PostgreSQL Drop Column
Overview
In PostgreSQL, the DROP COLUMN command is used to delete one or more columns from a table, allowing changes to the database structure. This action is permanent and erases the specified column(s) along with their data from the table. It's essential to make sure while using this command, as it cannot be undone, leading to potential data loss.
Do you know what will happen on the table if we drop a column in Postgresql? Read more to find out.
What is PostgreSQL DROP COLUMN Command?
The command DROP COLUMN in PostgreSQL allows for removing one or more columns from a table. It provides a way to modify the structure of a table by eliminating specific columns. When executing this command, you need to specify the name of the table and the column(s) to be dropped.
Dropping a column permanently removes it from the table, along with any data stored in that column. It alters the table's metadata, excluding the dropped column from the schema definition. It is crucial to exercise caution when using this command, as the removal is irreversible and can result in data loss.
Before performing a column removal operation, it is recommended to create a backup of the table to ensure data integrity. Additionally, it is essential to consider any dependencies or constraints associated with the column, such as foreign key relationships or triggers, as they may need to be modified or removed before executing the command DROP COLUMN in postgresql.
Syntax of PostgreSQL DROP COLUMN Command
The syntax for the DROP COLUMN command in PostgreSQL is as follows:
Now, let's break the syntax into points to understand it in a better way:
- ALTER TABLE: It is a SQL statement used to modify the structure of an existing table in the database.
- table_name: Replace this with the actual name of the table from which you want to remove a column. The table must already exist in the database.
- DROP COLUMN: This is the specific action we want to perform on the table. It indicates that we will remove one or more columns from the specified table.
- column_name: Replace this with the name of the column you want to drop. After executing the command, this column and its associated data will be permanently removed from the table.
You can drop multiple columns in a single command by separating the column names with commas:
Examples of PostgreSQL DROP COLUMN Command
To understand the postgresql DROP COLUMN command, let’s create a table user:-
Drop a Single Column in Postgres
To drop a single column named column_name from a table called table_name, you can use the following syntax:
For instance, to drop the column email from a table called users, you would execute.
Before dropping the column, the users table will be shown as below:

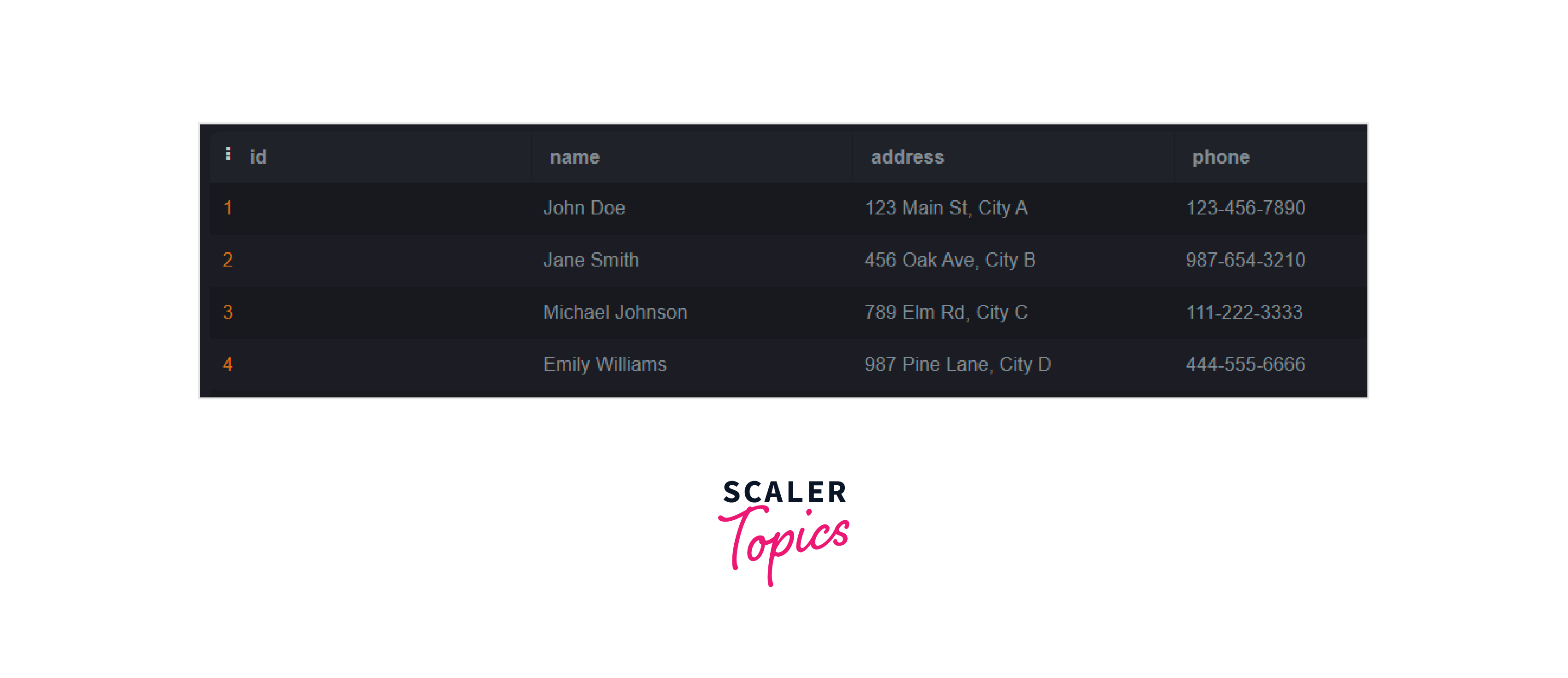
Output: After dropping the column, the users table will be shown as below:
Delete/Drop Multiple Columns in Postgres
To drop multiple columns simultaneously, separate the column names with commas:
Before dropping the columns, the users table looks like this:

For example, drop the columns address and phone from the customers table. Here's the code to delete/drop multiple columns in Postgres:
Output: After dropping the columns, the users table will be shown as below:

Drop a Column that doesn't exist
If you attempt to drop a column that doesn't exist, PostgreSQL will throw an error. To avoid the error, you can use the IF EXISTS option.
When the IF EXISTS statement is not used, then the following output will be generated:
Output:

The above error will occur because of the below-mentioned reasons:
- Typo in the Column Name: The column name provided in the DROP COLUMN statement might contain a typographical error or may not precisely match the actual column name in the table.
- Column Doesn't Exist: The email column does not exist in the users table. It's possible that the column was either already dropped or was never created in the table.
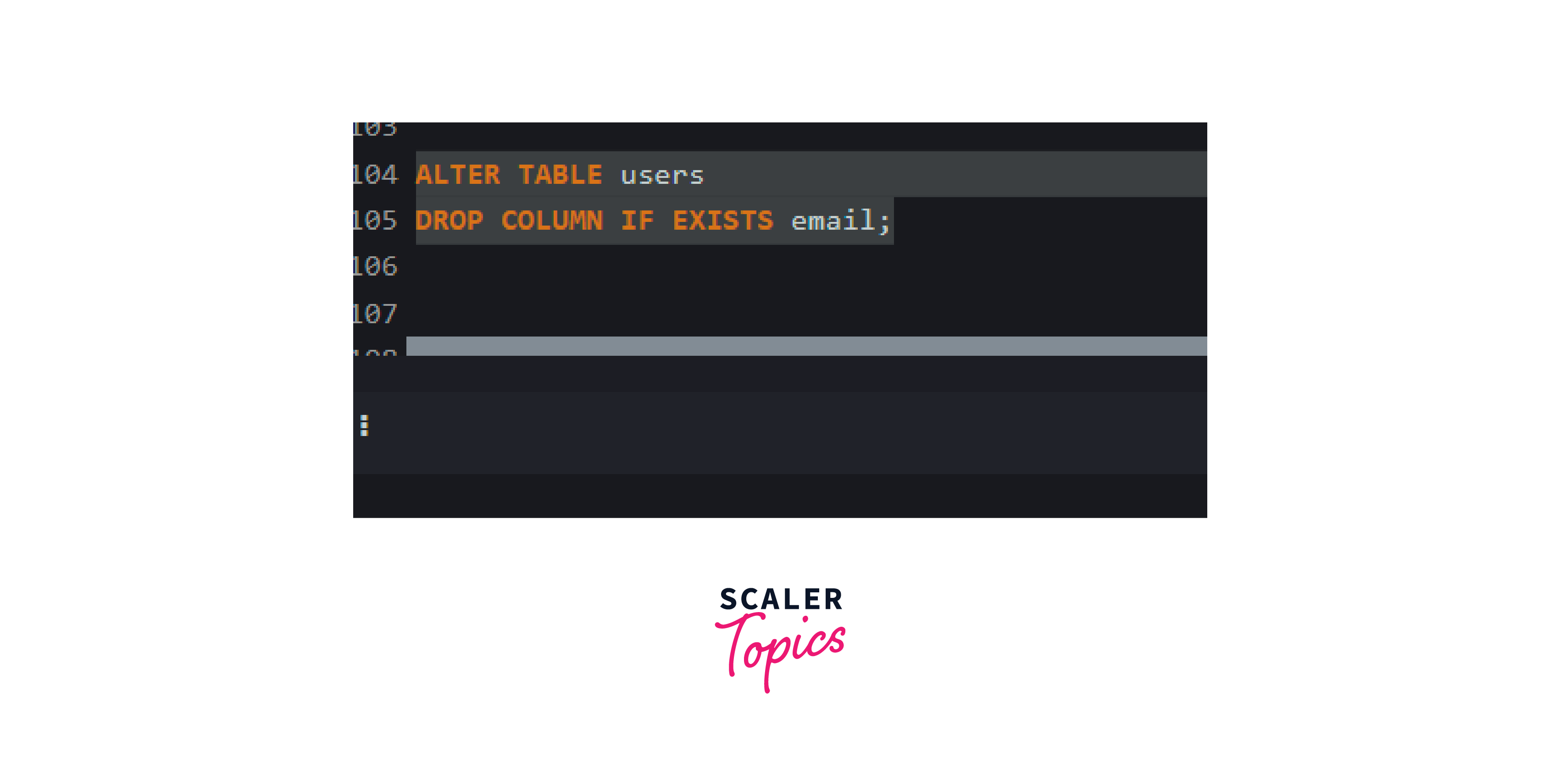
To avoid the error we can use the IF EXISTS keyword so that there will be no interruption in the database.
Output: After using the IF EXISTS statement, even if the column doesn't exist, the command will execute successfully without any error.
Avoid the Relation doesn't exist Error
In some cases, if you drop a column from a table that doesn't exist, PostgreSQL will raise a relation doesn't exist error. To show the error we will assume a table named emp that does not exist. To avoid this error, you can use the IF EXISTS keyword along with the CASCADE keyword.
Output: Below is the error that will occur when we execute the above statements and IF EXISTS and CASCADE keywords will not be used:

To handle this issue, we can use the following syntax:
Now, when we use both the keywords IF EXISTS and CASCADE on the existing table emp, the below code will be used:
This syntax ensures that if the table doesn't exist, the command will still execute successfully without raising an error.
Conclusion
- The DROP COLUMN in PostgreSQL allows the removal of specific columns from a table.
- It permanently eliminates the dropped column and the associated data from the table. Caution should be taken when using the command to avoid unintended consequences and data loss.
- It is recommended to create a backup before executing the DROP COLUMN operation for data integrity.
- Consider any dependencies or constraints associated with the column, such as foreign keys or triggers, and modify or remove them if necessary.
- The DROP COLUMN command is used to drop a single column or multiple columns simultaneously.
- The IF EXISTS option is used to avoid errors when dropping a column that doesn't exist.
- Using the CASCADE keyword with IF EXISTS ensures the successful execution even if the table doesn't exist.
- Proper syntax and careful consideration of the table and column names are crucial for the command to work correctly.
