R Installation
Overview
R is a powerful, open-source programming language and environment renowned for statistical computing and graphics. Installing R is the first step towards harnessing its robust data analysis, visualization, and statistical modeling capabilities. The installation process is straightforward across various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This article will guide users through the steps necessary to install R, offering tips for potential pitfalls and ensuring a smooth setup. By the end, users will be well-equipped to embark on their journey into the world of R, laying the groundwork for more advanced operations and packages.
Installing R on Windows OS
Installing R on Windows is a straightforward process, and the steps outlined below will ensure you have R up and running on your Windows system in no time.
1. Visit the CRAN Website:
- Start by navigating to the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) at https://cran.r-project.org/.
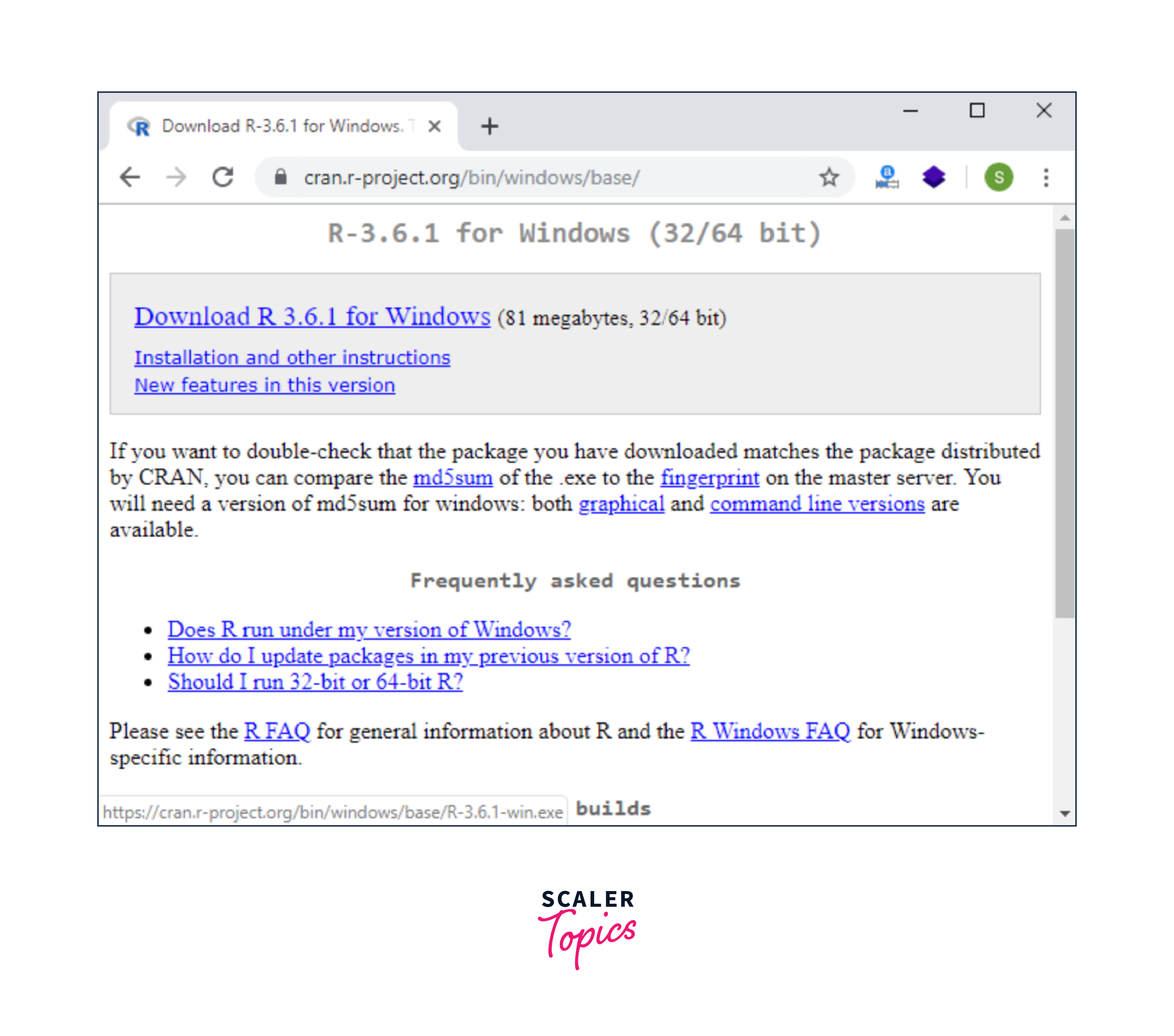
2. Choose the Right Version:
- Click on the link labeled "Download R for Windows." This will redirect you to the Windows subsection of CRAN.
- Here, select "base" to download the base distribution of R.
3. Download the Installer:
- Click the link labeled "Download R x.x.x for Windows" (where x.x.x is the latest version number). This will initiate the download of the R installer executable.
4. Install R:
- Once the download is complete, locate the downloaded .exe file (usually in the Downloads folder) and double-click it to run the installer.
- Follow the installation prompts. It's generally safe to proceed with the default settings. Choose an installation directory when prompted, or use the default directory provided.
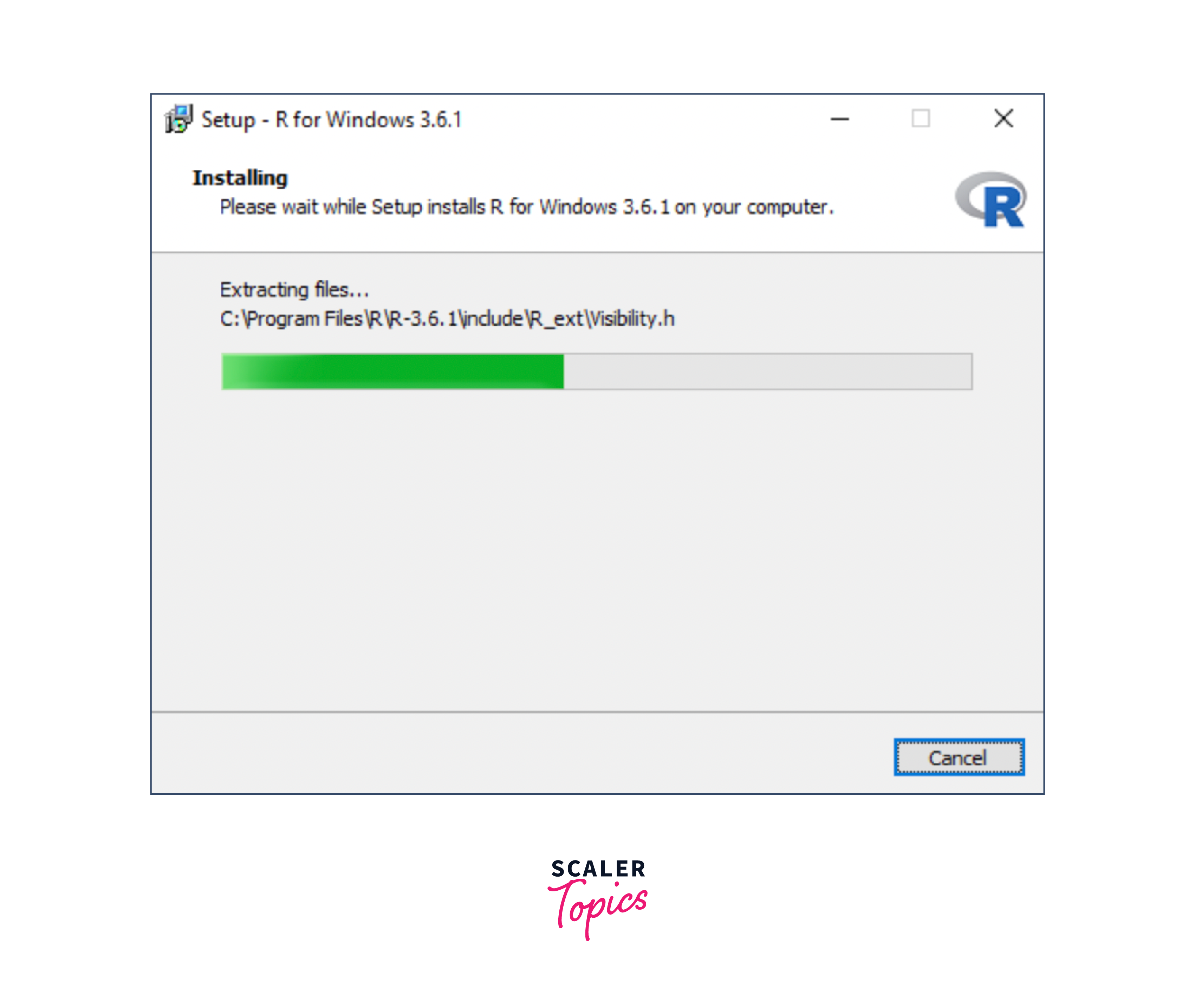
5. Complete the Installation:
- Once the installation process is completed, you can launch R by searching for it in the Windows start menu or navigating to the installation directory.
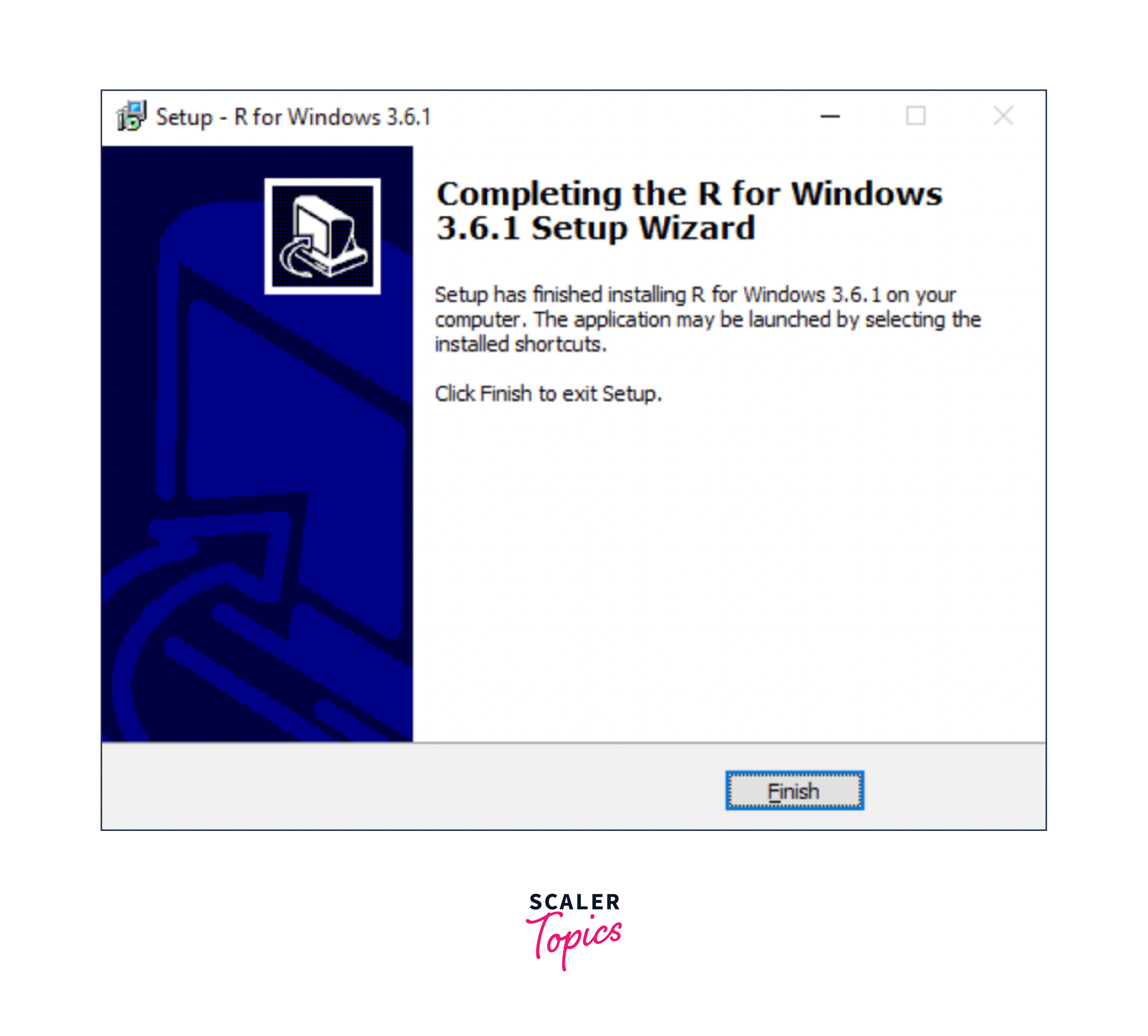
6. Optional: Install RTools (for package development):
- If you plan to develop or install R packages from source, you might also need RTools. It can be downloaded from the CRAN website under the Windows section.
Take Notice:
- Periodically check the CRAN website for updates. Regularly updating R ensures you have the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches.
- Consider using an integrated development environment (IDE) like RStudio for a more user-friendly experience with R on Windows.
These steps will give you a functioning R environment on your Windows system, ready for data analysis, visualization, and more.
Installing R on MacOS X
Installing R on MacOS X is quite intuitive, allowing Mac users to easily tap into R's extensive capabilities. Follow these systematic steps to ensure a smooth installation process:
1. Visit the CRAN Website:
- Go to the Comprehensive R Archive Network (CRAN) at https://cran.r-project.org/.
2. Select MacOS Version:
- Click on the link labeled "Download R for (Mac) OS X." This will take you to the MacOS subsection of CRAN.
3. Choose the Relevant Package:
- If you're using the latest version of MacOS, click on the link labeled "R-x.x.x.pkg" (where x.x.x is the latest version number) to download the R package for MacOS.
- For older versions of MacOS, you may need to scroll down and find the appropriate package in the "Binaries for legacy OS X systems" section.
4. Install R:
- Once the package has been downloaded, locate the .pkg file, usually in the Downloads folder, and double-click on it to start the installation process.
- Follow the on-screen prompts, agreeing to the license terms and selecting an installation location when necessary. The default settings are typically suitable for most users.
5. Verifying the Installation:
- You can find the R application in your Applications folder after installation. Launch it to ensure that it starts without any issues.
6. Optional: Installing Additional Tools:
- If you intend to develop R packages or need to compile R packages from source, you might also consider installing Xcode (available from the App Store) and the associated Command Line Tools, which provide essential utilities.
Take Notice:
- To enhance your R experience on MacOS, consider downloading and installing RStudio, a popular IDE for R. It offers a user-friendly interface, integrated plotting, and other tools.
- Keep an eye on the CRAN website for updates to R, ensuring you always have the latest features and security patches.
Following these steps, Mac users can seamlessly integrate R into their workflow, paving the way for in-depth data exploration, statistical analyses, and visualization projects.
Installing R on Linux
For Linux users, installing R is slightly more involved than Windows or MacOS, but it's still straightforward. Given the diverse range of Linux distributions, the installation procedure can vary. Here, we will focus on the installation process for some of the most popular distributions: Ubuntu/Debian and Fedora/Red Hat.
For Ubuntu/Debian:
1. Add CRAN Repository:
- Open a terminal.
- To ensure that you have the latest version of R, adding the official CRAN repository to your system is a good practice. You can do this with the following commands:
2. Add GPG Key:
- Secure APT ensures that packages are securely acquired. Add the key with the following:
3. Install R:
- Update the package list and install R:
For Fedora/Red Hat:
1. Add CRAN Repository:
- Depending on your version of Fedora, create a file /etc/yum.repos.d/cran.repo and add the repository. For Fedora 34, for example:
2. Install R:
- Install R using dnf (the successor to yum):
Post-Installation for All Distributions:
1. Verify Installation:
- In the terminal, type R and press Enter. This should launch the R console, indicating that the installation was successful.
2. Optional Tools:
- If you plan to develop or compile R packages, you might need to install additional development libraries. The specifics can vary based on the Linux distribution.
Take Notice:
- Many Linux users prefer to work with R using an IDE, like RStudio, for a more comprehensive and user-friendly experience.
- Always check for updates. Linux distributions frequently update software in their repositories, so regularly update your system to ensure you have the latest R version and features.
Following the steps tailored to your Linux distribution, you can integrate R into your Linux environment, enabling robust statistical analysis, data processing, and visualizations.
Installing R on Ubuntu
Ubuntu, a popular Debian-based Linux distribution, provides a relatively straightforward way to install and set up R. Follow these step-by-step instructions to have R running on your Ubuntu system:
1. Update System Packages:
- Before installing new software, updating existing packages is a good practice. Open a terminal and run:
2. Add CRAN Repository:
- To get the most recent version of R, it's advisable to add the official CRAN repository to your sources list. You can do this with the following commands:
3. Import CRAN GPG Key:
- This step ensures the authenticity of the packages. Add the CRAN GPG key with:
4. Install R:
- Now that your system is prepared, you can install R:
5. Confirm Installation:
- To ensure that R was installed correctly, type R in the terminal and press Enter. This action should launch the R console. You can exit by typing q() and pressing Enter.
6. Optional – Install R Development Libraries:
- If you plan to develop packages or need certain libraries, you might need the R development libraries:
Tips:
- If you plan to use R extensively, consider downloading and installing RStudio. This IDE for R provides a more interactive and user-friendly workspace.
- Periodically check for software updates. Ubuntu's repositories are regularly updated, and it's a good practice to keep your R installation current.
By adhering to this guide, Ubuntu users can seamlessly integrate R into their computing environment, setting the stage for advanced statistical analyses, data visualizations, and more.
Conclusion
The key takeaways from this article are:-
-
Ease of Installation: Irrespective of the operating system—be it Windows, MacOS, Linux, or Ubuntu—installing R is straightforward. Users can conveniently set up their statistical computing environment with just a few steps.
-
Diverse Ecosystem: The regular emphasis on adding the CRAN repository underscores R's expansive ecosystem. This repository ensures users have the most recent version of R and provides access to thousands of packages tailored for diverse analytical tasks.
-
Adaptability: R's adaptability is evident in its compatibility with multiple operating systems. Whether you're a Windows desktop user, a MacOS enthusiast, or a Linux lover, R integrates seamlessly into your preferred environment.
-
Complementary Tools: The recurrent mention of RStudio, a popular IDE for R, highlights the breadth of available tools that augment the R experience. These tools provide enhanced functionalities, aiding in tasks from simple data manipulation to complex analyses.
-
Continuous Learning: As with any powerful software, the journey doesn't end at installation. After setting up R, users are encouraged to explore, update regularly, and expand their knowledge to truly harness the capabilities of this dynamic statistical software.
