Print Left View of Binary Tree

The left view of a binary tree corresponds to the nodes of the tree, which would be visible to someone seeing the tree from its left side, as shown in the image below -
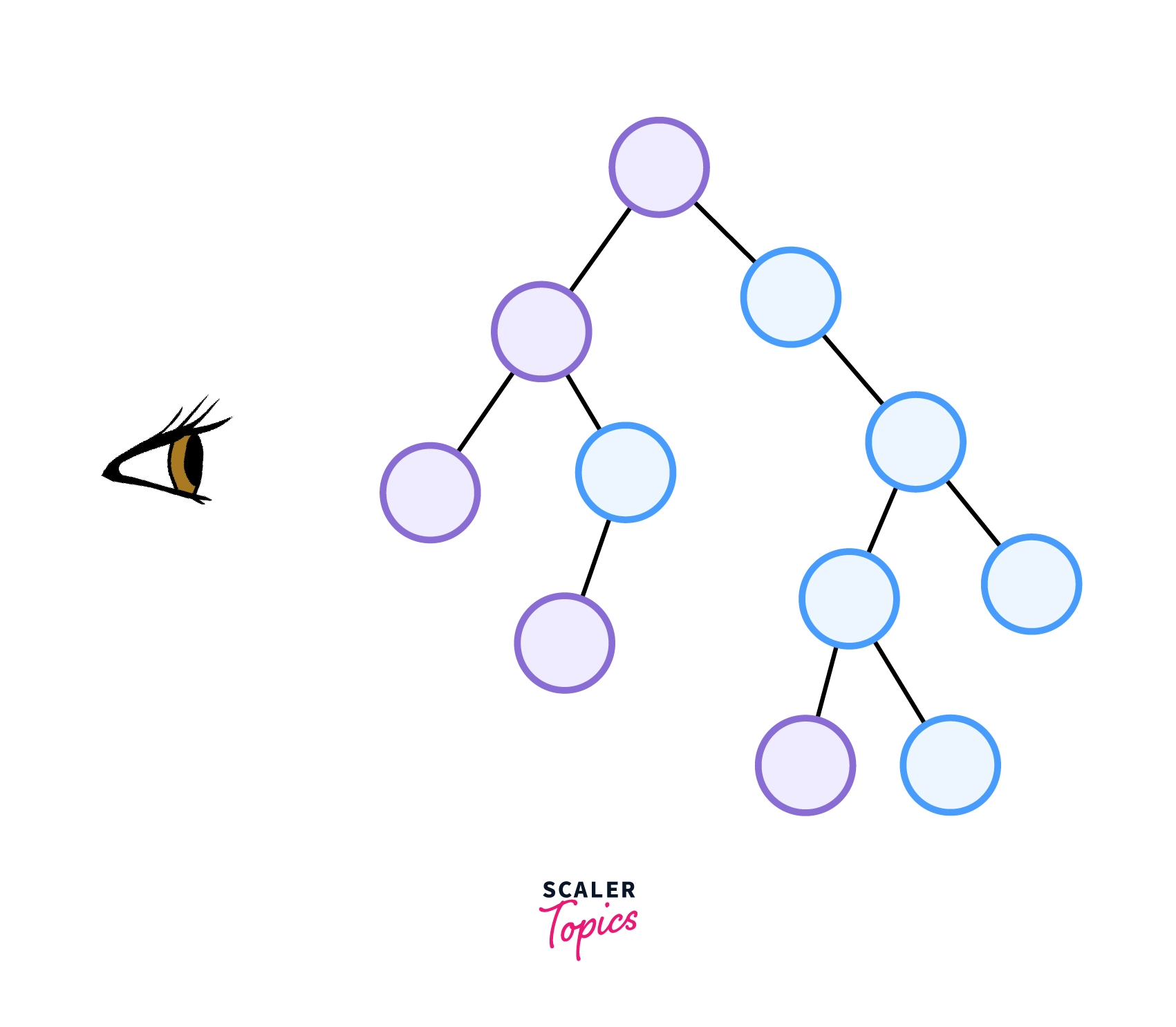
To print the left view of a binary tree, it's essential to recognize that the leftmost node at each level is visible from the left side.
Approach-1: Using Recursion
We can print a binary tree's left view using recursion.
Below is the implementation of the above approach -
The blueprint of code will be -
Variables -
- maxLevel - Global variable, which denotes the maxLevel traversed till now.
- level - Local variable, denoting the current level.
Methods -
- leftView - This wrapper function will call the leftView_Helper function passing root with the current level as 0.
- leftView_Helper - It will check whether the current level is greater than maxLevel. If yes, we will include the node in the answer and update the maxLevel. At last, we will recurse for the left subtree and then for the right subtree.
C/C++
Java
Output:
- Time Complexity - Since we are traversing all the nodes of the tree, time complexity is .
- Space Complexity - , though we don't use any array or auxiliary data structure, we must consider the recursive stack space used.
Approach-2: Using Level Order Traversal
The concept revolves around identifying and including all nodes in the left view that appear first in their respective levels. An effective strategy is to execute a level order traversal, ensuring the initial node at each level is noted.
To apply this concept, follow these steps:
- Execute a level order traversal across the tree.
- Maintain a record of the traversed level, noting the first node encountered at each level.
- Proceed to the subsequent level.
C/C++
- Java
Output:
- Time Complexity - Since we are traversing all tree nodes, the time complexity is .
- Space Complexity - Since we have used a queue data structure to store the given tree's left view, the space complexity is .
Approach -3 : Using Queue and a Null Pointer
The solution to this problem involves utilizing a queue and a null pointer to signify the beginning of each level. By placing a null pointer initially and, when encountering one, set a boolean flag to true, indicating that the subsequent element should be considered part of the left view.
Following is the execution based on the outlined strategy:
C/C++
Java
Output:
- Time Complexity - Since we are traversing all the tree nodes, the time complexity is .
- Space Complexity - , because we have used the queue, which stores the information about the nodes in the tree.
Conclusion
- In this article, we have seen what is meant by the left view of binary tree through a detailed example.
- We have discussed two recursive approaches to print the left view of binary tree. Both of them were traversing the tree in preorder fashion.
- Also, we have seen an iterative implementation using a queue data structure. In this approach, we were traversing the tree in the level order fashion.
