What Are File Servers In Linux?
How Do File Servers Work?
Linux file servers are used in managing and sharing files across a network. A file server in Linux is a specialized computer or software application that is used as a central storage for files and directories within a network. It provides a means for users within the network to access and manage files stored on the server.
File servers are used for storage and access of files and directories. The general working of file servers in Linux involves storing and managing files that are accessible over a network. Here is a brief explanation of their functions,
- File servers in Linux act as dedicated servers that store files on local disks or network-attached storage devices. These files can be organized into directories and subdirectories based on the server's file system structure.
- File servers make these stored files available to clients over a network. Clients can connect to the file server either within the local network or remotely through secure connections such as VPN.
- The file server allows multiple clients to access and retrieve files from the server.
- File servers implement secure permission management to control access to files and directories. Administrators can assign specific permissions to users or groups of users to certain files or directories.
- File server is highly secure as it is used to store and protect sensitive data. Various tools and techniques, such as user authentication, encryption, firewalls, and access controls, are used for security.
- File servers often include backup and recovery mechanisms to protect against data loss.
Features
Permission Management
Linux file servers offer permission management capabilities, allowing administrators to control who can access, modify, or delete files. This feature prevents unauthorized access to files. To manage permission in Linux, we must understand the principles behind privilege management and various command to achieve it. You can explore this article for such information.
File Locking
File-locking mechanisms are employed by file servers to prevent conflicts when multiple users attempt to access and modify the same file simultaneously. For example, if two users access a file at the same time, there may be a loss of information. Linux uses locks and file locking to ensure data consistency and avoids data corruption issues.
Conflict Resolution
In case conflicts do occur due to various reasons, like multiple users writing to the same file at the same time, Linux file servers provide mechanisms to resolve them efficiently. Users can either be alerted about the conflict, or the server can automatically merge changes based on predefined rules.
Distributed File System
Some advanced Linux file servers implement a distributed file system, which allows files to be stored across multiple servers, enhancing scalability, fault tolerance, and load balancing. This is highly used in parallel processing and sharding-based servers for efficiency.
File Server Protocols and Programs
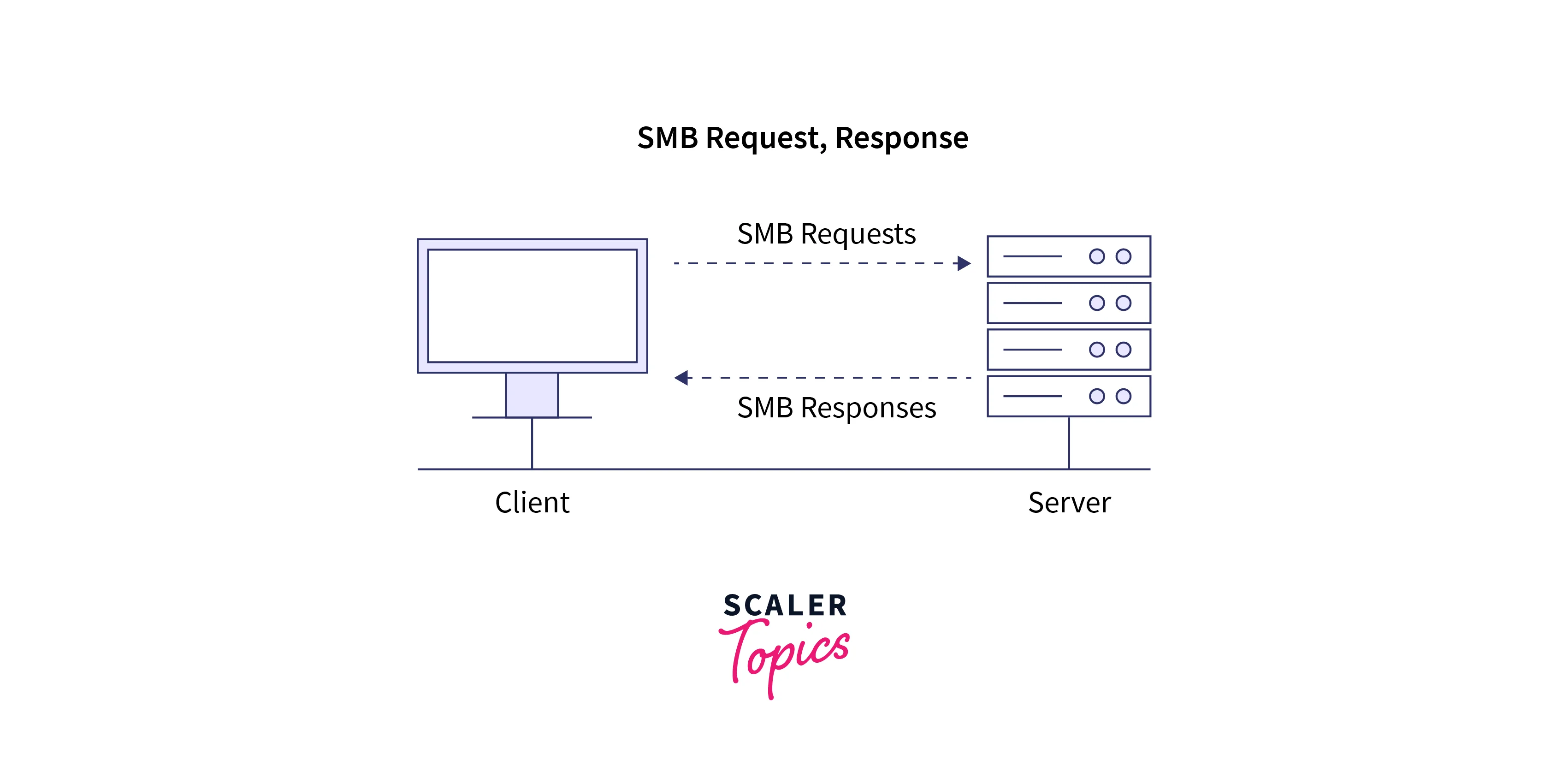
Server Message Block (SMB)
The Server Message Block (SMB) protocol is a network file sharing protocol widely used for communication between different operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS. It has features for file sharing and resource access across different networks. The most popular implementation of SMB in Linux is Samba. Let's explore the working steps of the Samba server,
- Clients initiate a request to access files or resources on an SMB server.
- The SMB server validates the client's credentials and permissions. After authentication, a session is established by connection with the server.
- The client sends requests to read, write, or modify files.
- The SMB server processes these requests, ensuring the necessary permissions are present for the client. The server also ensures that file locking and conflict resolution mechanisms are in place.
- The server provides the necessary protocols for efficient and reliable data transfer over the network.
- The Linux file servers responds to the client with the requested data or performs the requested actions.
By utilizing the SMB protocol, we can handle the communication and file transfer between the client and server, ensuring compatibility across different operating systems.
Network File System (NFS)
NFS is a Linux file servers protocol that enables file sharing between UNIX-like systems. It allows clients to mount remote directory Network File System (NFS) protocols are a set of protocols that enable file sharing between UNIX-like systems over a network. NFS allows clients to access remote directories and files as if they were local, providing transparent access to shared resources. Let's explore the working of NFS in more detail:
- The NFS server exports specific directories to be shared with clients. The configuration in this directory specifies the client permissions and access rights.
- The client has to mount the NFS file system to access the files. The client uses the mount command, specifying the NFS server's IP address or hostname and the exported directory's path to mount the server.
- Clients send requests to access the shared directories on the NFS Linux file servers.
- The server authenticates the client and verifies its permissions.
- Upon successful authentication, the server grants the client access to the requested files or directories.
- The client can then interact with the files as if they were locally available.
- The data is usually transferred in small chunks or blocks. To optimize performance, NFS employs various caching mechanisms. NFS uses a combination of client-side and server-side caching. Client-side caching stores frequently accessed data on the client's local disk, reducing the need for repeated network transfers.
- When a client modifies a file, the changes are immediately visible to other clients accessing the same file, ensuring data consistency.
- If a client loses connectivity with the NFS server, it attempts to re-establish the connection and resume operations when the server becomes available again.

We can easily share files and directories across a network by using the Network File System protocols.
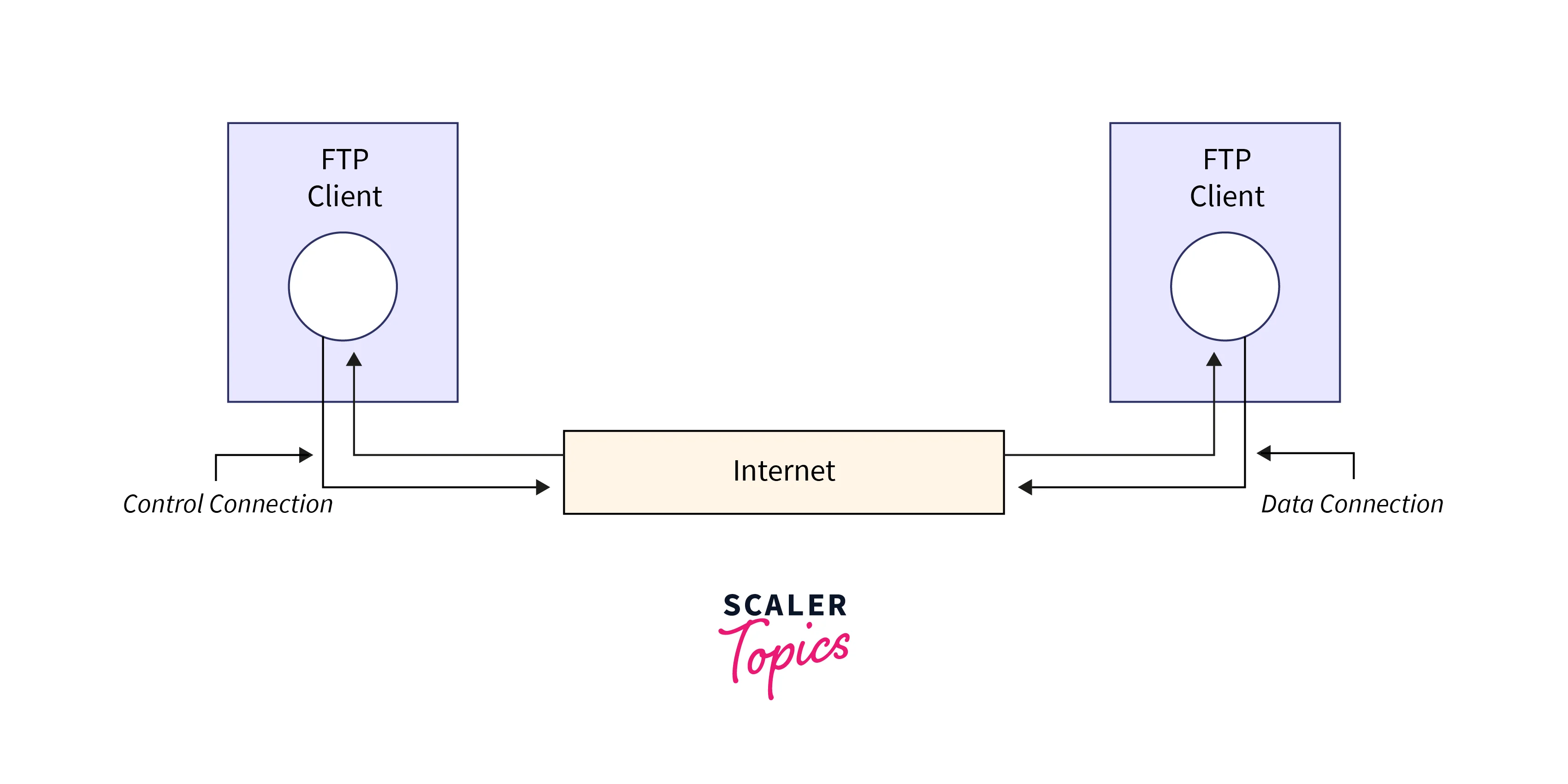
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Secure FTP (SFTP)
FTP and SFTP are protocols used for transferring files over a network. While FTP is not secure, SFTP adds encryption to ensure data confidentiality and integrity during file transfers. The working of FTP/SFTP Protocols follow the following steps,
- The FTP/SFTP server listens for incoming connections from clients.
- Clients establish a connection with the server using appropriate authentication credentials.
- Once connected, the client can request file transfers, directory listings, or other FTP/SFTP operations.
- The server validates the client's credentials and permissions before executing the requested operations.
- When transferring files, the server and client negotiate the transfer mode and data encoding.
- Data is transferred between the server and client using the established FTP/SFTP connection.
- For SFTP, the data is encrypted to maintain data confidentiality and integrity.
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) are also present to monitor network traffic and identify potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts.
File Server Security
The following methods can be used as part of security constraints in Linux file servers. By implementing these steps, organizations can enhance the protection of their sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate potential security risks.
- Implement user authentication mechanisms to ensure that only authorized individuals can access the file server. This can include password-based authentication or two-factor authentication (2FA), among others.
- Access control is used to define and enforce file permissions. Assign appropriate access rights to users or groups to restrict unauthorized access and prevent unauthorized modifications or deletions.
- Implement encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, to secure data transmissions between clients and the file server. This ensures that data is protected from interception or tampering during transit.
- Utilize secure file server protocols, such as SFTP or FTPS, which provide encryption for file transfers. Avoid using unencrypted protocols like FTP, which can expose sensitive data to eavesdropping.
- Deploy intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to monitor network traffic and identify potential security breaches or unauthorized access attempts. These systems can alert administrators and take preventive actions to mitigate threats.
- Configure firewalls to restrict access to the file server and allow only necessary network traffic. Implement firewall rules that permit only authorized users or IP addresses to connect to the server.
- Keep the file server software and operating system up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
- Implement regular data backups and establish a robust disaster recovery plan.
- Protect the physical infrastructure hosting the file server. Secure the server room or data center with appropriate physical access controls, surveillance systems, and restricted entry to authorized personnel only.
File servers vs. NAS vs. cloud storage
| Category | File Server | NAS (Network-Attached Storage) | Cloud Storage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | A dedicated server that stores and manages files accessible over a network. | A storage device connected to a network that provides centralized file storage and access to multiple clients. | Storage service provided by a third-party provider accessible via the internet. |
| Location | Typically located on-premises within an organization's local network. | Can be located on-premises or remotely connected to the network. | Hosted remotely by a third-party provider accessible over the internet. |
| Control | Offers full control over storage, security, access permissions, and configurations. | Provides control over storage, security, and access permissions but with more limited configuration options compared to a file server. | Provides limited control over storage, security, and access permissions, as these aspects are managed by the cloud storage provider. |
| Scalability | Scalability depends on the hardware capacity of the file server and its ability to handle increased demands. | Scalable storage capacity by adding more drives to the NAS device. | Highly scalable storage capacity, as users can easily increase or decrease storage space as needed. |
| Accessibility | Accessible within the local network or remotely through secure connections (e.g., VPN). | Accessible within the local network or remotely through secure connections (e.g., VPN). | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing users to access files from various devices. |
| Collaboration | Allows multiple users to collaborate on files stored on the file server. | Supports file sharing and collaboration among multiple users. | Enables file sharing and collaboration among multiple users with features like versioning and real-time collaboration. |
| Redundancy and Backup | Relies on manual backups and redundancy configurations to ensure data integrity and protection. | Often supports built-in redundancy and backup features to protect data in case of drive failures. | Cloud storage providers typically offer data redundancy and backup options to ensure data availability and protection. |
| Security | Provides greater control over security measures, such as encryption, firewalls, and access controls. | Offers security features like user authentication, access controls, and data encryption. | Cloud storage providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and data redundancy to protect stored data. |
| Cost | Requires upfront investment in hardware, maintenance, and IT expertise for setup and management. | Generally, an affordable solution with lower upfront costs, though additional hardware and maintenance costs may be incurred. | Cost structure typically involves recurring subscription fees based on storage usage. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for organizations that require extensive control, custom configurations, and specific security requirements. | Suitable for small to medium-sized businesses and home users needing centralized storage and basic file-sharing capabilities. | Suitable for individuals, small businesses, and enterprises looking for scalable storage, remote accessibility, and collaborative features. |
File Server Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Centralized file storage and management.
- Enhanced data security and permission control.
- Efficient collaboration and file sharing.
- Robust backup and recovery options.
- Cost-effective solution compared to cloud storage.
Disadvantages
- Requires dedicated hardware and maintenance.
- Network dependency for file access.
- Limited scalability for certain implementations.
Conclusion
- Linux file servers are dedicated servers that store and manage files accessible over a network, providing a central repository for file sharing and collaboration.
- These Linux file servers work by exporting specific directories for clients to access, utilizing protocols like SMB, NFS, and FTP/SFTP for file transfer.
- Features of Linux file servers include permission management, file locking, conflict resolution, and distributed file systems for efficient storage and access.
- File server protocols such as SMB, NFS, and FTP/SFTP enable clients to access and transfer files securely over a network.
- Security measures like user authentication, access controls, encryption, and firewalls are crucial for protecting data on file servers.
- File servers differ from Network-Attached Storage (NAS) and cloud storage in terms of control, location, scalability, accessibility, collaboration, and cost.
