Healthcare Analytics in Big Data
Overview
Healthcare analytics in big data entails analyzing enormous volumes of healthcare data obtained from diverse sources using various tools and approaches. The goal is to get useful insights and trends from this data to improve patient outcomes, lower healthcare costs, and optimize resource allocation. Big data frameworks like Spark, data link, PySpark and PyFlink can help analyze huge, complicated healthcare datasets. The application of healthcare analytics in big data has the potential to transform the healthcare business, resulting in better patient outcomes and enhanced healthcare delivery.
What are we building?
The healthcare analysis application can be created with SQL and numerous big data frameworks such as Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet to provide insights into various areas of healthcare data. The application enables healthcare practitioners, academics, and policymakers to swiftly and efficiently evaluate massive amounts of data, delivering useful insights that can aid in illness diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Overall, the healthcare analysis application developed with SQL and many big data frameworks is a strong tool capable of providing useful insights into healthcare data. As a result, this can help healthcare practitioners, researchers, and policymakers make more informed decisions, resulting in better patient outcomes.
Prerequisites
Several prerequisites must be met for the healthcare analytic application designed with SQL and numerous big data frameworks such as Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet to be effective. These prerequisites include a variety of libraries, big data frameworks, and software tools that allow the application to efficiently collect, process, and analyze enormous amounts of healthcare data.
- Apache Spark: Apache Spark is a robust open-source big data processing framework that can handle massive amounts of data. It can handle big datasets in real-time and process data in parallel across numerous nodes. Spark is used by the healthcare analysis application to process massive amounts of healthcare data fast and efficiently.

- PySpark: PySpark is the Python API for Spark, which enables developers to create Spark applications in Python. It provides Python developers with a straightforward interface for interacting with Spark and running Spark jobs. PySpark is used in healthcare analysis applications for data manipulation, transformation, and analysis.

- Data Link: Data Link is a big data management platform that allows data scientists to store and handle enormous datasets efficiently. It provides a simple and efficient method for storing and managing data from many data sources. For example, the healthcare analysis program uses the data link to store and manage vast healthcare data.
- PyFlink: PyFlink is a Python API for Apache Flink, a real-time data processing framework with low latency. It is a robust stream processing framework used to process real-time data streams. PyFlink is used in healthcare analysis applications for real-time data processing and analysis.
- Parquet: Apache Parquet is a columnar file format that provides optimizations to speed up queries. It is a far more efficient file format than CSV or JSON.
- SQL: SQL is the language used to manage relational databases. It provides a straightforward and fast method for managing and manipulating data in relational databases. For example, SQL is used by the healthcare analysis application to query and handle huge healthcare datasets.

- Matplotlib: A Python data visualization library. It has several features and tools for creating graphs, charts, and other data visualizations. Matplotlib is used to explain data insights and trends visually.
Overview of Healthcare Analytics
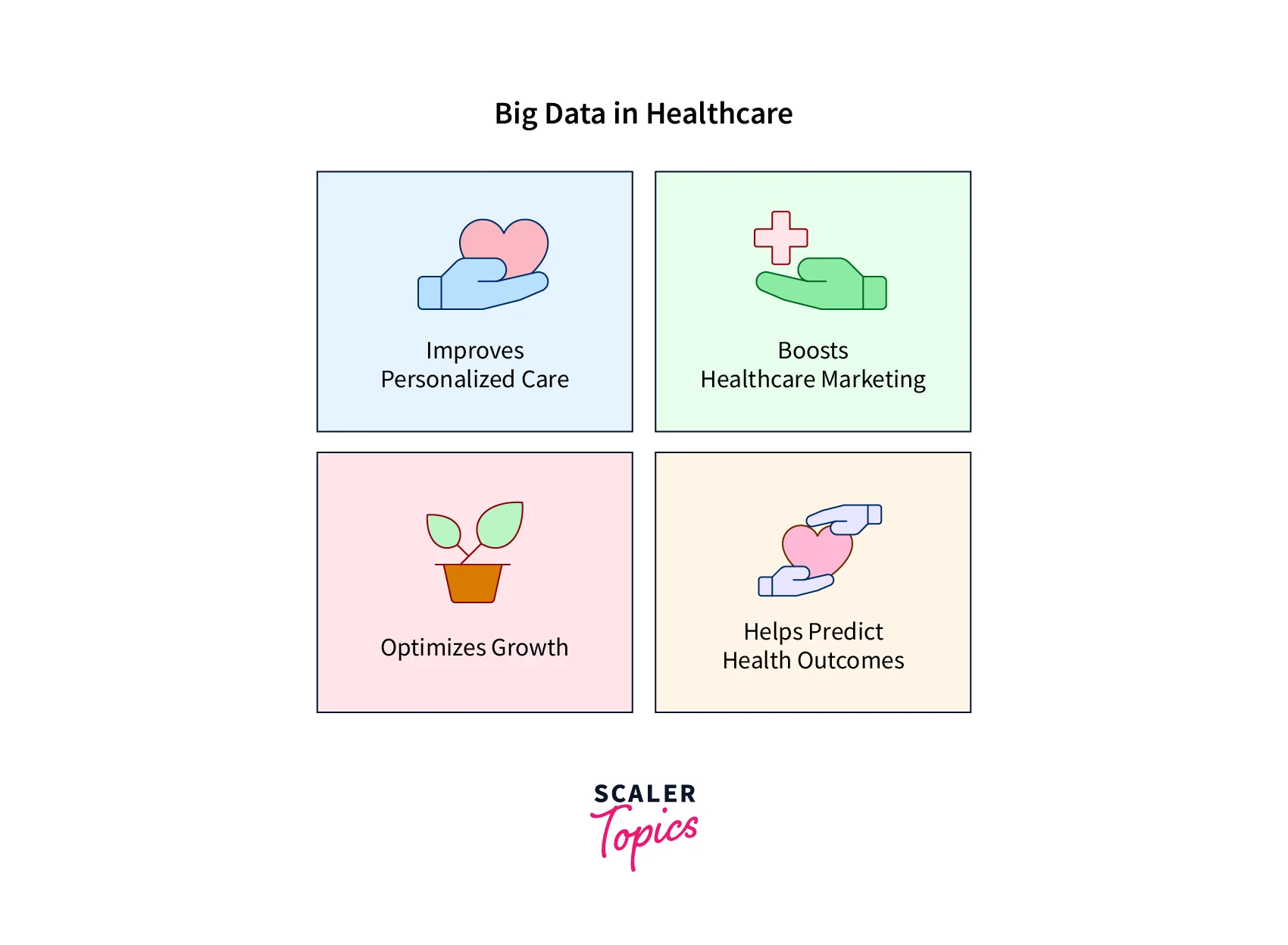
Healthcare analytics uses data and statistical tools to identify patterns and trends in healthcare data. It entails gathering, storing, processing, and analyzing data to improve patient outcomes, cut costs, and maximize resource allocation. Healthcare analytics can be applied in various settings, including clinical research, public health, and healthcare administration.
Healthcare analytics has become vital for healthcare workers as electronic health records and other healthcare data sources have become more widely available. It enables rapid and effective access to and analysis of massive amounts of healthcare data, aiding in illness diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Patient data, clinical data, financial data, and administrative data are all generated in the healthcare industry. Healthcare analytics can assist healthcare workers in making sense of this data, revealing information about patient outcomes, disease prevalence, healthcare utilization, and healthcare expenditures. It can also assist in identifying patterns and trends in data that can aid in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention.
Healthcare analytics can be classified into three types: descriptive, predictive, and prescriptive. Descriptive analytics entails evaluating historical data to determine what happened and why. The use of previous data to forecast future occurrences or outcomes is known as predictive analytics. Finally, prescriptive analytics is the application of data and statistical models to recommend the optimal course of action.
Healthcare analytics can be applied in various settings, including clinical research, public health, and healthcare administration. Healthcare analytics can help select patient cohorts for clinical trials, monitor the safety and efficacy of novel medications, and analyze treatment outcomes in clinical research. Healthcare analytics can be used in public health to monitor disease outbreaks, track vaccination rates, and identify locations with high disease burdens. Healthcare analytics can help manage healthcare by optimizing resource allocation, reducing costs, and improving patient outcomes.
Literature Review
Let us now explore existing literature on Big Data healthcare analytics, including the benefits, obstacles, and best practices for adoption. Finally, we will review case studies and successful healthcare analytics applications in Big Data initiatives.
Benefits of Healthcare Analytics in Big Data:
Healthcare Analytics offers numerous advantages to healthcare providers and institutions. Healthcare practitioners that can collect and analyze large amounts of data can acquire useful insights into patient care, find patterns, and make informed decisions. Healthcare Analytics can also assist in identifying individuals who are at risk for specific conditions, allowing healthcare providers to intervene early and avoid further issues. Furthermore, Healthcare Analytics can assist healthcare facilities in cost management by identifying inefficiencies and opportunities for development.
Challenges of Healthcare Analytics in Big Data:
While Healthcare Analytics has numerous advantages, it also has several implementation obstacles. One of the most difficult difficulties is data quality. Healthcare data can be insufficient, erroneous, or inconsistent, making analysis challenging. Another issue to consider is data security and privacy. Healthcare data is extremely sensitive and must be safeguarded against unwanted access. Finally, healthcare analytics also necessitates a lot of experience and resources, which might be difficult for smaller organizations.
Best Practices for Implementation:
Some recommended practices have been established to address the problems of integrating Healthcare Analytics with Big Data:
- It is critical to grasp the project's goals and objectives before beginning. This will aid in the collection and analysis of accurate data.
- It is critical to have the right team, including data scientists, healthcare specialists, and IT experts.
- A strong data infrastructure capable of handling the volume and complexity of healthcare data is essential.
- Effective data governance standards must be established to ensure data is used ethically and safely.
Case Studies and Successful Implementations:
There have been various successful Healthcare Analytics applications in Big Data initiatives. The University of Michigan Health System is one such example, having built a predictive analytics system to detect patients at risk of sepsis. Sepsis death rates were reduced by 53% thanks to the approach. The Veterans Health Administration, for example, created a Healthcare Analytics platform to improve patient care and cut costs. The technology identified patients at risk of hospital readmission, allowing healthcare providers to intervene and prevent readmission.
Finally, Big Data Healthcare Analytics can change patient care and enhance results. While there are certain obstacles to overcome, numerous benefits and best practices can assist in ensuring success. As a result, we should expect even more successful implementations and improved patient care as more healthcare organizations embrace Healthcare Analytics.
How are we going to build this?
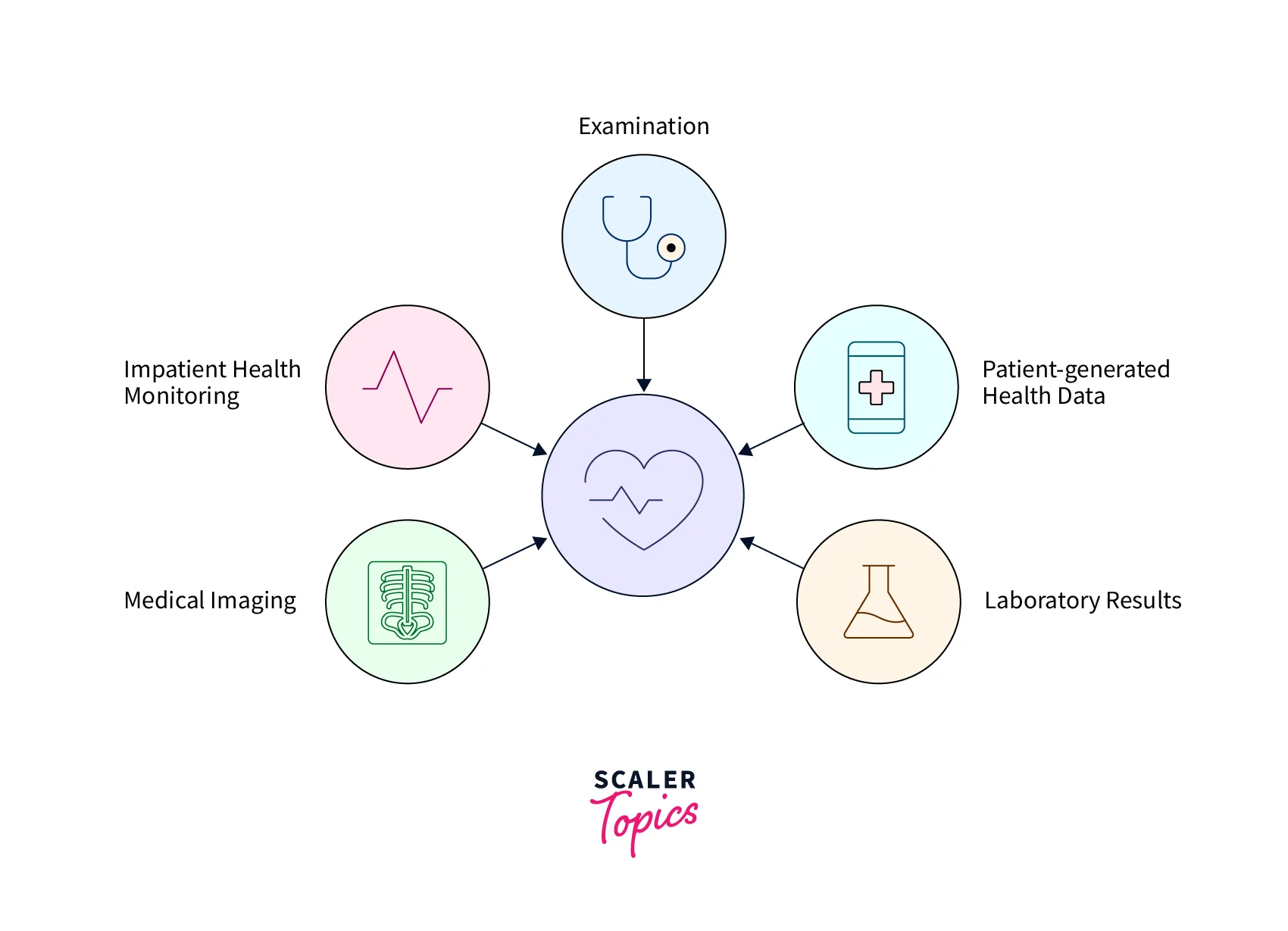
The application comprises four sections: data collection and preparation, data cleansing and transformation, healthcare analytics in big data implementation, and analysis visualization and insights. Data collection and preparation entails gathering and processing data from multiple sources, such as electronic health records, medical claims data, and patient-generated data, for analysis.
The data cleaning and transformation component entails cleaning and changing data to ensure correctness and consistency. The data is reviewed for mistakes, duplication, and missing values before being translated into an analysis-ready format.
Using healthcare analytics in big data entails processing and analyzing data using frameworks like Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet. The frameworks enable the efficient processing of massive amounts of data and include advanced analytics techniques such as machine learning and natural language processing.
The visualization and insights component of the analysis entails presenting the analyzed data in a visually appealing and understandable style. This component comprises data visualization tools like charts, graphs, and maps that assist users in spotting trends and trends in the data and gaining valuable insights.
Final Output
The final result of big `data healthcare analytics is a complete report that provides significant insights into numerous aspects of the healthcare sector. Data visualizations, statistical analyses, and predictive models are included in the study to help healthcare providers, academics, and policymakers make educated decisions.
The application's final output can assist healthcare practitioners in identifying patterns and trends in data that can aid in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. For example, depending on their medical history, lifestyle characteristics, and genetic markers, the report can identify patient cohorts at high risk of developing chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer. This data can assist healthcare providers in developing focused preventative and treatment strategies to enhance patient outcomes.
The report may also reveal information about healthcare utilization and expenses. The report, for example, can reveal areas with high healthcare consumption and expenses, such as ER visits or hospital readmissions. This data can assist healthcare systems in optimizing resource allocation, lowering costs, and improving patient outcomes.
Furthermore, big data healthcare analytics results can provide insights into illness prevalence and public health. The report, for example, can identify high disease burden areas, monitor disease outbreaks, and track vaccination rates. These data can assist public health professionals in developing targeted actions to limit disease transmission and improve overall population health.
Here's a rough diagram of the workflow and the various libraries and frameworks involved in the healthcare analysis application:
Requirements
Big data healthcare analytics entails analyzing and interpreting massive volumes of healthcare data to get insights into numerous elements of the healthcare industry, such as patient care, illness prevention, and healthcare utilization. Several critical needs must be addressed to apply healthcare analytics in big data successfully.
- Data Quality: The success of big data healthcare analytics depends on the data quality used. Ensuring the data is correct, complete, and free of errors, inconsistencies, or duplication is critical. In addition, data cleaning and validation strategies can improve data quality.
- Data Integration: Often, healthcare data is kept in several data sources, such as electronic health records, claims data, and clinical trial data. To do comprehensive healthcare analytics, data from numerous sources must be integrated to create a complete picture of the patient's health status.
- Data Security: Healthcare data contains sensitive information that must be safeguarded to protect patient privacy and meet legal standards. Strong security measures must be implemented to avoid unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security issues.
- Scalability: Healthcare data is rising exponentially, and the analytics infrastructure must be scalable to handle the growing volume of data. The analytics platform must analyze massive amounts of data quickly and efficiently to provide services.
- Analytics Frameworks: Healthcare analytics in big data requires the usage of many analytics frameworks, such as Spark, SQL, Parquet, PySpark, PyFlink, and others. These frameworks, which enable data processing, transformation, and analysis, must be integrated into the broader analytics infrastructure.
- User Interface: The final result of big data healthcare analytics is usually a thorough report that provides insights and recommendations to healthcare practitioners, researchers, and policymakers. The user interface must be friendly and intuitive, allowing stakeholders to quickly and efficiently access and analyze data.
Implementation of Big Data In Healthcare
Healthcare creates enormous amounts of data, which can provide significant insights to healthcare providers, insurance companies, and researchers. Unfortunately, data is frequently kept in multiple formats, making it difficult to access and evaluate. In this article, we will lead you through implementing healthcare analysis in big data using PySpark, Parquet, and other big data frameworks.
Data Collection and Preparation
The first stage in big data healthcare analysis is to collect and prepare the data. Data collection includes collecting information from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), claims data,clinical trials, andpatient-generated` data. To be efficiently analyzed, the acquired data must be structured. We must first identify the data needs and intended use case to prepare the data. Then, to guarantee that the data is consistent across all sources, we must identify the appropriate data fields and execute data mapping. Data cleaning and transformation are critical at this stage because they aid in eliminating errors and inconsistencies in the data.
Data Cleaning and Transformation
Data cleaning removes or corrects errors, duplications, or missing data from a dataset. This phase guarantees that the data for analysis is correct and dependable. Turning data into a format appropriate for analysis is known as transformation. Data aggregation, filtering, and standardization are all part of this process. Many large data frameworks, such as PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet, can be used to conduct data cleansing and transformation. For example, we can utilize PySpark's dropDuplicates() function to remove duplicates. Similarly, the filter() method can remove undesired data, and the fillna() function can fill in any missing data with a default value.
Implementing the Analytics in Big Data
The next step in healthcare analysis is to implement the analyses with big data frameworks such as SQL, PySpark, and Parquet. SQL is often used in healthcare analysis because it enables efficient querying and manipulation of huge databases. Because PySpark offers distributed computing, they may be used for big data processing and analysis. This makes it easier to analyze massive datasets. We may use SQL queries to extract important data and calculate averages, medians, and standard deviations to apply healthcare analytics. More complicated calculations, such as machine learning techniques and statistical models, can be performed with PySpark.
Analysis Visualization and Insights
The last stage of healthcare analysis is to visualize and convey the findings. Visualization aids in efficiently communicating information to various stakeholders. Tableau, Power BI, and D3.js are a few large data frameworks that can be used for visualization. We can use the matplotlib and seaborn packages with Python to implement analysis visualization. These libraries enable us to build bar charts, line charts, and histograms. Tableau and Power BI may also be used to create interactive dashboards that allow users to explore data and get insights.
Therefore, while healthcare analysis in big data might be complex, we can extract significant insights from healthcare data by taking an incremental approach and employing big data frameworks such as PySpark, Parquet, and SQL. As a result, healthcare providers, insurance companies, and researchers may make educated decisions and enhance patient outcomes with effective data collection and preparation, data cleaning and transformation, healthcare analytics implementation, and analytical visualization and insights.
Implementation of the Code
Here's an example of a healthcare analysis application built with big data frameworks. This implementation assumes that data has previously been gathered and is in a structured manner. (If the data is not in a structured format or has yet to be collected, we can collect and filter it in various ways, but that is not the prime concern of the current article).
This code is only an example, and it assumes the data is in CSV format. In the actual world, data may be stored in various formats, and data cleaning and transformation may be necessary to prepare the data for analysis. Furthermore, the analytics in this code are merely examples; more advanced analytics may be required depending on the use case.
Results
The healthcare business creates massive volumes of data, which can be analyzed to deliver important insights to healthcare practitioners, academics, and policymakers. The healthcare analysis application created with SQL and numerous big data frameworks such as Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet can serve the healthcare business in various ways.
The healthcare analysis software can provide information about patient outcomes, disease prevalence, healthcare utilization, and healthcare expenses. In addition, the program can assist healthcare practitioners in identifying patterns and trends in data that can aid in disease diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. For example, the program can identify people at high risk for specific diseases based on their medical history, lifestyle characteristics, and genetic markers.
The healthcare analysis application has public health, clinical research, and healthcare management applications. The tool can be used in public health to monitor disease outbreaks, track vaccination rates, and identify areas with high disease burdens. The program can be used in clinical research to identify patient cohorts for clinical trials, monitor the safety and efficacy of novel medications, and evaluate treatment outcomes. Finally, the program can be used in healthcare management to optimize resource allocation, minimize expenditures, and enhance patient outcomes.
It can be less expensive than traditional data analysis approaches such as manual data entry and analysis. The application may automate data collection, preparation, cleaning, and transformation, saving time and money. Furthermore, the program can analyze enormous amounts of data fast and efficiently, eliminating the need for costly hardware and software.
It can scale to handle massive amounts of data, making it suitable for usage in various healthcare systems. The application can run on a cluster of computers and handle data from several sources simultaneously. Furthermore, the program can process data in real-time, making it appropriate for usage in healthcare settings where quick data analysis is essential.
A healthcare analysis application built with SQL and multiple big data frameworks like Spark, data link, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet can benefit the healthcare business. The program can be used in public health, clinical research, and healthcare management to provide insights into patient outcomes, disease prevalence, healthcare utilization, and healthcare costs. Compared to traditional data analysis techniques, the application is more cost-effective. In addition, it can handle enormous volumes of data, making it suited for usage in healthcare systems of varied sizes. Effective healthcare analysis application deployment and Integration may give healthcare practitioners accurate and fast data analysis, eventually improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
Testing
Testing is essential to any software development process, and big data healthcare analysis applications are no different. This section will review the significance of testing and the many tests that can be run to assure the quality of the healthcare analysis application.
Importance of Testing: Testing is necessary to guarantee that the application functions properly and meets the users' needs. It aids in detecting faults and errors that can result in inaccurate results or even system failure. Testing also aids in improving the application's performance and dependability, which is critical in healthcare analysis where the stakes are high. Furthermore, testing ensures that the application is under industry norms and regulations.
Types of Tests:
- Unit Tests: Unit tests are used to check that specific components of an application, such as functions or modules, work properly. Unit tests are required in healthcare analytic applications to validate the accuracy of data conversions, aggregations, and calculations.
- Integration Tests: Integration tests are used to test how the application's components interact. This is critical in healthcare analysis systems that employ frameworks like Spark, PySpark, PyFlink, and Parquet to handle and analyze enormous amounts of data. Integration tests guarantee that these frameworks work in unison and that data is processed correctly.
- Performance Tests: Performance tests evaluate an application's performance under various workloads, such as processing huge amounts of data or running several queries concurrently. Performance testing is essential in healthcare analytic applications to guarantee that the program can handle the load and produce quick and accurate findings.
- Security Tests: Security tests validate the application's security features, such as authentication and authorization, to guarantee that unauthorized parties do not access or manipulate data. Security assessments are crucial in healthcare analysis programs that process and analyze sensitive patient data.
- User Acceptance Tests: User acceptability tests are used to test an application from the end user's standpoint. These tests guarantee that the application satisfies the users' needs and is simple to use. User acceptability testing in healthcare analytic applications is critical to guarantee that the program gives valuable insights to healthcare professionals and is user-friendly.
Conclusion
- Big data analytics in healthcare is a rapidly emerging field with the potential to transform healthcare delivery and patient outcomes.
- Healthcare workers can acquire important insights from huge and complicated data sets by combining big data frameworks like PySpark, PyFlink, Parquet, and SQL with advanced analytics approaches.
- The healthcare analytics application can assist healthcare workers in identifying patterns and trends in data that can aid in illness diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, optimize resource allocation, lower costs, and enhance patient outcomes.
- The app can also provide information about healthcare utilization and expenditures, disease prevalence, and public health.
- It is both affordable and scalable. The application's capacity to process massive volumes of data rapidly and efficiently can assist healthcare businesses in optimizing resource use and lowering expenses.
- The software can also be utilized in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, clinics, public health organizations, and research facilities.
