What is the Role of Testers in DevOps?
Introduction to DevOps Testing
According to recent studies, companies are increasingly adopting and focusing on DevOps practices to accelerate software delivery, improve collaboration, and enhance overall application quality. DevOps is popular these days. Companies are finally catching on to the benefits of merging development and operations teams, automating workflows, and constantly working to improve.
DevOps testing seamlessly integrates testing into the development and deployment workflows to enable early detection of defects, ensuring thorough testing of software applications before deploying to production, with DevOps testers working closely with cross-functional teams to maintain quality throughout the software delivery pipeline.
The role of the DevOps tester is diverse, taking on various responsibilities and activities, and contributing towards the success of the project.
Some Key aspects/roles of DevOps tester are:
- Collaborative Testing
- Continuous Testing
- End-to-End Testing
- Monitoring and Analysis
- Continuous Improvement
- Securing Software Applications
How Traditional Testing Worked
Software testing is not new and has been widely used in software development cycles. Earlier there used to be a separate testing phase that used to be done after the development was done, where the testers used to identify defects or errors and check if the applications meet certain requirements given by the clients or product owners. However, after DevOps & Agile came into the picture they revolutionized the traditional software development cycle which was slow, and expensive without proper communication between teams to more collaborative, iterative, and automated testing practices that are integrated into the development and deployment process.
Some Traditional testing methods that were used earlier were
-
Waterfall Testing: It's a traditional way of developing software where testing is typically done after the development phase, one step at a time. So basically, testers get their hands on the completed app or module and run a bunch of tests like checking if it works properly, how fast it runs, and if it's secure. But the downside is that if they find any problems, it can be a pain to fix them since it's towards the end of development. This can lead to more expensive costs and delays in releasing the app.
-
Manual Testing: It's a traditional way of testing where testers manually run test cases to spot defects in the application. Testers have a set of predefined test plans and cases that they follow, and then they record the results for analysis. Since manual testing is done by people, it can take a while and there may be room for error. Manual testing was never the best option for testing complex applications that go through a lot of changes in a small period.
-
Black-box Testing: In this method testers look at how the application functions without needing to know the technical details of its code or internal structure. They test it from an end-user point of view, making sure it meets all the requirements and works as expected. This method was designed to find out if the application is good and easy to use for the customers and not to find errors in code. There were many others which were being used, will cover it some other day.
The Cultural Shift
DevOps is a software deployment approach where the software is kept deployable at any point in time, rather than working on new features. To attain this a cultural shift was necessary, where Developers, Operations engineers, testers & Q.A teams work together as a team towards our common goal of creating processes that are quick, trustworthy, and can be replicated again. Traditionally they used to have different goals and responsibilities where the developers were focused on creating new features and operations focused on stability & availability. The cultural shift that brought DevOps resulted in bridging the Developers & Operations Engineers, where Quality Assurance & testing was everyone's responsibility. Someone wise once said
By adopting the new principles & practices organizations foster collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement, leading to faster delivery of high-quality software that meets customer needs and business goals. QA teams, in particular, can play a key role in driving this cultural shift and ensuring that quality remains a top priority throughout the software development and deployment process.
Features of Testing in a DevOps Environment
Over the years of Software development, people have found various & effective testing strategies to overcome problems, make it more collaborative, introduce new tools & technologies in the testing sphere etc. Previously we have discussed how testing was done traditionally. In the modern times
- Testing is a continuous and automated process resulting in continuous and faster delivery.
- Testing is done at every stage of the software development lifecycle.
- Each step of the cycle involves different forms of testing.
- Testing is no longer a single department/team's responsibility. The role & responsibility is shared collaboratively.
DevOps Adopts Shift Left Testing Approach
The Shift Left testing is exactly what it says. Didn't you get it? Let us see the S.D.L.C diagram, shall we?
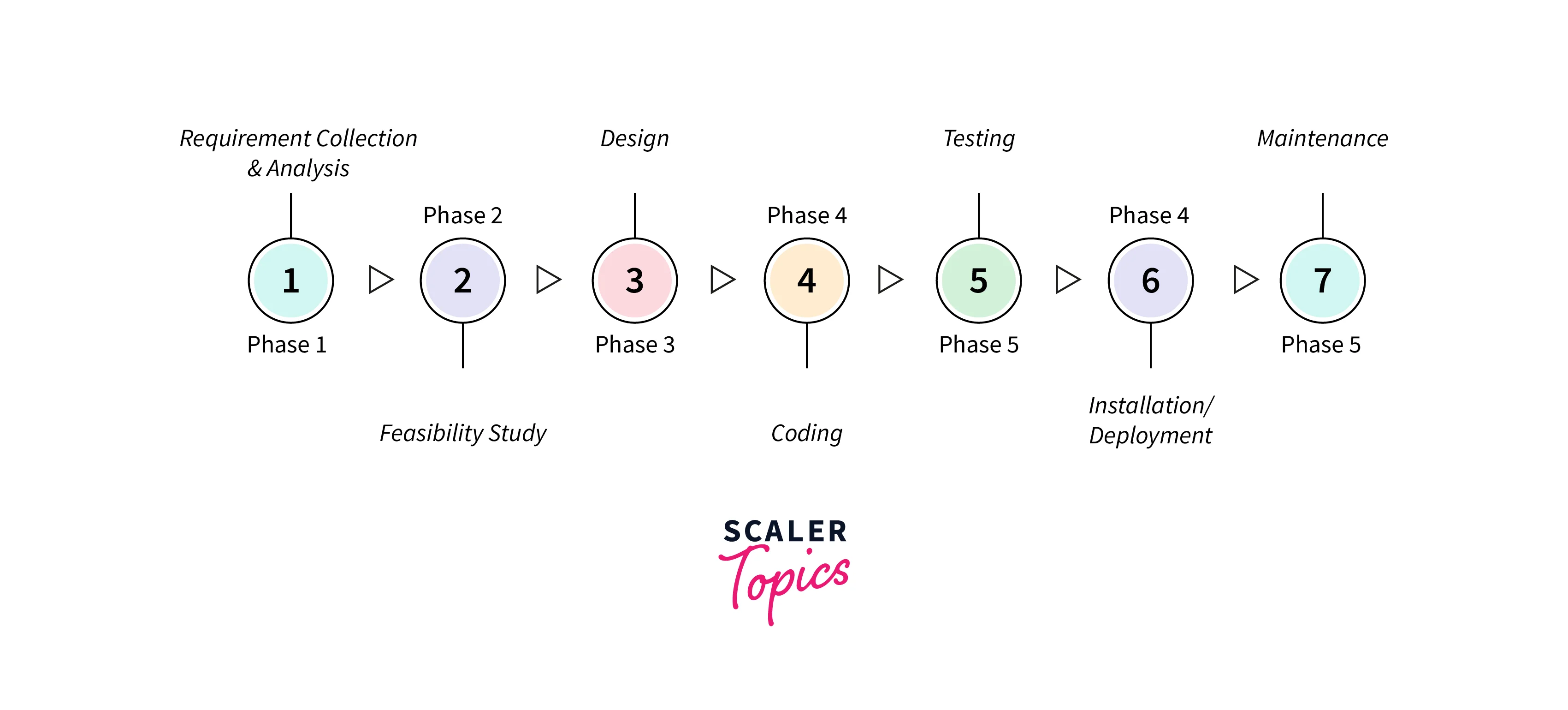
As we see here testing comes at the later part of the cycle so as the name suggests we will shift the testing phase as far left it goes. It is used to detect issues & mistakes early on in the development cycle.
You may ask Why shift left not right? In the traditional software development model, requirements where kept on the left side of the plan or in the early stages of the cycle while the delivery and testing requirements were on the right, but as we all know that moving forward new suggestions comes, many requirements are changed because of this buisness faces negative outcomes like increase in cost, more time to make the product for deployment, many unexpected errors etc.
Many of the defects that are faced during the development phase can be reduced & identified during the requiremnet phase. In many scenarios a shift left testing may not be an optimal solution for the project in such situations, a Shift Right testing strategy can be used too.
The Role of QA in DevOps
Quality Assurance as the name helps to ensure that the software which is being developed and deployed is of the highest quality and meets the desired functionality, reliability, security & usability. QA teams work collaboratively with development, operations, and other stakeholders to integrate testing into the DevOps process and continuously improve the quality of software being delivered.
However, two common roles that QA can play in DevOps are that of
-
QA as a Consultant: QA professionals provide expert advice and guidance on quality assurance practices, testing techniques, and tools, while also offering insights and recommendations on how to maintain quality into the DevOps pipeline, identifying potential risks, suggesting best practices for testing and automation, and helping teams improve their overall software quality, which includes setting up test environments, creating test data, and providing feedback on quality-related issues.
-
QA as a Strategist: QA strategists take a strategic approach to quality assurance in the DevOps environment, working closely with different teams to develop and implement quality strategies, frameworks, and processes, to select appropriate testing tools and technologies, design and implement automated testing frameworks, and drive continuous improvement efforts to enhance the overall quality of software, ensuring that quality is built into every stage of the DevOps pipeline.
10 Best Practices of QA in a DevOps Scenario
- Shift Left:
Involving QA teams early in the software development process for design, architecture, and requirements discussions can help catch defects and quality issues early, allowing for faster resolution and minimizing risks. - Continuous Integration & Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
To identify defects early and ensure software readiness for production, QA must closely collaborate with development and operations teams to establish a fully automated continuous testing process as part of the CI/CD pipeline. - Automation First:
QA should focus more on automating the testing process than manual testing for increasing efficiency & effectiveness. Automated testing should be integrated into the DevOps pipeline, including unit tests, integration tests and other types of tests. - Specific Requirements:
QA teams should actively participate in the requirements process and ensure that requirements are specific, clear, and aligned with quality objectives to avoid quality issues later. - Collaborative Approach:
QA should work in close collaboration with the Devs, Ops Engineer & other teams to increase productivity, communication & collaboration which includes regular meetings, sharing feedback, and addressing issues collectively. - Continuous Improvement:
QA team should continuously evaluate and improve their testing process tools and techniques. For improvement Feedback from production environments, retrospectives, and metrics analysis should be used. - Test Environment Management:
QA teams should ensure that the test environments are properly set up and managed, including configurations, data, and dependencies. Test environments should closely resemble production environments to ensure accurate testing results. - Specific Requirements:
QA teams should be proactively involved in the requirements process to help and guide development teams towards the proper direction & to provide proper requirements. - Use of Right Tool:
Mainly to leverage the benefits of test automation, the team needs to integrate the right testing tools for your organization, not some “best of” testing tool. - Proper Documentation:
The QA team or the DevOps testing team must always maintain proper documentation for the product for reference.
Selecting the Right Testing Tools
Choosing the right testing tool does not necessarily mean "The best testing tool" DevOps tester or QA team must identify which testing tool is the best suited for the project. It may vary from project to project and organization to organization.
When choosing the automation tool, the first thing to take note of is the, are the DevOps testers/ QA guys have a firm understanding of how to use the tool in a way which will save time and increase work efficiency. For example, some open-source testing tools require a decent level of programming skills to use them. Do your test engineers have this?
Once you have identified the tool, check the total cost of the tool, including training costs, updates, and maintenance, to see if it is within the testing budget. If not, what alternatives can we use? Always check if decent technical support is available for the tools.
Some of the most popular automation tools include:
- Selenium used for web application testing.
- JMeter used for performance and load testing.
- Katalon Studio used for automated web, API, desktop, and mobile testing etc.
Ready to Redefine Your DevOps Knowledge? Dive into DevOps Excellence with Our Specialized DevOps Course. Enroll Now!
Conclusion
- DevOps is a software deployment approach that merges development and operations teams, automates workflows and constantly works to improve.
- Quality Assurance teams play a key role in driving this shift and ensuring that quality remains a top priority throughout the software development and deployment process.
- Best practices for QA in a DevOps scenario include shift left testing, continuous integration and deployment, and automation first.
- Automated continuous testing should be integrated into the SDLC and the right testing tools should be selected, taking into account the cost, training, updates, and maintenance.
