C Fork() Function

The C fork function is used to create a duplicate of the calling process. When a process is duplicated, it forms two types of processes. The first one is the parent process from which a duplicate process has formed, and the second one is the child process that formed as a result of the duplication.
What is C fork() Function?
Below are the pre-requisites to understanding the C fork()-
- Process
- Different Stages of a process.
Forking is the process of creating a duplicate process from an existing process. The duplication process occurs when the C fork() is called. After the forking, there are two types of processes. The first one is the Parent process from which the duplicate processes are formed. The second one is the child process, which is the duplicate process that forms from the parent process.
The C fork() function has no parameters, and this function returns an integer value as the returned value. The values returned by the C fork() function are given below.
Negative Value
The C fork() function returns a negative value when the function fails to create a child process.
Zero Value
The C fork() function returns a zero value to the child process that is newly created. On successful duplication of a process, the PID of the child process is returned in the parent, and 0 is returned in the child process.
Positive Value
The C fork() function returns a positive value to the parent process or the caller. The positive value consists of the process ID of that particular child process that is being created.
Syntax of C fork() Function
The syntax of the C fork() function is as follows:
Parameters of C fork() Function
The C fork() function does not have any parameters.
Return Value of C fork Function
The C fork() function returns three integers as the return value. The three integers are like a positive value (it contains the process ID), a negative value (when the child process fails), or a zero (when the child process is created successfully).
How does the fork() Function in C work?
The C fork() function is a primary method of process creation of an operating system like Unix. The fork() creates a new copy of the calling function. The newly created process is known as the Child process, and the process from which the child process is created is known as the parent process. When there is closing or any unwanted avoidance in the parent function, the child process also crashes. Since the C fork() function is based on Threading, we should run the program on a local system to get the correct output.
Let us take an example to understand how the C fork() function works. We will use the C fork() function to print hello world many times.
Output:
In the above example, one output is the parent process, and the other is the child process.
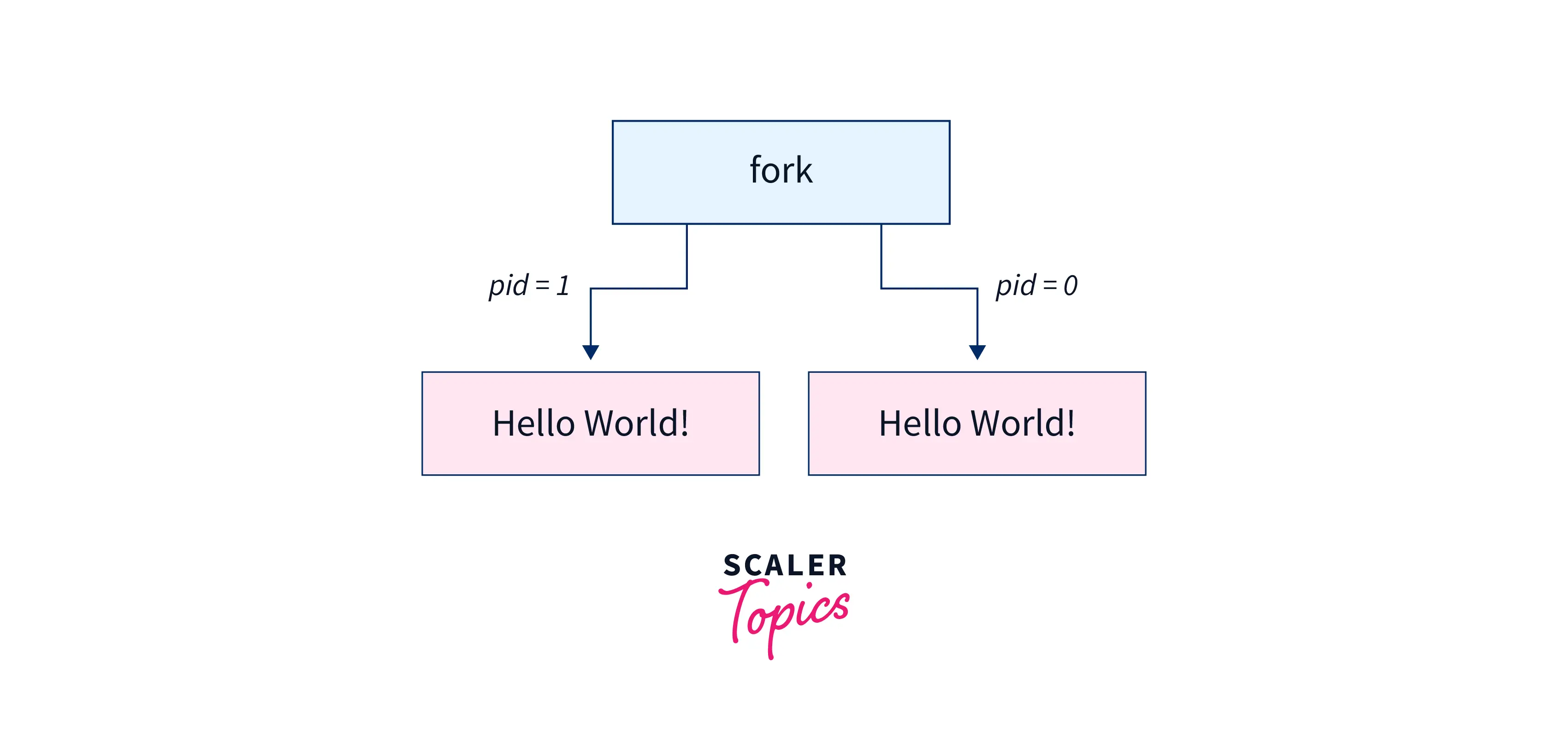
- In the above example, the number of times the C fork() function is used is 1. So the process will be forked in the form of 2 power of n. The value of n represents the number of fork() system calls.
Now, we will use the fork() function three times to call the process. Then the resultant output will be like 2 power of 3 is equal to 8.
Output:
Uses of fork() Function
The work of the C fork() function is to create a child process for the parent process. When we use the C fork() function in our program, we duplicate that particular calling function. This function creates the child process in the form of 2 powers of n, where n represents the number of calls that the function does.
C fork Examples
Now let us see some more examples of the C fork() function to understand this function in a better way. Each of the examples is provided with output and explanation.
Example 1
Output
Explanation
In the above example, we used the fork() function to create a child process from the main process. We printed the process ID and parent ID named PID and PPID from the child and parent process, respectively. We used the wait (NULL) on the parent process for the child process to be finished. Then, we use the exit() on the child process to finish the child process. The above code shows that the PID of the parent process is the PPID of the child process. From this, we can conclude that process 24738 is the child process of process 24731
Example 2
Output
Explanation
In the above example, the process id of the parent function is 1252. This id is also the process id of the main function. Then we created the fork. The process id 1253 represents the creation of a fork. This process will help print the output; after printing the output, the child process will be assigned a new id. After this, process ID 1252 will also print the content under the fork section. In this, the parent and child process IDs are the same. So, we can conclude that the new child process belongs to the earlier parent process.
Example 3
Output
Explanation
In the above example, we are using the loop to perform the fork function many times. First, we printed the natural numbers from 1 to 10, and then we used the C fork() function to print the process two times. The numbers printed the first time are the parent process, and the numbers printed again are the child process.
Conclusion
- The c fork function duplicates a calling process. When a process is duplicated, there are two types of process forms: the first is parent process, and the second one is child process.
- The process can be defined as the series of actions to execute a program. When a program is run, it is not directly executed.
- The syntax of the C fork() function is variable_name = fork();
- The C fork() function does not have any parameters. It returns three values: a negative value, a positive value, or a zero, depending on the action taken by the process behaviour.
- The C fork() process will be forked in the form of 2 powers of n, and the value of n represents the number of fork() system calls.
