How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a game-changer, reshaping industries and how we interact with technology. It's all about making machines smart like humans. AI comes in different flavours: there's symbolic AI that follows preset rules, machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL), where machines learn from data without being told what to do, natural language processing (NLP) for human-computer talk, computer vision for understanding images, and reinforcement learning for trial-and-error decision-making. This article dives into the nuts and bolts of how does AI work, exploring its different types, real-world uses, and what's driving its progress.
What is AI?
Within the field of computer science, artificial intelligence (AI) aims to build computers that can carry out activities that normally require human intelligence. Identifying patterns, making decisions, gaining experience, and comprehending natural language are some of these duties. With artificial intelligence (AI), computers will be able to think like humans do, solve complicated puzzles, and adjust to changing circumstances without continual human supervision. AI is fundamentally the creation of models and algorithms that can interpret data, learn from it, and make judgements or predictions based on the patterns they have discovered. There are many subfields within this field, each with its own set of approaches and techniques, such as computer vision, natural language processing, machine learning, and deep learning. AI helps increase productivity, automate processes, and open up new possibilities that were previously only possible for human intellect.
The Benefits of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not just a buzzword; it's a transformative technology with numerous benefits across various sectors. It is important to understand how does AI work, but before that let’s look at the advantages AI brings:
-
Reduction of Human Error: The reduction of human error is one of AI's most important advantages. Artificial intelligence (AI) is particularly good at activities that need consistency and accuracy, like manufacturing processes, where even small mistakes can have big repercussions. Artificial intelligence (AI) improves quality control and lowers costly errors by automating repetitive operations and carrying them out with unmatched accuracy.
-
Facilitation of Research and Data Analysis: The capacity to swiftly analyse large amounts of data is essential in today's data-driven environment. Because AI systems are skilled at handling and analysing large, complicated datasets, researchers can find patterns and insights that human analysts might miss. AI-driven data analysis speeds up innovation and promotes well-informed decision-making in a variety of fields, including genomic research, medication discovery, market analysis, and consumer behaviour forecasting.

- Unbiased Decision-Making: Bias is an inherent human trait that can influence decision-making in various contexts, from hiring processes to judicial sentencing. AI, however, operates without bias, making decisions solely based on data and predefined algorithms. This impartiality ensures fair and objective outcomes, mitigating the risk of discriminatory practices and promoting inclusivity and equality in areas such as recruitment, lending, and criminal justice.

- Automation of Repetitive Tasks: Routine, mundane duties deplete human resources and reduce output. AI is excellent at automating these kinds of jobs, freeing up human labourers to concentrate on higher-value tasks that call for imagination and analytical thought. AI-powered automation improves productivity, streamlines processes, and allows businesses to deploy their resources more wisely. Applications range from data entry and invoice processing to scheduling and customer support queries.
How does AI work?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) operates through a sophisticated process that involves several intricate stages. The following is a detailed understanding of how does AI work:
-
Input: The AI system begins its operation by ingesting data from diverse sources, including sensors, databases, or user interactions. This input data can encompass a wide range of formats, such as text, images, audio, or numerical data, depending on the nature of the task at hand.
-
Processing: Once the input data is received, the AI system engages in complex processing activities. This process involves employing various algorithms and models to analyze the input data comprehensively. Depending on the specific task, the AI system may undertake tasks such as pattern recognition, classification, regression analysis, natural language understanding, or image processing. Different AI techniques, including machine learning, deep learning, reinforcement learning, and symbolic reasoning, are utilized based on the requirements of the task and the characteristics of the input data.
-
Data Outcomes: Following the processing stage, the AI system generates outcomes or outputs based on its analysis of the input data. These outcomes can range from straightforward classifications or predictions to more complex actions, decisions, or recommendations. For instance, in a predictive maintenance scenario, an AI system may forecast equipment failures based on sensor data, while in an autonomous vehicle application, it may decide on steering and acceleration actions based on environmental inputs.
-
Adjustments: AI systems are designed to continuously learn and adapt based on feedback and new data. This adaptive capability, known as learning or training, allows the AI system to refine its algorithms and models over time, improving its performance and accuracy. During the adjustment phase, the AI system may incorporate new data into its training datasets, fine-tune its algorithms, or update its models to reflect evolving conditions or requirements. This iterative learning process enables AI systems to enhance their capabilities and effectiveness across various tasks and domains.
-
Assessments: As part of its operation, the AI system assesses its own performance to evaluate the accuracy and efficacy of its outputs. This assessment involves comparing the system's predictions, decisions, or recommendations to known outcomes or ground truth data. Additionally, the AI system may gather feedback from users or domain experts to refine its performance further and address any discrepancies or areas for improvement. By engaging in continuous self-assessment, AI systems strive to enhance their reliability, robustness, and overall effectiveness in fulfilling their intended objectives.
The Four Concepts of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) comprises a spectrum of capabilities and approaches, each representing a different level of sophistication in emulating human intelligence. These concepts, ranging from basic reactive machines to the aspirational goal of self-awareness, provide a framework for understanding the evolution and potential of AI systems. Let's dive into each concept in detail to understand how does AI work:
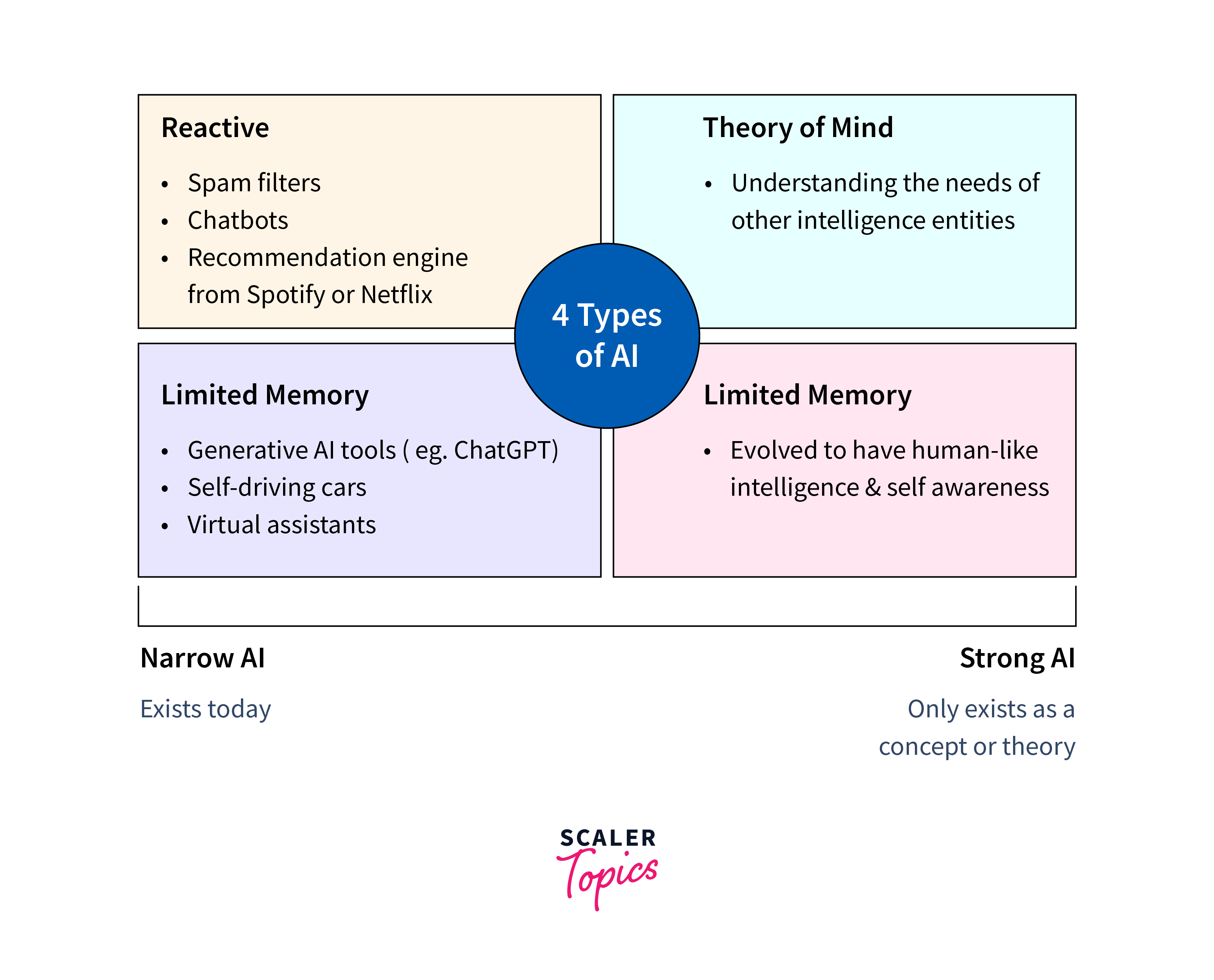
Reactive Machine
Reactive machines represent the foundational level of AI, focusing on immediate interactions with the environment based solely on the current input. These systems lack memory or the ability to learn from past experiences, operating solely based on predefined rules or algorithms. For example, chess-playing programs that evaluate board positions and select optimal moves without considering previous games or strategies are classic examples of reactive machines. While reactive machines excel in specific tasks with well-defined rules and limited variability, they lack the adaptability and flexibility to handle complex real-world scenarios.
Limited Memory
Moving beyond reactive machines, AI systems with limited memory possess the capability to retain and utilize past experiences to inform their decisions. Unlike reactive machines, which operate solely based on current input, systems with limited memory can incorporate historical data or observations to enhance their performance. Limited memory enables AI systems to exhibit adaptive behaviours and respond more effectively to dynamic environments, albeit within the constraints of their predefined algorithms and memory capacity.
Theory of Mind
Theory of mind, which aims to give machines an awareness of human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and perspectives, is a major advancement in AI capabilities. Although humans are naturally able to infer the mental states of others and predict their behaviours from those inferred mental states, artificial intelligence (AI) still faces significant challenges in simulating this cognitive skill. AI systems endowed with theory of mind would be able to perceive and react to human emotions, communicate with others in an empathic manner, and anticipate people's wants and preferences. This idea has significant ramifications for applications like social robots, virtual assistants, and healthcare companions, where human-machine interactions involve social and emotional dynamics in addition to task execution.
Self-Aware
At the pinnacle of AI aspirations lies the concept of self-awareness, wherein machines possess a consciousness or subjective awareness of their own existence and mental states. While the notion of self-aware AI evokes science fiction scenarios and philosophical inquiries, it represents the ultimate frontier in AI research and speculation. Self-aware AI systems would exhibit introspective abilities, reflecting on their own thoughts and experiences and potentially developing goals, desires, and motivations of their own. Achieving self-awareness in AI remains a speculative and ethically fraught endeavour, raising profound questions about the nature of consciousness, autonomy, and ethical responsibility in artificial beings.
How to Create Basic AI
Developing basic Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems involves a systematic approach that comprises several key steps. Having understood how does AI work, let's explore the creation steps in detail:
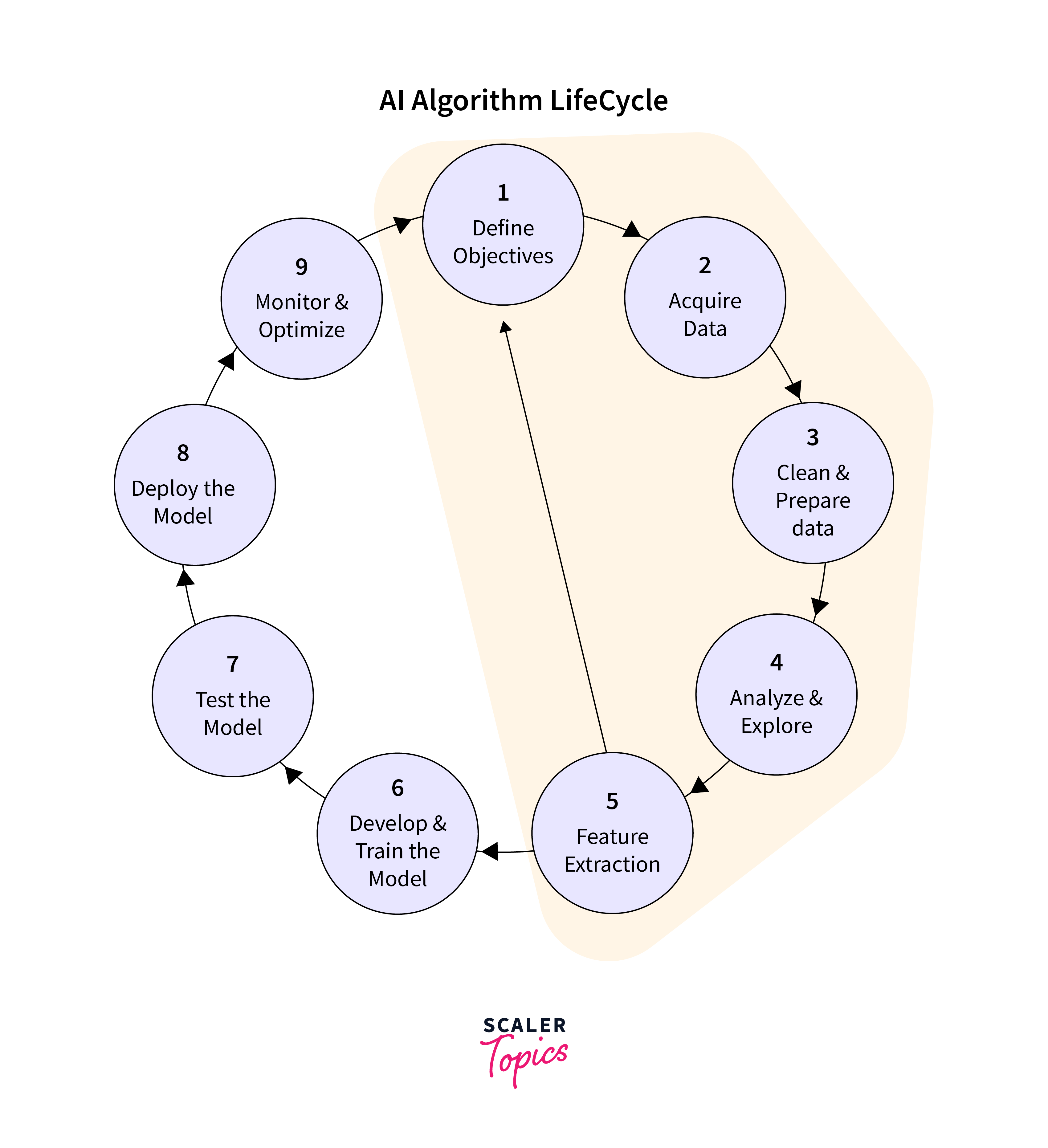
Define the Problem
Clearly defining the problem is the first step in developing any AI system. This means learning everything there is to know about the particular task or tasks that the AI system is meant to handle. Developers can efficiently identify the required inputs, outputs, and restrictions by precisely defining the problem's scope and objectives. This establishes the foundation for further development stages.
Define the Outcomes
Following the problem definition, it is essential to articulate the desired outcomes or goals the AI system aims to achieve. These outcomes serve as benchmarks for evaluating the system's performance and effectiveness. Whether it involves optimizing processes, improving decision-making accuracy, or enhancing user experiences, clearly defining measurable outcomes ensures alignment with stakeholders' expectations and guides the development process.
Organize the Dataset
Data plays a pivotal role in training AI models, making data organization a critical aspect of AI development. This step involves sourcing, collecting, and curating relevant datasets that accurately represent the problem domain. Data must be meticulously organized, ensuring it is clean, labelled, and properly formatted for training purposes. Techniques such as data preprocessing, feature engineering, and data augmentation may be employed to enhance the quality and diversity of the dataset, thereby improving the AI model's performance.
Pick the Right Technology
Selecting the appropriate technology stack and AI techniques is paramount for developing an effective AI solution. Depending on the problem's complexity and requirements, developers may leverage various AI approaches such as machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, or rule-based systems. Additionally, choosing the right programming languages, frameworks, and libraries that align with the selected AI techniques is crucial for the efficient development and deployment of the solution.
Test, Simulate, and Solve
The final step in creating a basic AI system involves rigorous testing, simulation, and validation to ensure its performance and reliability. This phase encompasses simulating real-world scenarios, evaluating the model's accuracy and robustness, and addressing any performance issues through iterative refinement and optimization. Techniques such as cross-validation, split testing, and stress testing are employed to validate the AI system's effectiveness under diverse conditions, ensuring it delivers consistent and reliable results.
By meticulously following these steps—defining the problem, determining outcomes, organizing the dataset, selecting technology, and testing the solution—developers can create basic AI systems that effectively address specific problems and deliver desired outcomes. Continuous monitoring, refinement, and adaptation are essential to ensure the AI system remains relevant and responsive to evolving needs and challenges, thereby maximizing its value and impact.
AI Use Cases for Marketers
The marketing industry is undergoing a change thanks to artificial intelligence (AI), which is providing creative ways to boost productivity, customise customer experiences, and spur company expansion. Let's examine a few important AI application cases that are changing the game for marketers:
Sales Forecasting
Predicting sales trends and demand patterns with accuracy is one of the biggest problems facing marketers. With the use of sophisticated algorithms, AI-powered sales forecasting evaluates past sales information, industry trends, and outside variables to produce precise projections of future sales volumes. Marketers may take advantage of new opportunities and reduce risks by using AI models to make data-driven choices, optimise inventory management, and allocate resources efficiently.
Personalized Marketing Campaigns
Personalization is key to engaging today's consumers and fostering long-term relationships. AI enables marketers to deliver hyper-personalized marketing campaigns tailored to individual preferences, behaviours, and demographics. Marketers may segment audiences and send tailored messages across numerous channels by using machine learning algorithms to analyse massive volumes of client data, such as browsing history, purchase trends, and social media interactions. Personalised marketing initiatives increase client happiness and brand loyalty in addition to increasing engagement and conversion rates.
Predictive Customer Analytics
Creating marketing tactics that are effective requires a thorough understanding of consumer behaviour and preferences. By analysing customer data and finding patterns, trends, and correlations that offer important insights into future customer behaviour, predictive customer analytics makes use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Marketers may maximise client acquisition, retention, and lifetime value by using predictive analytics models to discover high-value categories, predict customer demands, and customise marketing campaigns.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
In today's digital age, consumers expect immediate responses and seamless interactions with brands. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants enable marketers to deliver real-time customer support, answer queries, and assist with purchasing decisions across various touchpoints, including websites, social media platforms, and messaging apps. Chatbots can enhance customer experience and drive engagement by using machine learning algorithms and natural language processing (NLP) to interpret and reply to consumer requests, offer personalised recommendations, and enable transactions.
Content Optimization and Recommendations
Creating relevant and engaging content is essential for capturing audience attention and driving engagement. AI-driven content optimization and recommendation systems analyze user behaviour, preferences, and engagement metrics to deliver personalized content recommendations tailored to individual interests and preferences. By leveraging AI algorithms, marketers can optimize content strategies, identify popular topics, and deliver relevant content across channels to drive traffic, engagement, and conversions.
Marketing Attribution and ROI Analysis
Measuring the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and attributing conversions to specific touchpoints is critical for optimizing marketing spend and maximizing ROI. AI-powered marketing attribution models leverage advanced algorithms to analyze customer journeys, track interactions across multiple channels, and attribute conversions to various marketing efforts. By gaining insights into the most effective channels, campaigns, and touchpoints, marketers can allocate resources strategically, optimize campaign performance, and maximize ROI.
Automated Email Marketing
Email marketing remains a powerful tool for engaging customers and driving conversions. AI-powered email marketing platforms utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze customer data, predict engagement patterns, and personalize email content and timing for maximum impact. By automating email campaigns and personalizing content based on individual preferences, behaviours, and interactions, marketers can enhance open rates, click-through rates, and conversions, driving revenue and fostering customer loyalty.
Targeted Advertisements and Content Personalization
In today's digital landscape, targeted advertisements and personalized content are key strategies for marketers to engage with their audience effectively. Leveraging advanced technologies and data analytics, marketers can tailor their advertising efforts and content to individual preferences, behaviours, and demographics. Let's explore two crucial components of targeted advertisements and content personalization:
Lead Generation
One of the most important parts of marketing is lead generation, which is finding and pursuing prospective clients who have shown interest in a good or service. Data analytics and predictive modelling are used by AI-powered lead generation strategies to identify prospects who have the highest likelihood of becoming paying clients. Marketers may find high-quality leads by analysing consumer data, online behaviours, and interaction patterns. Then, they can customise their marketing strategies to nurture these leads through focused communication and personalised content, which will ultimately increase revenue and lead to conversions.
Dynamic Pricing
Dynamic pricing is a pricing approach that includes real-time price adjustments for goods and services based on a variety of variables, including supply and demand, rival pricing, and consumer behaviour. In order to maximise income and optimise pricing decisions, AI-driven dynamic pricing algorithms examine enormous volumes of data, including market trends, competition pricing, and previous sales data. Marketers may maximise profitability and competitiveness in the marketplace by utilising machine learning and predictive analytics to develop dynamic pricing plans that take into account evolving market conditions, customer preferences, and business objectives.
Enhance your business with AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing businesses across industries, offering transformative solutions to enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and drive growth. Let's explore how AI can enhance various aspects of your business:
Data Analysis and Insights
Data is a valuable asset for businesses, providing insights that drive strategic decision-making and business growth. AI-powered data analysis tools utilize advanced algorithms to analyze vast amounts of data, uncover patterns, trends, and correlations, and extract actionable insights. By leveraging AI-driven data analysis, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of customer behaviour, market dynamics, and operational performance, enabling them to make informed decisions and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
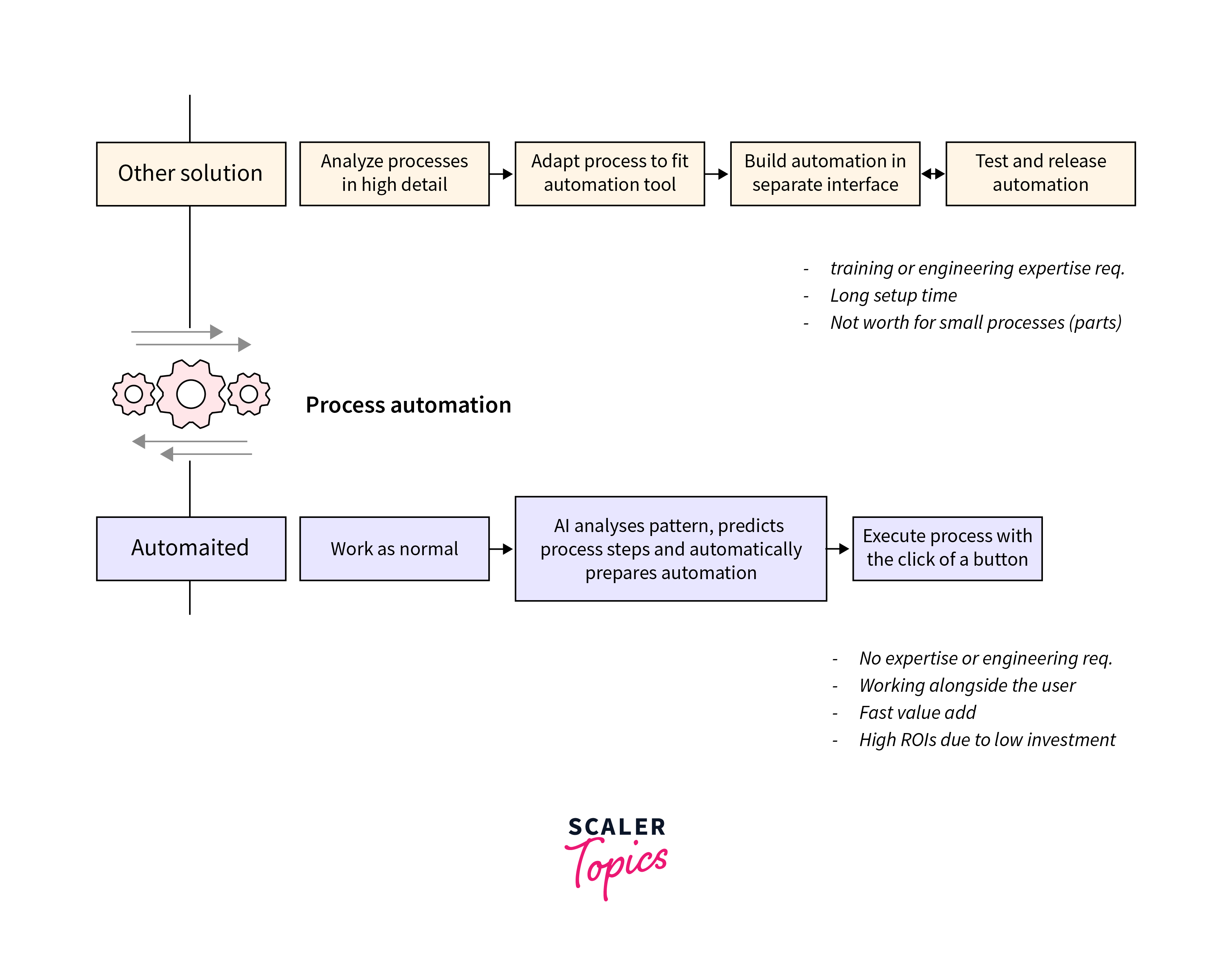
Process Automation
Streamlining repetitive and time-consuming tasks is essential for improving operational efficiency and productivity. AI-powered process automation solutions utilize machine learning and robotic process automation (RPA) to automate manual tasks, workflows, and business processes. By automating routine tasks such as data entry, document processing, and customer inquiries, businesses can reduce human error, lower operational costs, and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities that drive innovation and business growth.
Customer Engagement and Personalization
Delivering personalized experiences is crucial for building strong customer relationships and driving loyalty. AI-powered customer engagement solutions leverage data analytics, machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to deliver personalized interactions across various touchpoints. By analyzing customer data and preferences, businesses can tailor marketing messages, product recommendations, and customer support interactions to individual needs, driving engagement, satisfaction, and loyalty.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
Anticipating future trends and outcomes is essential for making proactive business decisions and staying ahead of the competition. AI-powered predictive analytics solutions utilize advanced algorithms to analyze historical data, identify patterns, and forecast future trends and outcomes. By leveraging predictive analytics, businesses can anticipate customer behaviour, demand patterns, and market trends, enabling them to make data-driven decisions, optimize resources, and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Supply Chain Optimization
Reducing expenses, preserving customer satisfaction, and guaranteeing on-time delivery all depend on effective supply chain management. Supply chain optimisation solutions driven by artificial intelligence (AI) leverage data analytics and machine learning to optimise several areas of the supply chain, such as demand forecasting, inventory control, and logistics scheduling. Businesses may cut lead times, minimise stockouts, and boost overall supply chain efficiency by utilising AI-driven supply chain optimisation. This will eventually increase customer satisfaction and spur corporate growth.
Fraud Detection and Security
Ensuring the safety of corporate operations and customer data necessitates taking proactive measures against fraud and cybersecurity risks. Machine learning algorithms are used by AI-powered fraud detection and security systems to instantly identify possible security risks and strange trends. Businesses may proactively identify and mitigate security risks, preserve sensitive data, and ensure regulatory compliance by utilising AI-driven fraud detection and security solutions. This approach protects business assets and upholds consumer trust.
Conclusion
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents unparalleled opportunities for businesses to enhance efficiency, drive growth, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
- By leveraging AI technologies and strategies, businesses can streamline operations, gain valuable insights from data, automate processes, and personalize customer interactions.
- Artificial Intelligence is transforming how businesses operate and compete in today's dynamic marketplace. Applications of AI range from data analysis and process automation to customer interaction and supply chain optimisation.
- Businesses can stay ahead of the curve, make wise decisions, and achieve new heights of success in an increasingly digital and data-driven world by embracing AI-driven solutions.
