Evolution of Cloud Computing
Overview
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses and individuals access, manage and deploy computing resources. It involves the delivery of various computing services over the Internet, providing a flexible and scalable solution for organizations of all sizes. This article dives into the evolution of cloud computing, tracing its journey from its inception to its current advanced state.
For more in-depth information on cloud computing, you can refer to resources like Scaler's Cloud Computing guide.
Evolution Stages of Cloud Computing
1. Early Concepts
The evolution of cloud computing traces back to the 1960s when the concept of time-sharing emerged. This allowed multiple users to access a single computer simultaneously, efficiently utilizing the available resources. However, the modern cloud computing model took shape in the late 1990s and early 2000s with the advent of virtualization technology and the internet.
2. Emergence of Virtualization
Virtualization played a pivotal role in shaping the evolution of cloud computing. It allowed multiple virtual machines (VMs) to run on a single physical machine, optimizing resource utilization and reducing infrastructure costs. Companies like VMware pioneered virtualization, which later became the foundation for cloud services.
3. Birth of Public Clouds
The early 2000s saw the emergence of public cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), offering scalable computing resources to users over the Internet. AWS introduced the concept of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), allowing users to rent virtualized hardware resources, such as servers and storage. This marked a significant shift in how businesses approached IT infrastructure.
4. Rise of Platform and Software Services
With the success of IaaS, cloud providers expanded their offerings to include Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Developers can build, deploy, and manage applications on a platform provided by PaaS without having to worry about the supporting infrastructure. SaaS provides ready-to-use software applications accessible via the cloud, eliminating the need for local installations.
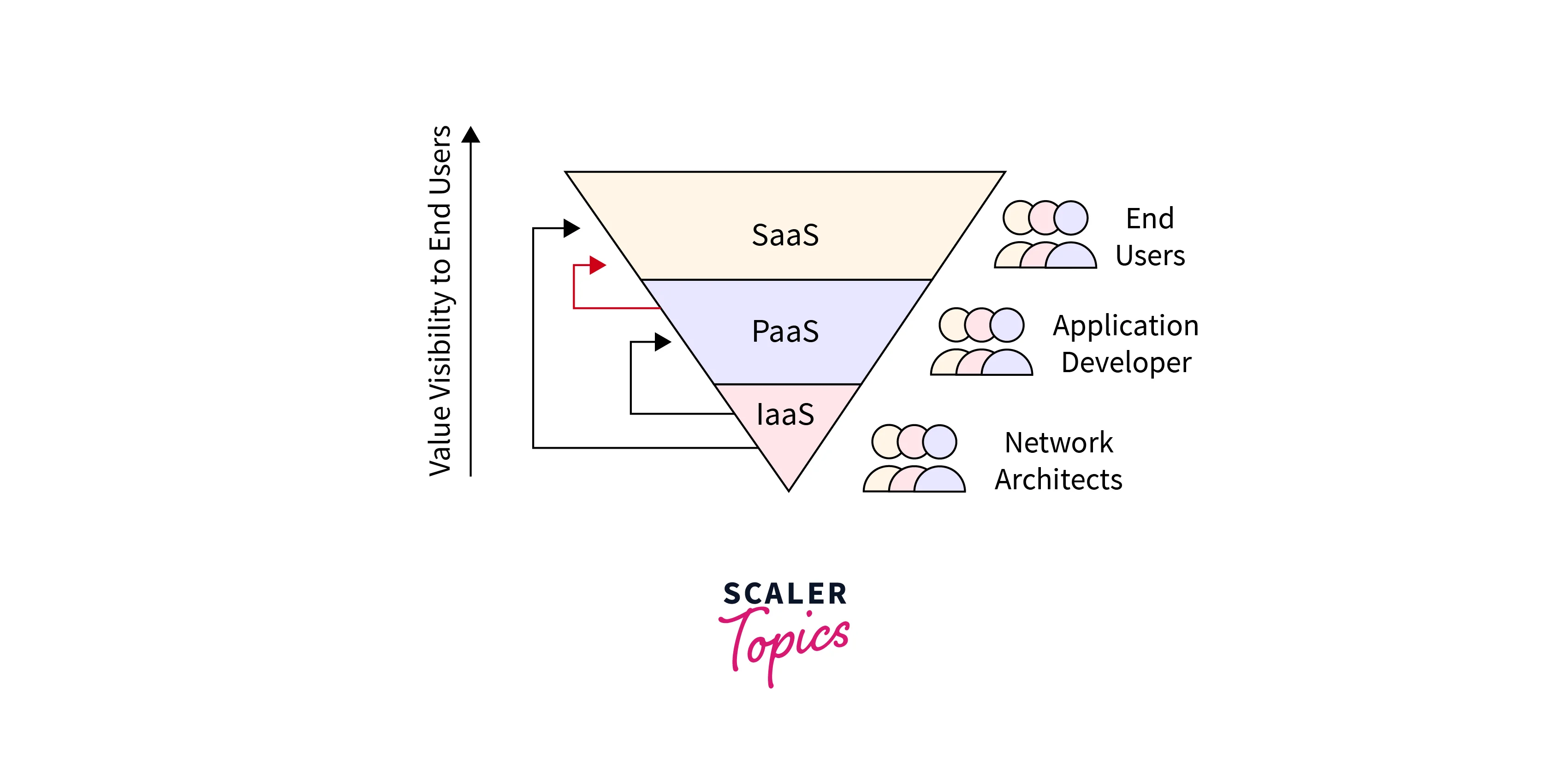
5. Hybrid and Multi-Cloud Environments
As cloud adoption grew, organizations started exploring hybrid cloud environments that combined on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud services. This approach offered greater flexibility and allowed businesses to address specific security and compliance needs. Additionally, multi-cloud strategies became popular, enabling organizations to use services from multiple cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in.
6. Edge Computing and Serverless Architecture
The evolution of cloud computing continued with the rise of edge computing and serverless architecture.
-
Edge Computing: Bringing Computing Closer to the Source
Edge computing is a paradigm shift in the world of cloud computing that addresses the limitations of traditional centralized cloud architectures. While cloud computing involves processing data on remote data centers, edge computing focuses on processing data at or near the data source, reducing latency and improving response times. This approach has gained prominence with the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, where data is generated at the edge of the network, often in remote or distributed locations.
-
Serverless Architecture: Focus on Code, Not Infrastructure
Despite its name, serverless architecture does not mean no servers are involved. Rather, it abstracts the management of servers away from developers, allowing them to focus solely on writing code. In traditional cloud computing models, developers must manage servers, provision resources, and scale infrastructure. Serverless computing shifts this responsibility to the cloud provider, who automatically manages the underlying infrastructure.
7. Advanced Technologies
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cloud computing, the integration of advanced technologies has increased the capabilities of cloud services to new heights. The convergence of cloud computing with technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and containerization has ushered in a new era of innovation, enabling businesses to leverage data-driven insights, streamline development processes, and achieve unparalleled efficiency.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The integration of AI and ML into cloud computing has revolutionized how data is processed, analyzed, and utilized. These technologies empower cloud services to perform tasks that were previously beyond the scope of traditional computing approaches.
-
Containerization with Docker and Kubernetes
Containerization has transformed the way applications are developed, deployed, and managed within the cloud environment. Due to their tendency to simplify application deployment and maintenance, two well-known containerization technologies—Docker and Kubernetes—have skyrocketed in popularity.
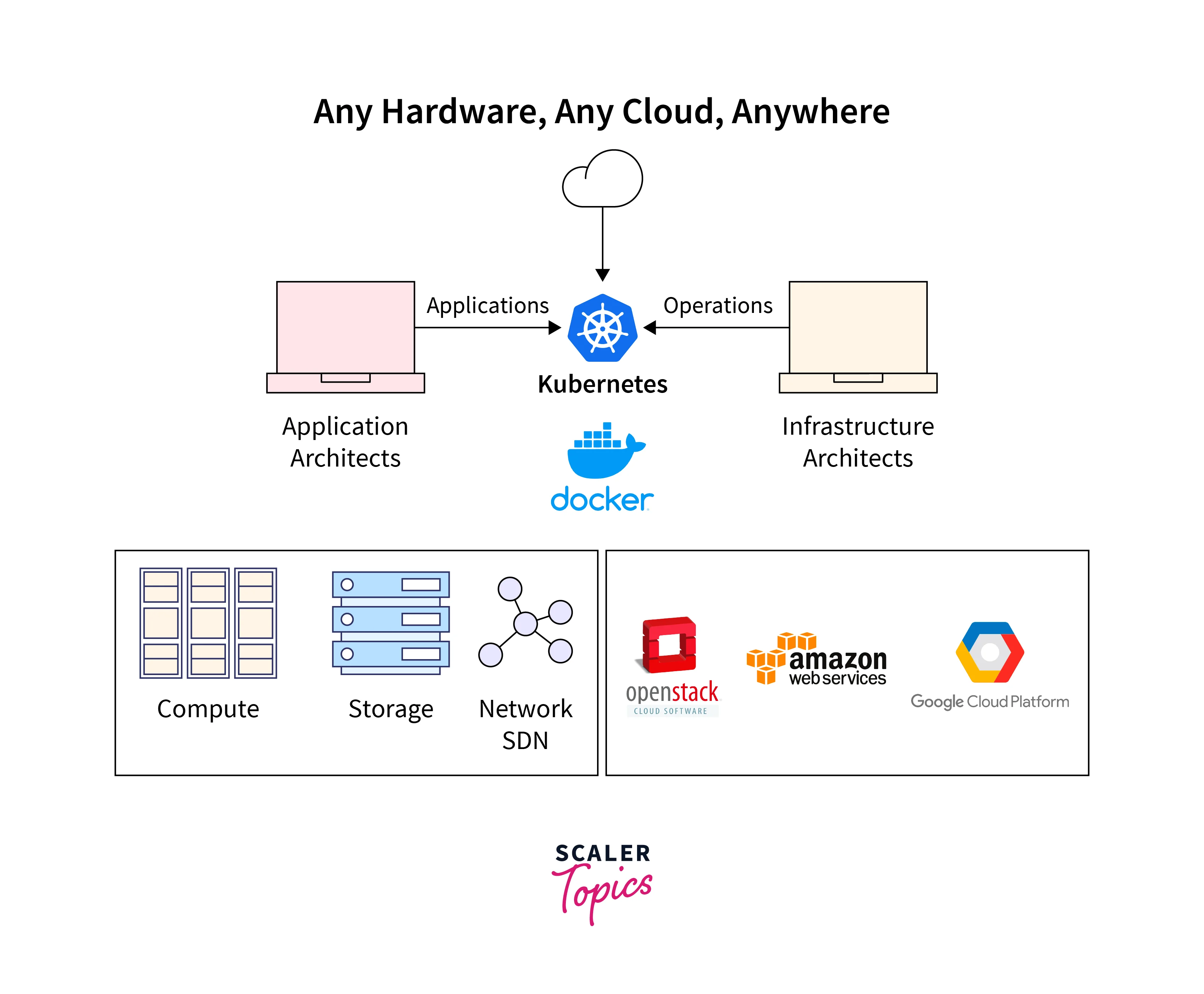
8. Future Trends
The evolution of cloud computing is an ongoing process, and several trends are shaping its future. These include the increased adoption of serverless computing, further advancements in AI and ML integration, enhanced security measures, and the development of more specialized cloud services to cater to specific industries and use cases.
FAQs
Q. What is the evolution of cloud computing?
A. The evolution of cloud computing traces its journey from early time-sharing concepts to today's advanced services, including virtualization, public clouds, hybrid environments, edge computing, and AI integration.
Q. How have advanced technologies impacted cloud evolution?
A. Advanced technologies like AI, ML, and containerization have transformed cloud computing by enabling predictive analytics, streamlined deployment, and powerful insights across industries.
Q. What are future trends in cloud evolution?
A. Future trends include increased serverless adoption, enhanced AI integration, improved security measures, and specialized cloud services tailored to specific industries and needs.
Conclusion
- The evolution of cloud computing has been a remarkable journey, transforming the way businesses operate and individuals access technology resources.
- Cloud computing has revolutionized the IT landscape from its early concepts rooted in time-sharing to the emergence of powerful public cloud platforms.
- Virtualization, public clouds, hybrid environments, advanced technologies, and future trends all contribute to the ongoing evolution of cloud computing.
- As we look ahead, it's clear that cloud computing will continue to adapt and innovate, offering solutions that cater to the ever-changing needs of the digital era.
