Container with Most Water

Problem Statement
You are given an array of integers of size n, where each value represents a coordinate position . n vertical lines are drawn such that the endpoints of line i are at and . Find the container that is formed by two lines along with the x-axis, where the container contains the most water.
Example
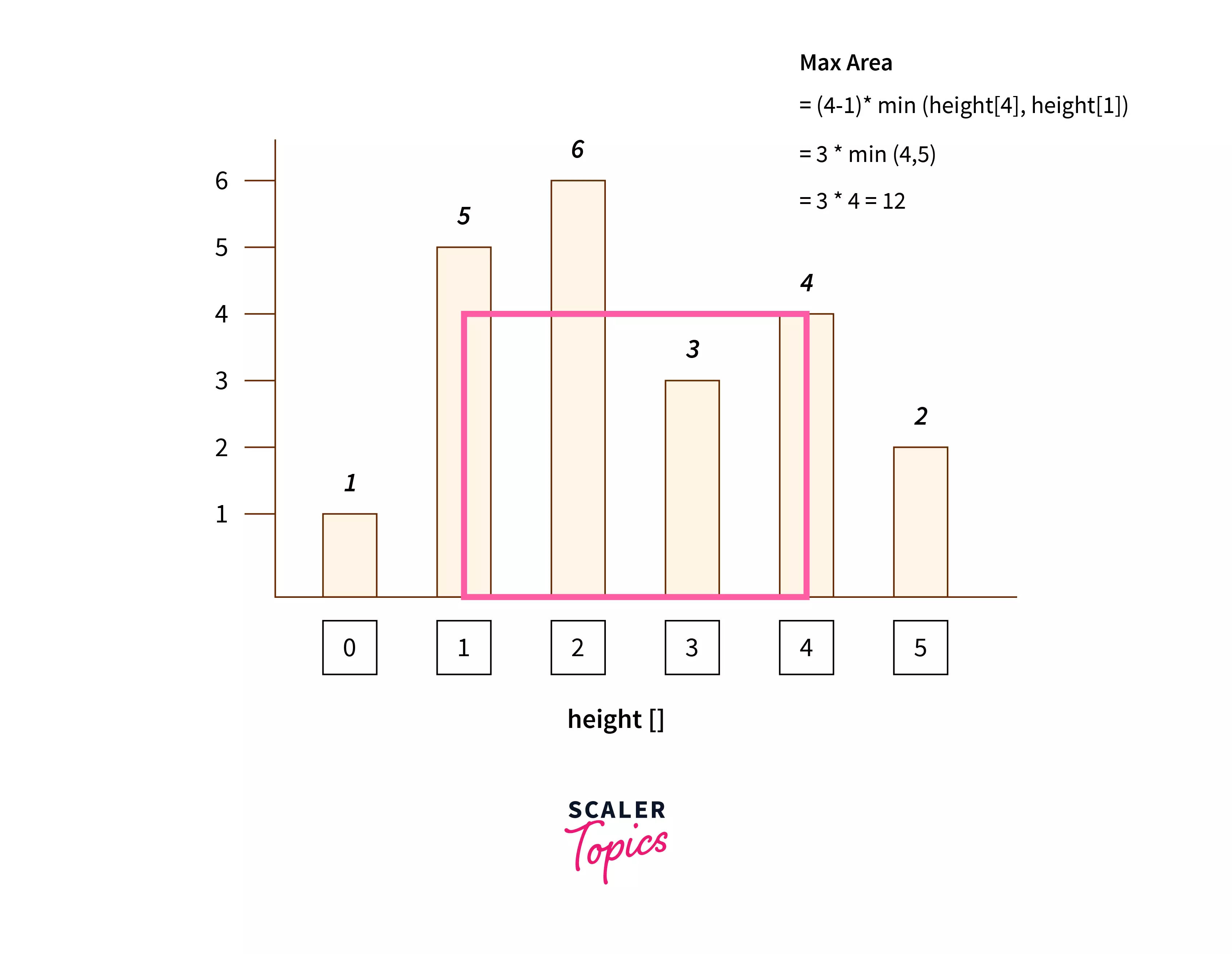
Input - 1
Output - 1
Explanation
The area shown in the blue section is the maximum area.
- 1 and 4 are distance 3 apart.
- Therefore, the size of the base = 3.
- Height of the container will be a minimum of
- Hence, The total area becomes units.
Input - 2
Output - 2
Explanation
Since there are only two endpoints, the area becomes .
Constraints
Algorithm - 1 : Naive Approach - Using Nested Loops
Intuition
The most basic and straightforward approach for a container with the most water is to check all the possible pairs of boundaries and find out a team that has a maximum area.
Algorithm
- Initialize a variable maxArea to track the current maximum area.
- Run a nested loop, the outer loop from to end .
- While the inner loop runs from to end with loop counter j.
- Find the area for every pair of boundaries i and j, and store the area in the variable maxArea, where maxArea= *. Update the variable maxArea, if the current area is greater than the maxArea.
- Return the maxArea.
Code Implementation
Code in C++ :
Code in Java :
Code in Python :
Output :
Time Complexity :
The time complexity is . Since two nested loops traverse the array.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity is . Since no extra space is used in the solution of the container with the most water.
Algorithm - 2 : Efficient Approach - Using Two Pointers
Intuition
We take two pointers, one at the start and one at the end of the array, and we keep track of the maximum area between the lines in a variable maxArea. At each step, we calculate the area formed by the two pointers, update the maximum area, and move the pointer pointing to the shorter line by one to the opposite end.
Check the below illustration of two pointer approach to solving container with most water problem :
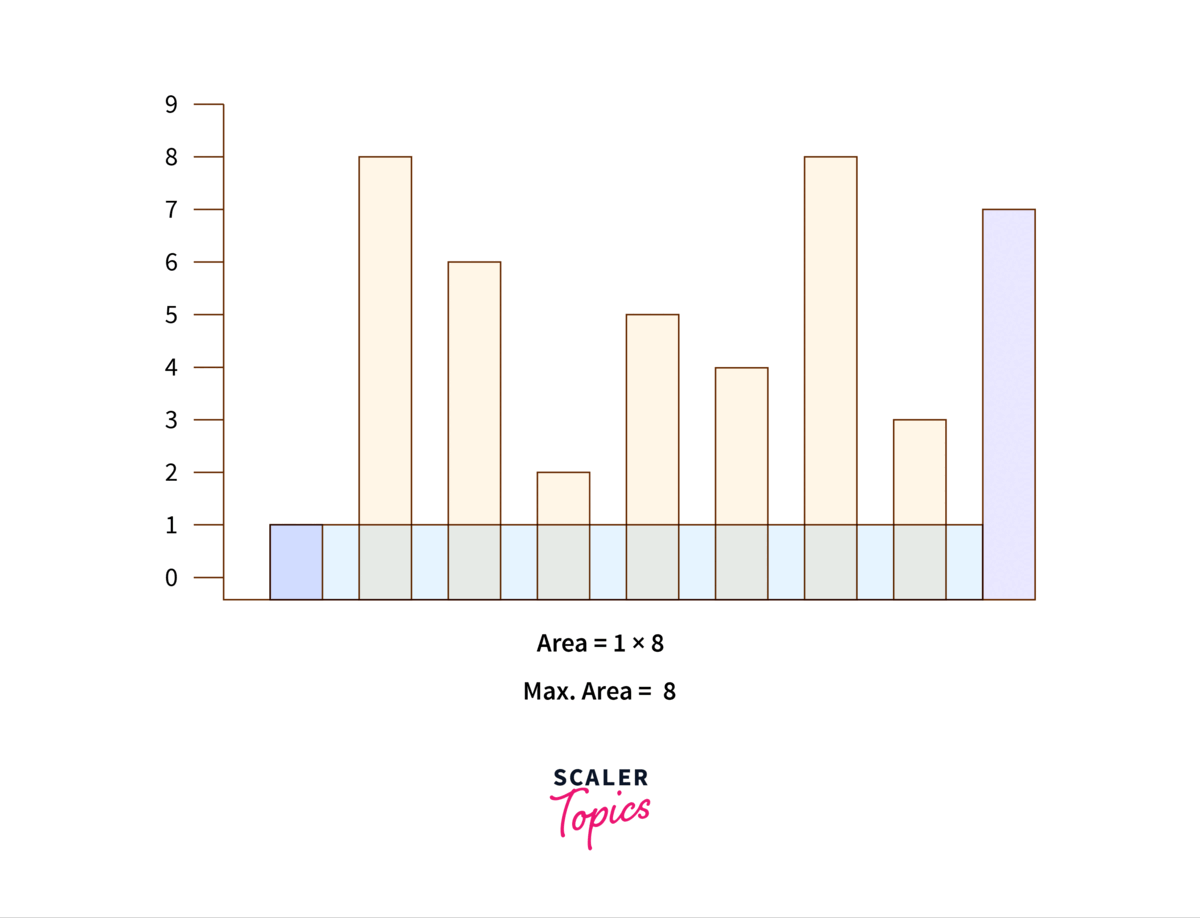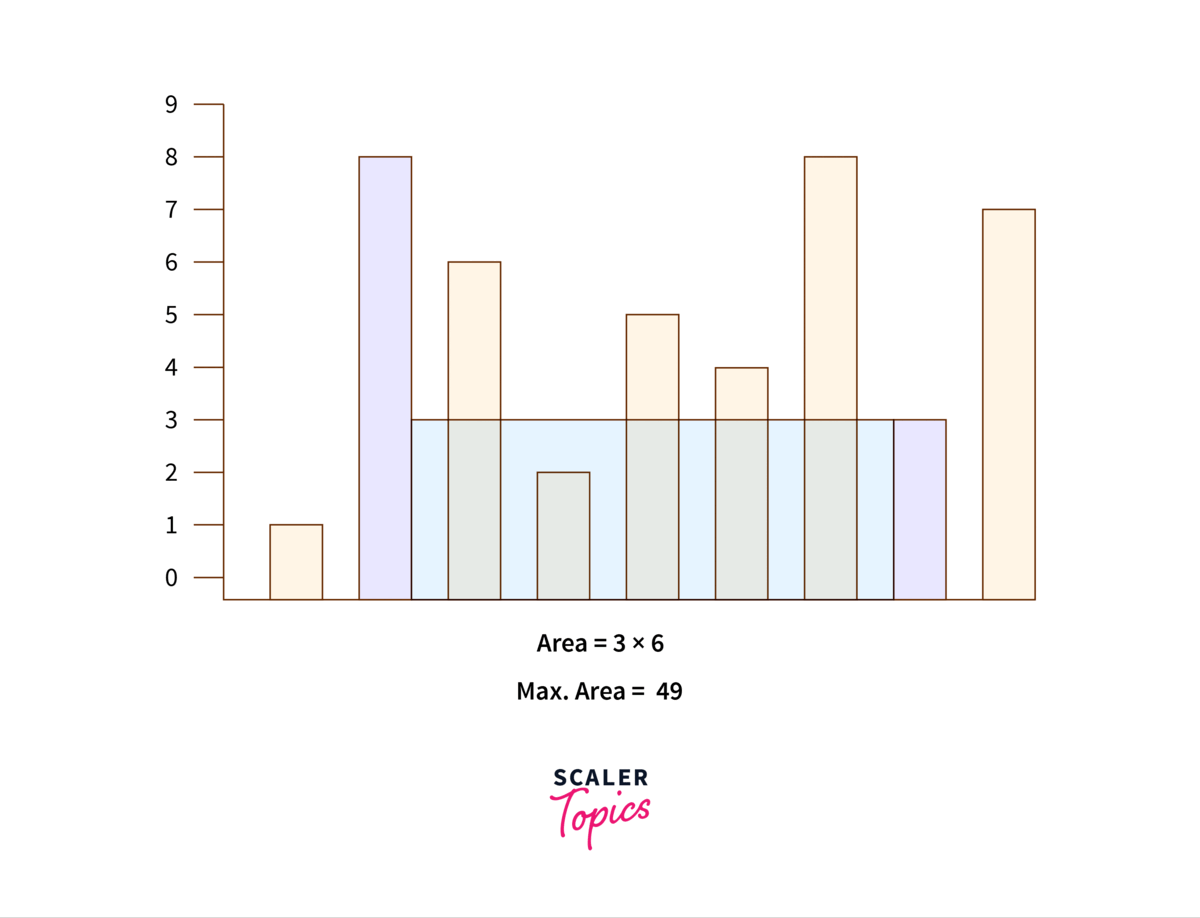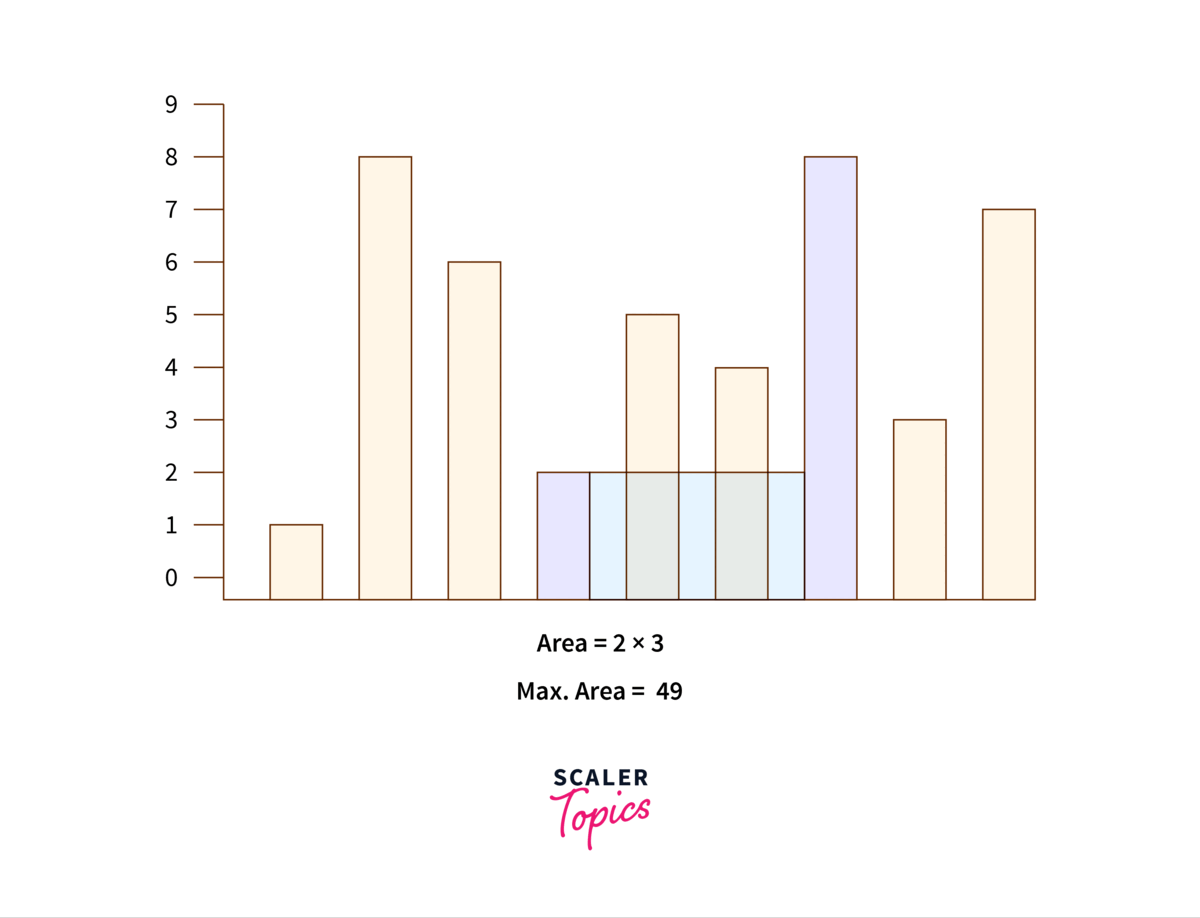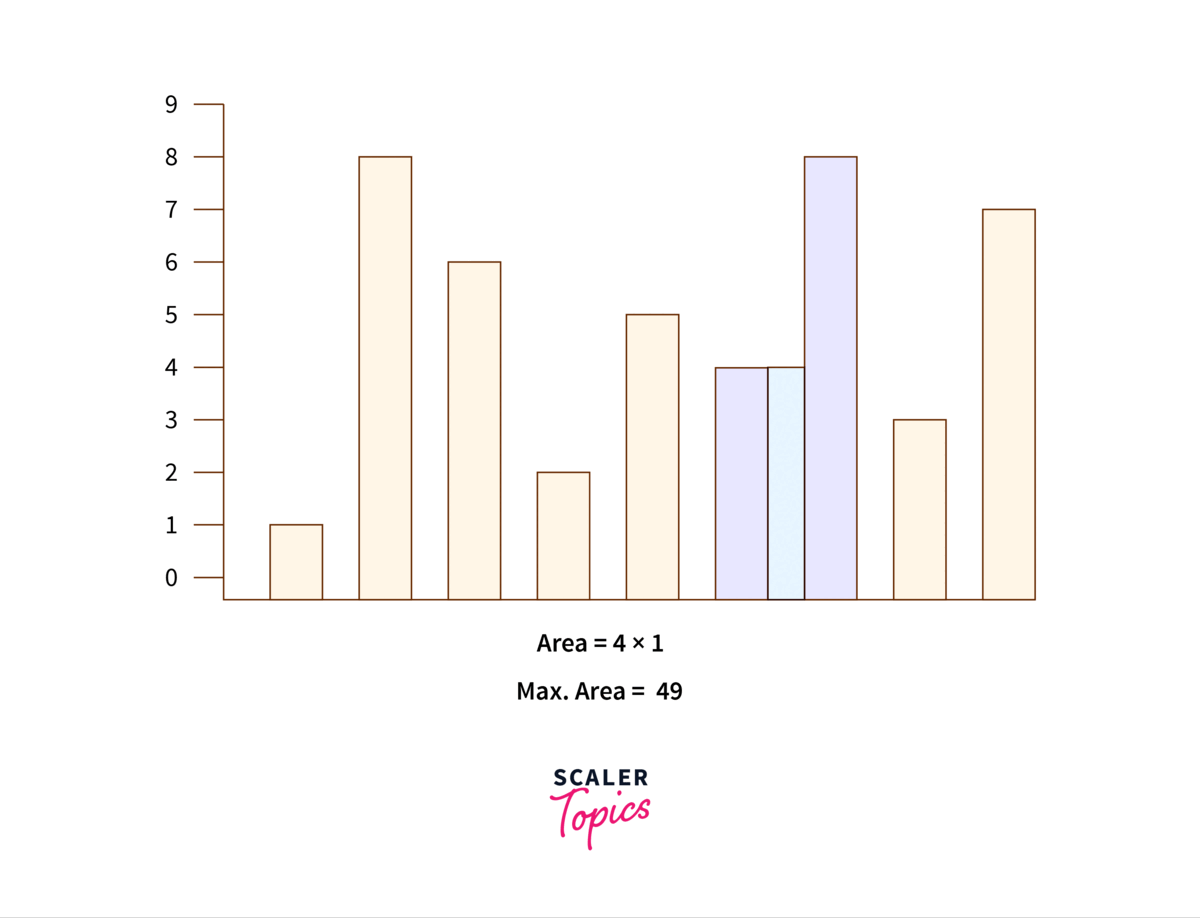
Algorithm
- Initialize a variable maxArea to track the current maximum area of a container with the most water.
- Keep two indices, and initialized at 0 and , respectively.
- Run a loop until the left index i is less than the right index j.
- Calculate the area formed between indices i and j, where area and update the maxArea.
- If the value at is lesser than then move index i by one right. Else move index j by one left.
- Return the maxArea.
Code Implementation
Code in C++ :
Code in Java :
Code in Python :
Output :
Time Complexity :
The time complexity is . Since only one traversal of the array is required.
Space Complexity :
The space complexity is . Since no extra space is used in the solution of the container with the most water.
Conclusion
- We have given an integer array of length n, where each value refers to a coordinate position .
- We have to find the two lines that form a container along with the x-axis, such that the container contains the most water.
- For eg, If the array is , the size of the base , Height of the container will be 7 and the area becomes units.
- The naive approach takes time complexity as two loops were used, and space complexity because no extra space is used.
- On the other hand, the efficient approach for a container with most water is using the Two-pointer Technique. It takes time complexity and as space complexity.
- We initialize a variable maxArea in both approaches to track the current maximum area.
FAQs
Q. How can the area between two points be calculated ?
A. The length is the distance between the two endpoints, and the minimum of the two heights is going to be the height because each consecutive block's width is considered to be 1. Hence, area .
Q. What is the most efficient approach to solve this problem ?
A. The most efficient approach for a container with the most water is using the Two-pointer Technique because it takes time complexity and as space complexity.
Q. Similar Coding questions to practice?
A. Refer to Trapping Rain Water
- Refer Triplet with Zero Sum
