Clone a Linked List with Next and Random Pointer

Problem Statement
A linked list of length n is provided. Every node also has a random pointer that could refer to any node in the list or to null.
The list should be built as a deep copy (A copy of an object that does not share the same references as the source object from which it was copied is said to be a deep copy of that object). The deep copy should be made up of exactly n new nodes, each of which has the value set to that of the corresponding node from the original copy. The next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list.
Example
Input:
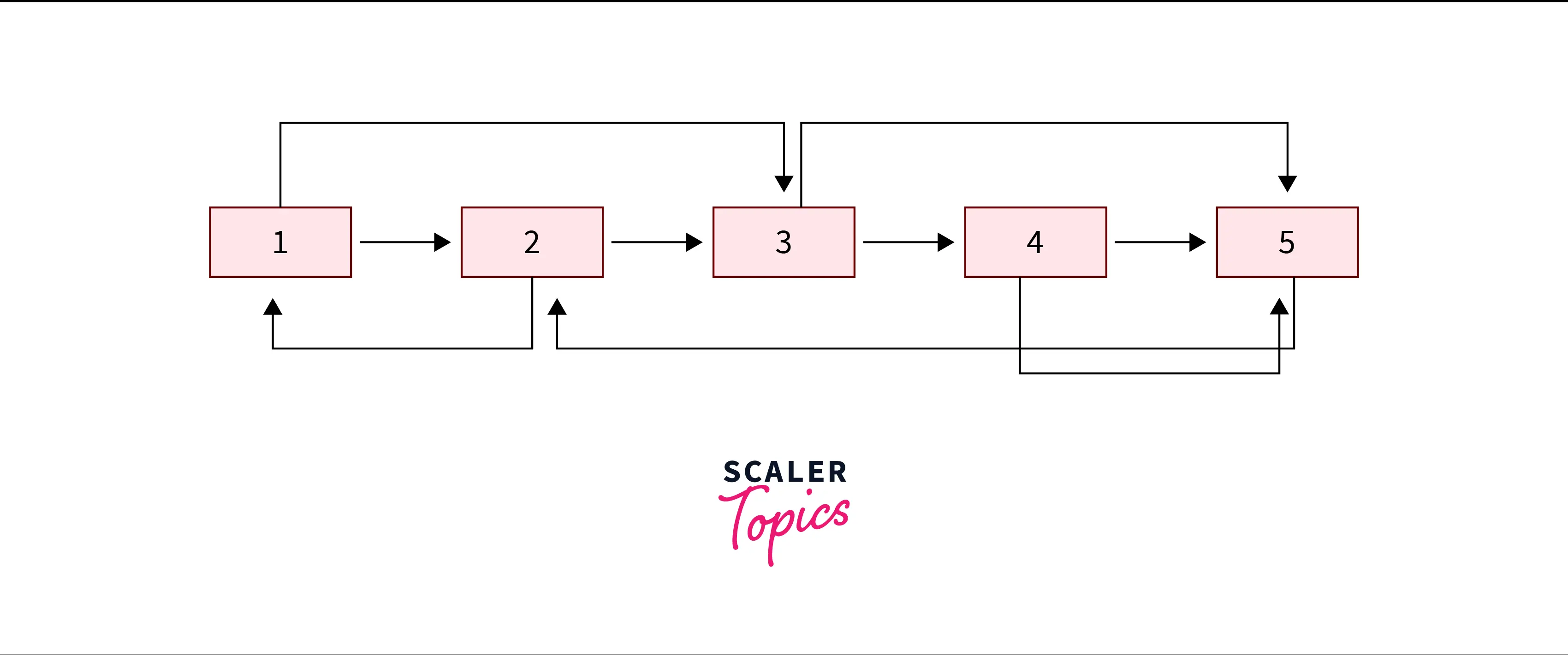
Output:
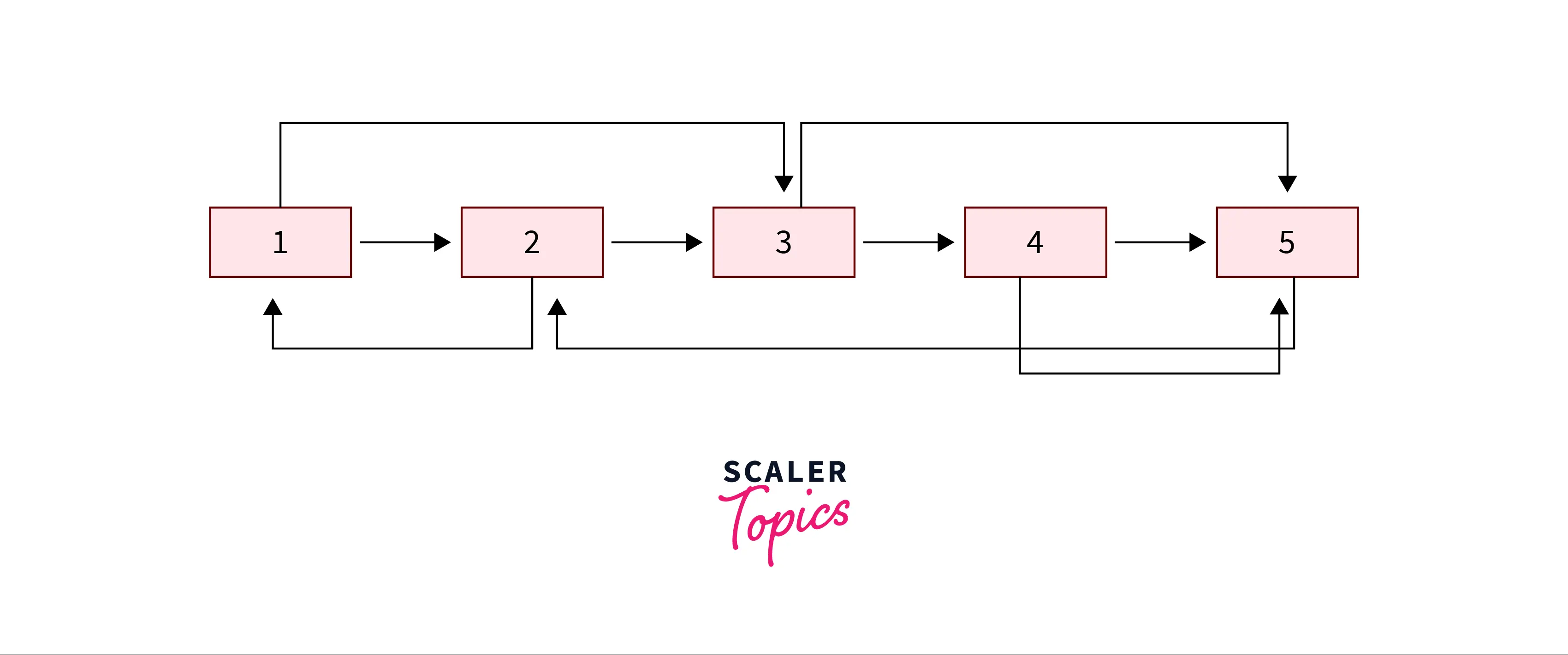
Explanation: Copy of the linked list is being created with next and random pointers.
Input:
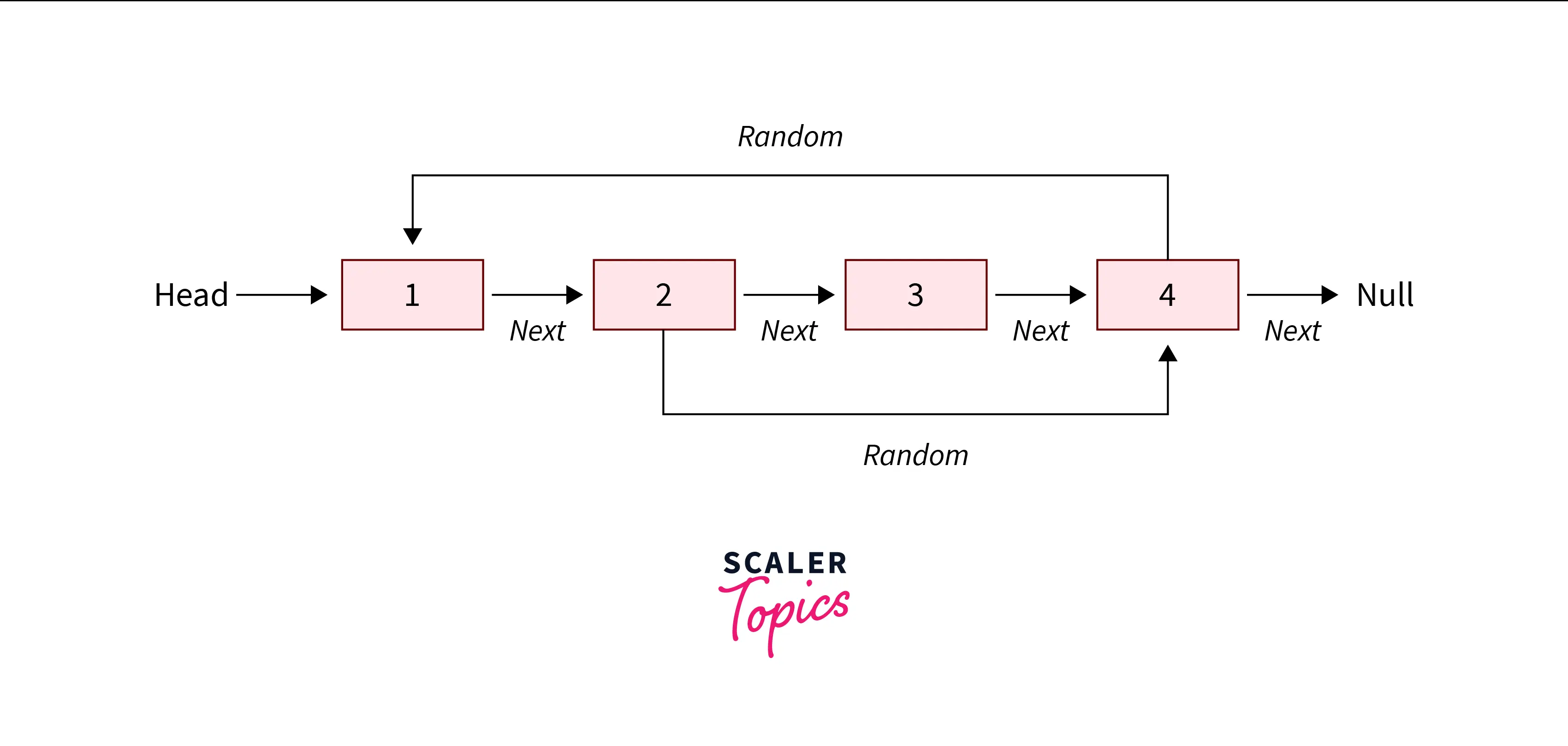
Output:
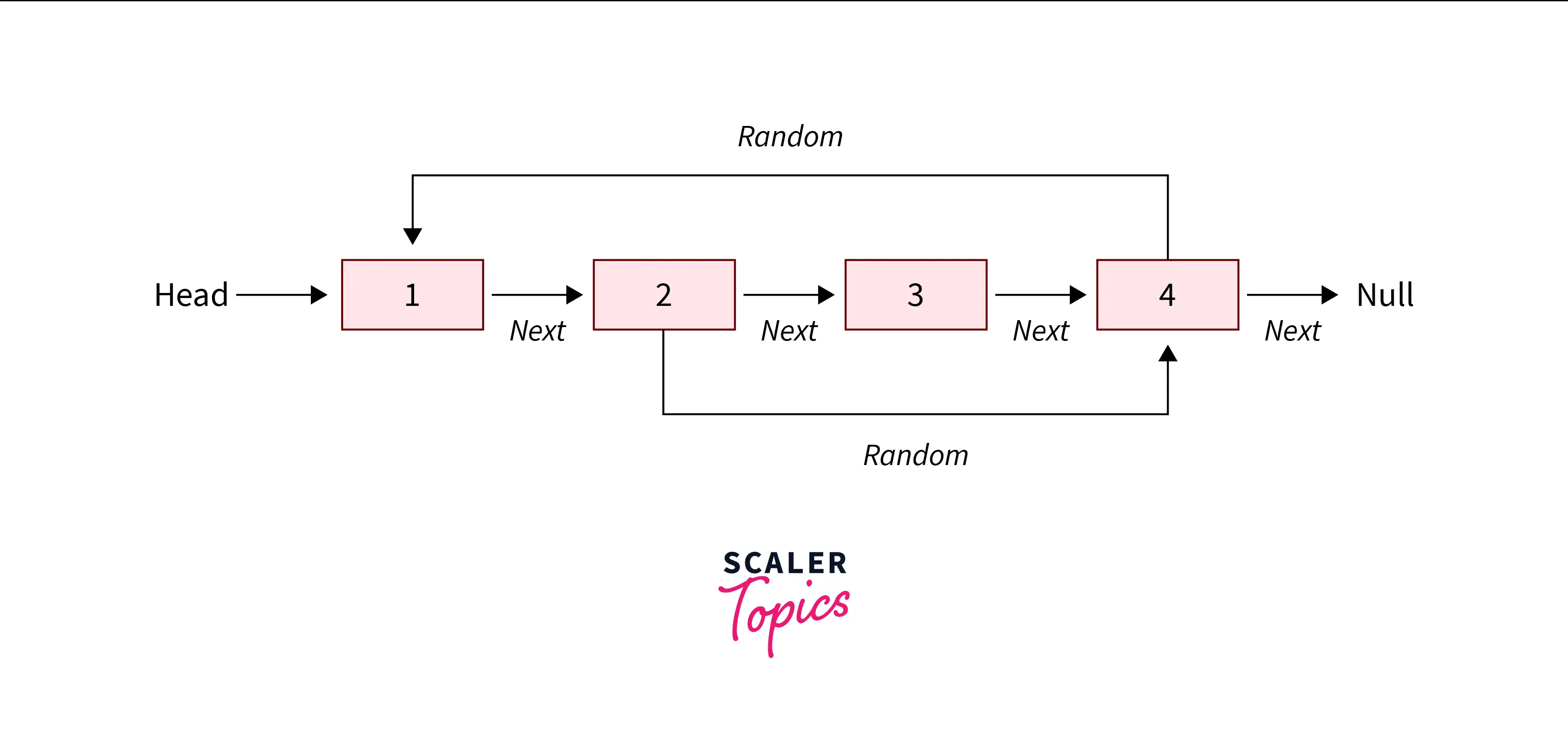
Explanation: Copy of the linked list is being created with next and random pointers.
Constraints
1<=length of linked list<=10000ts 1<=Data of Node<=1000
Approach 1 - Uses O(n) Extra Space
To clone a linked list with next and random pointer, This approach first saves the next and arbitrary pointers (from the original list) in an array before making a copy of the original Linked List.
- Go over the original linked list and create a data duplicate of it.
- Make an array containing the next and random pointer values for each node of the original linked list.
- Traverse the original linked list and using the values stored in the array adjust the next and random reference of cloned linked list nodes.
Python Implementation
C++ Implementation
Java Implementation
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 2 times, so linear time is taken for this approach. Space Complexity: O(N) => N space for storing N nodes in an array.
Approach 2 - Uses Constant Extra Space
To clone a linked list with next and random pointer, We’ll be implementing an algorithm that will require no extra space, lets see the algorithm for the same:
- In this approach, we will be using the approach of interweaving of nodes.
- In the original Linked List, make a copy of node 1 and place it between node 1 and 2, then make a copy of node 2 and place it between node 2 and 3. Continue by adding the duplicate of N after the Nth node.
- Now copy the random pointers in the interweaved nodes.
- After that, retrieve both the original and copied linked lists by rearranging the pointers
Python Implementation
C++ Implementation
Java Implementation
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 3 times, so linear time is taken for this approach. Space Complexity: O(1) => No Extra space is needed in this approach.
Approach 3 - Using Hashing
The idea for this approach is hashing, lets see the algorithm for the same:
- Go over the original linked list and create a data duplicate of it.
- Make a hash map of key value pair with original linked list node and copied linked list node to store both the nodes.
- Traverse the original linked list and using the values stored in hash map adjust the next and random reference of cloned linked list nodes.
Python Implementation
C++ implementation
Java Implementation
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 2 times, so linear time is taken for this approach. Space Complexity: O(N) => N space for storing N nodes in a HashMap.
Conclusion
- A linked list of length n is provided. Every node also has a random pointer that could refer to any node in the list or to null. The deep copy should be made up of exactly n new nodes, each of which has the value set to that of the corresponding node from the original copy (clone a linked list with next and random pointer).
- We can follow many approaches to clone a linked list with next and random pointer:
- Approach 1: Uses O(n) extra space
- Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 2 times, so linear time is taken for this approach.
- Space Complexity: O(N) => N space for storing N nodes in an array.
- Approach 2: Uses Constant Extra Space
- Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 3 times, so linear time is taken for this approach.
- Space Complexity: O(1) => No Extra space is needed in this approach.
- Approach 3: Using Hashing
- Time Complexity: O(N) => linked list has been traversed 2 times, so linear time is taken for this approach.
- Space Complexity: O(N) => N space for storing N nodes in a hashmap.
- Approach 1: Uses O(n) extra space
