing patterns.
- The implementation involves several steps, including data collection and preparation, data cleaning and transformation, implementing healthcare analytics, and analysis visualization and insights.
- PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks provide a scalable and efficient way to process large amounts of data, enabling retailers to analyze and make decisions based on a broad range of information.
- The use of PySpark and Parquet in the implementation provides a robust data processing engine that can handle large amounts of data and distributed SQL engine that can be used for processing and querying large datasets, respectively.
- The implementation of healthcare analytics using PySpark and other big data frameworks allows retailers to extract valuable insights from healthcare-related data and improve their healthcare services.
- Data visualization and insights play a critical role in the implementation, allowing retailers to understand trends, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions based on the analysis.
- The scalability of PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks makes it possible to analyze large datasets quickly and efficiently, enabling retailers to make decisions in real-time and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
- Implementing big data in retail using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks has achieved significant success in improving business outcomes, reducing costs, and increasing revenue.
- The cost-effectiveness of PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks makes it possible for retailers of all sizes to benefit from big data analysis and gain a competitive advantage in the retail industry.
