How to Echo a New Line in Linux?
Mastering the art of Linux echo newline commands is crucial for displaying formatted text output. This article guides various methods to echo a new line in Linux, enabling effective output formatting.
Display new Line with -e flag of echo command (recommended)
When working with the echo command in Linux, use the -e flag to display new lines. It enables the interpretation of escape sequences, making it easier to format your output. The escape sequence for a new line is the \n character. Here's how you can use it:
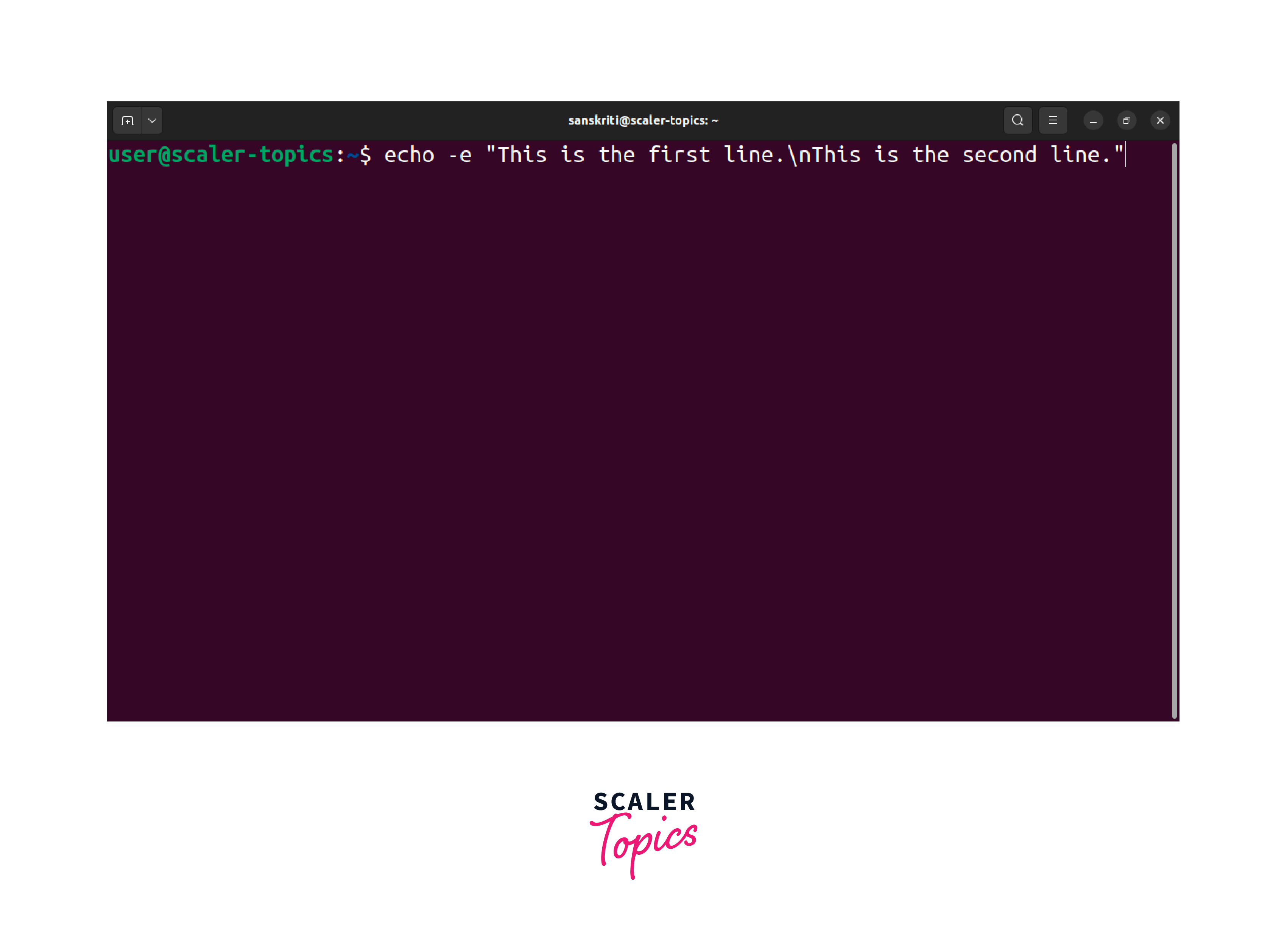
The -e flag instructs the echo command to interpret escape sequences, including the \n for a new line. When you execute the command, it will produce the following output:
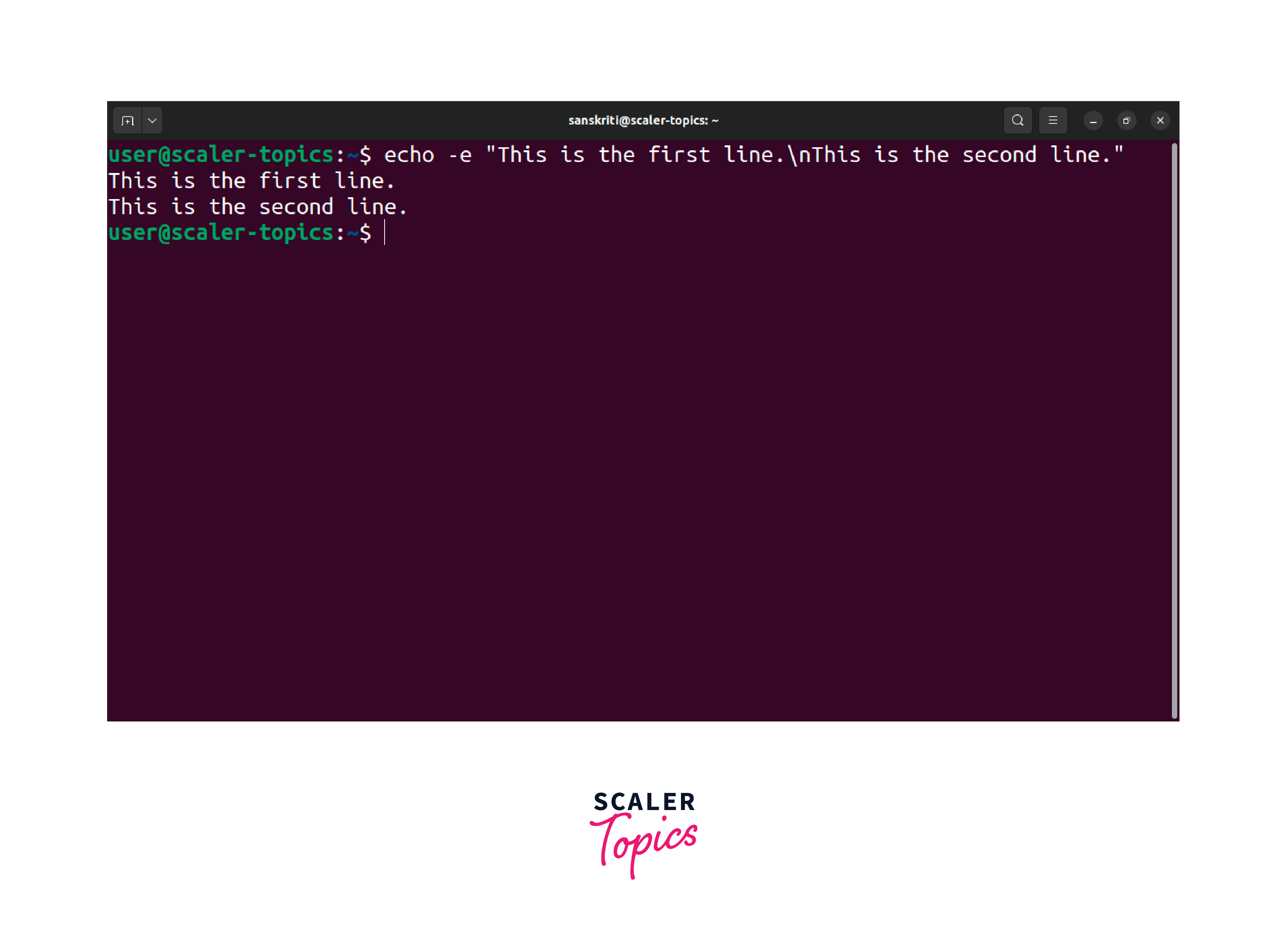
The -e flag can conveniently incorporate new lines within your text without enclosing them in quotes. This method offers a clean and readable way to echo multiple lines of text in Linux. It provides a straightforward way to format your text and improve readability.
echo a variable containing a new line
Linux provides effective ways to handle scenarios where you need to echo the contents of a variable containing newline characters. Here's how you can echo a variable with new lines:
In this example, we assign a multi-line string to the variable my_variable. By enclosing the variable within double quotes and using the -e flag with the echo command, the shell will interpret the new line character contained within the variable. As a result, executing the command will produce the following output:
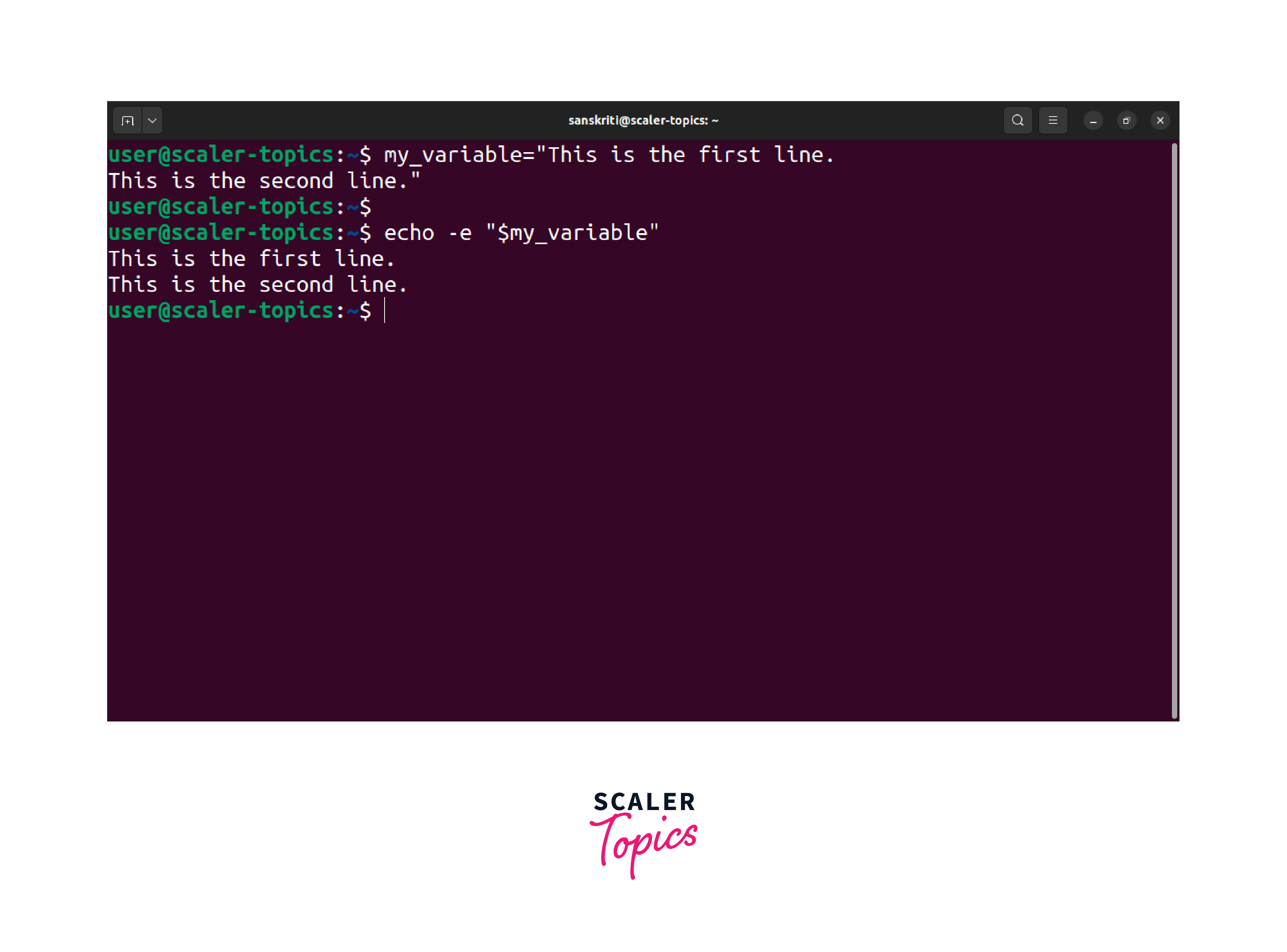
Using the -e flag and enclosing the variable in double quotes ensures proper recognition and formatting of the new line character, leading to the expected output. Without the -e flag, the echo command treats the new line character as part of the variable's literal value, resulting in undesired output.
With the knowledge of Linux echo newline techniques, you can unleash your creativity and effectively format your text output in various scripting and command-line scenarios.
Use the '$' Character Instead of the -e flag
In Linux, you can use the $ character as an alternative to the -e flag with the echo command to echo a new line. It simplifies the process and is helpful when the -e flag is unavailable or not preferred.
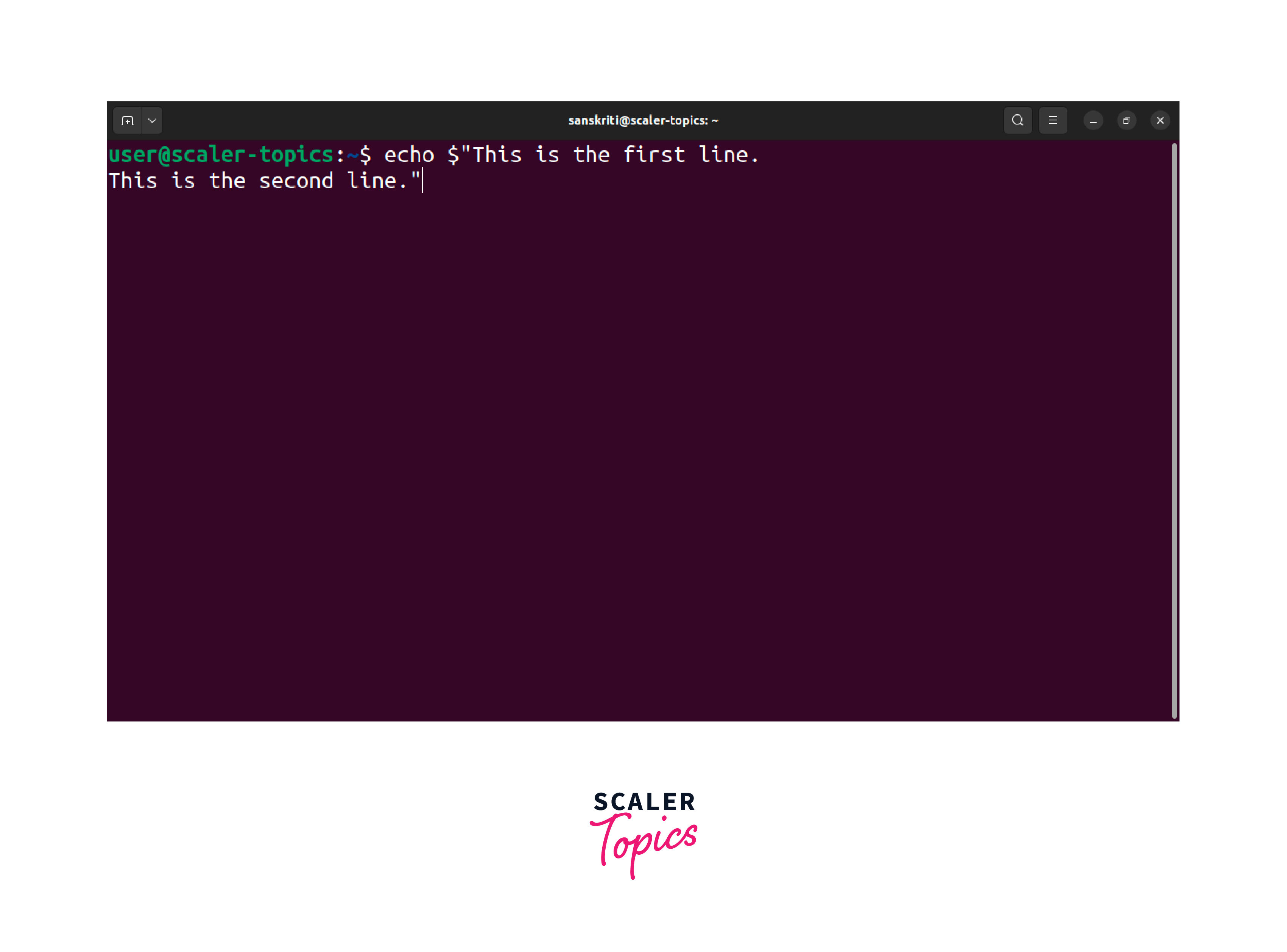
By preceding the opening double quotes with a $ character, the shell will interpret any escape sequences within the quoted string, including the \n for a new line. When executing the command, it will generate the following output
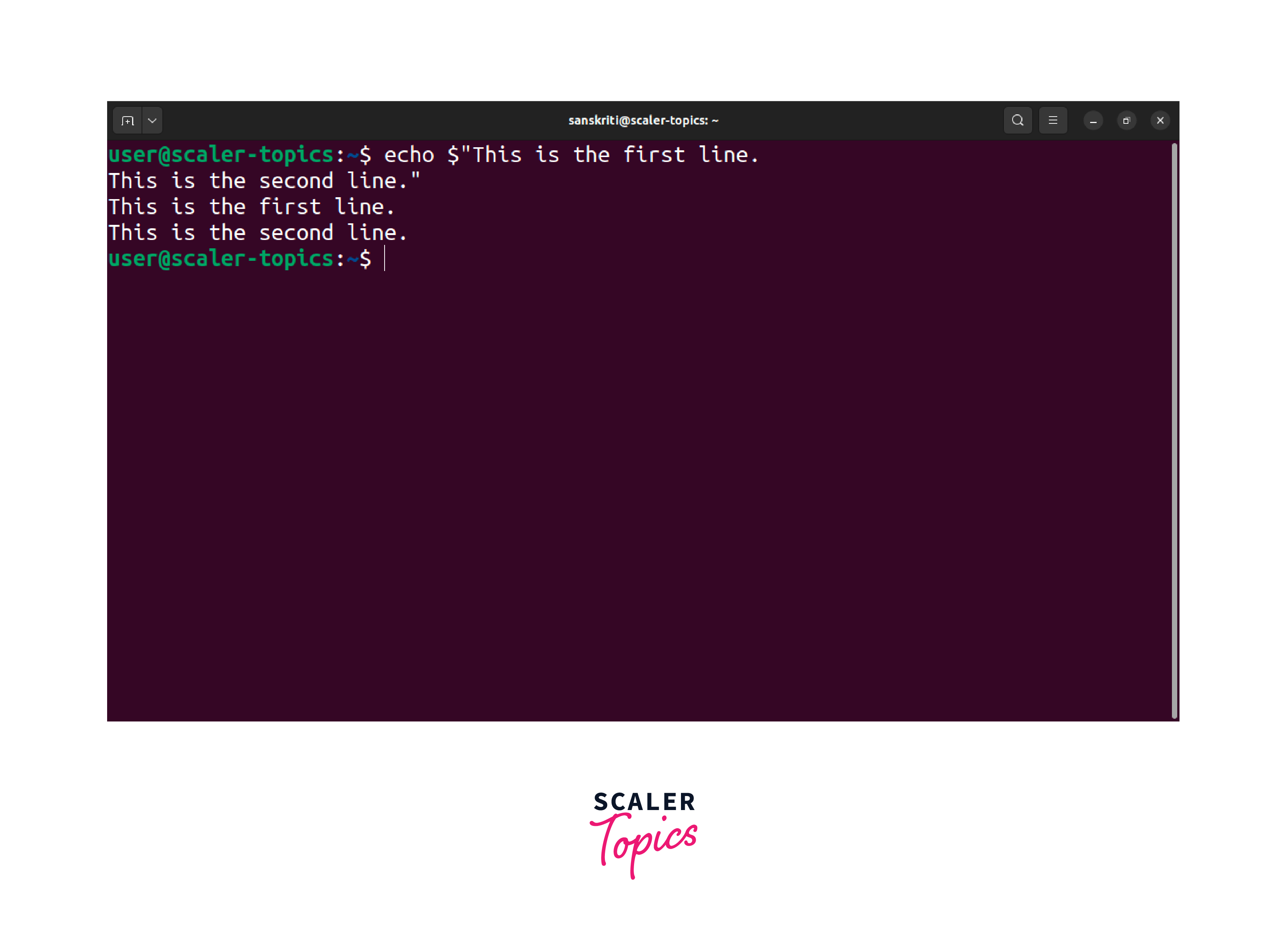
The $ character achieves the same result as the -e flag but with a different syntax. However, it lacks the flexibility of the -e flag as it only interprets escape sequences and doesn't support other formatting options.
Efficiently utilizing Linux echo newline capabilities can greatly enhance the readability of your terminal output. In the next section, we will learn another method to echo the newline.
echo your echo to Print Something with New Line
In certain situations, you may need to echo the output of an echo command to print text that includes a new line. This technique involves nesting echo commands within one another to achieve the desired output. Here's an example:
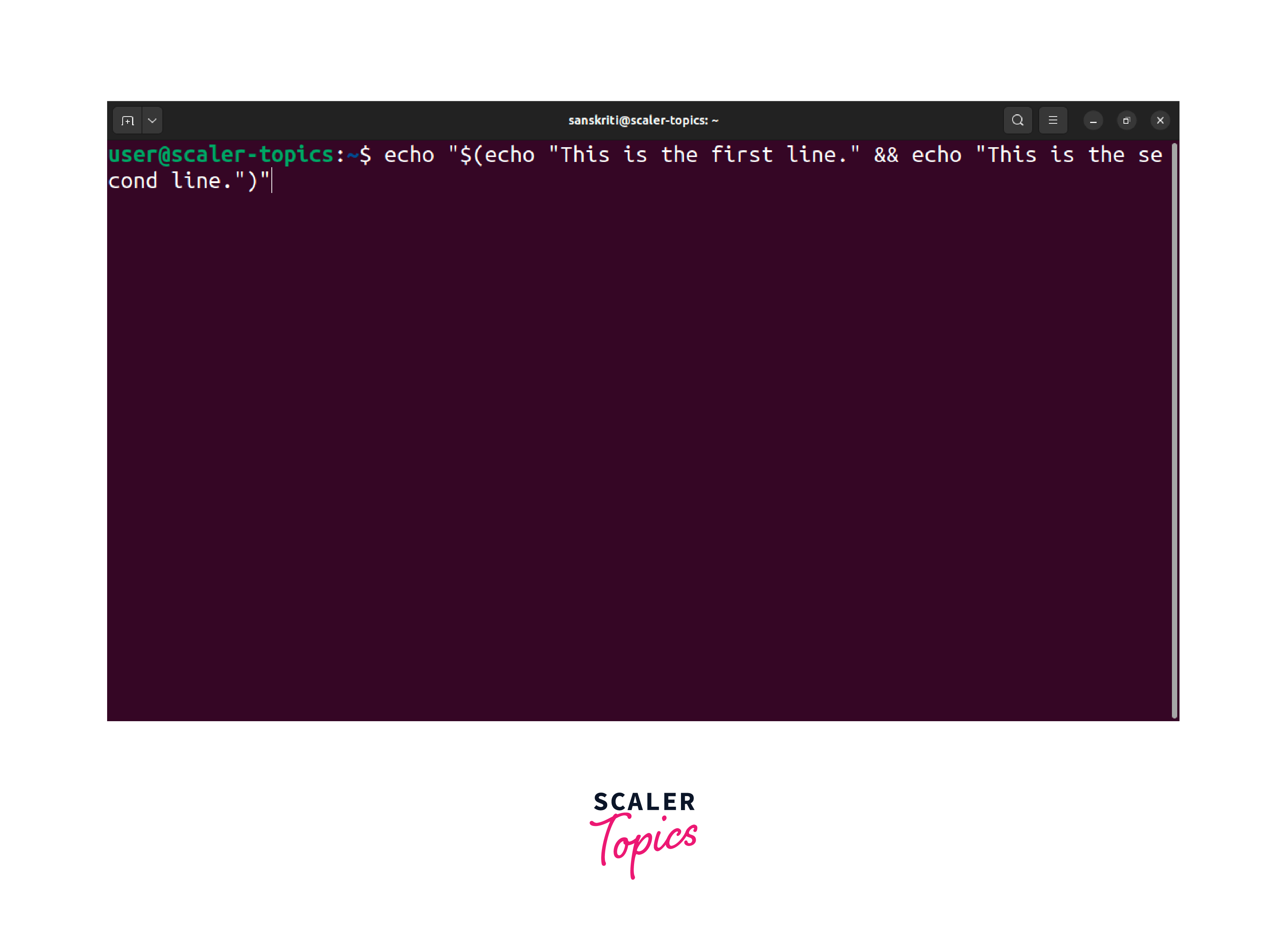
In this example, we use the inner echo commands to generate the desired lines of text, and the outer echo command is responsible for printing the entire output. The above command, on execution, will output the following:
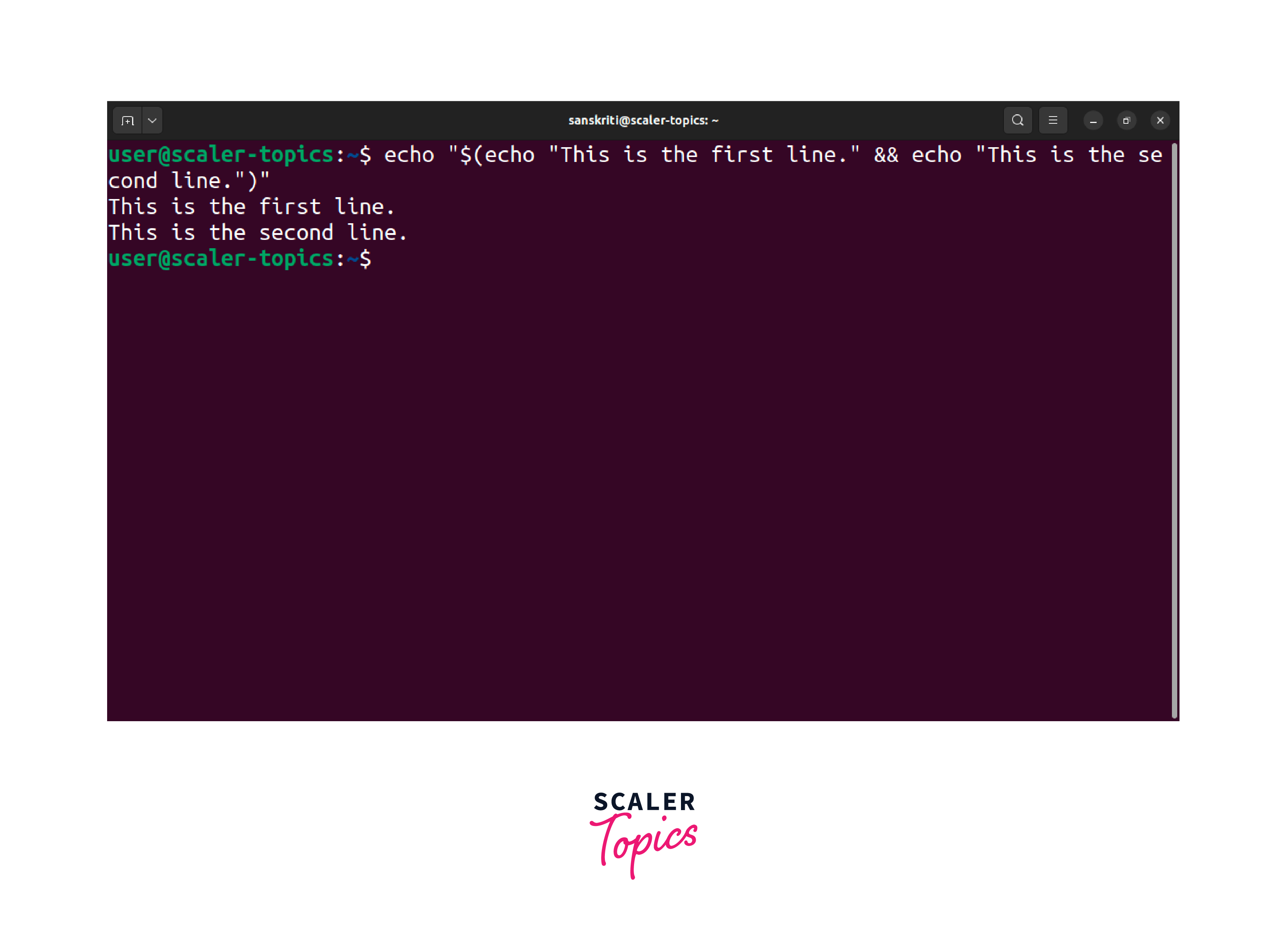
Nesting the echo commands in this manner can effectively print text with new lines using the outer echo command.
This method is not the most efficient approach in terms of performance. Nesting multiple echo commands can create unnecessary overheads. Therefore, consider alternative methods, such as the ones mentioned earlier, whenever possible.
Use printf to print newline in Bash shell
The print command in the Bash shell is an effective method for printing new lines. Its flexibility and formatting options make it a powerful tool for controlling the output layout.
We will utilize the \n escape sequence within the string passed to printf to print a new line. Let's take an example:
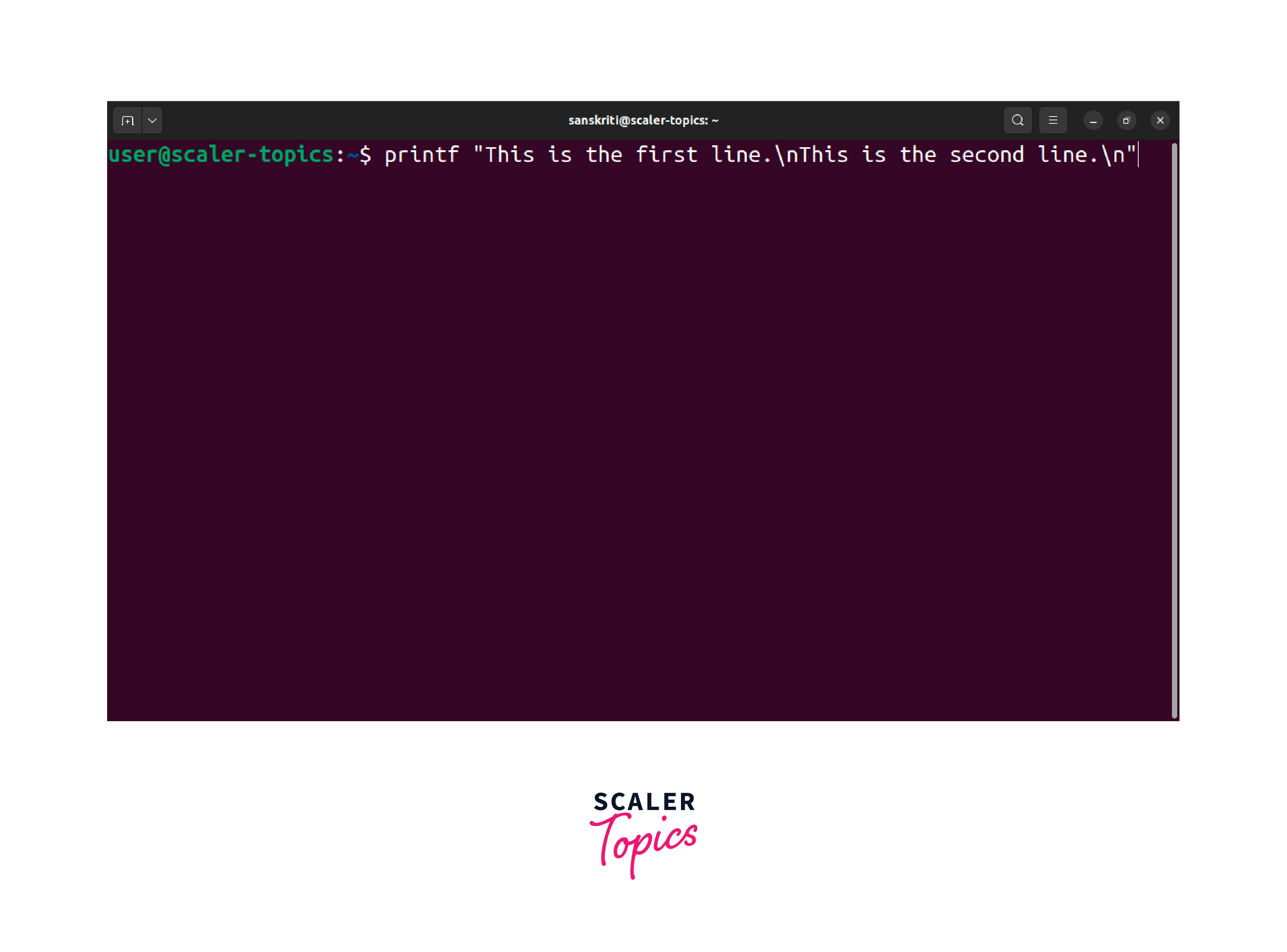
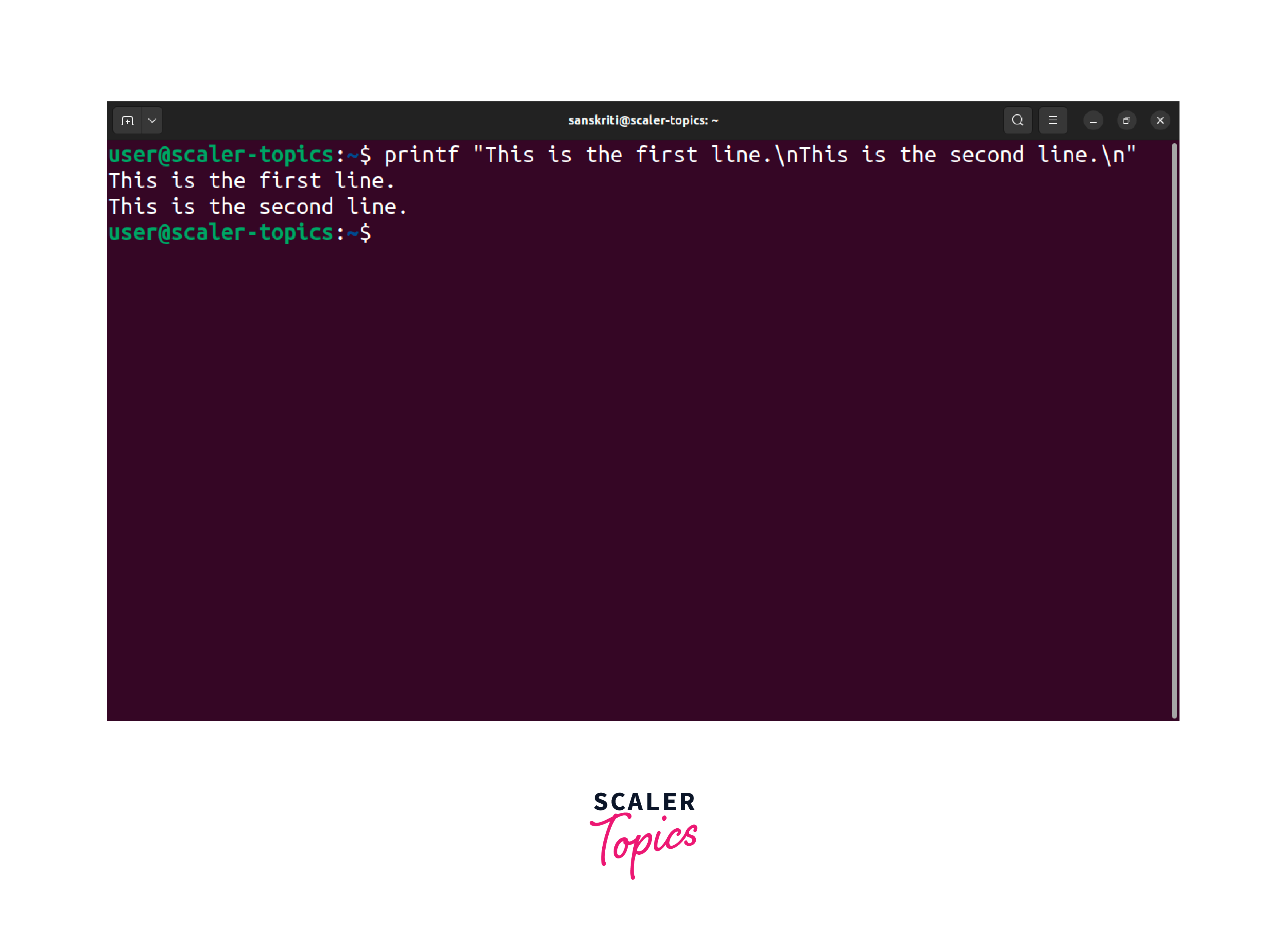
In Linux echo newline using print instead of the echo command. It helps you explicitly include the newline character within the string and attain the desired output.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this article presented various methods to echo a new line in Linux. The key takeaways include:
- Use the -e flag with echo to interpret escape sequences and display new lines effectively.
- Enclose variables with new lines in double quotes and use -e for proper interpretation.
- The $ character can be an alternative to the -e flag, but its compatibility may vary.
- Consider alternative approaches when nesting echo commands for new line output to avoid inefficiencies.
- Utilize printf for advanced formatting options and precise control over the output layout, including explicit new line inclusion.
By employing these methods, you can format Linux output with new lines, enhancing readability in scripts and commands.
