Cloud Firestore in Flutter
Overview
Cloud Firestore is a flexible and scalable NoSQL document database provided by Firebase, a platform for developing mobile and web applications. It allows developers to store, retrieve, and sync data in real time between clients and the cloud. Firestore uses a document-based model to organize data into collections and documents, where each document contains a set of key-value pairs.
Introduction
Firebase is a comprehensive mobile and web development platform provided by Google. It offers a wide range of services and tools to help developers build, test, and deploy applications more efficiently. One of the core components of Firebase is its real-time NoSQL database called Cloud Firestore.
Firebase simplifies the process of adding a database to your app by providing a fully managed cloud-hosted database solution. Here's how Firebase helps in adding a database to your app:
-
Easy Integration:
Firebase seamlessly integrates with various app development frameworks and platforms, including Flutter, Android, iOS, and web, making it accessible and compatible with different app environments.
-
Scalability and Performance:
Firebase offers a scalable, highly available infrastructure for database handling, handling large volumes, concurrent requests, and optimizing performance.
-
Real-time Data Sync:
Firebase enables real-time data synchronization between clients and the cloud. This means that any changes made to the database from one client are instantly propagated to other connected clients, allowing for real-time collaboration and updates.
-
Offline Data Persistence:
Firebase offers offline data persistence, allowing your app to function even when the device is offline. Data changes made offline are automatically synchronized with the server once the device is back online, ensuring data consistency and availability.
-
Security and Authentication:
Firebase provides built-in security features, including authentication and access control mechanisms. You can easily integrate user authentication using Firebase Authentication and enforce security rules to control who can access and modify your database.
Setting up Cloud Firestore
1. Open Firebase Console:
Begin by visiting the Firebase console and logging in to your account. Once you're logged in, you will be presented with a dashboard.
2. Create a New Project:
On the dashboard, click on the Get Started button or Add Project to create a new project. This will take you to the Add Project screen.
3. Enter Project Details:
Create a project by providing a name and following the setup steps, then proceed to the project screen. Set up Firebase with your Android app by clicking the Android icon on the project screen.
4. Modify app-level build.gradle:
Open your project's app-level build.gradle file. Inside this file, locate the defaultConfig section and enter the package name you noted in the previous step. Additionally, you can include any other optional fields if desired.
5. Download google-services.json:
In the Firebase console, locate the section that provides the google-services.json file. Download this file, ensuring that it is named google-services.json. Now move this file to the root directory of the Android app module, at the app-level build.gradle file.
6. Add plugins and dependencies:
Open the google-services.json file, The first block contains the classpath for the project-level build.gradle file, while the second block contains a plugin and dependencies for the app-level build.gradle file.
By following these steps, you will have successfully set up Firebase for your project. This allows you to integrate various Firebase services into your app and utilize their functionalities to enhance your application's capabilities.
Creating a Firestore Database
Firestore uses collections as containers for organizing documents based on common characteristics or purposes, similar to tables in a traditional database.
Firestore collections organize documents by identifying each document with a unique ID. They offer logical organization and flexibility in defining fields. Firestore supports querying collections, enabling real-time synchronization of changes, and enabling seamless collaboration and updates. This collection-based structure provides scalability, flexibility, and efficient data management for applications.
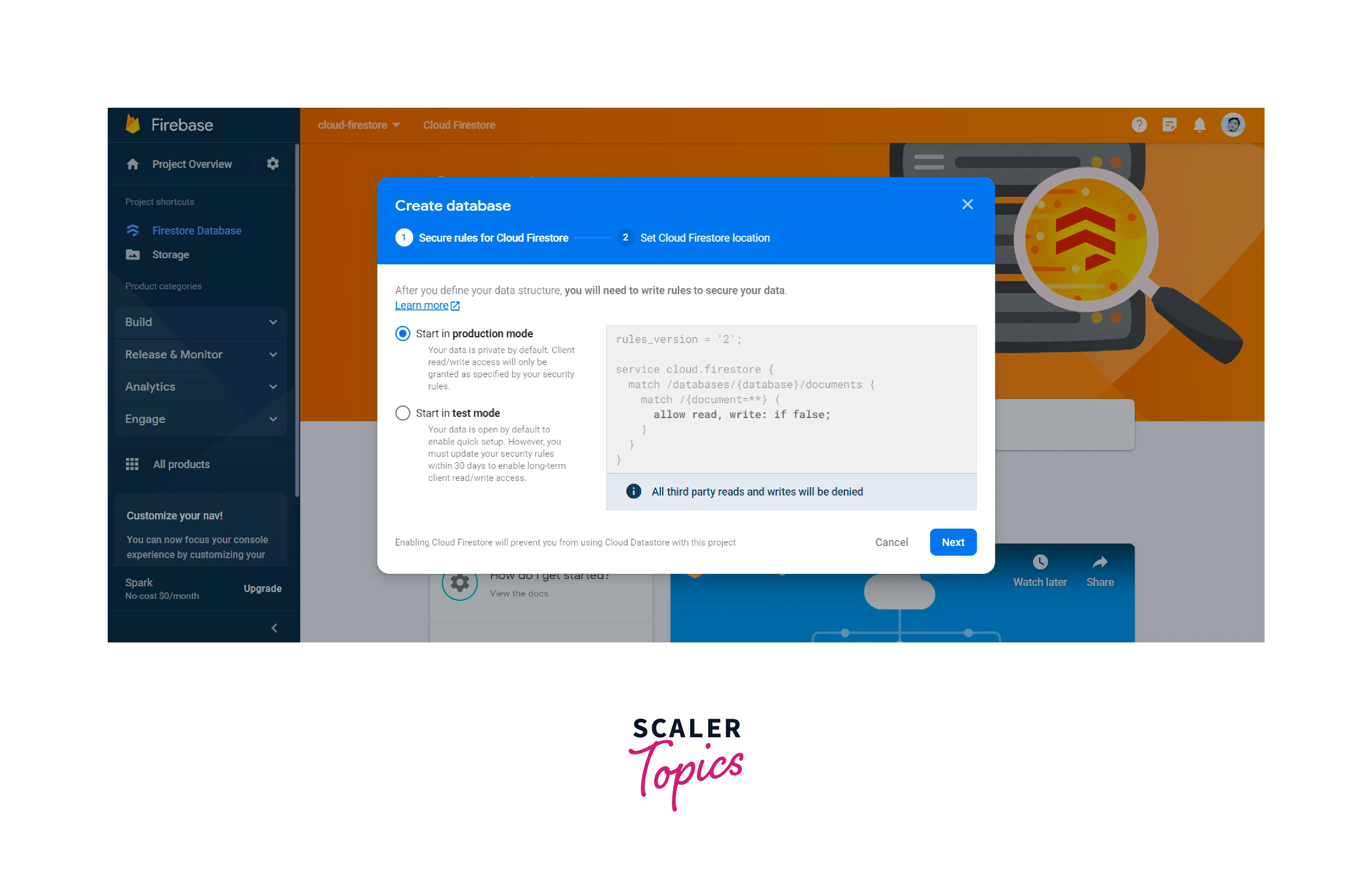
Follow these steps to create your database -
- Access the Firebase Console and select or create your project.
- Navigate to the Firestore section and create a new database.
- Choose the mode (e.g., Production or Test) and geographical location for your database.
- Create collections as containers for related data and add documents with key-value pairs to store information within the collections.
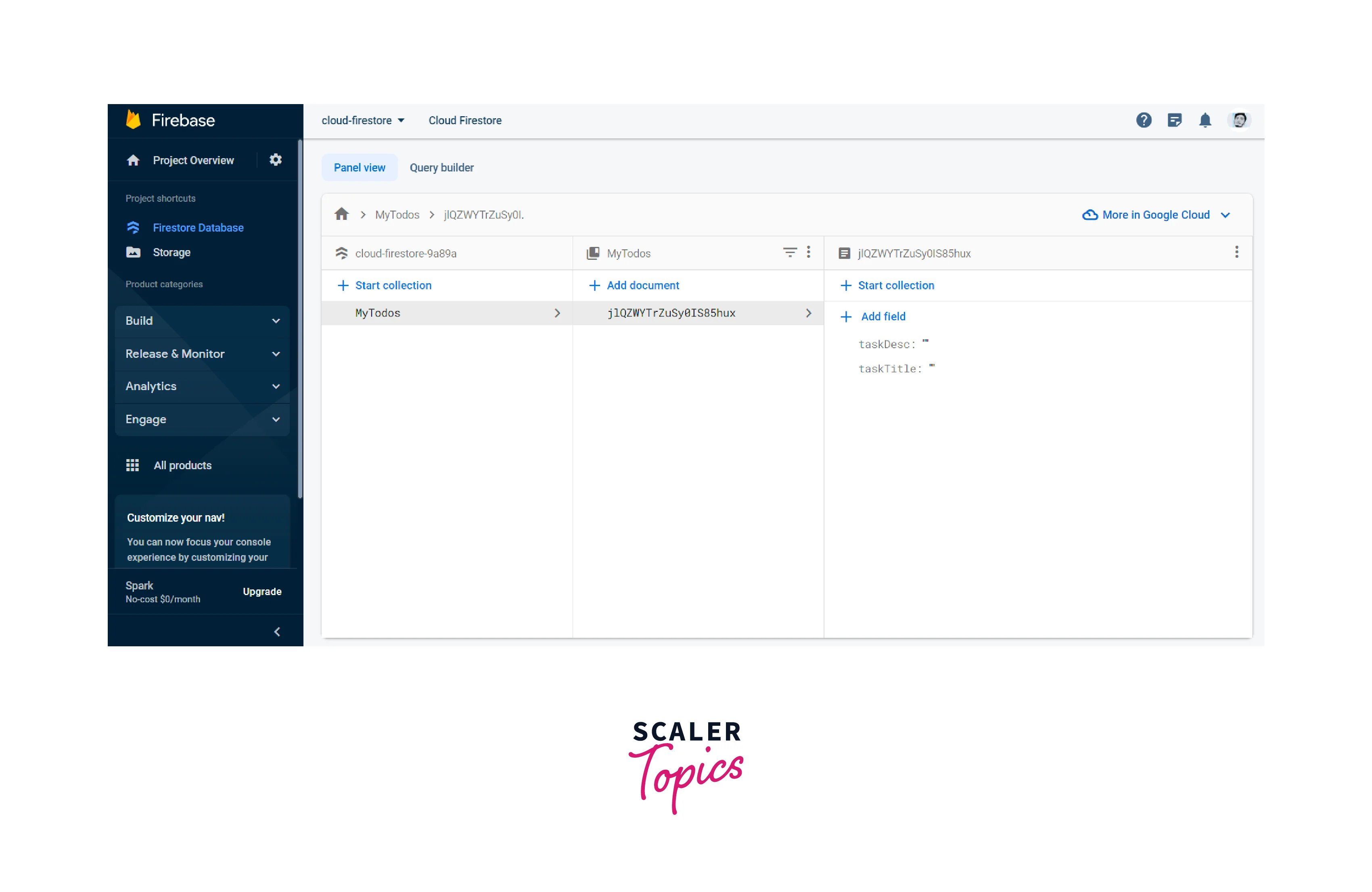
Reading Data from Firestore
Reading data from Firestore involves retrieving documents or collections from the database. Firestore provides powerful querying capabilities to filter and sort data based on specific criteria. Let's explore how to read data from Firestore using an example of a to-do list** app.
First, ensure that you have set up Firebase Firestore and established a connection to your project. Then, follow the steps below to read data from Firestore:
Import Firestore Package
To interact with Firestore in your Flutter app, import the cloud_firestore package:
Retrieve a Collection
To read data from Firestore, start by retrieving a collection. In our to-do list example, we assume that tasks are stored in a collection called tasks. Use the collection() method to get a reference to the collection:
Read All Documents in a Collection
To retrieve all documents within the tasks collection, use the get() method on the collection reference. The get() method returns a Future that resolves to a QuerySnapshot containing the documents:
In the code above, the getTasks() function uses the get() method to retrieve the documents within the tasks collection. It then iterates over each document using the forEach() method and prints the title and description of each task. You can access other fields in a similar manner.
Real-time Updates with Streams
Firestore also supports real-time updates using streams. By using a StreamBuilder, you can listen to changes in the Firestore collection and update the UI automatically. Here's an example:
In the above code, the StreamBuilder listens to changes in the tasks collection using the snapshots() method. It rebuilds the UI whenever there are updates in the collection. The ListView displays the title and description of each task using a ListTile. You can customize the UI to suit your specific needs.
Reading Data from Firestore
Writing data to Firestore allows you to create, update, and delete documents within collections. In this section, we will explore how to write data to Firestore:
Create a New Task
To add a new task to Firestore, use the collection() method to reference the tasks collection. Then, use the add() method to create a new document within the collection:
In the code above, the createTask() function takes the title and description of the task as parameters. It uses the add() method to create a new document in the tasks collection, with the specified fields. Any additional fields can be included as key-value pairs in the document.
Update an Existing Task
To update an existing task, you need to reference the specific document within the collection and use the update() method:
In the code above, the updateTask() function takes the task ID, new title, and new description as parameters. It uses the doc() method to reference the specific document within the tasks collection, and then updates the desired fields using the update() method.
Delete a Task
To delete a task, you need to reference the specific document within the collection and use the delete() method:
In the code above, the deleteTask() function takes the task ID as a parameter. It uses the doc() method to reference the specific document within the tasks collection, and then deletes the document using the delete() method.
Firestore Security Rules
Firestore Security Rules are a powerful feature of Firestore that enables you to control access to your database and enforce data validation and security measures. These rules determine who can read, write, and modify data in your Firestore database. Let's dive into the details of Firestore Security Rules:
Security Rule Structure:
Firestore Security Rules are written in a declarative syntax and follow a specific structure. They are defined within a service declaration and a match statement. The service declaration identifies the Firestore service, and the match statement specifies the path to the documents the rules apply to. Here's an example structure:
Basic Read/Write Rules:
Firestore Security Rules allow you to define who can read and write data in your Firestore database. You can set rules at the collection or document level. For example, you can allow anyone to read a collection or document using allow read: if true;. Similarly, you can restrict write access based on specific conditions using allow write: if <condition>;. The condition can include variables like request, resource, and auth.
Granular Operations:
Firestore Security Rules provide flexibility for defining rules for specific operations like get, list, create, update, and delete. This granularity allows you to have different conditions and access controls for each operation. For example, you can allow users to create new tasks in a to-do list but only allow them to update or delete their tasks.
Hierarchical Data and Wildcards:
Firestore organizes data in collections and documents, allowing for hierarchical structures. Firestore Security Rules support hierarchical data with the use of wildcards. Recursive wildcards ({name=**}) match any segment of a path between slashes, while chained match statements allow you to specify rules for subcollections within documents. This is useful when organizing tasks within categories or subcategories in a to-do list app.
By leveraging Firestore Security Rules effectively, you can ensure the security, integrity, and privacy of your data in Firestore. It is crucial to carefully design and test your security rules to align with your application's requirements and protect against unauthorized access and data manipulation
Example Application
Now let's create an example to-do list app that incorporates the features we discussed, including setting up Firestore, reading data, writing data, and applying security rules.

This code sets up a basic to-do list app with the ability to add tasks and display them in a ListView. The tasks are stored in the Firestore collection named tasks and are associated with the current user's ID. The user can add a task by entering a title and description and tapping the Add Task button. The tasks are then fetched from Firestore and displayed in a ListView. Each task item has a delete button that allows the user to delete the task from the Firestore database.
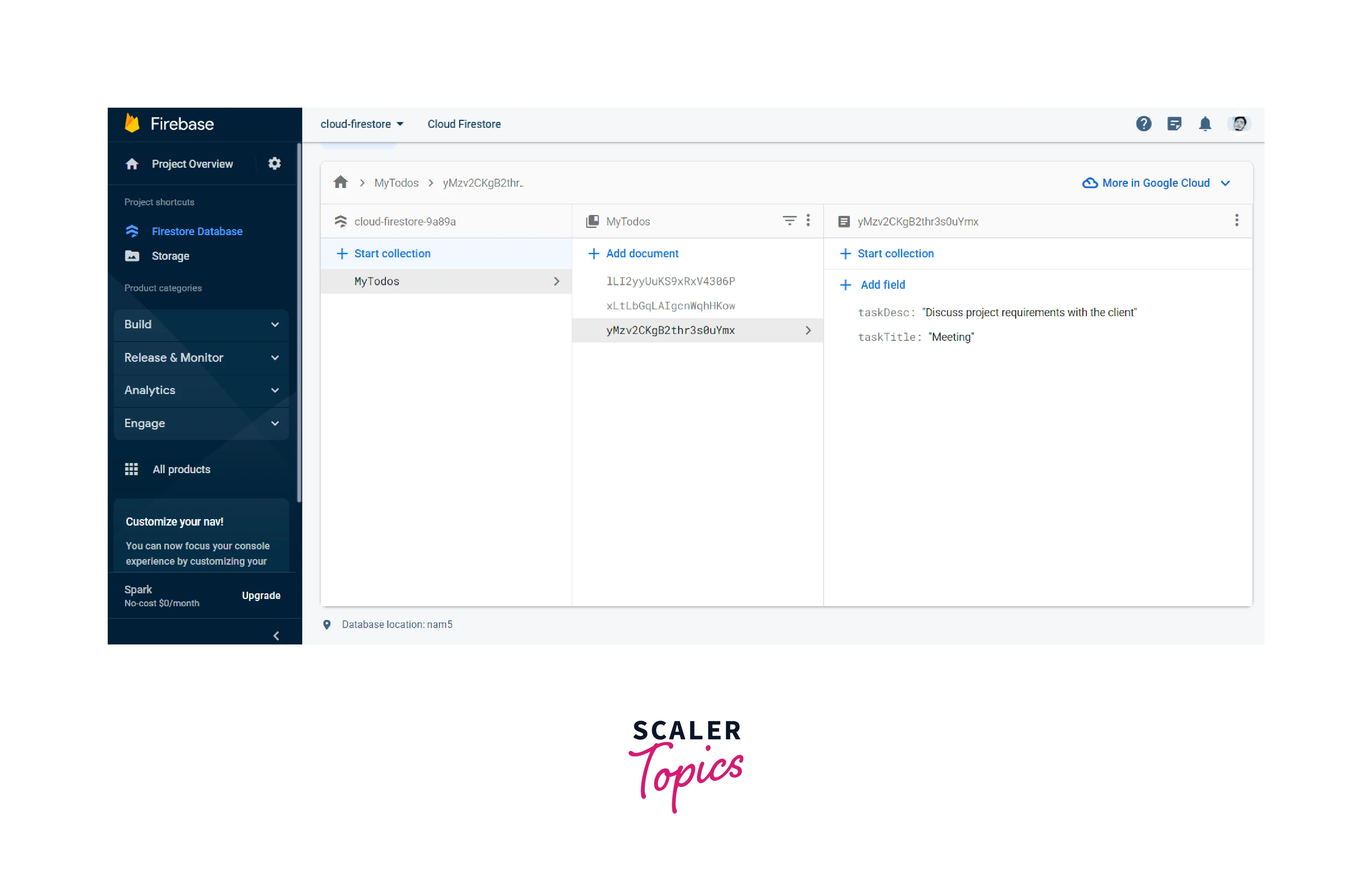
Note: Make sure you have set up Firebase and Firestore in your Flutter project and initialized Firebase Authentication before using this code.
Conclusion
- Cloud Firestore in Flutter is a powerful combination that allows developers to build robust, real-time, and scalable applications with a flexible NoSQL database.
- Cloud Firestore setup involves creating a Firebase project, integrating with the Flutter app, and configuring dependencies.
- Creating a Firestore database involves organizing data into collections and documents, which provide a structured and scalable approach to storing and retrieving data.
- Streams and StreamBuilders make it simple to read data from Firestore, allowing for real-time updates and efficient data synchronization between the app and the database.
- Firestore enables users to create, update, and delete documents, enabling CRUD operations on data through Firestore instance methods.
- Firestore Security Rules ensure database security by restricting read and write operations, ensuring data privacy and integrity, and controlling access to data.
