Virtualization in Cloud Computing and Types
Overview
Virtualization in cloud computing involves creating virtual versions of computing resources such as servers, storage, and networks, allowing multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical infrastructure. This enables efficient resource utilization, scalability, and flexibility in deploying and managing applications in the cloud. Virtualization plays a pivotal role in optimizing hardware usage and enhancing the overall performance and cost-effectiveness of cloud services. In this article we will also see types of virtualization in cloud computing.
- Host Machine: The machine on which the virtual machine is going to be built is known as Host Machine.
- Guest Machine: The virtual machine is referred to as a Guest Machine.
Work of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization plays a pivotal role in cloud computing, enabling users to share infrastructure and reduce costs. Cloud providers manage the underlying physical resources, but their services often come at a premium. Virtualization empowers users to outsource IT maintenance to external providers, streamlining operations and optimizing expenses. This cost-saving advantage makes virtualization a cornerstone of cloud computing.
Benefits of Virtualization
The huge growth in the adoption of virtualization and cloud computing is because of the various benefits it provides over traditional computing. Some of these benefits include:
- We can gain better performance and use resources more efficiently in existing computational resources using CPU utilization.
- Since virtual machines are logically separated from the host system and from each other, an attack on one won’t bring down the others. This lets us boost security and availability of VMs.
- We can run many VMs over the same host hardware. This lets us reduce the costs for operation and maintenance of hardware and software
- VMs provide better reliability and disaster recovery than traditional systems, hence letting us rest easy in terms of operation capabilities.
- Virtualization is also environment friendly, as lesser physical resources need to be consumed than a traditional network of a similar scale.
Drawback of Virtualization
- Significant Initial Investment: While cloud adoption offers long-term cost savings, the upfront investment in transitioning to cloud infrastructure can be substantial.
- Learning Curve for New Infrastructure: Shifting from traditional servers to the cloud demands skilled personnel. Employing or training staff proficient in cloud technologies becomes essential for seamless integration and operation.
- Data Security Concerns: Hosting data on third-party platforms introduces potential security risks. The vulnerability to cyber attacks poses a challenge, necessitating robust measures to safeguard against unauthorized access or data breaches.
Characteristics of Virtualization
i) Managed Execution: The execution of the programs can be controlled, with the possibility of it being run on various computer environments.
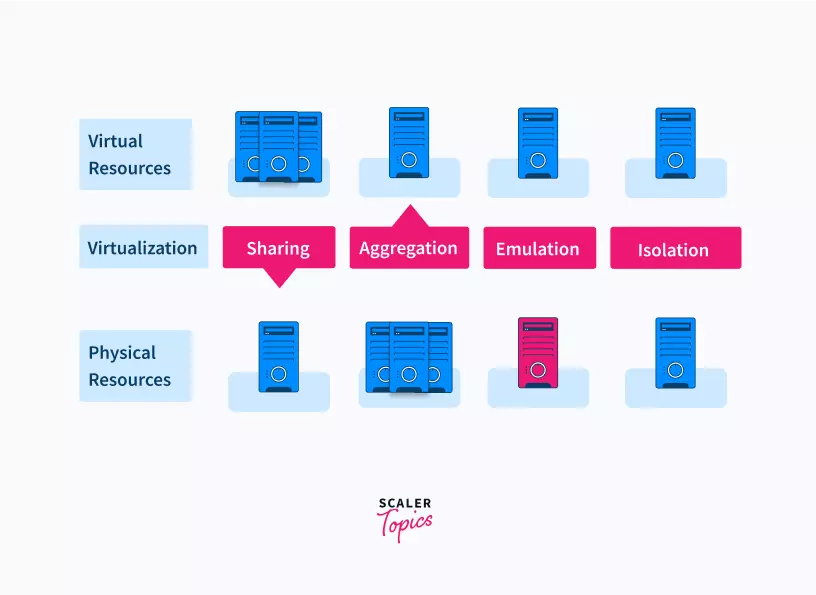
The above figure shows how the various characteristics of virtualization are implemented in the architecture.
ii) Sharing: Virtualization enables separate computing environments to share the same hosts. This helps to decrease the number of servers required to be set up, and in effect reduce power consumption. Resources are shared to decrease the amount of hardware that is needed to run the system.
iii) Aggregation: While sharing involves multiple computing environments sharing one host, the opposite is also possible in virtualization. A group of separate hosts can be consolidated together to appear as one single host to the user. This is called aggregation of resources, and each consolidated group is called a ‘cluster’.
iv) Emulation: Emulation means using a program or a device to imitate the working of another program or device. A program/device completely different to the host can be emulated on the host device through virtualization.
v) Isolation: Virtualization enables the virtual machine(VM) or the guest application to be completely separate from the host machine. An application called the Virtual Machine Manager, also called hypervisor, acts as the middleman between the guest and host machines. This lets the harmful actions from either the guest or host from harming the other.
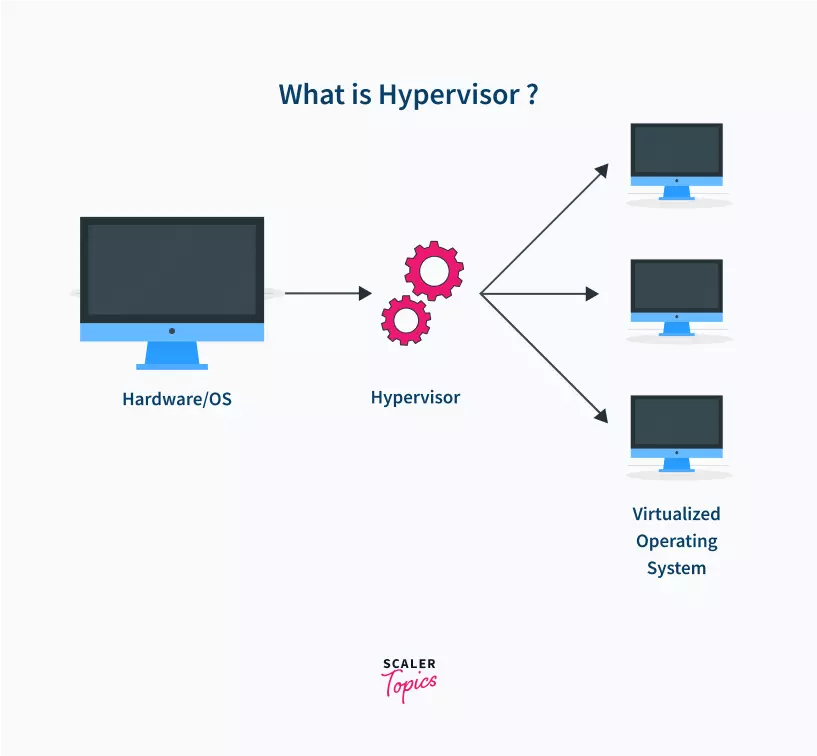
vi) Portability: As we’ve seen above, the virtual image of the guest OS can be downloaded and run on different hosts, and can be run safely and moved to other hosts. The applications can also be run on other hosts without recompilation.
Types of Virtualization
Here are six types of virtualization in cloud computing possible when talking about virtualization techniques:
Application Virtualization
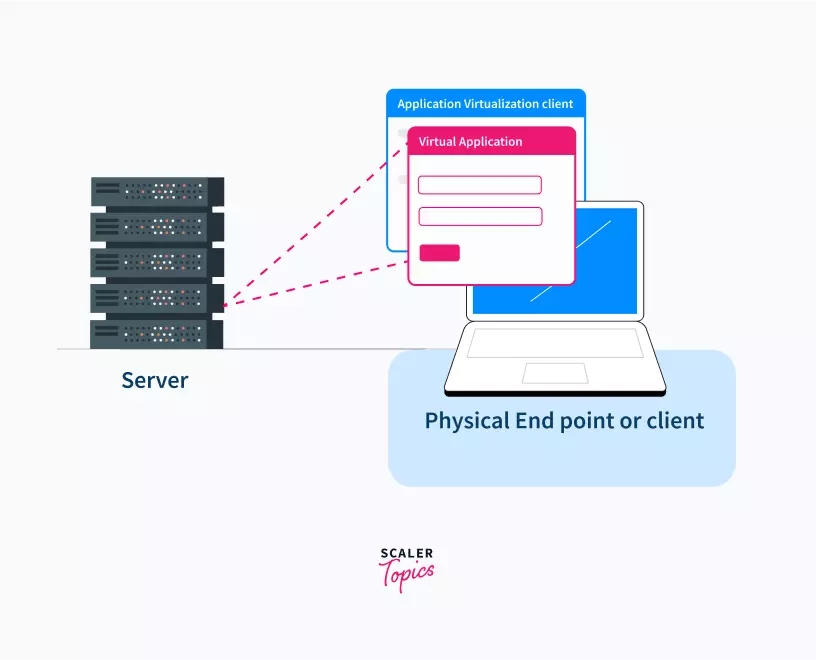
This is among the types of virtualization in cloud computing that enables users to have remote access to an application from a server. The server contains all the data and information of the application running on it, but it can be accessed from another system in a different geographical area through the internet.
Network Virtualization
This is among the types of virtualization in cloud computing that enables us to combine the various available resources by judiciously separating the available bandwidth into different channels. This lets us run multiple virtual networks at the same time, with each channel having different systems communicating.
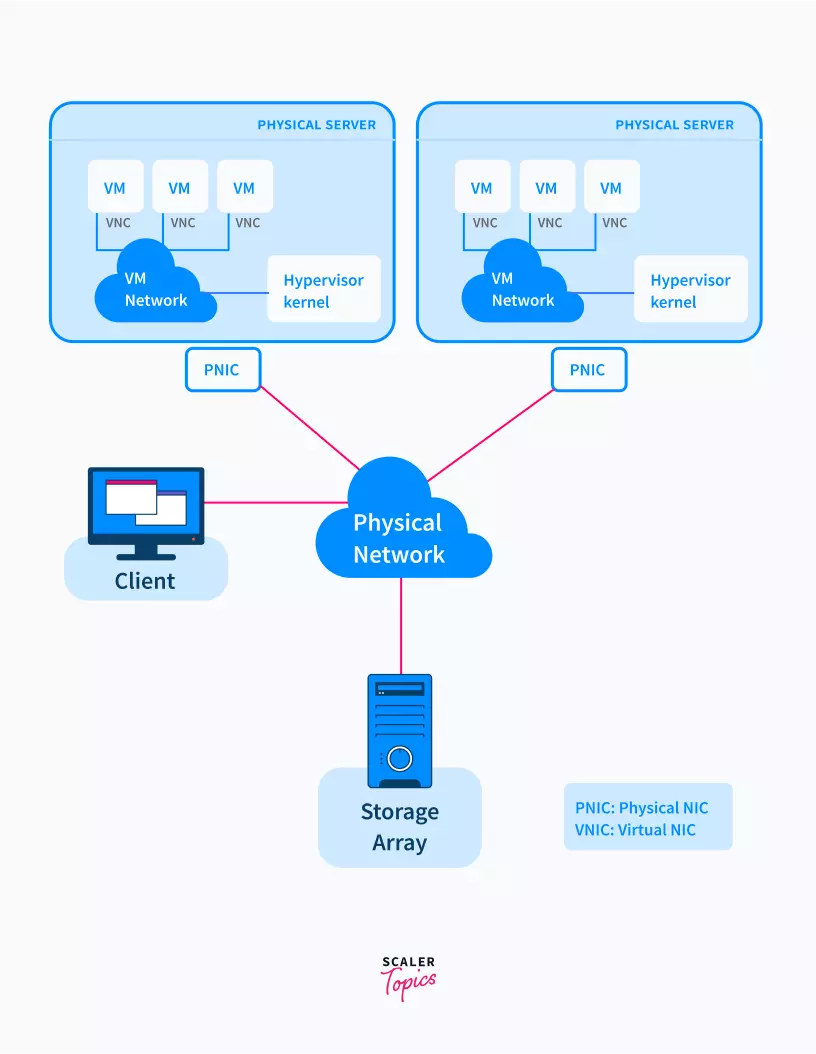
Here, to the client, the different physical server networks that lie on the internet aren’t visible. This enables the client to view the entire network as one big system.
Desktop Virtualization
This is among the types of virtualization in cloud computing that allows the user’s operating system to be accessible from a remote server in a far off data center. It allows the user to access the OS from any system virtually without having to store any data on one client system. A huge benefit of this is that the user can run many different operating systems at the same time without having to reboot or change system settings.
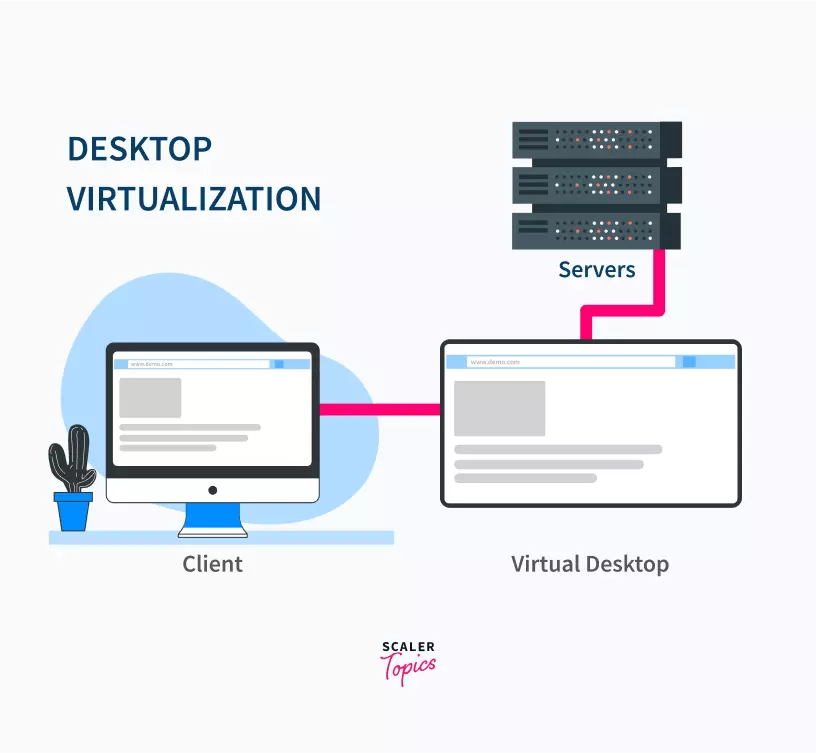
As we can see above, the client can communicate with the servers using the virtual desktop. The user can now access the OS (virtual desktop) to communicate with the server from any client system.
Storage Virtualization
This enables the data given as input and generated as output to be stored on a vast array of servers at a remote data center/s. All the memory storage systems are controlled by the virtual storage systems. The data from multiple sources are stored as a common repository.
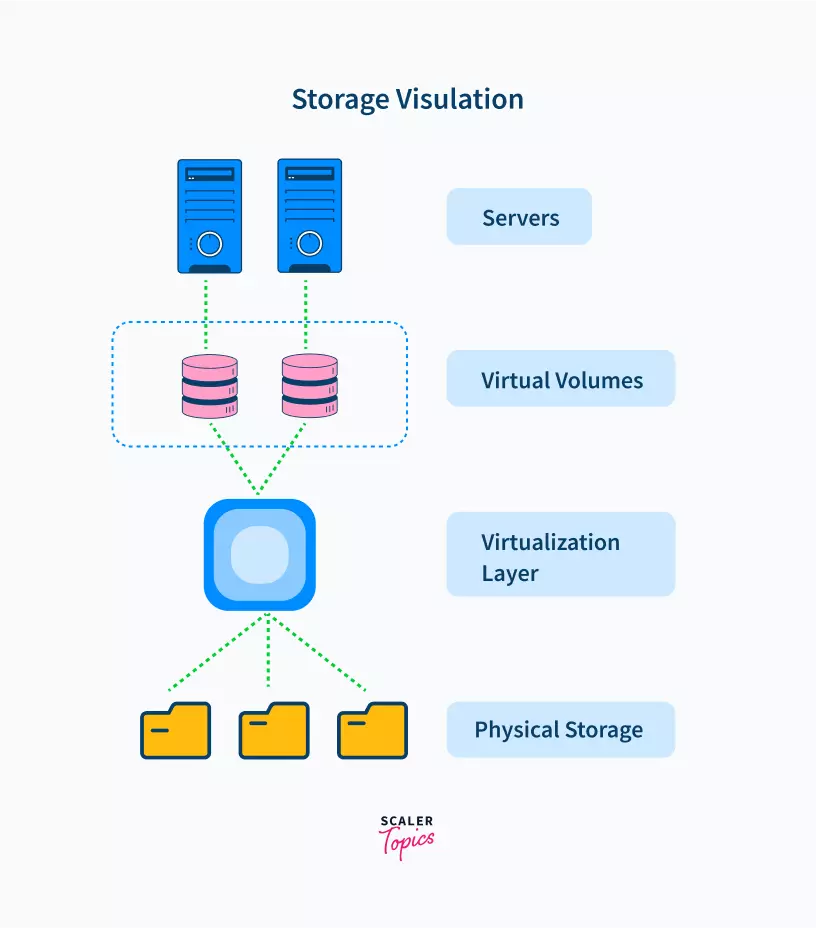
As the above picture shows, data can be stored on multiple physical storage servers but appear to the user that it is being stored on one single system.
Server Virtualization
This enables one central server to be restructured into multiple smaller virtual servers that mimic the functioning of the central server. Each virtual server has its own OS and works in an isolated manner.
With server virtualization, it is now possible to process multiple requests at the same time without overloading the main server with requests. This also increases the availability of the server resource as one server failing won’t have an effect on the functioning of the others.
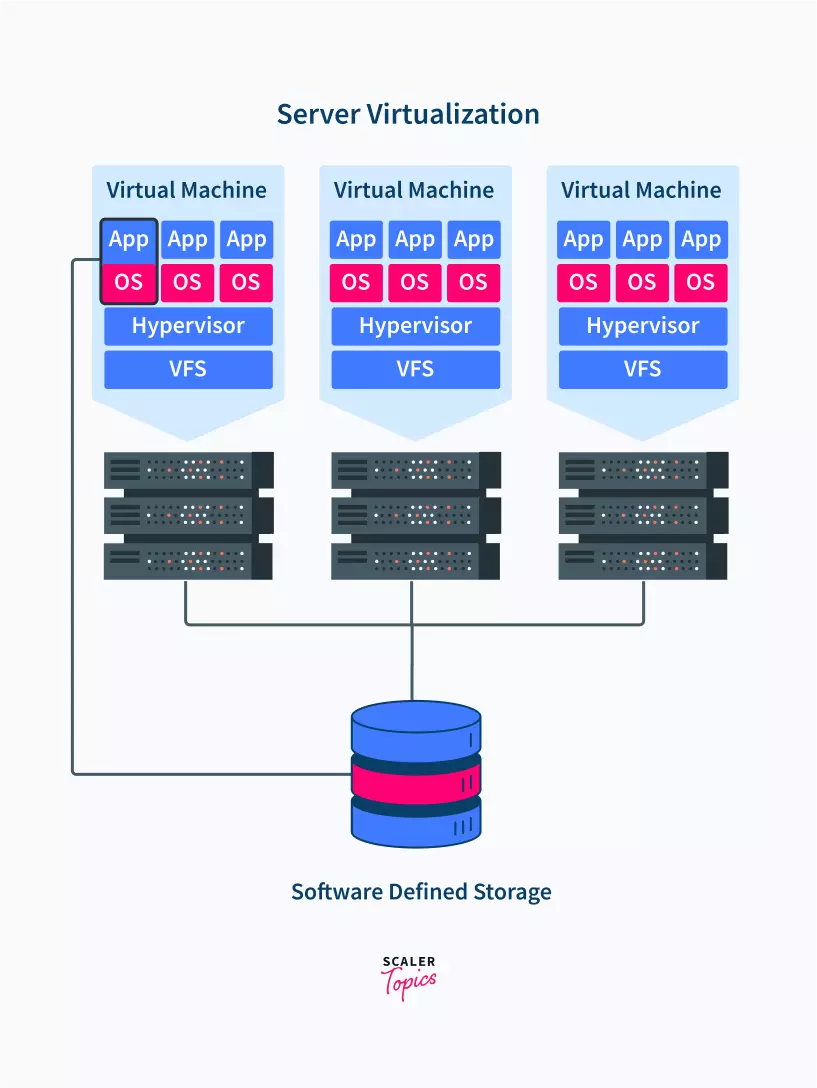
As the figure shows, the data coming from the user can be processed by multiple different servers, but to the user, it appears as if one single server is processing all its requests.
Data Virtualization
This enables the various devices to receive and process data without having to know when and how the data was collected. The data is formatted logically in a way that the virtual view of the data can be accessed by the various stakeholders without having to see the background processes that took place to process that data
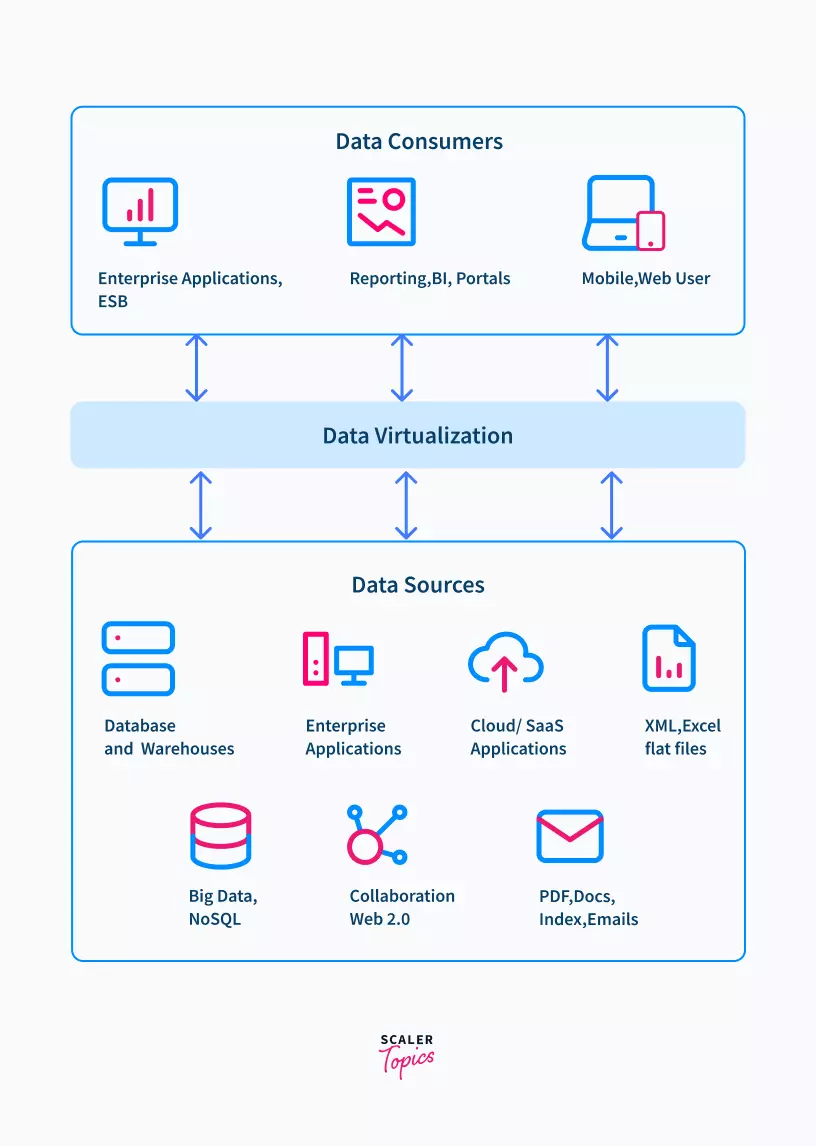
As we can see in the picture above, the data virtualization allows the data processors and data consumers to be separate. This lets the consumers receive data from the sources without having to know when, where or how the data was processed. This significantly increases security as the client doesn’t know where the data is coming from.
Uses of Virtualization
- Data Integration:
- Business Integration:
- Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) Data Services:
- Searching Organizational Data:
Conclusion
- With virtualization, users can pool resources together and create a virtual environment that can be accessed from anywhere in the world at a reduced cost.
- Virtualization is a very cost effective way to increase the collective security, confidentiality, availability and accessibility of data.
- Virtualization also ensures reliability and scalability of the infrastructure that enables these massive processes.
- There are different types of virtualization in cloud computing: Application Virtualization, Network Virtualization, Desktop Virtualization, Storage Virtualization, Server Virtualization and Data virtualization.
- Today, VMWare, Amazon, Citrix and Microsoft are three of the most well known companies that provide virtualization softwares that enable better data processing.
- Microsoft’s Hyper-V platform is well integrated with its Azure cloud services. Amazon’s EC-2 is also well integrated with its AWS cloud services.
