Difference between Arduino and Raspberry Pi
Overview
In the world of embedded systems, two popular platforms have emerged as go-to choices for hobbyists, makers, and even professionals: Arduino and Raspberry Pi. These compact devices have revolutionized the way people approach electronics and programming, enabling a wide range of projects from simple blinking LEDs to sophisticated robotics and home automation systems. While both Arduino and Raspberry Pi serve similar purposes, they are distinct in their capabilities, features, and use cases. In this article, we will explore the difference between Arduino and Raspberry Pi, helping you decide which platform is best suited for your project.
What is Arduino?
Arduino is an open-source hardware and software platform designed for building interactive electronic projects. It consists of a microcontroller that can be programmed to perform various tasks and respond to inputs from sensors, buttons, and other devices. Arduino boards come in various sizes and configurations, each with its own set of features. The Arduino IDE (Integrated Development Environment) provides a user-friendly interface for writing, compiling, and uploading code to the Arduino board.

Features of Arduino
-
Simplicity:
Arduino is known for its simplicity and ease of use, making it an ideal choice for beginners. The programming language is based on C/C++, but the syntax is simplified and beginner-friendly.
-
Low Power Consumption:
Arduino boards are designed to consume minimal power, making them suitable for battery-powered and energy-efficient projects.
-
Real-time Interaction:
Arduino is well-suited for projects that require real-time interaction and quick response to inputs, such as robotics and automation.
-
Analog and Digital I/O:
Arduino boards have a combination of analog and digital input/output pins, allowing you to interface with a wide range of sensors and actuators.
-
Dedicated Microcontroller:
Each Arduino board is built around a specific microcontroller, which determines its processing power and capabilities.
What is Raspberry Pi?
Raspberry Pi, on the other hand, is a single-board computer (SBC) developed by the Raspberry Pi Foundation. Unlike Arduino, Raspberry Pi is a complete mini-computer capable of running a full-fledged operating system (such as Linux) and applications. It's designed to be versatile and can handle tasks beyond simple electronics, such as web browsing, word processing, and multimedia playback.
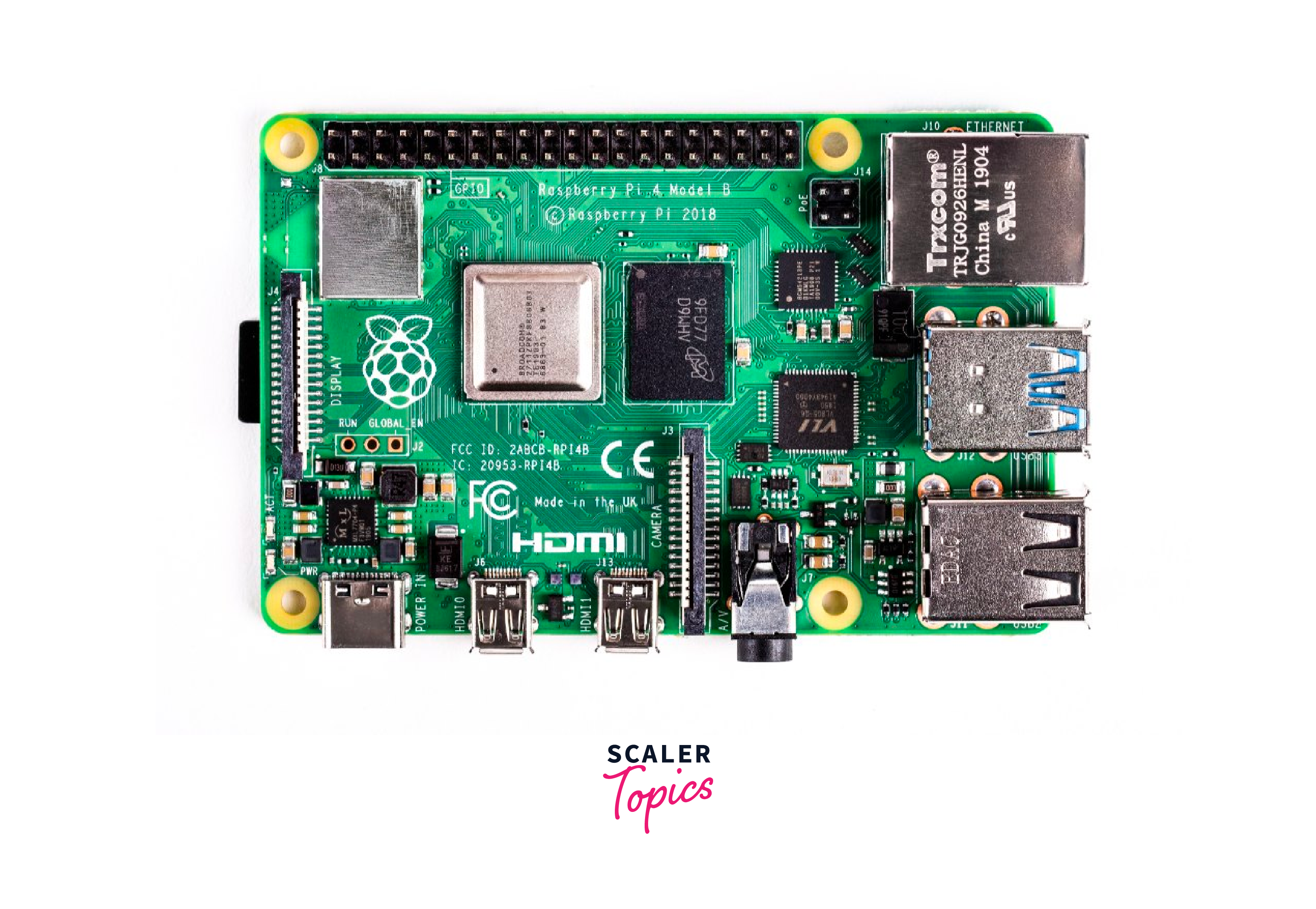
Features of Raspberry Pi
-
Full Operating System:
Raspberry Pi runs on a variety of operating systems, including various flavors of Linux, giving you access to a wide range of software applications.
-
Processing Power:
Raspberry Pi boards are equipped with more powerful processors compared to Arduino, enabling them to handle more complex tasks.
-
Multimedia Capabilities:
With HDMI output and support for audio, Raspberry Pi is capable of handling multimedia playback, making it suitable for media centers and entertainment projects.
-
Networking:
Raspberry Pi has built-in networking capabilities, including Ethernet and Wi-Fi, allowing for easy connectivity and remote access.
-
General-Purpose I/O:
While Raspberry Pi does have general-purpose input/output pins, they are not as numerous or specialized as those found on Arduino boards.
Difference between Arduino and Raspberry Pi
Let's break down the key differences between Arduino and Raspberry Pi in a tabular format:
| Aspect | Arduino | Raspberry Pi |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Microcontroller platform | Single-board computer (SBC) platform |
| Programming Language | Simplified C/C++ | Various languages, including Python |
| Operating System | No full OS; runs Arduino sketch | Runs full-fledged operating systems |
| Processing Power | Limited (depends on microcontroller) | Higher, similar to entry-level computers |
| Connectivity | Basic I/O, sensors, actuators | I/O, USB, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth |
| Multimedia Capabilities | Limited (basic audio, visual) | Full multimedia support, including HDMI |
| Power Consumption | Low | Higher, may require more power |
| Real-time Interaction | Yes | Less suitable for real-time applications |
| Complexity | Simple and beginner-friendly | More complex, suitable for advanced users |
| Use Cases | Robotics, automation, simple tasks | Web browsing, programming, media center |
Which One to Choose?
The difference between Arduino and Raspberry Pi influences the decision of which one to choose. The choice depends on the nature of your project and your requirements. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed choice:
Advantages of Arduino
-
Real-time Interactivity:
Arduino excels at real-time applications, making it suitable for projects that require immediate responses to sensor inputs or external triggers.
-
Simplicity:
Arduino's simplified programming language and user-friendly IDE are perfect for beginners and those who want to quickly prototype and experiment.
-
Low Power:
If your project needs to run on battery power or has strict energy requirements, Arduino's low power consumption is advantageous.
-
Cost-Effective:
Arduino boards are generally more affordable, which is beneficial for projects with budget constraints.
Disadvantages of Arduino
-
Limited Processing Power:
Arduino's processing power may restrict the complexity of your projects, especially those involving extensive calculations or multimedia.
-
Lack of Full OS:
Arduino cannot run a full operating system, limiting its capabilities to specialized tasks.
-
Memory Constraints:
Arduino boards often have limited memory available for storing code and data. This constraint can become a challenge when dealing with larger projects that require substantial memory space for variables, arrays, and other data structures.
-
Scalability:
While Arduino is great for simple to moderately complex projects, it might not be as suitable for highly scalable applications. If your project demands significant expansion in terms of functionalities, sensors, or devices, you might encounter limitations in managing these complexities effectively.
Advantages of Raspberry Pi
-
Versatility:
Raspberry Pi's ability to run a full operating system and support various programming languages opens up a wide range of applications beyond electronics.
-
Processing Power:
The higher processing power of Raspberry Pi allows it to handle more complex computations and tasks.
-
Multimedia Capabilities:
If your project involves multimedia playback, graphics, or audio, Raspberry Pi's capabilities are a significant advantage.
-
Networking:
Raspberry Pi's built-in networking features facilitate remote access and communication.
Disadvantages of Raspberry Pi
-
Complexity:
Raspberry Pi is more complex, both in terms of hardware and software, which might be overwhelming for beginners.
-
Higher Power Consumption:
Due to its greater processing power and capabilities, Raspberry Pi typically consumes more power than Arduino.
-
Resource Intensity:
Given its broader functionalities, running resource-intensive tasks on Raspberry Pi might lead to performance challenges, whereas Arduino's focus on specific tasks can result in more predictable performance outcomes.
-
Cost:
While Raspberry Pi offers impressive capabilities, it comes at a higher cost compared to many Arduino boards. This cost factor could influence decisions, especially in projects with tight budget constraints.
Conclusion
- Arduino and Raspberry Pi are prominent platforms when it comes to embedded systems, each catering to distinct project needs.
- Arduino's simplicity, real-time interactivity, and low power consumption make it suitable for beginners and quick prototypes.
- Raspberry Pi's versatility, processing power, multimedia capabilities, and networking options are advantageous for more complex projects.
- The choice between the two depends on factors like project requirements, programming knowledge, and budget constraints.
- Arduino is preferable for real-time applications and cost-effective projects with limited processing needs.
- Raspberry Pi shines in handling more sophisticated computations, multimedia tasks, and running full operating systems.
- Both platforms empower users to unleash their creativity and innovate across various domains of electronics and programming.
