Risk Management in Cloud Computing
Overview
Cloud computing services have seen exponential growth by individuals, businesses, and organisations over the past few years. Though cloud services provide a boost to the business and have immense advantages, cloud-based information systems are exposed to threats that can have adverse effects on organisational operations, assets, and individuals. Therefore, risk management plans in cloud computing are implemented by organisations to mitigate cloud-based risks, improve system security, and expedite business growth.
What is Risk Management in Cloud Computing?
Before learning risk management, let us take a glance at cloud computing. Cloud computing is a technology that allows its user to access resources such as storage, memory, network, and computing; these resources are physically present at any geographical location, but can be accessed over the internet from anywhere in the globe. This advancement in technology has revolutionised the working of businesses and organisations. More and more organisations are investing in cloud deployment infrastructure rather than on-premise infrastructure. This mobilization of technology introduces new risks associated with cloud computing, which needs to be treated with foresight. To manage these risks, risk management plans are implemented by organisations. Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling threats to an organisation's system security, capital and resources. Effective risk management means attempting to control future outcomes proactively rather than reactively. In the context of cloud computing, risk management plans are curated to deal with the risks or threats associated with the cloud security. Every business and organisation faces the risk of unexpected, harmful events that can cost the organisation capital or cause it to permanently close. Risk management allows organisations to prevent and mitigate any threats, service disruptions, attacks or compromises by quantifying the risks below the threshold of acceptable level of risks.
Process of Risk Management
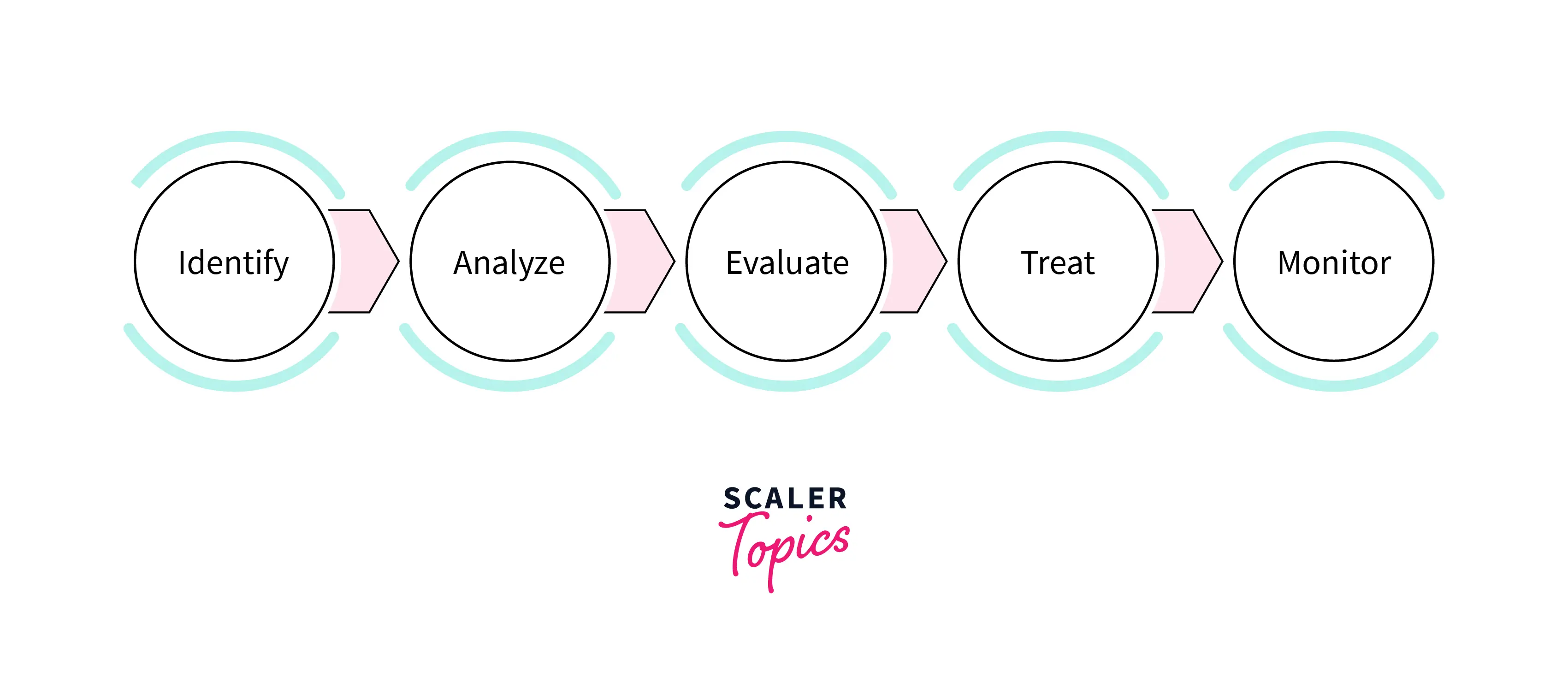
Risk management is a cyclically executed process comprised of a set of activities for overseeing and controlling risks. Risk management follows a series of 5 steps to manage risk, it drives organisations to formulate a better strategy to tackle upcoming risks. These steps are referred to as Risk Management Process and are as follows:
- Identify the risk
- Analyze the risk
- Evaluate the risk
- Treat the risk
- Monitor or Review the risk
Now, let us briefly understand each step of the risk management process in cloud computing.
-
Identify the risk - The inception of the risk management process starts with the identification of the risks that may negatively influence an organisation's strategy or compromise cloud system security. Operational, performance, security, and privacy requirements are identified. The organisation should uncover, recognise and describe risks that might affect the working environment. Some risks in cloud computing include cloud vendor risks, operational risks, legal risks, and attacker risks.
-
Analyze the risk - After the identification of the risk, the scope of the risk is analyzed. The likelihood and the consequences of the risks are determined. In cloud computing, the likelihood is determined as the function of the threats to the system, the vulnerabilities, and consequences of these vulnerabilities being exploited. In analysis phase, the organisation develops an understanding of the nature of risk and its potential to affect organisation goals and objectives.
-
Evaluate the risk - The risks are further ranked based on the severity of the impact they create on information security and the probability of actualizing. The organisation then decides whether the risk is acceptable or it is serious enough to call for treatment.
-
Treat the risk - In this step, the highest-ranked risks are treated to eliminate or modified to achieve an acceptable level. Risk mitigation strategies and preventive plans are set out to minimise the probability of negative risks and enhance opportunities. The security controls are implemented in the cloud system and are assessed by proper assessment procedures to determine if security controls are effective to produce the desired outcome.
-
Monitor or Review the risk - Monitor the security controls in the cloud infrastructure on a regular basis including assessing control effectiveness, documenting changes to the system and the working environment. Part of the mitigation plan includes following up on risks to continuously monitor and track new and existing risks.
The steps of risk management process should be executed concurrently, by individuals or teams in well-defined organisational roles, as part of the System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) process. Treating security as an addition to the system, and implementing risk management process in cloud computing independent to the SDLC is more difficult process that can incur higher cost with a lower potential to mitigate risks.
Types of Risks in Cloud Computing
This section involves the primary risks associated with cloud computing.
-
Data Breach - Data breach stands for unauthorized access to the confidential data of the organisation by a third party such as hackers. In cloud computing, the data of the organisation is stored outside the premise, that is at the endpoint of the cloud service provider(CSP). Thus any attack to target data stored on the CSP servers may affect all of its customers.
-
Cloud Vendor Security Risk - Every organisation takes services offered by different cloud vendors. The inefficiency of these cloud vendors to provide data security and risk mitigation directly affects the organisation's business plan and growth. Also, migrating from one vendor to another is difficult due to different interfaces and services provided by these cloud vendors.
-
Availability - Any internet connection loss disrupts the cloud provider's services, making the services inoperative. It can happen at both the user's and the cloud service provider's end. An effective risk management plan should focus on availability of services by creating redunadancy in servers on cloud such that other servers can provide those services if one fails.
-
Compliance - The service provider might not follow the external audit process, exposing the end user to security risks. If a data breach at the cloud service provider's end exposes personal data, the organisation may be held accountable due to improper protection and agreements.
Apart from these risks, cloud computing possesses various security risks bound under 2 main categories.
- Internal Security Risks
- External Security Risks
Internal Security Risks
Internal security risks in cloud computing include the challenges that arise due to mismanagement by the organisation or the cloud service provide. Some internal security risks involve:
- Misconfiguration of settings - Misconfiguration of cloud security settings, either by the organisation workforce or by the cloud service provider, exposes the risk of a data breach. Most small businesses cloud security and risk management are inadequate for protecting their cloud infrastructure.
- Malicious Insiders - A malicious insider is a person working in the organisation and therefore already has authorized access to the confidential data and resources of the organization. With cloud deployments, organisations lack control over the underlying infrastructure; making it very hard to detect malicious insiders.
External Security Risks
External security risks are threats to an organisation arising from the improper handling of the resources by its users and targeted attacks by hackers. Some of the external security risks involve:
- Unauthorized Access - The cloud-based deployment of the organisation's infrastructure is outside the network perimeter and directly accessible from the public internet. Therefore, it is easier for the attacker to get unauthorized access to the server with the compromised credentials.
- Accounts Hijacking - The use of a weak or repetitive password allows attackers to gain control over multiple accounts using a single stolen password. Moreover, organizations using cloud infrastructure cannot often identify and respond to such threats.
- Insecure APIs - The Application Programming Interfaces(APIs) provided by the cloud service provider to the user are well-documented for ease of use. A potential attacker might use this documentation to attack the data and resources of the organisation.
Need for Risk Management
Above discussed risks are the primary security concern for individuals, businesses, and organisations. If actualized, some risks may cause a business to close. These risks need to be treated proactively by implementing risk management strategies. By implementing a risk management plan and considering the various potential risks or events before they occur, an organisation may save money and time and protect its future. This is because a robust risk management plan will help an organisation establish procedures to prevent potential threats and minimise their impact if they occur. This ability to understand and control risks allows organisations to be more confident in their business decisions. Moreover, effective risk management helps organisations to understand the processes deeply and provide information that can be used to make informed decisions to provide increased levels of security and ensure that the business remains profitable. In cloud computing, the organisation sets risk management plans which help them to identify appropriate cloud vendors and service providers, make proper service-level agreements and set up better budgeting plans.
Benefits of Risk Management
Risk management enables organisations to ensure any potential threats to cloud-deployments security, assets, and business plans are identified and treated before they derail the organisation's goals. It has far-reaching benefits that can fundamentally change the decision making process of the organisation. Here are some benefits of robust risk management:
-
Forecast Probable Issues - The risk management process in cloud computing identifies all the possible risks or threats associated with the cloud service provider, the cloud vendor, the organisation, and the users. It helps an organisations to mitigate risks by implementing appropiate control strategies and create a better business plan.
-
Increases the scope of growth - Risk management in cloud computing forces organisations to study the risk factors in detail. Thus, the workforce is aware of all the possible catastrophic events; and the organisation creates a framework that can be deployed to avoid risks that are decremental to both the organisation and the environment. Hence, risk management enables organisations to take a calculated risks and accelerate their growth.
-
Business Process Improvement - Risk Management requires organisations to collect information about their processes and operations. As a result, organisations can find inefficient processes or the scope for improvement in a process.
-
Better Budgeting - Organisations implementing risk management strategies often have clear insights into the finances. Thus, they can create more efficient budgets to implement risk management plans and achieve the organisational goals.
Data Protection Risk Cloud's Impact on IT Operations
With IT companies switching infrastructure to cloud deployments, the risk for data protection becomes essential. The area-specific data protection laws make it hard for companies to comply with the regulations. Moreover, with personal data stored in the cloud, determining the geographical location of the data can be challenging. Therefore, it becomes difficult to hold the applicable law. Hence, developing a hurdle in the IT operations of the company. Let us consider an example; an enterprise uses cloud infrastructure to provide services to its users. The personal data of its users could be stored anywhere in the world such as EU, India and each geographical region has its own data protection rules and regulations. To comply with these regulations, the enterprise must provide different solutions, which increase the workload and redundancy for IT operations.
Best Practices for Risk Management in Cloud Computing
An effective risk management process is a mix of coordinate governance and internal controls. It coordinates the engagement of managers, employers, and stakeholders at each step to embrace risk-taking as an avenue for growth and opportunity. The following are the best practices to manage the risks in cloud computing:
-
Choose the cloud service provider wisely - Perform cloud vendor risk assessment for contract clarity, availability, security, ethics, compliance, and legal liabilities. Make sure, the cloud service provider(CSP) has service providers that can deliver the services accordingly.
-
Deploy Technical Safeguards such as Cloud Access Security Broker - Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) are on-premise or cloud-based software which acts as intermediary between cloud service providers and consumers, to monitor the activities and enforce organisation security policy for accessing cloud applications.
-
Establish controls based on risk treatment - After identification, analysis, and evaluation of the risk. Dedicated measures need to be taken to mitigate risks and drive the business processes to improve. Organisations should delete unwanted data from the hosted cloud.
-
Optimized cloud service model - Adopt a cloud service model that promotes achieving a business solution, minimizes risks, and optimizes cloud investment cost.
-
Strategize Availability of Services - Create redundancy of servers by regions and zones. In this way, if one connection fails, it will not stop the operation of the services.
Conclusion
- With the boost in cloud deployments by organisations, risk management in cloud computing helps to identify and mitigate the risks and protect organisation assets.
- Risk management in cloud computing follows a process that involves identification, analysis, evaluation, treatment, and monitoring of the risks.
- Cloud computing involves a high risk of data breaches, availability and cyberattacks.
- Risk management in cloud computing helps organisations to derive a better business solution while forecasting and minimizing maximum risk factors.
- Good practices such as better availability, CSP selection, and technical safeguards deployment should be followed to minimize cloud-based risks.
