Cloud Security
Overview
The technology, rules, procedures, and services that shield cloud data, applications, and infrastructure against dangers are referred to as cloud security. Both the cloud service provider and the client are accountable for cloud security.
What is Cloud Security?
Cloud security is a set of practices and tools created to handle both internal and external security risks to businesses. As they migrate cloud-based tools and services into their infrastructure, organizations need cloud security.
In recent years, the phrases digital transformation and cloud migration have become commonplace in business contexts.
Why is Cloud Security Important?
Understanding the security standards for keeping data safe has become essential as organizations continue to migrate to the cloud. Accountability and security of data assets are not ensured with the management of the cloud by cloud computing service providers.
With the continued development of the digital environment, security concerns have progressed. Organizations may encounter serious governance and compliance issues when handling client information, regardless of where it is housed, if they don't take proactive measures to increase their cloud security.
However, putting in place sufficient defenses against contemporary cyberattacks is essential for successful cloud adoption. Cloud security solutions and best practices are essential for maintaining business continuity.
How Does Cloud Security Work?
Cloud security aims to achieve the following:
- In the event of data loss, enable data recovery.
- Defend networks and storage against nefarious data theft.
- Prevent data breaches due to neglect or human mistake.
- minimize the effects of any system or data breach.
Cloud security is established by using encryption, Identity access management (IAM), data backup and disaster recovery, or other such options.
What Makes Cloud Security Different?
There are a few ways in which cloud security, as a modernized cyber security solution, differs from traditional IT approaches.
Data storage: Building all IT frameworks in-house for intricate, personalized security measures have long been discovered by organizations to be expensive and restrictive. Frameworks built on the cloud have reduced the costs of system development and maintenance, but they also provide consumers with less autonomy.
Scaling speed: Apps and infrastructure built for the cloud are highly modular and deploy quickly. Concerns arise when a company's desire for convenience and updates outpaces its capacity to maintain security.
End-user system interfacing: Cloud systems also connect with numerous additional systems and services that need to be protected for both businesses and individual users.
Cloud Security Challenges
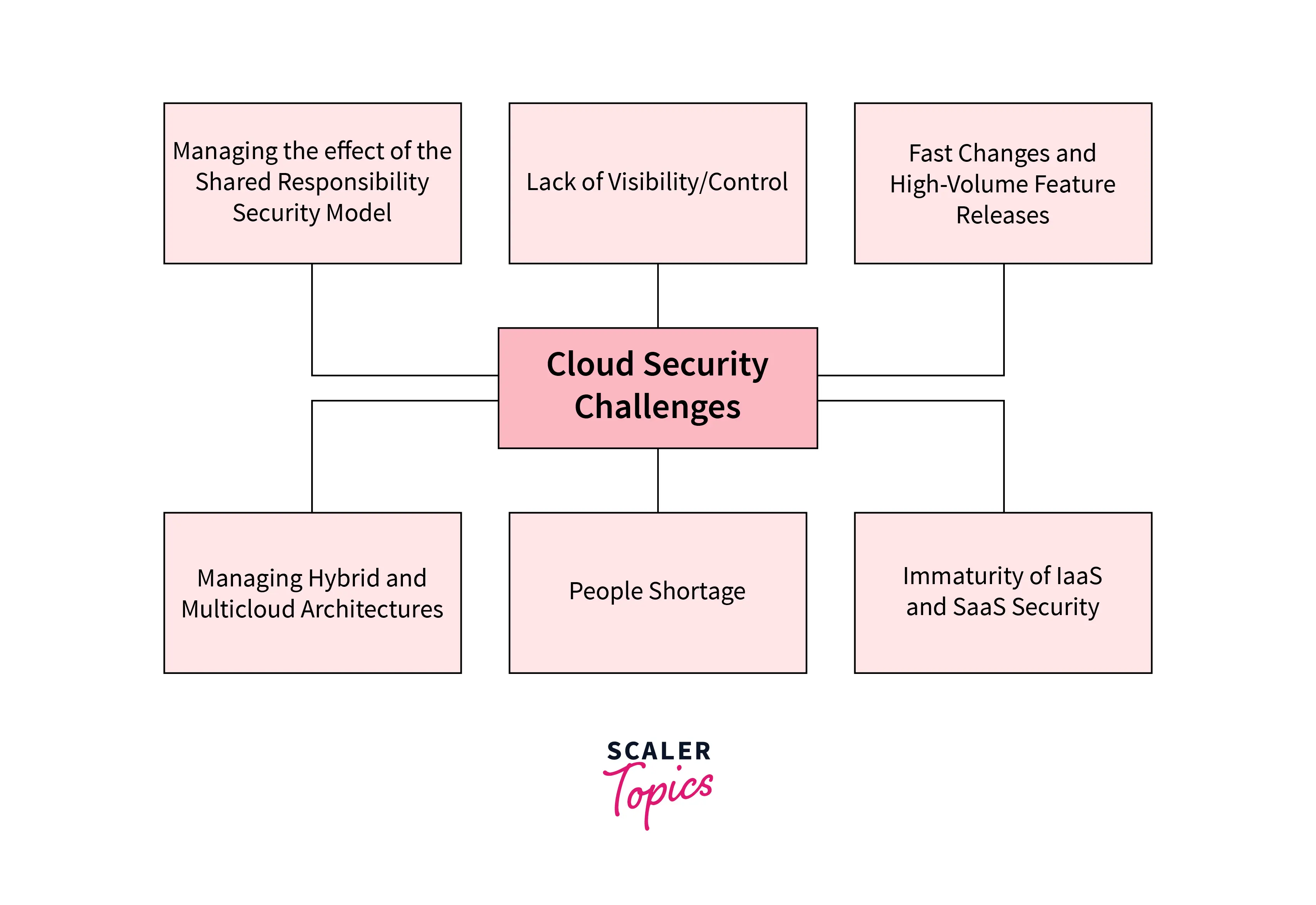
- Lack of visibility - Because many cloud services are accessible outside of corporate networks and through third parties, it can be simple to lose track of how and by whom your data is being viewed.
- Multitenancy - Multiple client infrastructures are housed under one roof in public cloud settings, therefore your hosted services might be broken by hostile attackers as side damage when they target other companies.
- Access management - While businesses may be able to control and limit access points across on-premises systems, enforcing the same sorts of limitations in cloud settings can be difficult.
- Misconfigurations - Misconfigurations might occur when the proper privacy settings are not created or when the administrator passwords are left in place.
How to Secure the Cloud?
- One of the finest strategies to protect your cloud computing systems is encryption. Either you encrypt your data before uploading it to the cloud yourself, or you utilize a cloud provider that will do so for you as part of the service.
- One more effective technique for cloud security is configuration. Basic flaws like incorrect setup lead to a lot of cloud data breaches. You greatly reduce your danger to the security of the cloud by avoiding them.
- Any cloud installation should also include fundamental cyber security guidelines. These tips include creating secure passwords, utilizing a password manager, routinely backing up your data, etc.
- Verify the security of your cloud provider. Cloud security providers must contribute to the development of a secure cloud environment and shoulder some of the liability for your data security.
Types of Cloud Security Solutions
There are 4 primary types of cloud security solutions. Let us take a look at them.
-
Identity and access management - For all users seeking to access both on-premises and cloud-based services, it enables companies to create policy-driven enforcement processes and to give digital identities to track users.
-
Data loss prevention (DLP) - It provides a selection of technologies and services intended to guarantee the safety of regulated cloud data. All data is secured by DLP systems using a mix of warnings, encryption, and other preventative steps.
-
Security information and event management (SIEM) - In cloud-based environments, it offers a complete security orchestration solution that automates threat monitoring, detection, and response.
-
Business continuity and disaster recovery - Disaster recovery solutions are a cornerstone of cloud security and give businesses the tools, services, and standards required to quickly recover lost data and return to business as usual.
Hybrid Cloud Security Solutions
For customers in small businesses, medium-sized organizations, and corporate settings, hybrid cloud security services might be a very wise decision. They are typically too sophisticated for personal use. However, it is these businesses that potentially benefit from the cloud's combination of accessibility and size with on-site control of certain data.
A company may manage how its data is accessed and kept by segmenting its services. Separating data can also help your company better adhere to regulatory requirements for data compliance.
Hybrid cloud environments can also be used to achieve redundancy. Organizations can maintain operations if one data center is taken offline or attacked with ransomware by using daily operations from public cloud servers and backing up systems in local data servers.
Benefits of Cloud Security
Here are the top benefits of cloud security:
- Proactive threat management - Cloud architects make sure that security is implemented across all of your endpoints which provides proactive threat management.
- Data security - From creation to disposal, a strong cloud security solution safeguards the whole data lifecycle. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and backups are used to secure sensitive data.
- Regulatory compliance - For compliance and to safeguard sensitive data, top-tier cloud security solutions manage and maintain increased security around infrastructure.
- Scalability - A scalable cloud computing system may adapt capacity, security coverage, and pricing in response to changes in demand.
Conclusion
- Taking steps to prevent dangers from your cloud is cloud security.
- Cloud security is established by using encryption, IAM, and disaster recovery.
- Cloud security has various merits and challenges. IAM, DLP, and SIEM are some security solutions for the cloud.
