Intersection of Two Linked Lists

Implement a program to detect the intersection point of two linked lists, where one list accidentally merges with the other, forming an inverted Y-shaped structure.
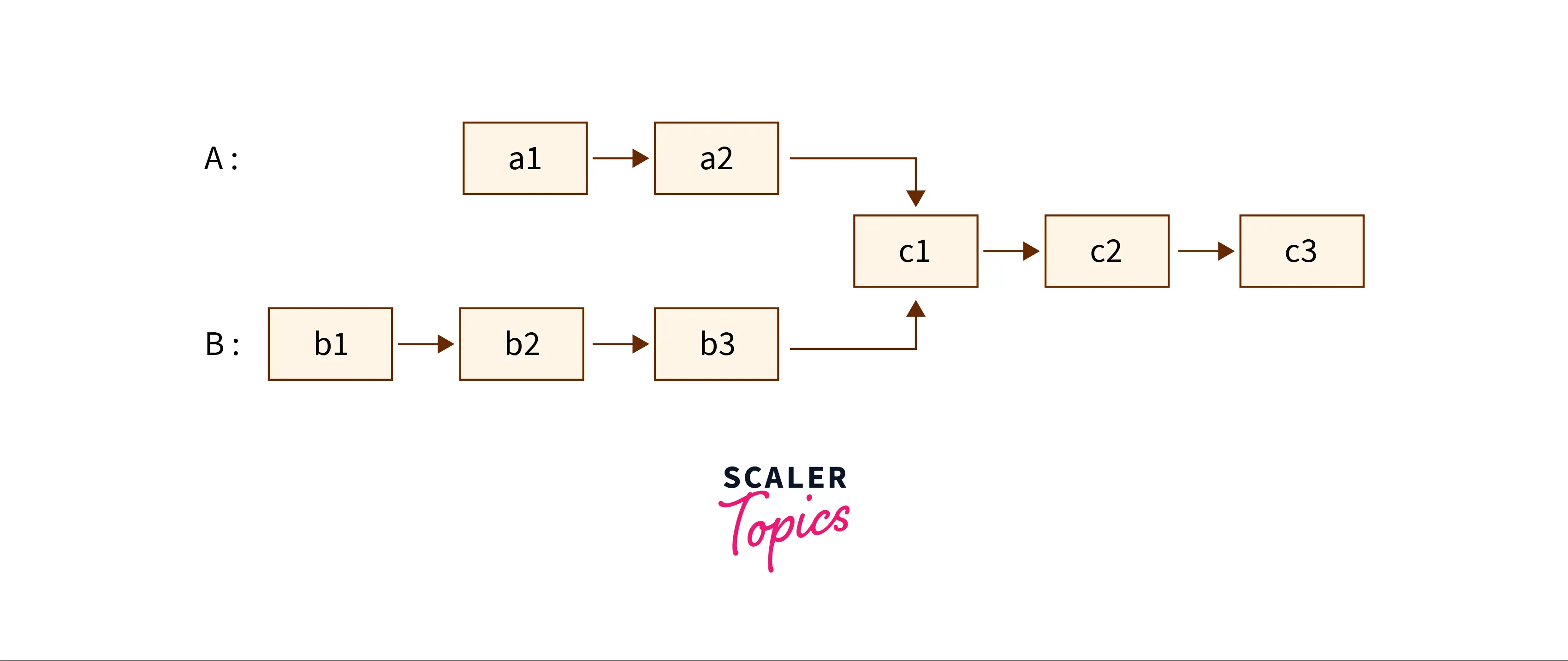
For example, the following two linked lists have common nodes starting from c1. Thus, c1 is the intersection point of two linked lists.
Approach 1: Using Two Nested Loops
Utilize two nested for loops, where the outer loop iterates over each node of the first list, and the inner loop iterates over each node of the second list. Within the inner loop, check if any nodes from the second list match the current node of the first linked list.
Code Implementation
C++ Code
Java Code
Python Code
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the algorithm is O(m * n), where m and n denotes the count of nodes in the given two linked lists.
Space Complexity
The space complexity is O(1), as we do not use any extra space.
Approach 2: Using Hashing
To find the intersection point of two linked lists, we iterate over one list and store its nodes in a hash set. Then, we traverse the other list and check if each node is in the set. If we find a common node, it's the intersection point. Otherwise, there's no intersection.
Code Implementation
Let's look at the code implementation of the above approach in C++, Python, and Java.
C++ Code
Java Code
Python Code
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the above method is O(m+n) as the linked lists get traversed once.
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the above method is O(m) as the nodes of the first linked list is get stored in the hash table.
Approach 3: Using Difference in Node Count
In this approach to find the intersection of linked lists, we use the difference in the count of nodes. Both the linked lists get traversed to find their lengths. We get the longer linked list by counting the difference in the number of nodes which is k. The longer linked list gets traversed until both the linked lists have the same number of nodes. We move through the linked lists at an equal speed until they reach the intersection point.
Steps Involved :
- Traverse both linked lists and keep a count on the number of nodes. Let the number of nodes in the first linked list be c1 and the second c2.
- Check which one is larger and calculate the difference d = abs(c1 - c2) in the number of nodes of the linked lists.
- Make sure that the longer linked list is the first one. Swap the linked lists whenever required.
- Traverse the longer list till d nodes as both the linked lists will be left with an equal number of nodes.
- Traverse the linked lists simultaneously and compare the address of each node until they reach the intersection point.
- Return the common node present at the point of intersection. If there is no common node, return null.
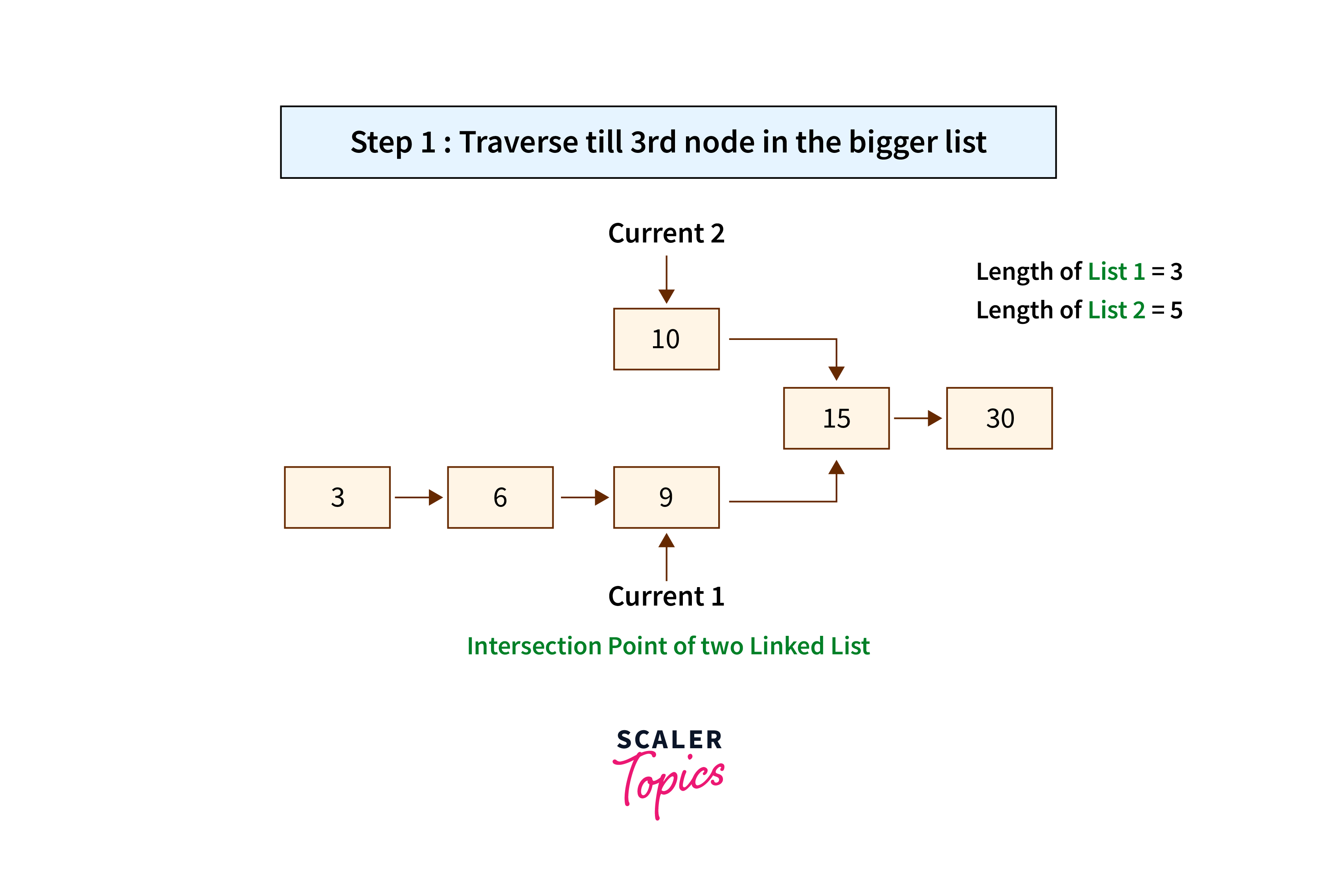
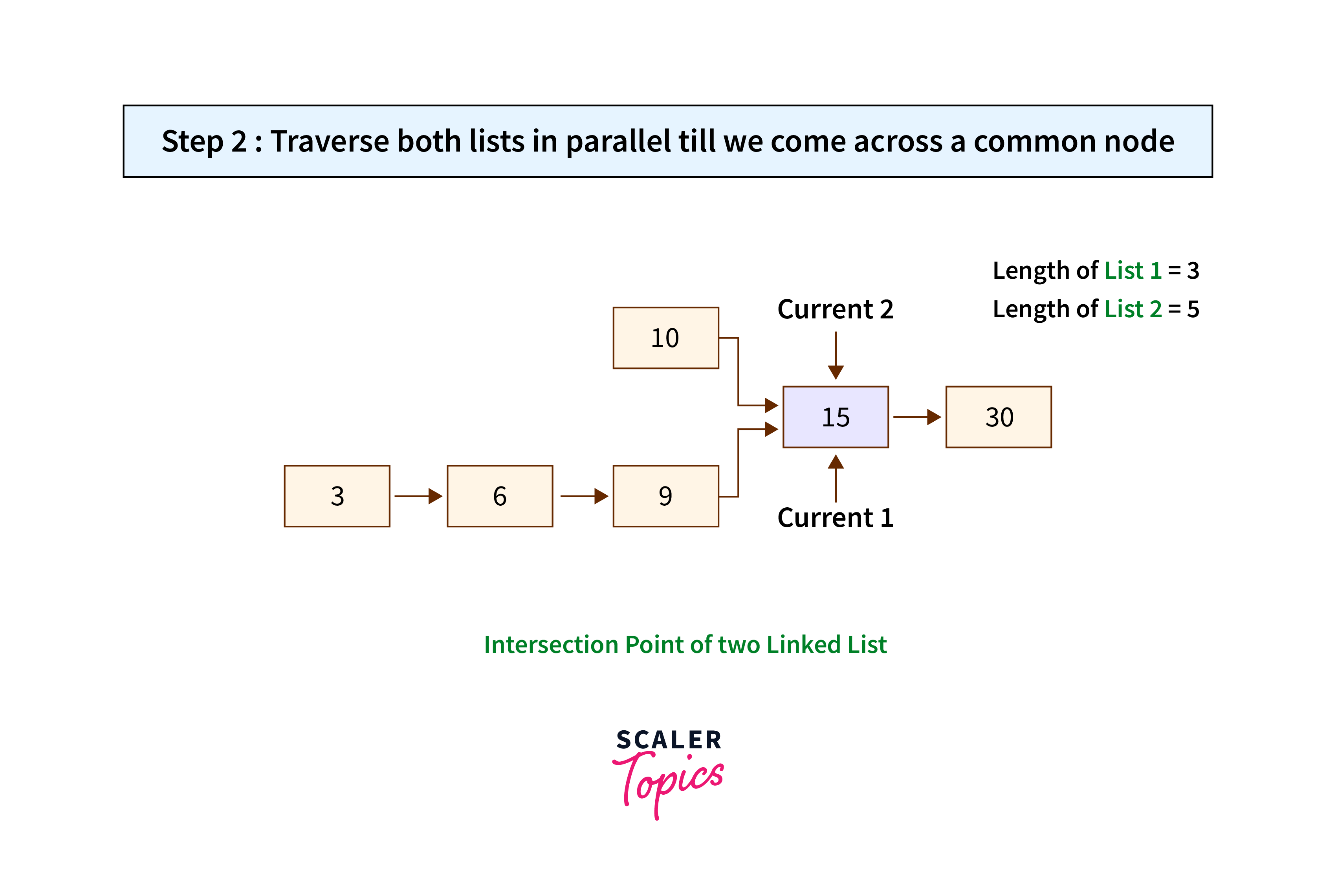
Code Implementation
C++ Code
Java Code
Python Code
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the above method is O(m+n) as both the linked lists get traversed one by one, where m is the length of the first linked list and n of the second linked list.
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the above method is O(1).
Approach 4: Using Two Pointer Technique
In this approach to find the intersection of two linked lists, we use the two-pointer technique. We take two pointers pointing to the head node of both the linked lists. Each pointer reaching the end of the linked list gets reassigned to the head of the other linked list. It makes the two pointers at a distance equal to the intersection point. When both pointers reach a common node and are not null, it is said to be the intersection point.
Steps Involved
- Initialize two pointers - head1 pointing to the head of the first linked list and head2 pointing to the head of the second linked list.
- Advance through both the linked lists until it reaches the end.
- When head1 points to the end of the first linked list, it gets assigned to the head of the second linked list.
- When head2 points to the end of the second linked list, it gets assigned to the head of the first linked list.
- When both pointers point to a common node and are not null, we get the intersection point of the linked lists and return it.
Code Implementation
C++ Code
Java Code
Python Code
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity to find the intersection point of two linked lists using the two-pointer technique is O(m+n).
Space Complexity
The algorithm has a space complexity of O(1), indicating that it uses a constant amount of extra space regardless of the size of the input linked lists.
Approach 5: Making Loop in the First List
This approach uses Floyd’s Cycle Detection Algorithm. This approach converts the first linked list to a circular linked list by connecting the tail node to the head node. Two pointers point to the head node and the node from the head, which is the total number of nodes in the loop of the circular linked list. The pointers move at the same speed until the intersection of the two linked lists is reached.
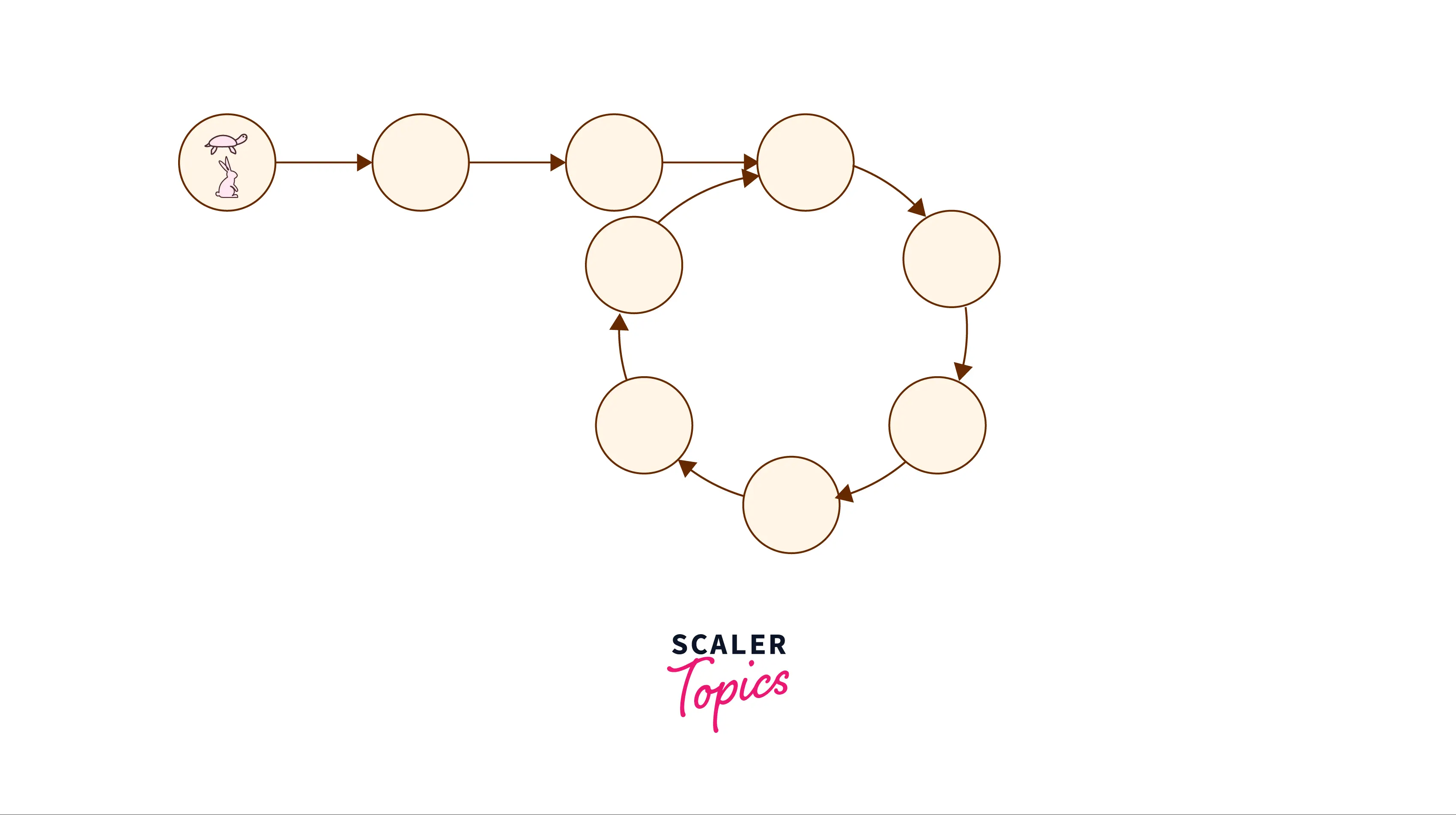
Steps Involved
- Traverse the first linked list and take a count of the nodes.
- Convert it into a circular linked list by joining the head node to the tail node.
- Since the length of the loop formed by the first linked list is already known, traverse the same number of nodes in the second linked list and keep a pointer at it.
- Set another pointer at the beginning of the second linked list.
- Move the pointers simultaneously until they reach a common node.
- Return the value of the node at the point of intersection.
- Remove the cycle from the first linked list.
Code Implementation
Let's look at the code implementation of the above approach in C++, Python, and Java.
C++ Code
Java Code
Python Code
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity
The time complexity of the above method is O(m+n) as both the lists get traversed linearly, where m and n are the counts of nodes in the first and the second linked list, respectively.
Space Complexity
The space complexity of the above method is O(1), as we do not use any extra space.
Conclusion
- This article shows that we can find the intersection point of two linked lists using the following eight methods -
- Using Two Nested Loops
- Using Hashing
- Using Difference in Node Count
- Using Two Pointer Technique
- Making Loop in the First List
- Using the two-pointer technique, we can optimize the time complexity from O(m*n) in the nested loop approach to O(m), significantly improving the efficiency of the algorithm.
- The space complexity varies from O(m) using the hashing technique to O(1) using the other techniques.
