Understanding CrashLoopBackOff Error and Ways to Fix its
Overview
In the fast-paced world of modern software development, deploying and managing applications at scale can be a daunting task. This is where Kubernetes comes to the rescue. As a leading container orchestration platform, Kubernetes has revolutionized the way applications are deployed, scaled, and managed. With its robust set of features and self-healing capabilities, Kubernetes has become the go-to choice for organizations worldwide.
However, even the most powerful systems encounter hiccups from time to time. In the realm of Kubernetes, one of the common challenges developers and operators face is the enigmatic "CrashLoopBackOff" Kubernetes error. When this error surfaces, it indicates that a container within a Kubernetes Pod is stuck in a constant loop of crashing and failing to start successfully. While it may sound intimidating, fear not! We are here to shed light on this issue and guide you through the path to resolution.
In this article, we will explore the causes behind the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes error and provide you with practical solutions to overcome it.
CrashLoopBackOff Error in Kubernetes
Picture this: you've just deployed your shiny new application on Kubernetes, expecting it to conquer the digital realm with its brilliance. But instead, you find yourself caught in a frustrating loop of disappointment. Your application's container keeps crashing, attempting to start, failing, and then crashing again. It's like a relentless dance of chaos, leaving you scratching your head and wondering, "What on earth is going on?"
Welcome to the world of CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes pod error. This error occurs when a container, housed within a Kubernetes Pod, repeatedly fails to start successfully and falls into an endless cycle of crash and burn. It's like a Groundhog Day nightmare for your application, and it's time to put an end to it.
Why does this happen, you may wonder? Well, the reasons can be as diverse as the colors of a neon rainbow. From resource allocation quirks to sneaky configuration gremlins and even the occasional network hiccup, a variety of factors can contribute to the CrashLoopBackOff pod error. But fret not, for we are about to embark on a journey of unraveling these causes and equipping you with the knowledge to triumph over this maddening issue.
In the following sections, we will shine a light on the most common culprits behind the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes error. We will explore scenarios where insufficient resources lead to container temper tantrums, instances where initialization failures dampen the application's spirit, and encounters with configuration demons that sow seeds of chaos. So, gear up, dear reader, as we dive into the depths of Kubernetes troubleshooting and unlock the secrets to banishing the CrashLoopBackOff error once and for all!
Common Causes of CrashLoopBackOff in Kubernetes
The CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes pod error can be triggered by a variety of issues, preventing your container from starting successfully and trapping it in an endless loop. Let's delve into the most common causes behind this frustrating phenomenon and explore them in more detail:
- Insufficient Resources:
When your container lacks the necessary resources, such as CPU, memory, or storage, it may struggle to load properly and trigger the CrashLoopBackOff error. This can happen if your application is demanding more resources than allocated. For example, if your container requires 2GB of memory, but you only allocated 1GB, it will result in a resource shortage and the CrashLoopBackOff error.
- Failed Reference:
If your container references scripts or binaries that are missing or unavailable within the container, it can result in startup failures and trigger the CrashLoopBackOff error. For instance, if your container relies on a script to perform a specific task during startup, but that script is missing or located in the wrong directory, it will fail to execute, causing the CrashLoopBackOff error. - Setup Error:
Issues with the initialization setup in Kubernetes, such as misconfigured init-containers, can prevent your container from starting correctly. Init-containers are containers that run and complete before the main container starts. If there are errors in the init-container configuration, it can lead to startup failures and trigger the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes pod error. For example, if an init-container fails to download required dependencies or initialize necessary configurations, the main container won't start properly, resulting in the CrashLoopBackOff error. - Configuration Loading Error:
If a server or application within your container fails to load the required configuration file properly, it can result in startup failures and trigger the CrashLoopBackOff pod error. This can happen if the configuration file is missing, has incorrect permissions, or contains errors. For example, if a web server fails to load its configuration file, it won't start listening on the correct port or load the necessary settings, causing the CrashLoopBackOff error. - Misconfigurations:
General misconfigurations in the file system can disrupt the container's startup process and contribute to the CrashLoopBackOff error. This can include incorrect file permissions, incorrect file paths specified in the configuration, or missing files. For instance, if your container expects a configuration file in a specific directory, but the file is located elsewhere or has the wrong permissions, it will fail to start properly and trigger the CrashLoopBackOff error. - Connection Issues:
DNS or kube-dns problems that hinder connectivity to external services can cause the CrashLoopBackOff error when your container relies on those services. For example, if your application depends on an external database service but cannot establish a connection due to DNS resolution issues or network connectivity problems, it will fail to start and result in the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes pod error. - Deploying Failed Services:
Attempting to deploy services or applications that have already failed, usually due to lacking access to other required services, can result in the CrashLoopBackOff error. For example, if your application requires a database service to be running, but the database service failed to start or is not accessible, any subsequent attempts to deploy the application will fail, triggering the CrashLoopBackOff error. - Missing Dependencies:
Incorrect or missing configurations in crucial files can prevent the container from starting correctly, triggering the CrashLoopBackOff error. Double-check all file locations and configurations, ensuring that all necessary dependencies and configurations are present. For instance, if your application expects a specific configuration file in the "/config" directory, but the file is missing or located in a different directory, the container will fail to start and result in the CrashLoopBackOff error.
How to Fix CrashLoopBackOff Error in Kubernetes
After understanding the potential causes of the CrashLoopBackOff state, it's essential to know how to identify and resolve the specific issue affecting your Pod. Let's explore the following steps to debug and fix the CrashLoopBackOff error:
Check the Pod Description
The kubectl describe pod command provides detailed information about a specific Pod and its containers:
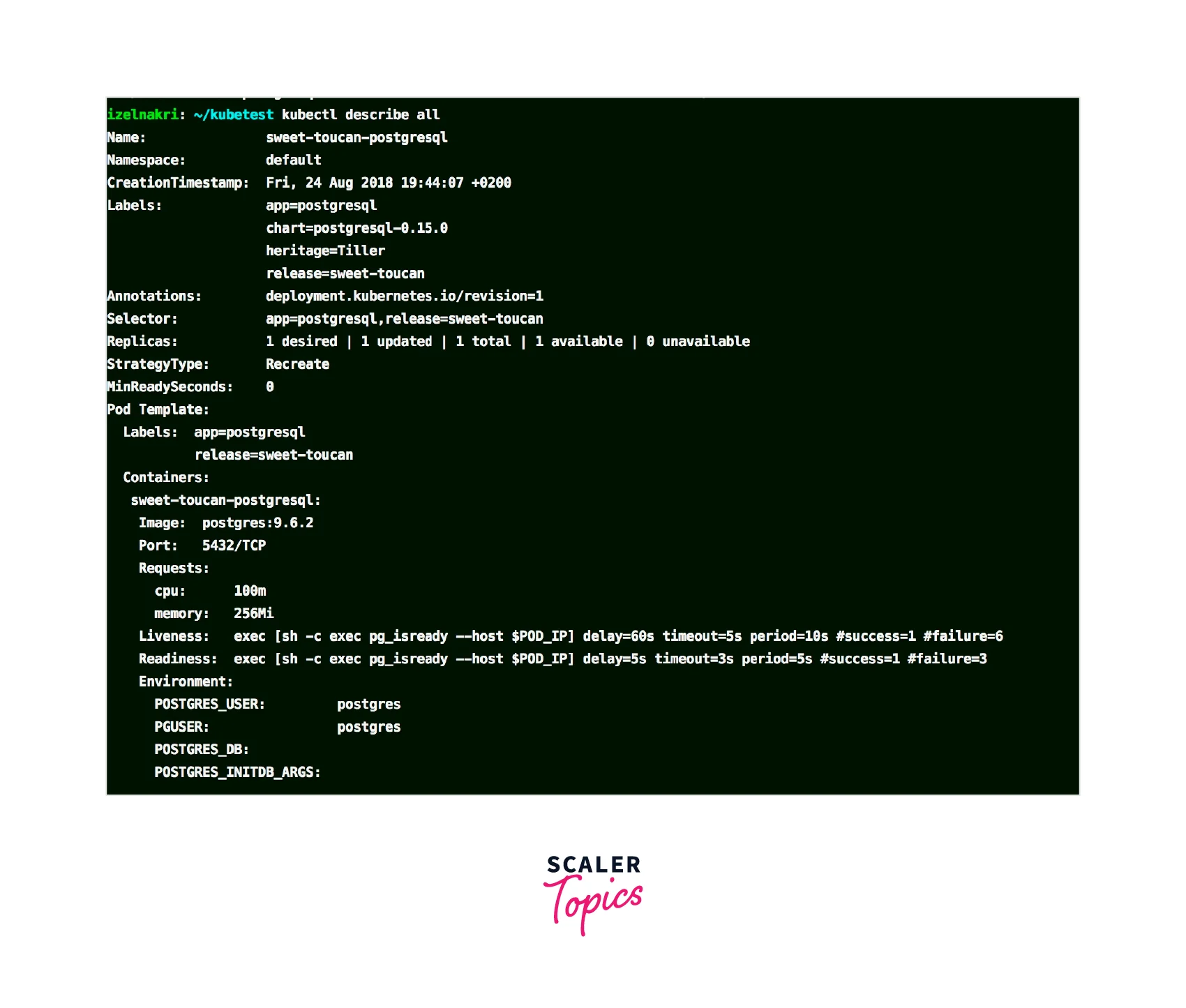
From the output of kubectl describe pod, examine the following information:
- The current state of the Pod should be "Waiting."
- The reason for the Waiting state is typically "CrashLoopBackOff."
- The last state should be "Terminated."
- The reason for the last termination is often "Error."
By analyzing this information, you can identify potential misconfigurations in the Pod definition, container settings, pulled image, allocated resources, or missing/wrong arguments.
Check the Pod Logs
View the logs for all containers in the Pod:
Alternatively, view the logs for a specific container in the Pod:
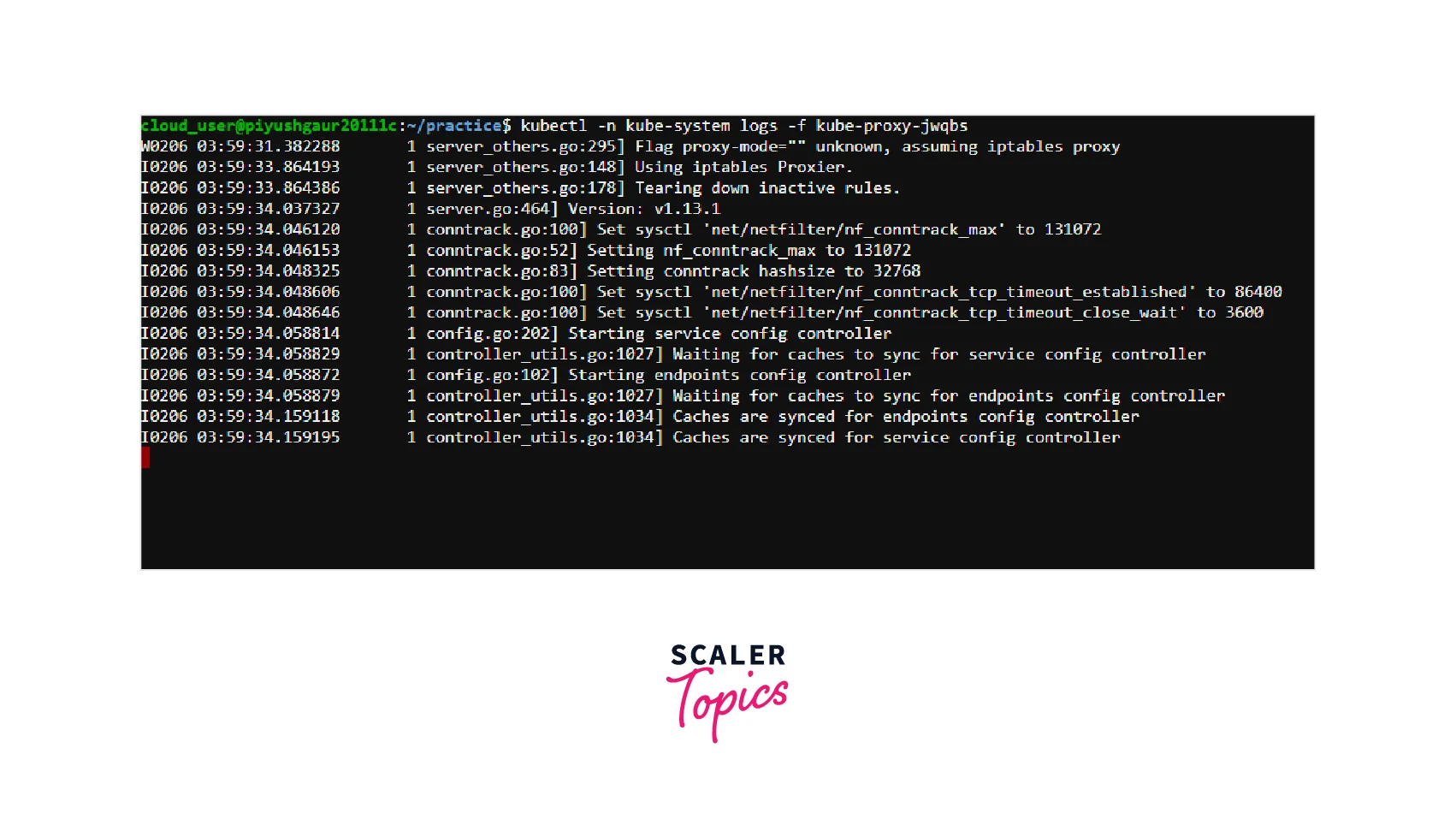
Inspecting the logs can provide valuable information if there is a misconfiguration or erroneous value present in the affected Pod.
Check the Events
List all events in the cluster:
To view events related to a specific Pod, use:

Events can provide additional insights into the CrashLoopBackOff error, helping you identify any recurring issues or failures associated with the Pod.
Check the Deployment
If your Pod is part of a Deployment, inspect the Deployment for misconfigurations that may contribute to the CrashLoopBackOff error:

Review the output for any potential misconfigurations or issues within the Deployment definition that might affect the desired state of the Pod.
By following these steps and carefully examining the output, you can identify and address the root cause of the CrashLoopBackOff error. Whether it's fixing misconfigurations, adjusting resource allocations, or resolving dependencies, taking these actions will help you break free from the frustrating loop and ensure your containers start successfully.
FAQs
Q: How do I determine the cause of the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes error?
A: To identify the cause, you can start by checking the description of the Pod using the kubectl describe pod command. Look for the "State" and "Last State" sections, which provide valuable information about the error and the container's previous state. Additionally, examining the logs, events, and deployment configurations can help pinpoint the underlying issue.
Q: What should I do if my container is in a CrashLoopBackOff state due to resource limitations?
A: If resource limitations are causing the CrashLoopBackOff error, you should review the resource requests and limits specified in the Pod definition. Increase the resource allocation appropriately to ensure the container has enough CPU, memory, and storage to run successfully. Adjusting resource limits can help prevent resource exhaustion and resolve the CrashLoopBackOff state.
Q: How can I troubleshoot a CrashLoopBackOff error related to misconfigurations?
A: Misconfigurations can lead to the CrashLoopBackOff error. To troubleshoot, carefully review the Pod's definition, container configurations, and associated files. Verify that the necessary files are present and correctly referenced within the container. Use tools like kubectl describe pod and kubectl logs to gather information about any specific misconfigurations or errors. Correcting the misconfigurations should resolve the CrashLoopBackOff state.
Q: What steps can I take to resolve the CrashLoopBackOff error caused by dependencies or missing files?
A: If the CrashLoopBackOff error is due to missing dependencies or files, ensure that all necessary dependencies are included in the container image. Check the file paths and permissions within the container to ensure they align with the expected configurations. Use commands like kubectl logs and kubectl exec to investigate if any specific files are failing to load. By ensuring all dependencies and files are correctly present and configured, you can overcome the CrashLoopBackOff error.
Conclusion
- The CrashLoopBackOff error in Kubernetes occurs when a container within a Pod repeatedly fails to start successfully, leading to an endless loop of crashes.
- Common causes of the CrashLoopBackOff Kubernetes pod error include insufficient resources, locked files or databases, failed references to scripts or binaries, setup errors, configuration loading issues, misconfigurations, connection problems, deploying failed services, and missing dependencies.
- To troubleshoot the CrashLoopBackOff error, you can check the Pod description, examine the container logs, review events, and inspect the Deployment configuration.
- Use kubectl describe pod to gather detailed information about the Pod's state, including any misconfigurations or errors.
- Analyze the logs using kubectl logs to identify any specific issues or error messages within the containers.
- Check events with kubectl get events to understand any recurring problems associated with the Pod.
- Inspect the Deployment configuration with kubectl describe deployment to ensure it does not contain any misconfigurations that could cause the CrashLoopBackOff error.
