Generative AI
Overview
Generative AI is a subfield of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating algorithms that can generate fresh, original content or data that is equivalent to previously published materials. In order to find structures and patterns in the data already available, generative AI models employ deep learning techniques. Using this knowledge, they go on to create fresh data that, in terms of format or style, resembles the original data.
We'll read extensively about this subject in this essay.
Introduction
Within the larger subject of machine learning and artificial intelligence, generative AI (AI) is a fast-developing subfield. It entails using algorithms and models to create fresh material that is similar to or inspired by current data. This content can take the form of photographs, videos, music, texts, and more. Since it has applications in a variety of fields, including art, design, entertainment, marketing, and scientific study, generative AI has drawn a lot of attention.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI, also known as creative AI, is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on producing new content, such as pictures, movies, music, texts, or other types of data, that is either inspired by or comparable to preexisting data. Generative AI is focused on creativity and creating fresh, unique, and varied outputs, as opposed to classical AI, which is often employed for tasks like classification or prediction.
The possibility of creating false or misleading material, copyright violations, and biases in generated content are only a few of the ethical and social issues that Generative AI brings. It is essential to carefully evaluate the ethical ramifications and ensure responsible and ethical usage of these technologies as generative AI develops.
How does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI uses machine learning methods and models to produce new content that is comparable to or drawn from preexisting data. Giving the model the capacity to learn from a big body of data while capturing the underlying patterns, structures, and features of the data is the basic principle. After being trained, the model can then extrapolate from the patterns it has learnt to create new content.
Generative AI has a variety of ways, and the choice of approach is determined by the nature of the generated data and the desired result. Typical methods include the following:
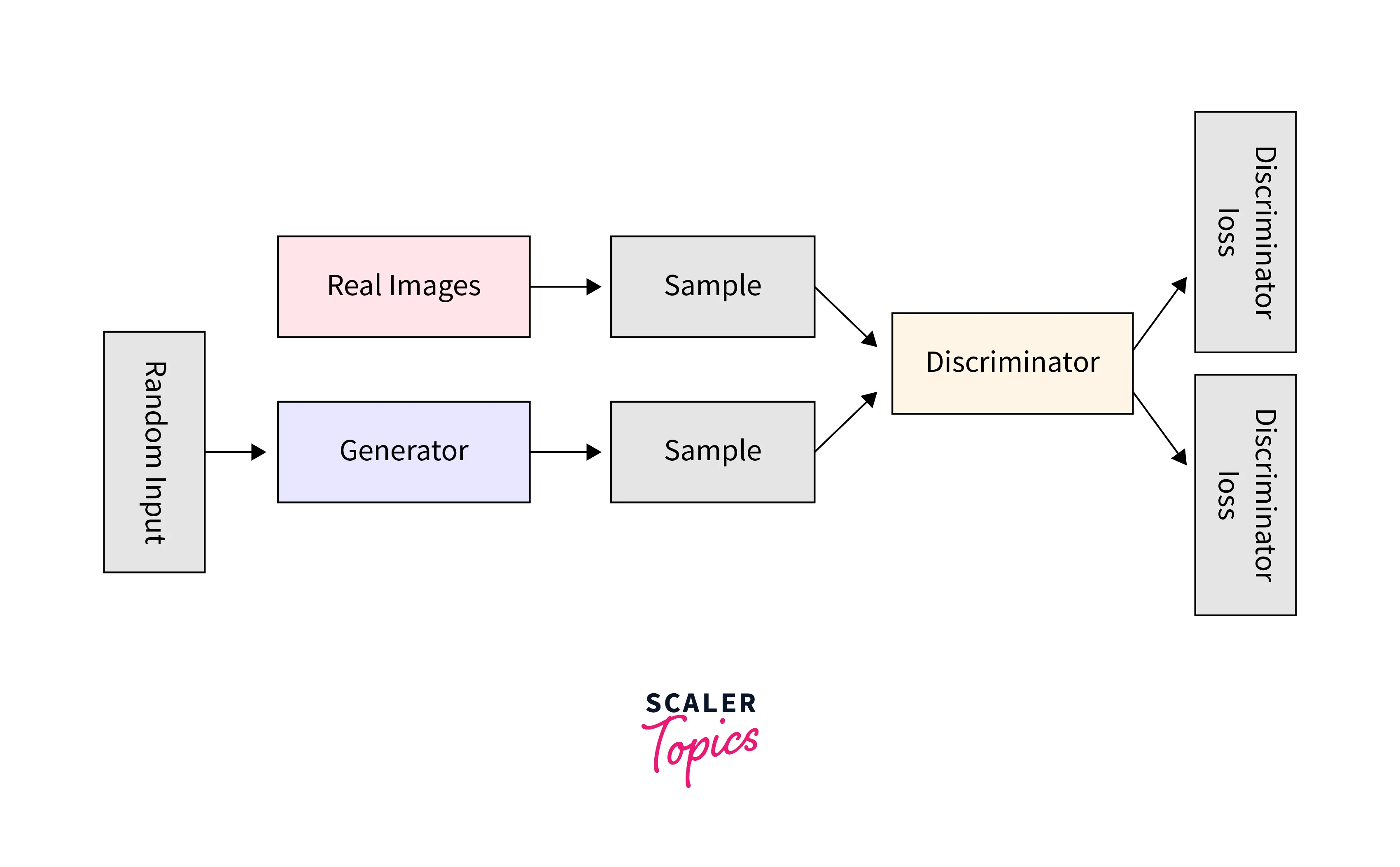
1. Generative Adversarial Networks
A generator and a discriminator are required to generate "GANs," via a process called "adversarial training". While the generator tries to make content that can fool the discriminator, the discriminator seeks to distinguish between actual and manufactured content accurately. Because of this competition between the generator and the discriminator, the generator continually improves its ability to produce realistic material.
2. Variational Autoencoders
A particular class of probabilistic model called a VAE(Variational Autoencoders) learns to compress incoming data into a smaller latent space, then decodes samples from this latent space to produce new information. VAEs learn to simulate the distribution of the data in the latent space by combining encoder and decoder neural networks.

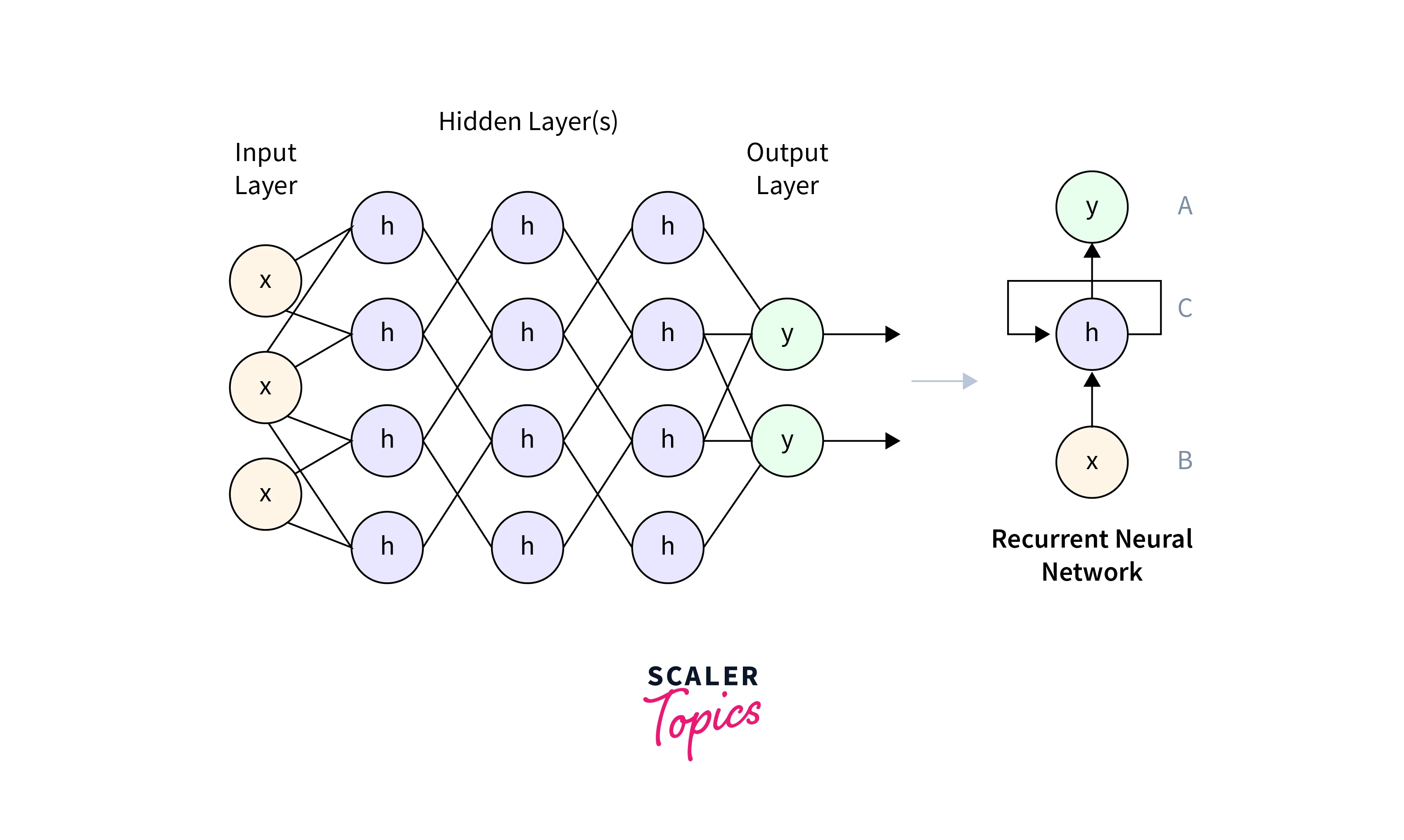
3. Recurrent Neural Networks
RNNs are a particular kind of neural network that are made to model sequential data, like music or text. By taking a sample from a previously learned probability distribution at each step of the sequence and creating new data one point at a time, RNNs can learn to create new material.
Additional methods include Transformers, which are popular for producing text-based content, and Generative Adversarial Imitation Learning (GAIL), which combines GANs and reinforcement learning to produce content that imitates a certain behavior or policy.
How To Build A Generative AI Model?
A generative AI model is created by following many crucial steps described follows
Step 1. Defining the Problem Statement
First, we must specify the issue that we want your generative AI model to address. What kind of data are we looking to produce? Is it written words, music, visuals, or something else? What qualities should the content that is generated have? For choosing the best strategy and creating the architecture of your generative AI model, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the issue you're trying to solve.
Step 2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
The type of data that we want the model to produce must be represented in a sizable dataset, which must be gathered. The model will be trained using this dataset. The dataset should encompass a wide variety of data variances and be representative of the content we wish to provide. Once we receive the dataset, we might need to preprocess it to make sure it is adequate for training the model by normalizing, scaling, or augmenting the data.
Step 3. The Right Approach
Generative AI can be approached in a variety of ways, including using GANs, VAEs, RNNs, and others. The method you choose will rely on the kind of data you want to produce, the qualities you want the content to have, and the constraints imposed by the data and computer resources at your disposal. The strategy that best matches your problem must be carefully chosen because each approach has advantages and disadvantages of its own.
Step 4. Model Training
After choosing a strategy, you must create the architecture of your generative AI model. Depending on the strategy used, this entails specifying the neural network's layers, neurons, and connections as well as any other structures. The model must then be trained using the preprocessed data. The model gains the ability to recognize the underlying structures and patterns in the data during training, allowing it to produce new content.
Step 5. Evaluation
You must examine the efficacy of your generative AI model after training. Visual inspection, quantitative measurements, and user feedback are just a few of the metrics and methods you can use to judge the quality of the material that is generated. In order to increase the model's performance, you might need to refine and iterate on it by changing hyperparameters, altering the architecture, or gathering more data.
Step 6. Deployment and Optimization
Finally, you must introduce your generative AI model into a production environment if necessary. The performance of the model might need to be optimised for high-throughput or real-time content generation. It might also need to be incorporated into a platform, system, or application. Performance may need to be closely monitored, and improvements may need to be made on a regular basis, to ensure that the generated material complies with the set quality requirements.
In addition to having a solid understanding of the problem, the available data, and the best course of action, developing a generative AI model requires skills in data preprocessing, model creation, training, evaluation, and deployment. Experimentation, fine-tuning, and optimisation may be required for this iterative and dynamic process in order to achieve the desired results.
What Kinds Of Output Can A Generative AI Model Produce?
Depending on the kind of data it is trained on and the particular methodology employed, a generative AI model can generate a wide range of outputs. The following are examples of the common outputs that generative AI models can create
1. Images
Images can be created by generative AI models, either from scratch or by editing already-existing images. For instance, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) can produce images with certain styles, textures, or qualities, whereas Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can produce realistic images of faces, objects, scenes, or artwork.
2. Text
Text can be generated by generative AI models as paragraphs, phrases, or single words. Text generation models can be used to produce content like news articles, fiction, poetry, and computer code. For text creation tasks, recurrent neural networks (RNNs) and transformer-based models are frequently employed.
3. Music and Audio
Melodies, beats, sound effects, and speech can all be produced by generative AI models for music or audio content. New melodies, remixes, and audio samples can all be produced via music generation models. Music and audio generation tasks can be performed using WaveNet, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and other deep learning models.
Moreover, generative AI models can produce various kinds of material, like 3D models, commercial designs, architectural designs, simulations of scientific data, and more. The problem and training data used to create the generative AI model can be utilised to tailor the output, which is not constrained to a single domain or kind of material.
What Kinds Of Problems Can A Generative AI Model Solve?
The applications of generative AI models are numerous, and they can be used to address a variety of issues in a variety of fields. Examples of issues that generative AI models can aid in resolving
1. Content Creation
Generative AI models are capable of producing unique content for artistic reasons, including producing original writing, music, art, and other kinds of creative expression. These models can help writers, musicians, artists, and other creative professionals create new work or experiment with various artistic mediums.
2. Art and Entertainment
In the entertainment sector, generative AI models can be applied to make animations, special effects, virtual character designs, and other imaginative tasks. These models can improve the interactive and visual aspects of media such as virtual reality, video games, and movies.
3. Medical and Scientific Research
By producing accurate data, simulations, or models for analyzing diseases, drug discovery, protein folding, genomics, and other scientific domains, generative AI models can support medical and scientific research. These models can aid scientists in formulating hypotheses, investigating various possibilities, and making predictions.
4. Data Augmentation
Machine learning algorithms' training datasets can be supplemented with augmented data produced by generative AI models. This can be useful when there are few or insufficient data sets available for training or when more diverse data sets are required to boost model performance. To develop more varied and representative training datasets, generative models can produce realistic synthetic data that can be mixed with actual data.
5. Simulation and Prediction
For forecasting and prediction purposes, generative AI models are capable of producing simulated data. For instance, generative models can replicate stock prices in the financial sector, weather patterns in climate modelling, and patient data in the healthcare sector for disease prediction. Making educated decisions and understanding and predicting complex systems are both facilitated by these simulations.
Generative AI Models
Due to their amazing capacities for producing high-quality and realistic data, there are several examples of generative AI models that have attracted a lot of interest in recent years. Among the notable examples are:
1. Dall E
A generative model called DALL-E created by OpenAI can produce visuals from textual descriptions. It is based on a variation of the VQ-VAE-2 (Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoder 2) architecture and is named after the well-known surrealist artist Salvador Dal. Combining components of discrete vector quantization with variational autoencoders (VAEs), DALL-E may produce a variety of high-resolution images (VQ).
The model then generates images that correspond to these prompts, frequently producing original and creative visual interpretations of the textual input. DALL-E takes textual prompts as input, which can be simple descriptions like "a two-story pink house" or more complex prompts like "a futuristic cityscape at sunset with flying cars and glowing skyscrapers."
2. ChatGPT
OpenAI created ChatGPT, a large language model based on the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) architecture. ChatGPT is capable of producing logical and contextually appropriate responses because it was trained on a substantial amount of text material from the internet. Questions, prompts, assertions, and instructions are just a few of the text-based inputs that ChatGPT can comprehend and reply to.
Depending on the context of the input and the linguistic patterns it has learned, it can engage in interactive conversations with users and answer with insightful, creative, or interesting comments.
3. BARD
Google's conversational AI chat service, BARD, is currently in development. With the main distinction being that Google's service will obtain its data via the internet, it is intended to operate similarly to ChatGPT. Google and Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai announced BARD in a statement on February 6.
Google's Linguistic Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA) technology forms the foundation of Google Bard. Transformer, a 2017-released neural network architecture from Google, served as the foundation for LaMDA. Due to Google's open-source release of Transformer, it has served as the foundation for various generative AI tools, such as the GPT-3 language model used in ChatGPT.
Limitations of Generative AI Models
While strong and creative, generative AI models can have several drawbacks. Following are a few typical drawbacks of generative AI models:
-
Computational complexity
Deep learning models, in particular, can be computationally expensive and may need a lot of processing power, as well as high-performance GPUs and plenty of memory, for training and inference. -
Limited data for training
The information and patterns available in the training data are the only ones that generative AI models can use to improve their performance. The model may have trouble producing accurate and coherent outputs if it comes across data that differs greatly from its training data. -
Ethical and legal concerns
The possibility of creating fake content, disseminating false information, or breaching copyrights or intellectual property rights are only a few ethical and legal issues that might be raised by generative AI models. An crucial factor to take into account is making sure generative AI models are used responsibly and ethically.When implementing generative AI models in various applications, it's critical to be aware of these limits and take them into account. You need also to apply the proper validation, verification, and ethical concerns to ensure the responsible and useful usage of these models.
Applications of Generative AI
Applications for generative AI models can be found across many industries and fields. Common uses for generative artificial intelligence include:
-
To create artwork, design virtual characters, build virtual locations, or produce realistic textures and visual effects, generative AI models can create realistic images from scratch or modify already-existing images.
-
Textual content can be produced using generative AI models, including articles, poems, novels, product descriptions, and more. This applies to industries including content development, copywriting, creative writing, and language generation in natural settings.
-
In areas like music composition, sound editing, and virtual instruments, generative AI models may produce music, audio, and sound effects ranging from simple melodies to sophisticated compositions.
-
Advertising content creation and optimization can be assisted by generative AI models, which can produce ad copy, graphics, and videos.
-
Based on user preferences and behavior, generative AI models can produce tailored recommendations for goods, services, information, and experiences, increasing user engagement and happiness.
Conclusion
We can summarize this article with the following few points
- Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that focuses on producing new content, such as pictures, movies, music, texts, or other types of data, that is either inspired by or comparable to preexisting data.
- The fundamental idea of how the Generative AI model works is to give the model the ability to absorb knowledge from a sizable body of data while capturing the underlying patterns, structures, and traits of the data. The model can then produce new material by extrapolating from the patterns it has learned after being trained.
- Defining the problem statement, data collection and preprocessing, choosing the right approach, model training, evaluation, and deployment are the major and most important steps for creating a model.
- Generative AI model can solve problems like, content creation and data augmentation as well as can help in medical and scientific research.
- Generative AI models can be used for creating fake content, disseminating false information, or breaching issues are ethical and legal concerns.
