DeepFake Detection
Overview
Deepfake detection technology, which uses artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, can create realistic synthetic media, such as images, videos, or audio recordings. While these techniques can be used for entertainment or creative purposes, they can also be used maliciously to spread disinformation or defame individuals.
Introduction
The term "deepfake" is a portmanteau of "deep learning" and "fake." Deepfake technology has rapidly advanced in recent years, making it easier than ever to create synthetic media that is difficult to distinguish from authentic media.
While there are legitimate uses for deepfake technology, such as in the film and entertainment industry, there is growing concern that deepfakes could be used to spread disinformation, defame individuals, or even blackmail people.
The potential harm that deepfakes can cause has led to a growing interest in developing methods for deepfake detection. Deepfake detection typically involves using machine learning algorithms to analyze a given piece of media and identify signs that it may have been artificially generated.
Basics of Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks are a type of machine learning algorithm inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. An artificial neural network consists of layers of interconnected nodes, each of which performs a simple computation on its inputs. By combining the outputs of these nodes, an artificial neural network can learn complex patterns in data and make predictions based on that data.
There are many different types of artificial neural networks, but some common types include feedforward networks, recurrent networks, and convolutional networks. Each of these types of networks is well-suited to different types of tasks, such as image recognition or natural language processing.
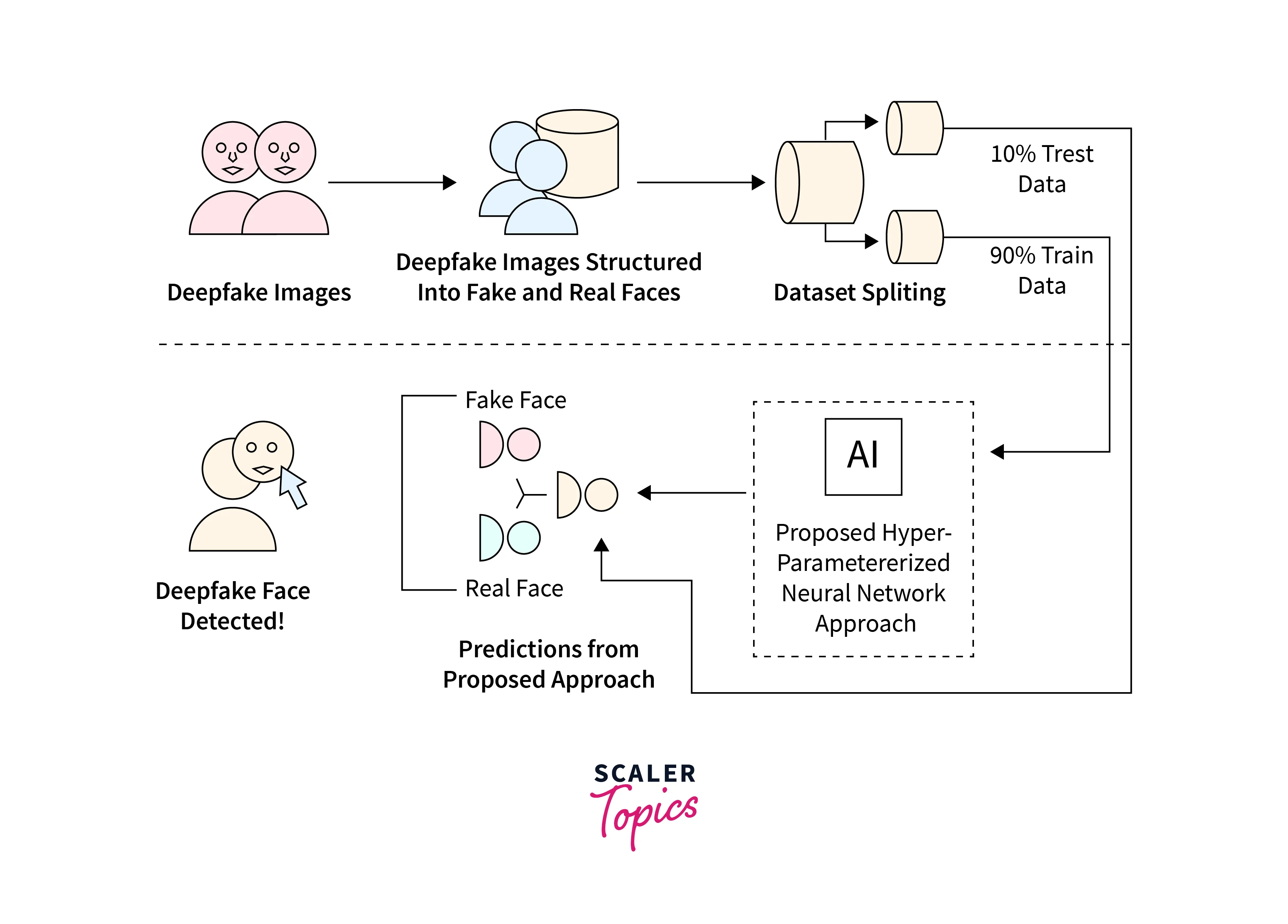
What is Deepfake Generation And Detection?
Deepfake generation involves using AI to create manipulated media that appears to be real but is actually fake. Deepfake detection uses various techniques, including machine learning algorithms, to identify whether a video or audio recording has been synthesized using AI. Lets see a detailed overview in the next section.
Deepfake Generation
Deepfake generation involves using artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to create synthetic media that is difficult to distinguish from authentic media. Deepfake generation typically involves training a deep neural network on a large dataset of real media, such as videos or images, and then using that network to generate new synthetic media.
One common approach to deepfake generation involves using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs). GANs consist of two neural networks: a generator network and a discriminator network.
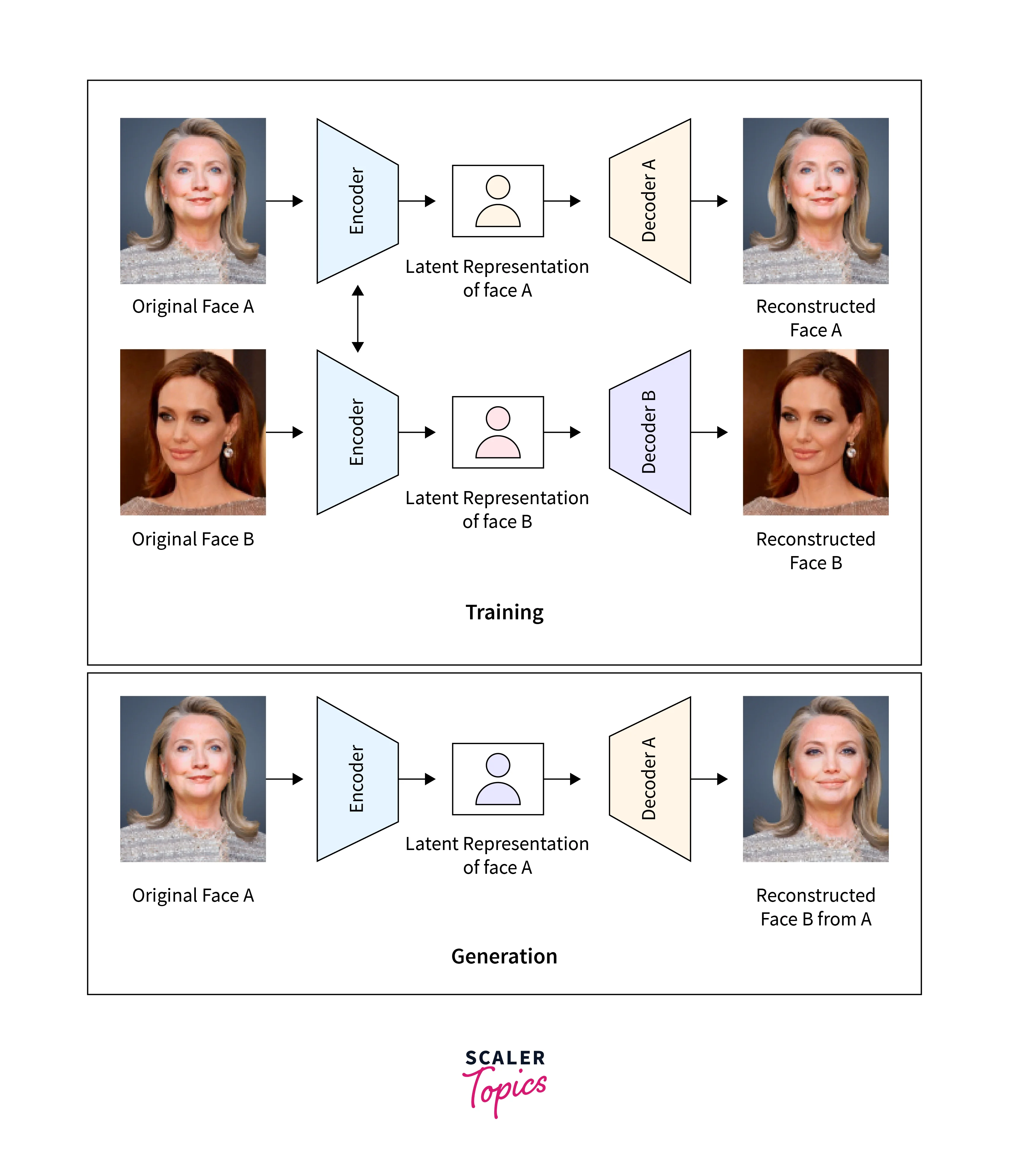
The generator network creates synthetic media, while the discriminator network attempts to distinguish between real and synthetic media. The two networks are trained together, with the generator network attempting to create media that can fool the discriminator network into thinking it is authentic.
Deepfake Detection
Deepfake detection involves using machine learning algorithms to analyze a given piece of media and identify signs that it may have been artificially generated. There are many different approaches to deepfake detection, but some common techniques include:
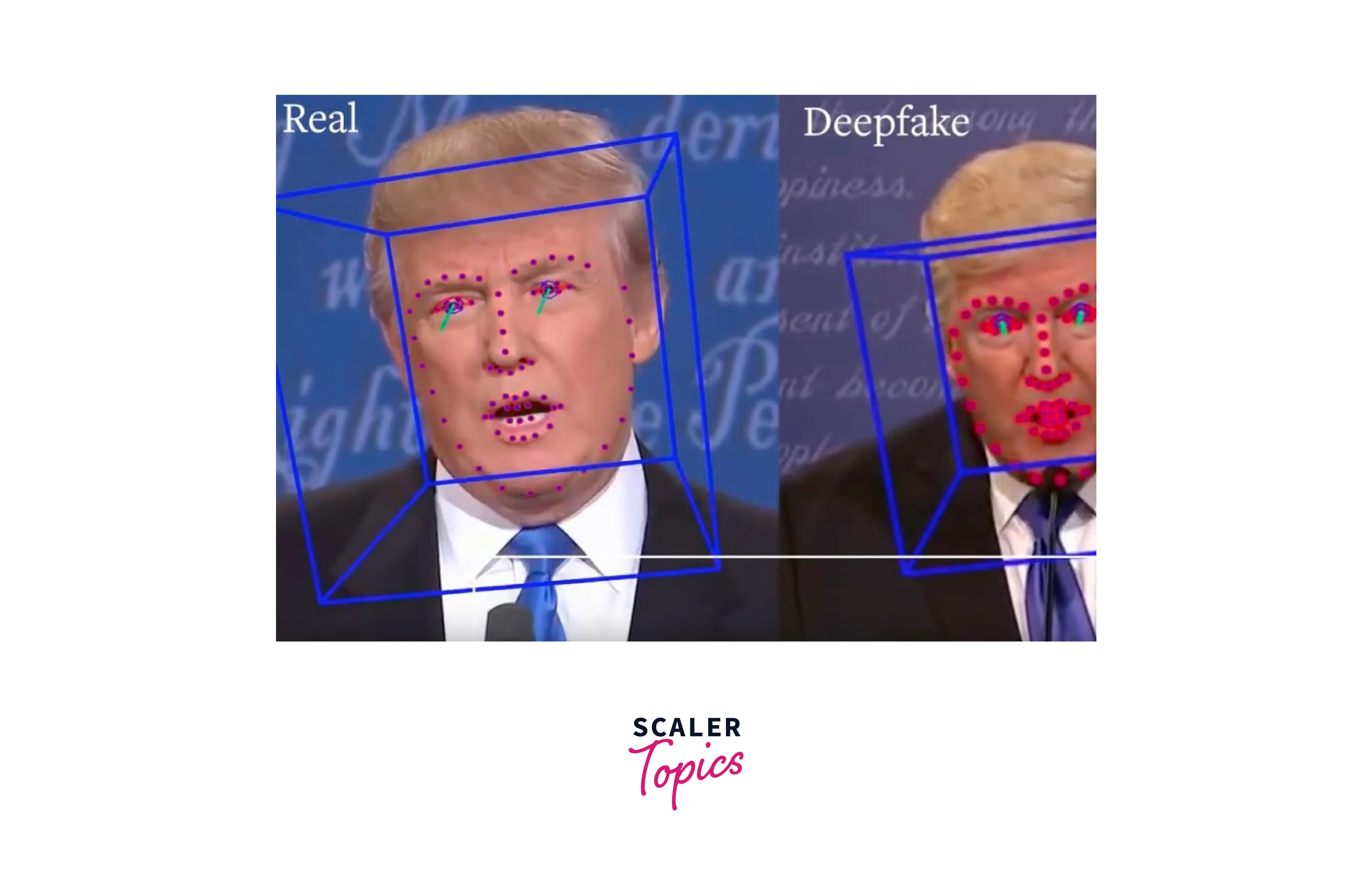
- Face manipulation detection: This technique involves analyzing the facial features in a video or image and looking for signs that they have been manipulated. For example, deepfake videos may have subtle differences in facial expressions or inconsistencies in lighting or shadows.

- Audio analysis: This technique involves analyzing the audio in a video or audio recording and looking for signs that it has been artificially generated. For example, deepfake audio recordings may have inconsistencies in tone or pitch that are not present in authentic recordings.
- Forensic analysis: This technique involves analyzing various metadata and other information associated with a piece of media, such as the file format, compression settings.
-
Image Detection Models
Image detection models use machine learning algorithms to identify and classify objects with deepfake images. These models are commonly used in applications such as self-driving cars, facial recognition systems, and image search engines. Image detection models can be trained on large datasets of labeled images, and can then be used to make predictions on new, unseen images.
There are several types of image detection models for deepfake detection, including convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and object detection models. CNNs are a type of artificial neural network that are particularly well-suited to image processing tasks. CNNs can automatically learn features from raw image data, making them highly effective for tasks such as image classification and object recognition.
-
Video Detection Models
Video detection models build on the capabilities of image detection models to identify and classify objects within a video stream. These models can be used for applications such as surveillance systems, sports analysis, and video search engines.
There are two main approaches to video detection: biological signals analysis and spatial and temporal feature analysis.
-
Biological Singles Analysis
Biological signals analysis involves analyzing the physiological responses of individuals who are viewing a video to determine the emotional content of the video. This approach is based on the idea that certain physiological responses, such as changes in heart rate or skin conductance, can indicate emotional arousal.
Biological signals analysis can be used to detect the emotional content of a video, which can be useful in applications such as advertising and market research. However, it is not well-suited to detecting the presence of deepfakes, as deepfakes are designed to mimic the appearance of authentic videos.
-
Spatial And Temporal Features Analysis
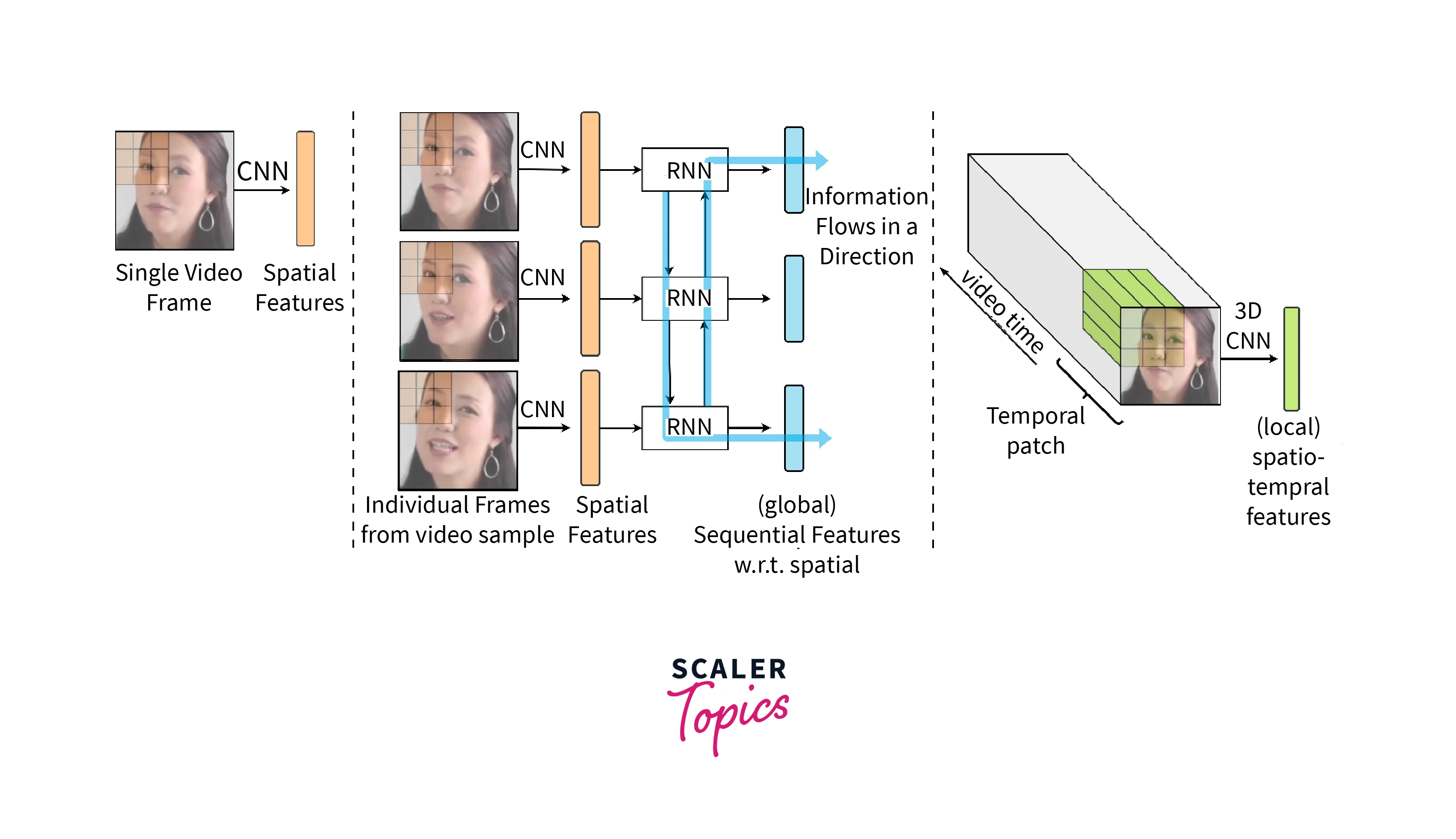
Spatial and temporal feature analysis involves analyzing the spatial and temporal features of a video to identify signs of manipulation or editing. This approach is well-suited fro deepfake detection, as deepfakes often have subtle differences in lighting, shadows, and facial expressions that are not present in authentic videos.
Spatial and temporal feature analysis can be performed using a variety of techniques, including optical flow analysis, frame-by-frame analysis, and motion magnification. These techniques involve analyzing the movement and appearance of objects within the video to identify inconsistencies or irregularities that may indicate the presence of a deepfake.
-
Available Public Datasets
There are several public datasets available for deepfake detection research. These datasets are frequently updated and expanded to support ongoing research in deepfake detection, and they provide valuable resources for developing and testing new algorithms and models. Lets know some popular public datasets below.
Flickr-Faces-Hq, Ffhq
FFHQ is a dataset of high-quality images of human faces, collected from the photo-sharing website Flickr. The dataset contains over 70,000 images, each with a resolution of 1024x1024 pixels. The images are diverse in terms of gender, age, and ethnicity, and are ideal for training deep learning models for face recognition and other applications.

100k-Faces
100K Faces is a dataset of 100,000 images of human faces, collected from the internet. The images are labeled with metadata such as age, gender, and ethnicity, and can be used for training and testing face recognition models.
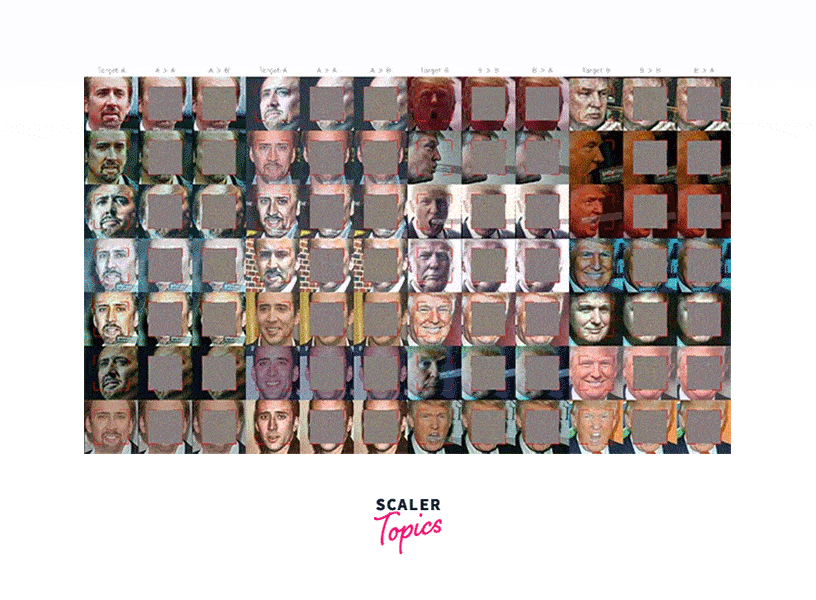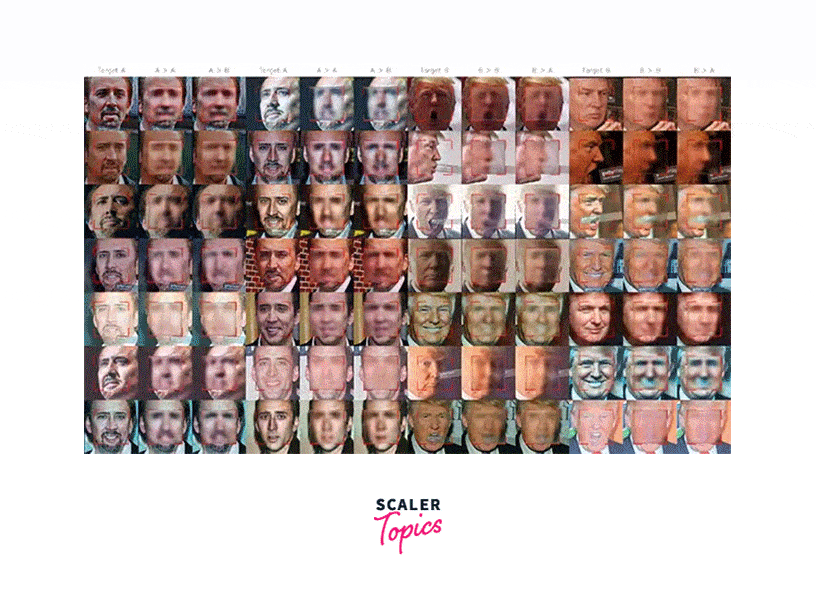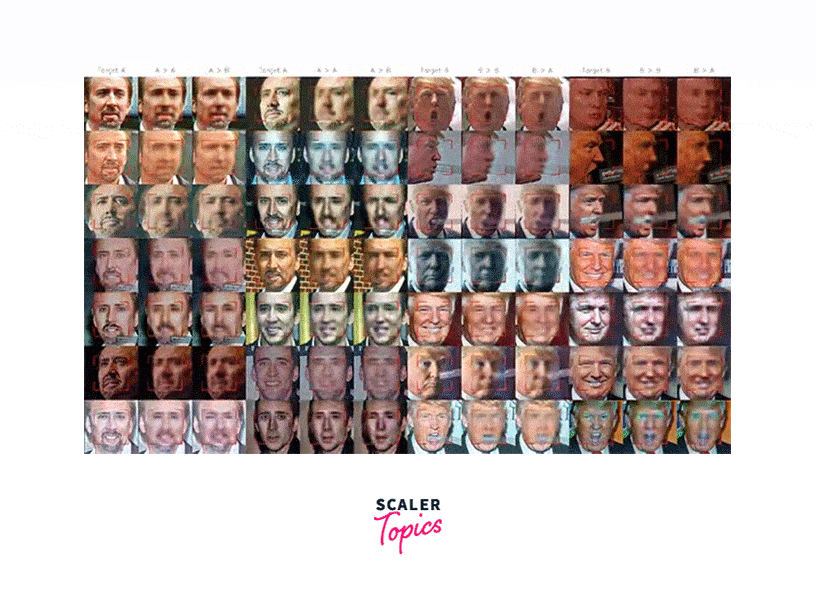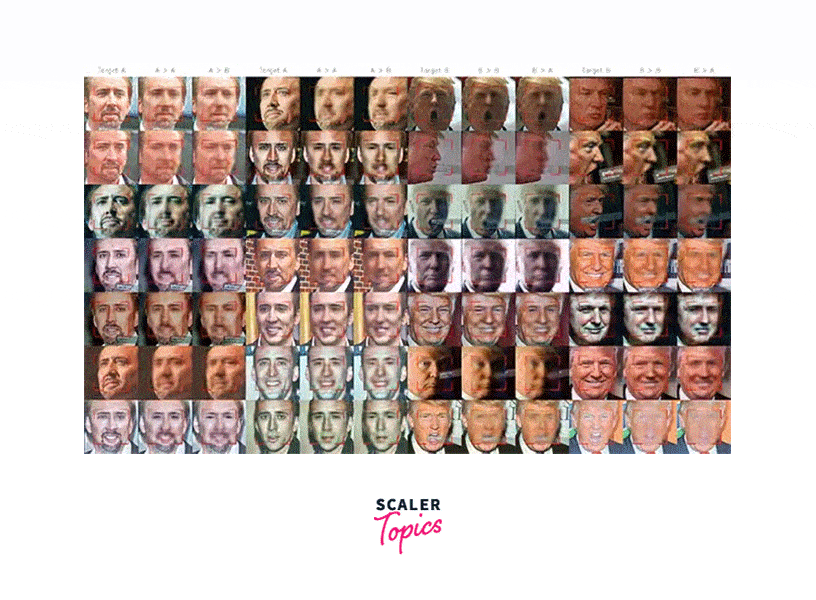
Fake Face Dataset (Dffd)
The DFD is a dataset of synthesized images of human faces, designed to help researchers develop methods for deepfake detection. The dataset contains over 1,000 images, each of which has been manipulated in various ways to create a realistic deepfake.

Casia-Webface
CASIA-WebFace is a dataset of face images collected from the internet, containing over 500,000 images of over 10,000 subjects foo deepfake detection. The images are labeled with metadata such as age, gender, and ethnicity, and can be used for training and testing face recognition models.
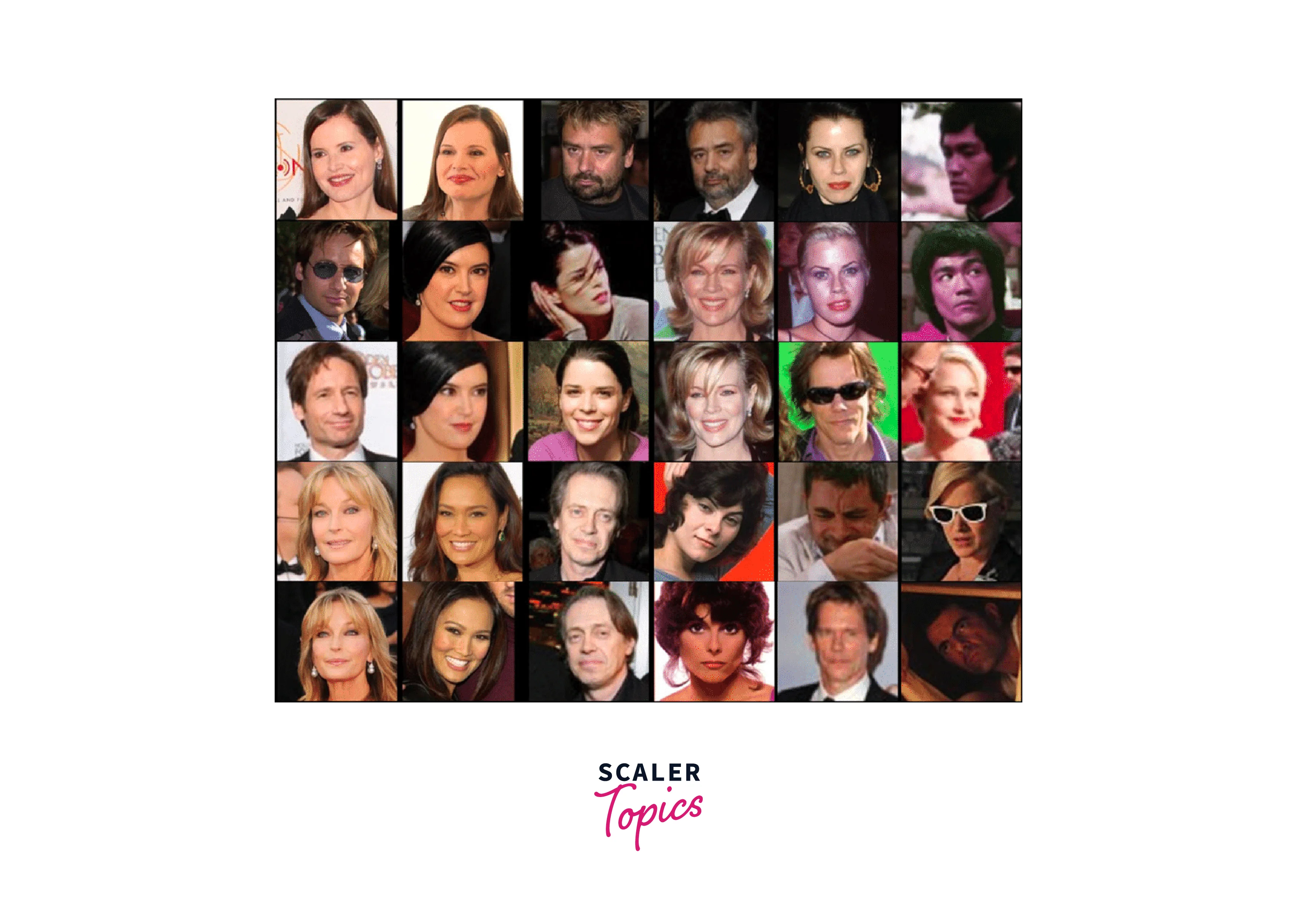

Vggface2
VGGFace2 is a dataset of face images collected from the internet, containing over 3.3 million images of over 9,000 subjects. The images are labeled with metadata such as age, gender, and ethnicity, and can be used for training and testing face recognition models.

The Eye-Blinking Dataset
The Eye-Blinking Dataset is a collection of videos of people blinking their eyes. The dataset can be used for training and testing eye-blink detection models, which can be useful in applications such as driver monitoring systems.
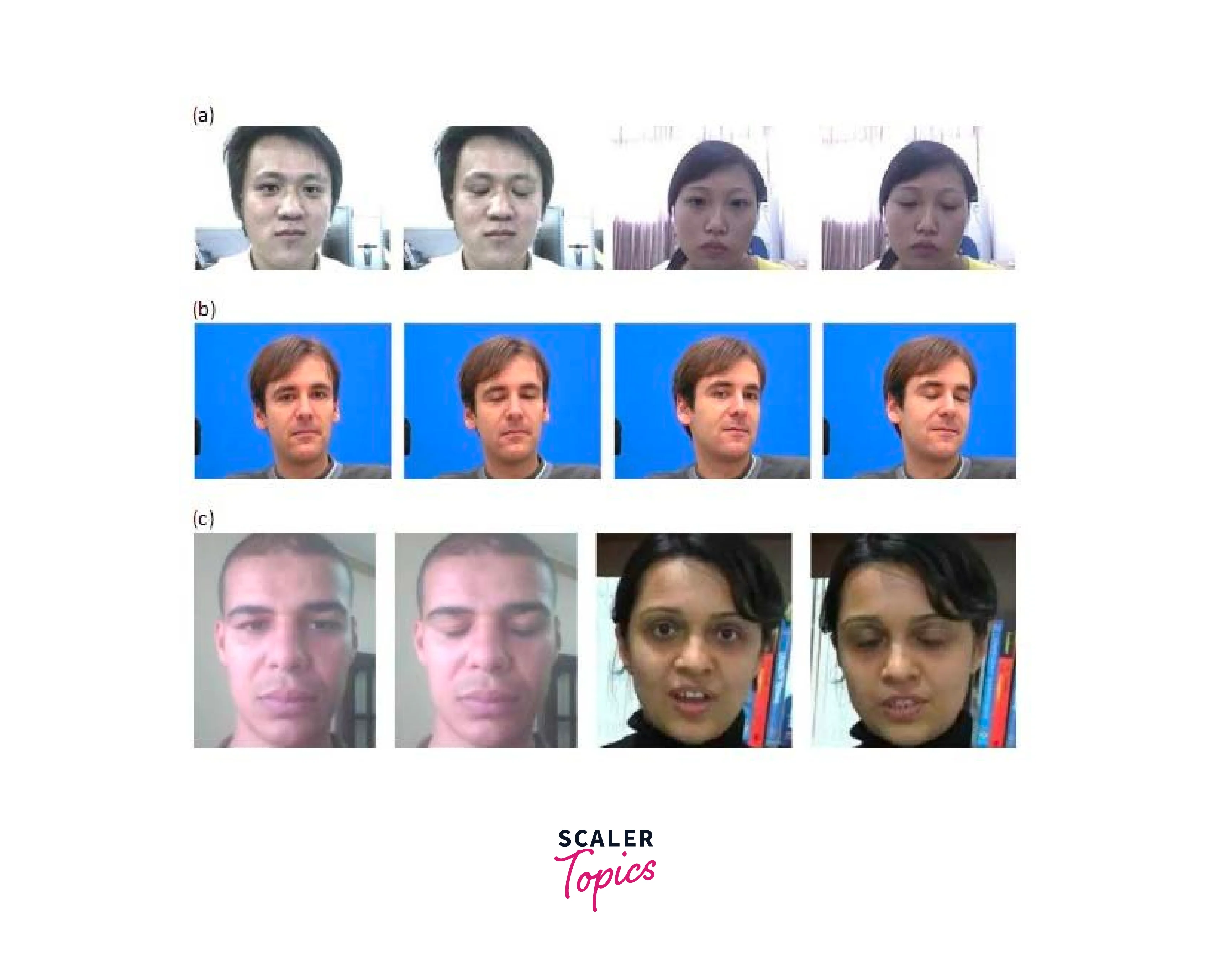

DeepfakeTIMIT
DeepFakeTIMIT is a dataset of manipulated videos that can be used for training and testing deepfake detection models. The dataset contains over 1,000 videos, each of which has been manipulated in various ways to create a realistic deepfake.

Leaderboards Used To Track Progress in Deepfake Detection
Leaderboards are an important tool used to track progress in the field of deepfake detection. They are essentially online platforms that allow researchers to compare the performance of their deepfake detection models against those developed by other researchers. By measuring the effectiveness of different models in identifying deepfakes, leaderboards can help to identify which techniques are most effective, which datasets are most challenging, and which areas require further research. Now, let us explore them.
Challenges And Open Issues
Deepfake detection with deepfake images and videos faces several challenges and open issues, including the lack of standardized datasets, rapidly evolving deepfake technology, adversarial attacks, privacy concerns, difficulty in detecting audio deepfakes, and lack of interpretability in detection methods.
-
Generalization: One of the main challenges in deepfake detection is the ability to generalize models to detect deepfakes that are created using different techniques or on different datasets. Deepfake detection models that perform well on one dataset may not work well on another, which makes it difficult to develop a universal deepfake detection model.
-
Adversarial attacks: Adversarial attacks refer to techniques used to evade deepfake detection by exploiting weaknesses in the model. These attacks can be used to manipulate the input data or the model itself, which can result in undetectable deepfakes. Developing robust deepfake detection models that are resistant to adversarial attacks is an ongoing challenge.
-
Scalability: As the volume of digital media continues to grow exponentially, deepfake detection models need to be scalable and able to process large amounts of data in real-time. However, current deepfake detection models often require significant computational resources and may not be scalable to meet the demands of real-world applications.
-
Explainability: Deepfake detection models often use complex machine learning algorithms that are difficult to interpret, which makes it challenging to understand how the model is making its predictions. Developing explainable deepfake detection models that can provide insights into the reasoning behind their predictions is an ongoing challenge.
-
Misuse: While deepfake detection technology has the potential to be used for positive applications such as improving media authenticity, it can also be used for malicious purposes such as spreading propaganda and disinformation. Developing policies and regulations to prevent the misuse of deepfake detection technology is an important open issue.
Implementing DeepFake Detection in Python
DeepFake Detection in Python requires a combination of computer vision techniques and deep learning algorithms. It is a complex and challenging task that requires specialized knowledge and expertise in both fields.
To implement DeepFake Detection in Python, you can follow these general steps:
- Collect and preprocess data: Obtain a dataset of real and fake images/videos, and preprocess them (e.g., resize, crop, normalize) to prepare them for use in training and testing models.
- Train a model: Use a deep learning framework like TensorFlow, PyTorch, or Keras to build and train a deepfake detection model. The model should take in an image or video frame as input and output a prediction of whether the input is real or fake.
- Evaluate the model: Evaluate the performance of the model on a separate validation dataset to measure its accuracy and identify areas for improvement.
- Test the model: Test the model on a separate test dataset to measure its real-world performance and ensure it is not overfitting to the training data.
- Deploy the model: Once the model is trained and tested, it can be deployed for use in detecting deepfakes in real-world scenarios.
There are several libraries and frameworks available in Python that can be used for DeepFake Detection, including TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, OpenCV, and Dlib. These libraries can provide pre-trained models or allow you to build your own models for detecting deepfakes.
Additionally, there are several open-source projects available on GitHub that can serve as a starting point for building your own deepfake detection model.
Here is a small sample code using Keras to build a simple deepfake detection model:
Step 1: Import the necessary libraries:
The libraries we are importing here are:
- os: for working with operating system interfaces (to read the dataset files)
- cv2: for image and video processing (to read the video frames)
- numpy: for numerical operations (to work with the video frames and labels)
- tensorflow: for building and training the deep learning model
- keras: for building and compiling the deep learning model
- train_test_split: for splitting the dataset into training and testing sets
Step 2: Define the data preprocessing function:
The preprocessing function takes the path to the directory containing the deepfake videos as an input. It first loads the dataset from the given directory and separates the real and fake videos. It then extracts the frames from the videos and creates the labels. It splits the data into training and testing sets and normalizes the pixel values of the frames. Finally, it returns the preprocessed data.
Step 3: Define the deep learning model:
This function takes the input shape of the video frames as an input. It defines a simple deep learning model using Keras, which consists of three convolutional layers, three max pooling layers, a flatten layer, and two fully connected layers. It compiles the model with the Adam optimizer and binary cross-entropy loss function, and accuracy as the evaluation metric. Finally, it returns the compiled model.
Step 4: Define the main function for implementing the DeepFake Detection: The main function first calls the preprocess_data function to get the preprocessed training and testing data. It then calls the build_model function to get the compiled deep learning model. It fits the model on the training data and evaluates it on the testing data. Finally, it prints the test accuracy of the model.
Step 5: Call the main function: This code block checks if the script is being executed directly or imported as a module, and calls the main function if it's being executed directly.
Note that this is just a simple example and there are many ways to improve the performance of the model, such as using more complex architectures, incorporating more data augmentation techniques, and tuning the hyperparameters.
Ouput: The output of the sample code using Keras to build a simple deepfake detection model would be something like this:
The output shows the progress of the model during training and the final test accuracy of the model. The model starts with a random initialization of weights and biases and trains for 10 epochs. After each epoch, it reports the training and validation loss and accuracy. Finally, it evaluates the model on the test data and reports the test accuracy. In this case, the final test accuracy is 0.9525, which means that the model is able to correctly classify 95.25% of the test videos.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, deepfake detection is a critical area of research that aims to identify manipulated images and videos generated using advanced artificial intelligence techniques.
- While there are many challenges and open issues in deepfake detection, such as the lack of standardized datasets, evolving technology, and adversarial attacks, researchers are continually developing new models and techniques to improve detection accuracy.
- Python provides powerful libraries and frameworks that can be used to build and train deepfake detection models, making it easier for researchers and developers to create effective solutions to this growing problem.
- As deepfakes continue to become more prevalent, it is crucial to continue to advance deepfake detection techniques to protect against their potential misuse.
