How to Integrate Django with MongoDB: Complete Guide
Overview
Django is a well-known Python web framework noted often referred to as Django MongoDB for its ease of use, scalability, and robustness. While Django is typically associated with relational databases such as PostgreSQL or MySQL, it is also capable of smoothly integrating with NoSQL databases such as MongoDB. This article will walk you through the process of integrating Django MongoDB using MongoDB Engine, Djongo(a Django MongoDB connector), and PyMongo, allowing you to use the power and flexibility of both technologies in your online applications.
Introduction to Django
Python-based high-level web framework Django helps programmers to create web applications rapidly and effectively. It follows the model-view-controller (MVC) architectural pattern, which encourages reusable code and neat design.
Features
- Object Relational Mapping (ORM): Django offers a high-level ORM that enables programmers to use Python objects and queries to communicate with the Django MongoDB database.
- Admin Interface: Django provides an admin interface that makes it simple to manage the data for the Django MongoDB application.
- URL Routing: Django has a robust framework for mapping URLs to view functions, allowing for tidy and manageable URL architectures in Django MongoDB.
- Templating Engine: The process of developing dynamic web pages is made simpler by the built-in templating engine that Django offers for Django MongoDB.
- Authentication and Authorization: To secure web applications, Django has strong authentication and authorization capabilities in Django MongoDB.
- Testing Framework: Django provides a thorough testing framework for creating unit tests and guaranteeing the application's quality.
Requirements
You will require the following to integrate Django with MongoDB:
Django: Use pip to install Django, preferably the most recent version. Refer to Install Django for more details. MongoDB: Install MongoDB on your computer or use a cloud-based service to access MongoDB. Refer to Installing MongoDB for more details. MongoDB Driver: You will require either MongoEngine, PyMongo, or Djongo, depending on the integration strategy.
Use cases
Django MongoDB work well together for several use cases, including:
- Content Management Systems: Building platforms for content management systems (CMS) that can handle a lot of unstructured data.
- Real-Time Analytics: Real-time analytics involves storing and analyzing live data streams, such as those from IoT sensors or user interactions.
- Social Networks: Building social networking networks with adaptable schema needs.
- E-commerce applications: Creating scalable e-commerce platforms with complex product catalogues and inventory control.
Introduction to MongoDB
A popular open-source NoSQL database management system is MongoDB. For current applications, it offers excellent scalability, flexibility, and performance by handling unstructured and semi-structured data. BSON (Binary JSON), a flexible JSON-like data format used by MongoDB, makes it simple to integrate with a wide range of programming languages and frameworks.
How to Connect MongoDB with Django?
Step 1: First you have to set up a virtual environment.
For Windows:
For macOS/ Linux:
Step 2: Install Django
For using mongodb+srv:// URIs, install dnspython by executing the following command:
Using MongoEngine
To connect Django and MongoDB using MongoEngine, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install MongoEngine
First, install the MongoEngine library using pip by running the following command:
Step 2: Configure MongoDB Connection Settings In your Django project, open the settings.py file (it is a Python file that has module-level variables) and add the following configuration settings for connecting to MongoDB:

Step 3: Define MongoEngine Models In Django, models represent the structure of your data. Create a new Python file, for example, models.py, and define your MongoEngine models.
Here's an example of a simple model:
This example creates a Book model with three fields: title, author, and year. You can define more complex models based on your application's needs.
You can find the models.py file in your app folder inside your Django project.
Step 4: Perform Database Operations You can now use the MongoEngine API to perform database operations.
For example, to create a new book and save it to the database:
In this example, the create_book view function creates a new Book instance, sets its attributes, and saves it to the MongoDB database using the save() method.
Using PyMongo
Step 1: Install PyMongo Install the PyMongo library using pip by running the following command:
For using mongodb+srv:// URIs, install dnspython by executing the following command:
PyMongo allows us to operate many databases simultaneously by giving the connection instance the correct database name.
Make a sample PyMongo session first. There are two methods for doing this:
- Any view wishing to communicate with MongoDB can utilize the client we construct in the utils.py file. In your project folder, make a utils.py file (in the same place as manage.py), and then instantiate the client:
- Using the connection_string is another method to obtain the connection:
where,
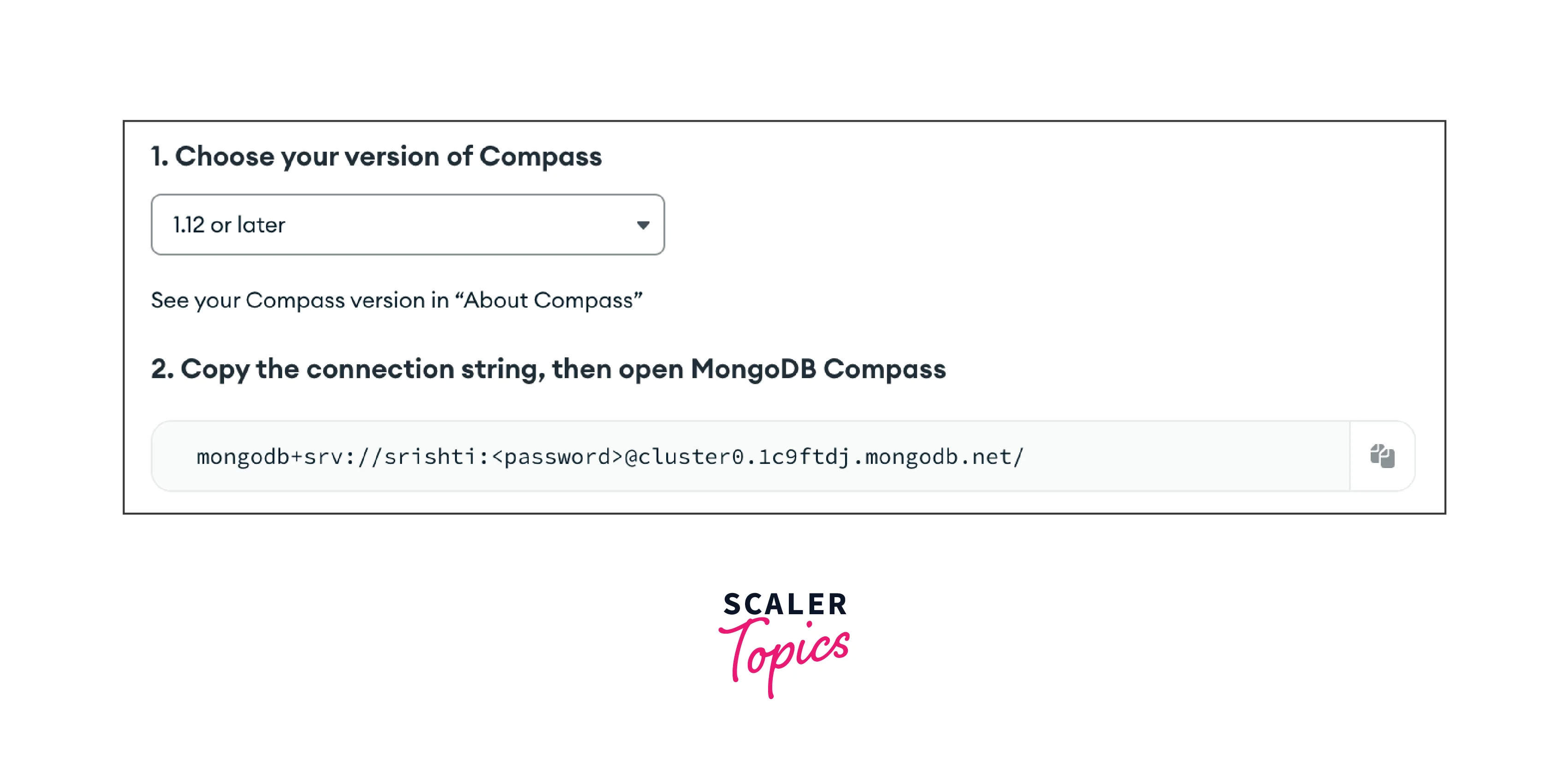
You can get the connection string in your cluster created by you in the MongoDB cloud.
Click the connect button and select the tool by which you want to access the data.


In my case, I will select Compass as I have already installed MongoDB Compass. You can download it from here.
Using Djongo
To connect Django and MongoDB using Djongo, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install Djongo First, install the Djongo library using pip by running the following command:
Step 2: Configure Django's settings.py In your Django project, open the settings.py file and configure the database settings to use Djongo as the database backend:
If your database is secured or not on localhost then you can also give the host, username, and password.

Step 3: Check in your settings.py that your app name is added to the installed_app list.

Step 4: Run Migrations Run the Django migrations to create the MongoDB collections based on your defined models:
Django MongoDB Tutorial
We will be using Djongo to make the todo app.
Pre-requisites:
- Django and djongo must be installed.
- Create a project by running the following command in the terminal:
- Go to the settings.py file and edit the database section.
Add username and password from your MongoDB database or cluster you created.
- Run the following command before making the app
After that create your app by running the following command:
- Your app directory will be created where you will see a Python file named models.py. Edit it using the following command:
Make sure that your app name is added in the INSTALLED_APP in the settings.py file in your project directory.
- Create an html file for your todo app and add it to your app folder.

- Go to the views.py file that already exists in your app folder and add the following commands:
- Add the path to your views files to access your html file in urls.py that already exists in your djangoproject1 folder.
- Run the following command in your terminal to run your app:
And your app will look like this:

FAQs
Q. Are there any limitations or differences when using Django with MongoDB compared to traditional databases?
A. Yes, there are some differences and limitations. For example, MongoDB is a schema-less database, so you may need to handle schema-related issues differently. Additionally, some advanced relational database features may not be available in MongoDB.
Q. Does Django support MongoDB's advanced features like sharding and replication?
A. Django itself does not provide direct support for MongoDB's advanced features like sharding and replication. However, you can leverage MongoDB's native drivers and features directly in your Django application when using libraries such as PyMongo.
Conclusion
- MongoDB is a NoSQL document database, and Django is a popular Python web framework.
- You can use a variety of libraries, such as PyMongo, Djongo, or MongoEngine, to connect Django with MongoDB.
- You may communicate with MongoDB using Python code thanks to PyMongo, a MongoDB Python driver.
- Djongo is a Django database connector for MongoDB that makes Django's ORM and MongoDB compatible.
- With the help of MongoEngine, an Object-Document Mapping (ODM) library, you may use MongoDB to create models and carry out database operations in Django.
