Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI] by ITU
The Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI), led by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), benchmarks countries' commitment to cybersecurity globally. It serves as a trusted reference, promoting awareness and understanding of cybersecurity's significance and dimensions.
Global Cybersecurity Index - India's Rank & Cybersecurity
- India advanced 37 positions on important cybersafety metrics to land in place in the ITU's Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2020 ahead of the sixth anniversary of Digital India (1 July 2021).
- India was ranked fourth in the Asia Pacific area, demonstrating its dedication to cybersecurity.
- China and Pakistan, which are neighbors, were ranked 33 and 79, respectively.
- The outcome demonstrates a significant overall strengthening and improvement across all cybersecurity-related metrics.
- With strong steps to protect data privacy and citizen online rights, India is establishing itself as a global IT giant, claiming its digital sovereignty.
- The following picture displays India's standing and scores according to the many criteria used to calculate the Global Cybersecurity Index:
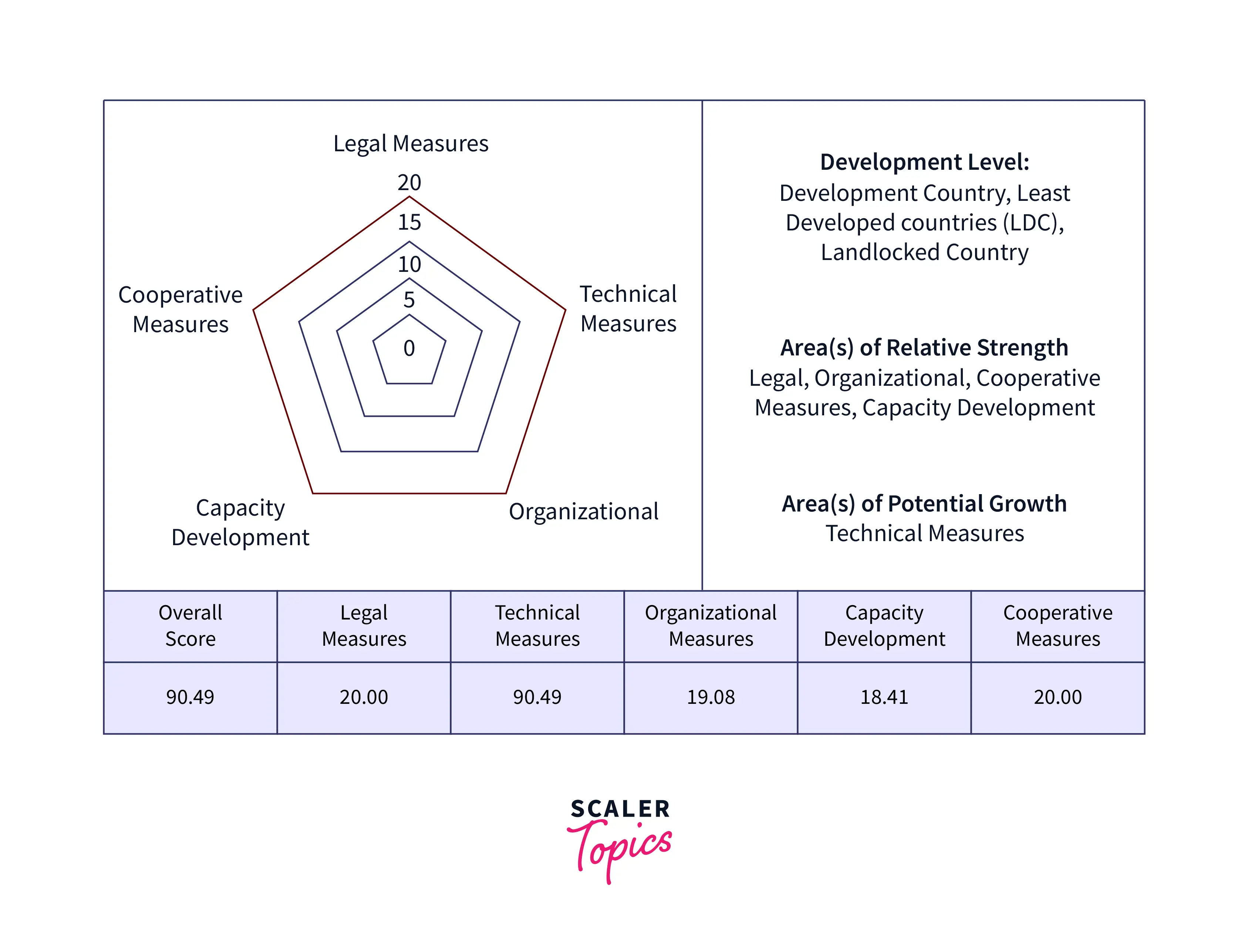
Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI] Key Highlights
- The ranking was officially introduced on June 29, 2021.
- Overall, the United States of America received a score of 100 in GCI 2020, placing it in first place.
- The last on the list are: Equatorial Guinea ranked 180 the list, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea ranked , and Micronesia, the Vatican, and Yemen ranked .
- Denmark is regarded as having the most robust cybersecurity infrastructure among all nations. With a cybersecurity score of 8.91, the government is performing rather well on the cybersecurity exposure index.
- China is said to have the strongest cyber defense capabilities, followed by the United States, Israel, the Netherlands, France, Canada, and the UK. Russia is recognized as the largest short-term danger to cyber security. However, other analysts believe that China will prove to be more dangerous and dangerous in the long term.
- India was one of the top 3 countries that during the pandemic experienced risky server access and ransomware attacks.
- The top 5 nations on the GCI list are:
- The United States of America.
- Saudi Arabia and the United Kingdom
- Estonia.
- Spain, Singapore, and South Korea.
- Russia, Malaysia, and the United Arab Emirates.
Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI] - Region-Wise Top Countries
| Region | Country | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Africa | Mauritius | 96.89 |
| America | United States of America | 100 |
| Arab States | Saudi Arabia | 99.54 |
| Asia-Pacific | Korea (Rep. of) | 98.52 |
| Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) | Russian Federation | 98.06 |
| Europe | United Kingdom | 99.54 |
Challenges to Cybersecurity
- Digital divides between nations lead to an unsustainable online ecosystem.
- The post-COVID era's growing reliance on digital technology has shown digital inequalities that must be eliminated through strengthening capability.
- Terrorists employ advanced methods to spread their message and stir up hatred in cyberspace.
- The use of cybersecurity tools to strengthen a complicated security environment, is entirely vulnerable to human mistakes. Due to a lack of domestic development in cybersecurity hardware and software, organizations are exposed to cyberattacks.
- The business's commitment to protecting devices, data, and information is the most important factor.
FAQs on Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI]
Q: Who publishes the GCI, or Global Cybersecurity Index?
A: The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), a specialized UN organization that regularly increases cybersecurity awareness internationally and assesses the commitment of all its member nations, analyses and publishes the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI).
Q: How many countries are included in the Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI]?
A: 194 nations in total are included in the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI).
Q: What place did India hold in the GCI 2020?
A: According to the Global Cybersecurity Index published in June 2021, India was placed 10th worldwide.
Q:. Which nation scored the highest on the 2020 Global Cybersecurity Index?
A: With a score of 100, the United States of America placed first in the GCI 2020.
Q: How did India get listed among the top 10 nations in the Global Cybersecurity Index?[GCI]?
A: India is a rising IT behemoth in Asia and has made a name for itself online. By taking strong measures to defend online citizens' rights and data privacy, it demonstrates its digital sovereignty. Additionally, Indian startups increased from $740 million in 2019, which helped India move up to the tenth spot on the Global Cybersecurity Index [GCI] list.
Q: Why is the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) essential?
A: The Global Cybersecurity Index enables nations to determine where action has been taken, what action may be insufficient, and grasp the landscape of accomplishments, complementing other cybersecurity initiatives. Measures on the number of cyberattacks or vulnerabilities do not always represent the efforts made by nations, businesses, or people to safeguard their cybersecurity since cybersecurity is a multifaceted and international concern. The Worldwide Cybersecurity Index aids in assessing the global efforts made by nations to guarantee a safe cyber environment for everyone.
Q: How was the evaluation carried out?
A: Five parameters were used in the evaluation. They are:
- Legal measures
- Technical measures
- Organizational measures
- Capacity Development
- Cooperation
An overall score is then derived from the performance.
Q: How is India coping with cybersecurity risks?
A:
- India is developing its initial cyber security plan.
- Computer Emergency Response Teams (CERT) are in charge of organizing and assisting national or government-level responses to computer security events or crises.
- A reporting website for cybercrime has been established so that anyone may file complaints about sexually explicit materials, child pornography, or anything depicting child sexual abuse or rape.
- A program for the development of an Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) has been put in place to deal with cybercrime concerns in the country in a comprehensive and coordinated way.
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Center (NCIIPC) was created to safeguard the nation's critical information infrastructure.
Conclusion
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) introduced the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) in 2015 to gauge the dedication of 193 ITU Member States and the Condition of Palestine1 to cybersecurity, highlight areas for improvement, and inspire nations to take action by increasing awareness of the state of cybersecurity globally.
- The GCI has evolved to reflect the changing threats, goals, and resources associated with cybersecurity to provide a more realistic picture of the security measures implemented by various nations.
- This research seeks to better understand nations' commitments to cybersecurity, highlight gaps, promote the adoption of best practices, and offer insightful information that nations can utilize to strengthen their cybersecurity postures.
- The GCI results demonstrate the overall development and progress of all five cybersecurity agenda elements, while regional disparities in cyber capacity continue to exist.
