Null Safety Support for Flutter
Overview
Null safety is a groundbreaking feature introduced in Flutter that aims to enhance the reliability and robustness of code. With null safety, developers can eliminate the dreaded null reference errors, a common source of bugs and crashes in software development.
Introduction
Null reference errors have long been a bane for developers, causing unforeseen crashes and frustrating debugging sessions. In the dynamic world of Flutter app development, where speed and efficiency are crucial, addressing these issues is paramount. Enter null safety, a groundbreaking feature introduced in Flutter that revolutionizes how developers handle null references and brings unprecedented reliability to codebases.
Null safety in Flutter is a paradigm shift, providing developers with powerful tools to prevent null reference errors at compile-time rather than dealing with them during runtime. By embracing null safety, developers can leverage nullable and non-nullable types, ensuring variables are explicitly marked as either capable of holding null values or guaranteed to always have valid data. This approach enhances code quality, reduces bugs, and boosts the overall stability of Flutter applications.
In this article by Scaler Topics, we will explore the world of null safety in Flutter, examining its significance and the benefits it brings to developers.
Prerequisites
-
Dart SDK version:
Null safety in Flutter requires using a Dart SDK version that supports null safety. Starting from Dart 2.12, null safety is officially supported. Therefore, it is essential to have the appropriate version of the Dart SDK installed.
-
Flutter version:
To leverage null safety in Flutter, developers need to have a compatible version of the Flutter framework. Flutter 2.0 and later versions support null safety out of the box. Updating to the latest stable version of Flutter ensures access to null safety features.
-
Code migration:
Migrating existing codebases to null safety is a crucial prerequisite. Developers need to analyze and update their code to make it null-safe. This involves reviewing variable types, adding null checks, and resolving any potential null-related issues in the codebase.
-
Library compatibility:
It is important to ensure that the libraries and packages used in the Flutter project are null-safe or have null-safe versions available. Incompatible libraries may introduce flutter null safety issues and cause conflicts within the codebase. It is recommended to update libraries to their null-safe versions or find alternative null-safe libraries.
-
Development environment:
Using a compatible Integrated Development Environment (IDE) that supports null safety features is highly recommended. IDEs such as Visual Studio Code with the Flutter and Dart extensions or Android Studio with Flutter and Dart plugins provide helpful tools for working with null safety, including code analysis, hints, and refactoring support.
-
Developer knowledge and understanding:
Before implementing null safety in Flutter, developers should have a solid understanding of the concepts and features related to null safety. Familiarity with nullability annotations, null checks, and handling nullable and non-nullable types is essential to effectively adopt null safety in Flutter development.
By meeting these prerequisites, developers can successfully leverage null safety in Flutter, ensuring more robust and reliable code while taking advantage of the benefits it offers.
Principles of Flutter Null Safety
Null safety in Flutter is guided by a set of principles that help developers write more reliable and robust code. These principles serve as the foundation for understanding and utilizing null safety effectively. Here are the key principles:
-
Non-nullable:
The principle of non-nullable states that variables in null safety are non-nullable by default. This means that variables are expected to always hold a valid value and cannot be assigned a null value unless explicitly marked as nullable. By enforcing non-nullability, null safety helps eliminate null reference errors, as developers are required to handle null cases explicitly and ensure that variables contain valid data at all times.
-
Adoptable:
The principle of adaptability emphasizes that null safety is designed to be incremental and adaptable at various stages of development. Developers can gradually introduce null safety into their codebase, starting with specific files, packages, or modules, and then expanding its usage over time. This flexibility allows developers to integrate null safety into existing projects without requiring a complete rewrite, enabling a smooth transition and minimizing disruption to the development process.
-
Fully Sound:
The principle of full soundness ensures that null safety in Flutter guarantees the absence of null reference errors at compile-time. Sound null safety means that the type system is designed to prevent null values from flowing through the code unchecked, providing strong static guarantees. With full soundness, developers can rely on the compiler to identify potential null reference errors and provide compile-time warnings or errors, helping them catch and address these issues before they occur at runtime.
These principles collectively form the foundation of null safety in Flutter, enabling developers to write more reliable and robust code. By enforcing non-nullability, offering adaptability, and ensuring full soundness, null safety in Flutter significantly reduces the risk of null reference errors, improves code quality, and enhances the overall development experience.
What are Nullable and Non-Nullable Types?
In Flutter's null safety, nullable and non-nullable types refer to the ability of variables to hold null values or to always have a valid value, respectively. These types play a crucial role in preventing null reference errors and ensuring code reliability. Here's a breakdown of nullable and non-nullable types:
-
Nullable Types:
Nullable types are denoted by adding a question mark (?) after the type declaration. Variables declared with nullable types have the flexibility to hold either a valid value or a null value. Nullable types are useful when a variable may or may not have a value or when working with optional data. To safely access properties or perform operations on a nullable variable, null-aware operators such as the null-aware access operator (?.) are used to handle potential null values.
Example:
-
Non-Nullable Types:
Non-nullable types are the default in null safety and indicate that a variable must always have a valid value and cannot be null unless explicitly marked as nullable. Variables declared with non-nullable types guarantee that null reference errors will not occur at runtime. Non-nullable types are specified without the question mark (?) after the type declaration.
Example:
-
Assertion Operator (!):
The assertion operator (!) is used to assert that a nullable variable has a non-null value at a specific point in the code. It informs the Dart analyzer that the variable is expected to have a valid value and should not be null. The assertion operator is useful when developers have performed null checks or other operations to ensure that a nullable variable is not null and want to communicate this expectation to the analyzer. Example:
-
Type Promotion:
Type promotion is a mechanism in Dart that allows the compiler to infer that a variable is non-nullable within a specific code block, even if its type is originally nullable. This occurs when the compiler can determine that the variable has been assigned a non-null value or passed through a null check. Once a variable is promoted to non-nullable, developers can safely use it without requiring explicit null checks. Example:
By understanding nullable types, the assertion operator, and type promotion, developers can effectively handle nullability in their code and leverage Flutter's null safety features to enhance code reliability and prevent null reference errors.
Sound and Unsound Flutter Null Safety
In Dart, null safety refers to a type system feature that aims to prevent null reference errors at compile-time, providing stronger guarantees about the absence of null values in code. However, there can be distinctions between sound and unsound null safety in Dart:
-
Sound Null Safety:
Sound null safety ensures that the type system guarantees the absence of null reference errors at compile-time. In a sound null safety system, the compiler tracks nullability information for variables and ensures that nullable variables are handled appropriately to prevent null-related issues. Sound null safety provides strong static guarantees, minimizing the risk of null reference errors during runtime.
-
Unsound Null Safety:
Unsound null safety refers to situations where the type system does not provide complete guarantees about the absence of null reference errors. It can occur when the type annotations or type system rules are not strictly enforced, allowing null values to flow through the code unchecked. Unsound null safety can introduce the potential for null reference errors, leading to unexpected crashes or undefined behavior at runtime.
Note: It's worth noting that as of Dart 2.12 and later, Dart's null safety is designed to be sound. This means that the type system aims to provide comprehensive guarantees about nullability, minimizing the chances of null reference errors. Sound null safety helps improve code reliability, maintainability, and overall development experience by catching potential null-related issues early during compilation.
By adopting sound null safety practices and leveraging the features and tools provided by the Dart language, developers can write more robust and reliable code while minimizing the risk of null reference errors and their associated consequences.
How Null Safety Migration Works in Flutter?
Null safety migration in Flutter involves updating existing codebases to leverage the benefits of null safety, including enhanced code reliability and improved error prevention. The migration process typically consists of the following steps:
-
Ensure that all dependencies are ready for migration:
Before starting the migration, it's crucial to ensure that all the dependencies used in your project are ready for null safety. Check the documentation, release notes, or official websites of each dependency to determine if they have released null-safe versions. If a dependency has not yet migrated to null safety, you may need to find alternative packages or consider contributing to the migration effort of that particular dependency.
-
Use the migration tool to migrate
Flutter provides a migration tool called Dart Migrate to automate the process of updating your codebase for null safety. This tool analyzes your code and suggests modifications based on null safety guidelines. Run the dart migrate command in your project's root directory, and the tool will make automated changes to your code, including adding nullability annotations, updating variable types, and suggesting null checks where necessary.
-
Analyze your migrated code statically
After using the migration tool, it's essential to perform static code analysis using the Dart analyzer. The analyzer examines your migrated codebase and provides feedback on potential issues related to null safety. It flags any null reference errors, missing null checks, or other problematic code patterns. Address these issues by carefully reviewing the analyzer's feedback and making the necessary modifications to ensure proper null safety handling.
-
Verify that the tests are passing
Thoroughly test your migrated codebase to validate its functionality and ensure that null reference errors have been properly addressed. Run your existing test suite and verify that all tests pass successfully. Additionally, consider augmenting your test suite to include specific scenarios that test nullability and potential edge cases related to null safety. Comprehensive testing is crucial to catch any regressions or unforeseen issues that may have emerged during the migration process.
-
Packages that are null-safe should be published
If you maintain or develop packages that are part of your project, it's important to migrate them to null safety as well. Update your packages to leverage null-safety features and release null-safe versions. Publishing null-safe packages allows other developers who have migrated their projects to null-safety to benefit from your updated packages.
Throughout the migration process, it's advisable to refer to Flutter's official documentation on null safety, take advantage of community resources, and consult best practices. These resources can provide additional guidance, tips, and solutions to common challenges encountered during the null safety migration process.
By following these steps and ensuring thorough testing, you can successfully migrate your Flutter project to null safety, leveraging its benefits for improved code reliability and error prevention.
Reasons for Flutter Null Safety Migration
-
Eliminate Null Reference Errors:
Flutter Null safety enforces non-nullability by default, reducing the risk of null reference errors. By explicitly indicating nullable and non-nullable types, the compiler helps catch potential null-related issues, preventing crashes and unexpected behavior caused by accessing null values.
-
Enhanced Code Reliability:
With null safety, variables are guaranteed to have valid values. This improves the overall reliability of your codebase by eliminating the possibility of null-related errors, and ensuring that variables are properly initialized before use.
-
Improved Code Readability:
Flutter Null safety makes nullability explicit in the code, improving code readability. It becomes clear which variables can be null and which cannot, making it easier for developers to understand and reason about the behavior of their code.
-
Early Error Detection:
The Dart analyzer performs static analysis during the null safety migration process, providing feedback on potential null reference errors and other nullability issues. This helps catch and address these errors early in the development cycle, reducing the likelihood of encountering them at runtime.
-
Stronger Type System:
Null safety enhances Dart's type system, allowing for more precise type annotations and better static analysis. This strengthens the type safety of your code, reducing the occurrence of type-related bugs and making your codebase more robust and maintainable.
-
Seamless Interoperability:
Migrating to null safety ensures compatibility with null-safe versions of dependencies. This allows you to benefit from the latest features, improvements, and bug fixes in libraries and packages, ensuring seamless interoperability with the broader Flutter ecosystem.
-
Better Developer Experience:
By leveraging null safety, developers can focus more on writing code and less on defensive null checks. The reduced concern for null reference errors improves the developer experience, leading to increased productivity and a smoother development workflow.
-
Gradual Adoption:
Flutter null safety allows for incremental adoption, enabling you to migrate specific files, packages, or modules at your own pace. This flexibility allows you to prioritize critical parts of your codebase for migration and minimizes disruption to ongoing development efforts.
-
Community Support:
Null safety is becoming the standard in Flutter development. By migrating to null safety, you can tap into a growing community of developers, resources, and libraries that embrace and provide support for null safety. This community support can assist you in navigating challenges and sharing best practices.
-
Future-Proof Your Codebase:
Null safety is the future of Flutter. By migrating your codebase to null safety, you ensure its compatibility with future versions of Flutter and take advantage of upcoming enhancements, optimizations, and features. This future-proofing ensures that your codebase remains relevant and maintainable as the Flutter ecosystem evolves.
Considering these elaborated reasons, you can fully understand the benefits of null safety migration in Flutter, including improved code reliability, reduced null reference errors, enhanced developer experience, and compatibility with the evolving Flutter ecosystem.
Advanced Features of Null Safety in Flutter
Null safety in Flutter introduces several advanced features that enhance code robustness, improve developer productivity, and provide a more seamless development experience. Here are some of the advanced features of null safety in Flutter:
-
Null Safety Operators:
Null safety introduces powerful operators that simplify null handling in code. The null-aware access operator (?.) allows accessing properties or calling methods on an object only if the object reference is non-null. This operator saves developers from writing explicit null checks and reduces the risk of null reference errors. Additionally, the null-aware assignment operator (??) allows providing a default value if an expression evaluates to null, ensuring a fallback value when dealing with nullable variables.
-
Late Initialization:
Null safety introduces the late keyword, which enables late initialization of non-nullable instance variables. By marking a variable as late, developers can defer its initialization to a later point in code execution, ensuring that the variable is assigned a valid value before being accessed. Late initialization helps in scenarios where a non-nullable variable's value is not available immediately upon declaration, such as when initializing in constructors or async operations.
-
Non-Nullable by Default Libraries:
Null safety allows developers to utilize third-party libraries that embrace non-nullability. Non-nullable by default libraries ensure that APIs provided by those libraries are designed to work seamlessly with null safety, reducing the chances of null reference errors when integrating external dependencies into your Flutter projects.
-
Migrating Existing Projects:
Null safety provides tools and guidelines for migrating existing Flutter projects to utilize null safety. The migration process involves automatically analyzing code to identify and update potential nullability issues, generating migration suggestions, and providing migration reports to guide developers in gradually adopting null safety without disrupting the existing codebase.
By leveraging these advanced features, developers can enhance code reliability, reduce null reference errors, and take advantage of a more efficient and streamlined development workflow in Flutter. These features empower developers to write more robust and resilient applications while benefiting from the productivity gains brought about by null safety.
Example App
-
Create the Task class
In the lib folder, create a new file called task.dart. This file will define the Task class.
-
Create the TaskList widget
In the lib folder, create a file task_list.dart. This file will define the TaskList widget, which displays the list of tasks.
-
Create the main application
In the lib folder, open the main.dart file, and replace its content with the following code:
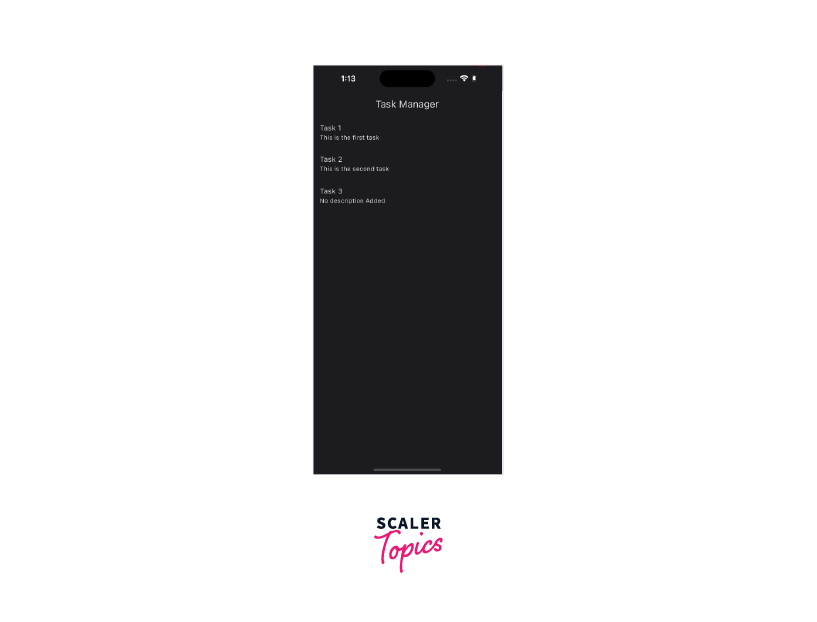
In this example, we've used null safety to ensure that the description property of the Task class can be null. Additionally, the tasks list in the TaskList widget is allowed to be null.
If null safety were not implemented, the application would behave differently:
-
Null Description:
If the description property in the Task class were not allowed to be null, we would need to provide a default value or an empty string for the description in the Task constructor. However, this might not always be appropriate, especially if we genuinely want the description to be null for some tasks.
-
Null List:
Without null safety, we would need to manually check if the tasks list is null before accessing its length or elements. Failure to do so could lead to a runtime null-reference error.
Null safety is essential in this application because it allows us to handle cases where the description is missing for some tasks or where the tasks list itself is null. By leveraging null safety, we can catch potential null-related errors at compile-time, making the application more reliable and reducing the risk of crashes due to null values.
Conclusion
- Null safety in Flutter ensures that variables are explicitly declared as nullable or non-nullable, reducing the risk of null pointer exceptions and improving code reliability.
- It provides improved type checking during compile-time, catching potential null-related issues early and reducing debugging time.
- Migrating to null safety requires developers to update their codebases, making necessary adjustments to variable types, and add null checks.
- Null safety improves interoperability with Dart libraries and packages, enhancing compatibility and stability.
- It encourages the adoption of best practices for handling null values, promoting defensive programming and error-handling strategies.
Overall, Flutter null safety leads to safer and more maintainable code, resulting in better user experiences and more stable applications.
