MeanShift and CamShift in Computer Vision
Overview
MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are two popular techniques used in computer vision for object tracking. MeanShift is a non-parametric iterative algorithm that can locate the maxima of a density function, allowing it to track an object in a video sequence. It works by iteratively shifting a window to the mode of the density function until convergence. CamShift is an extension of MeanShift that dynamically adjusts the size and orientation of the search window, allowing it to track objects with changing sizes and orientations. It also includes a probability model for object appearance that makes it more robust to changes in illumination and occlusions.
Introduction
Computer Vision is a field of study that involves teaching machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world around us. This information can be in the form of images, videos, or even live camera feeds. One of the key challenges in computer vision is object tracking, which involves detecting and following objects in a video sequence.
MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are two widely used algorithms in computer vision for object tracking. These algorithms are particularly useful for tracking objects that move through a video sequence in a non-linear or unpredictable manner. They are widely used in applications such as surveillance systems, self-driving cars, and robotics, among others.

MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are both based on the idea of tracking an object by iteratively shifting a window to the mode of a density function. The density function can represent the probability distribution of object pixels in an image, and the mode corresponds to the object's current location. These algorithms can be used to track objects in real time, even in situations where the object is partially occluded, changes size, or moves in a complex way
What is the MeanShift Algorithm?
The MeanShift algorithm is a non-parametric iterative technique used for object tracking in computer vision. It works by iteratively shifting a window towards the mode of a probability density function, until it reaches convergence. The mode of the density function corresponds to the location of the object being tracked.

The process is then repeated by recalculating the density function with the new window location and shifting the window towards the new mode. This process is repeated until convergence, which occurs when the shift of the window is negligible.
The MeanShift algorithm is particularly useful for object tracking because it can adapt to changes in the object's appearance, size, and shape. It is widely used in applications such as surveillance, robotics, and self-driving cars.
Explanation of MeanShift Algorithm
The Meanshift algorithm selects a window around the object of interest in the first frame of a video sequence. The window can be represented by a rectangle, circle, or any other shape that encloses the object. The density function is then calculated by estimating the probability distribution of pixels inside the window.
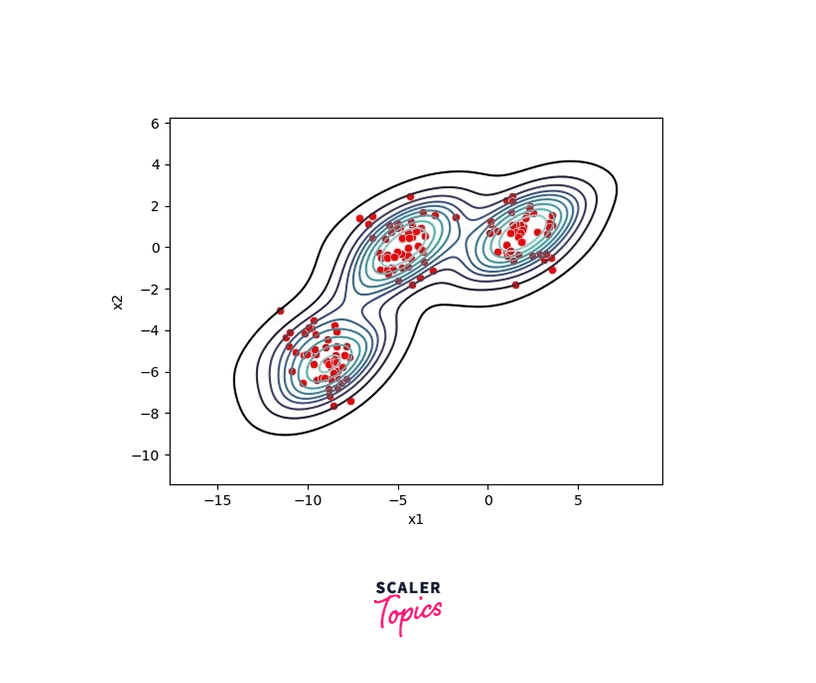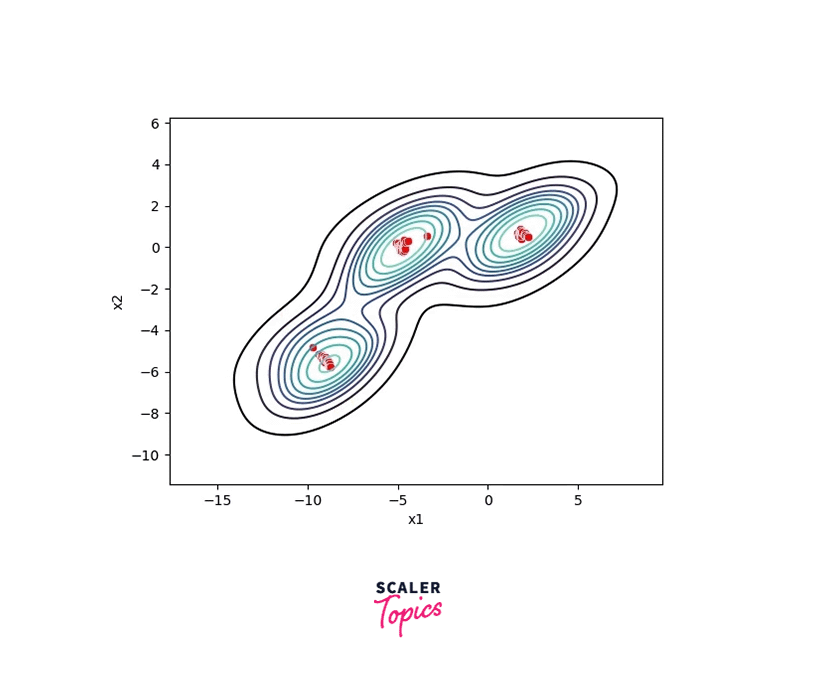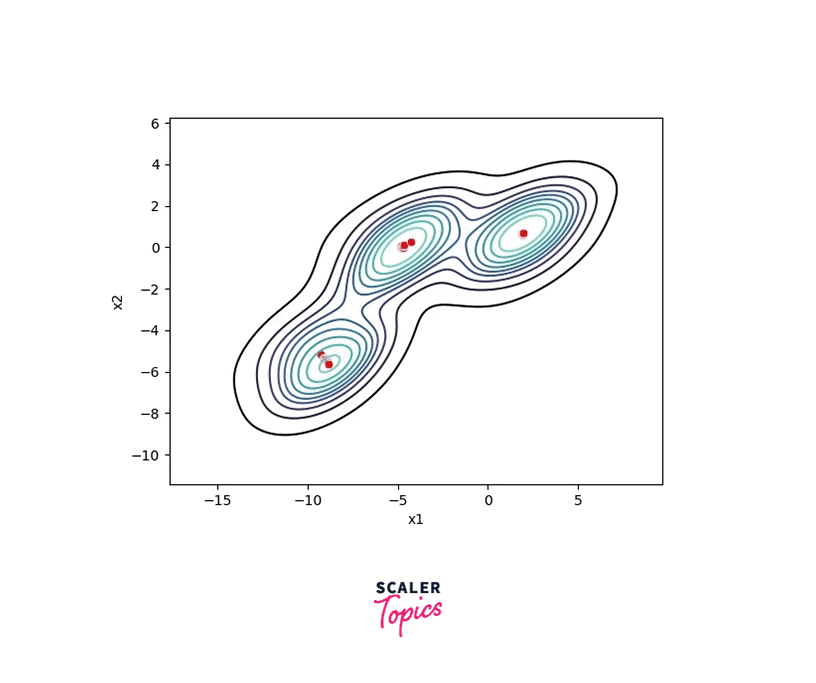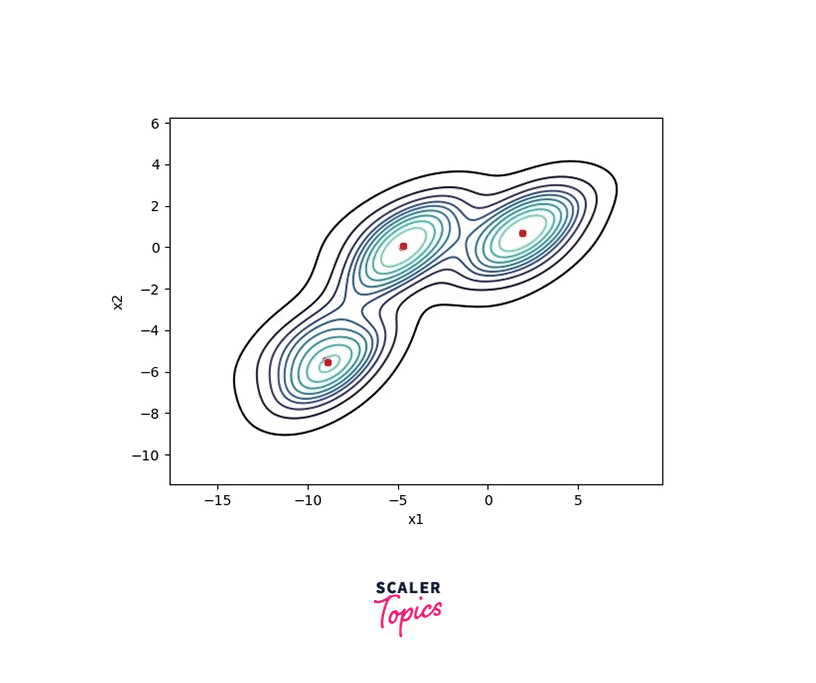
The MeanShift algorithm then shifts the window to the mode of the density function, which corresponds to the location of the object. This shift is calculated by computing the weighted average of the pixel values inside the window, with the weights determined by the probability values of the density function.
Mathematical Formula and Equations
The MeanShift algorithm can be mathematically represented as follows:
-
Initialize the window:
center of the initial window
-
Calculate the density function:
where is the kernel function, is the window size, and is the number of data points inside the window.
-
Shift the window:
where is the weight of data point .
-
Repeat until convergence:
The process is repeated until convergence, which occurs when the shift of the window is negligible.
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| Kernel function | |
| Data point | |
| Current window center | |
| Next window center | |
| Window size | |
| Weight of data point | |
| Probability density function |
Steps Involved in MeanShift Algorithm
The MeanShift algorithm involves the following steps:
- Initialize the window:
Choose an initial window center and window size . - Calculate the density function:
Calculate the probability density function for each data point within the window. This is done by computing the kernel density estimator of the data points within the window using a kernel function . - Shift the window:
Compute the weighted mean of the data points within the window to obtain a new window center . - Repeat until convergence:
Repeat steps 2 and 3 until the window center converges to a stable location.
The algorithm converges when the shift of the window center between successive iterations becomes negligible. The final window center represents the mode of the underlying probability density function.
Implementation of MeanShift Algorithm using OpenCV
Object tracking is a fundamental task in computer vision that involves locating and following specific objects of interest in a video sequence. The MeanShift algorithm is a popular technique used for object tracking, offering simplicity and effectiveness. In this section, we will explore the implementation of the MeanShift algorithm using OpenCV, a powerful open-source computer vision library.
The step-by-step instructions for implementing the MeanShift algorithm using OpenCV are given below:
Import OpenCV and Numpy to implement the Meanshift Algorithm.
Step 1: Load the input video using the cv2.VideoCapture() method.
Step 2: Initialize the tracker
Initialize the tracker by specifying the initial location of the object to be tracked using a bounding box. Set the termination criteria for the Mean Shift algorithm.
Step 3: Extract the region of interest (ROI)
Extract the region of interest (ROI) from the first frame of the video using the bounding box coordinates. Convert the ROI to the HSV color space.
Step 4: Calculate the histogram of the ROI
Calculate the histogram of the ROI in the Hue channel. Normalize the histogram to a range of 0 to 255.
Step 5: Convert to the HSV color space.
Convert each frame of the video to the HSV color space. Backproject the histogram over the entire frame to obtain a probability distribution.
Step 6: Apply the Mean Shift algorithm
Apply the Mean Shift algorithm to the probability distribution to obtain the new location of the object.
Step 7: Draw a rectangle around the new location of the object
Step 8: Close the windows
Sample Output
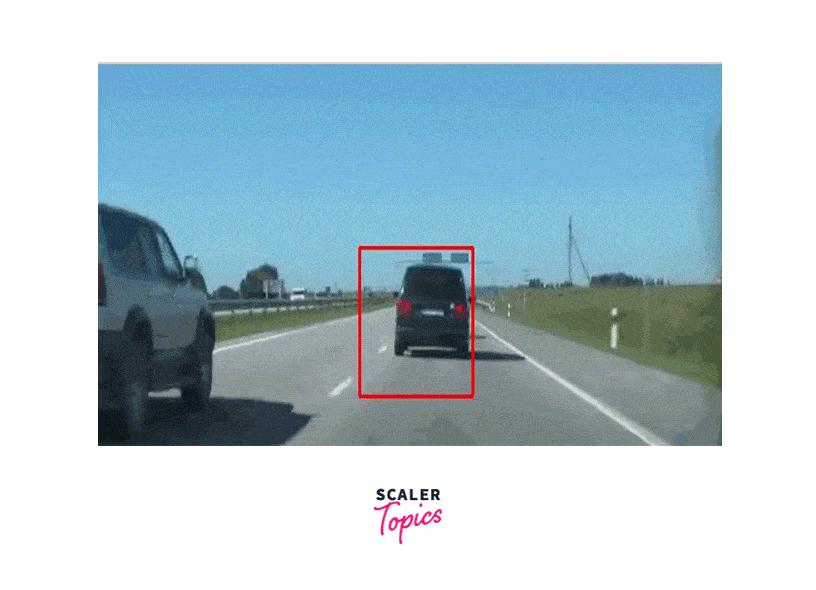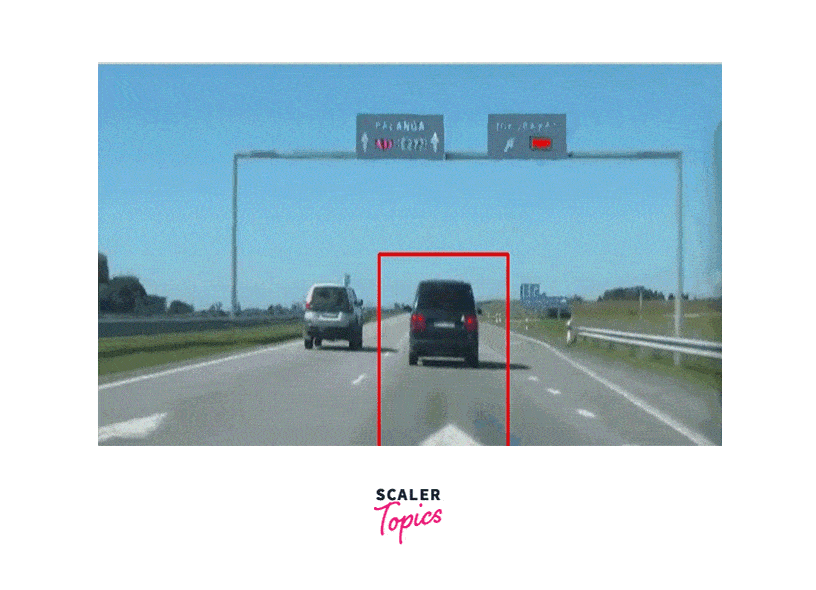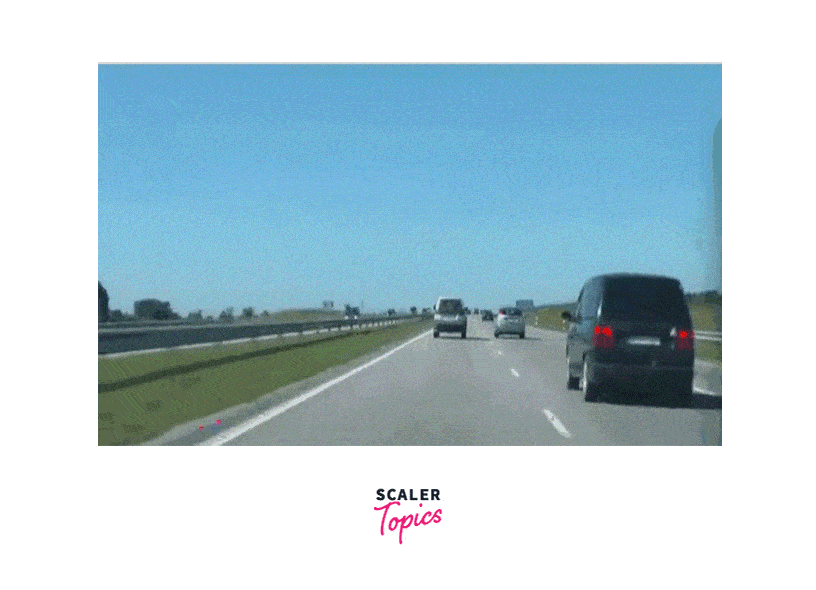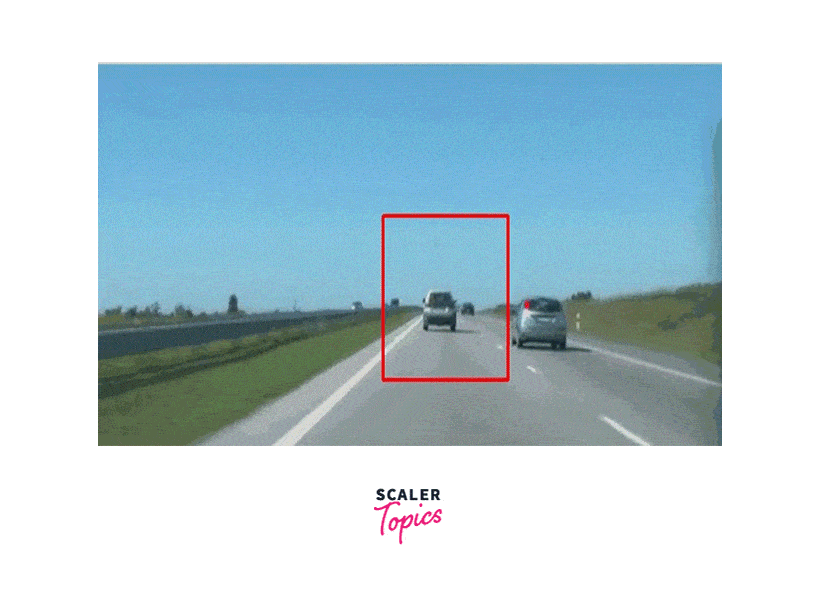
What is the CamShift Algorithm?
The CamShift (Continuously Adaptive Meanshift) algorithm is a popular computer vision technique used for object tracking. It is a variation of the MeanShift algorithm that is capable of dynamically adjusting the size and orientation of the search window based on the movement and size of the object being tracked.
The algorithm works by first creating a color histogram of the object being tracked in the first frame of the video sequence. This histogram represents the color distribution of the object and is used to model the object in subsequent frames. In each frame, the CamShift algorithm searches for the object by iteratively applying MeanShift to a search window that is initially placed around the object's estimated location.
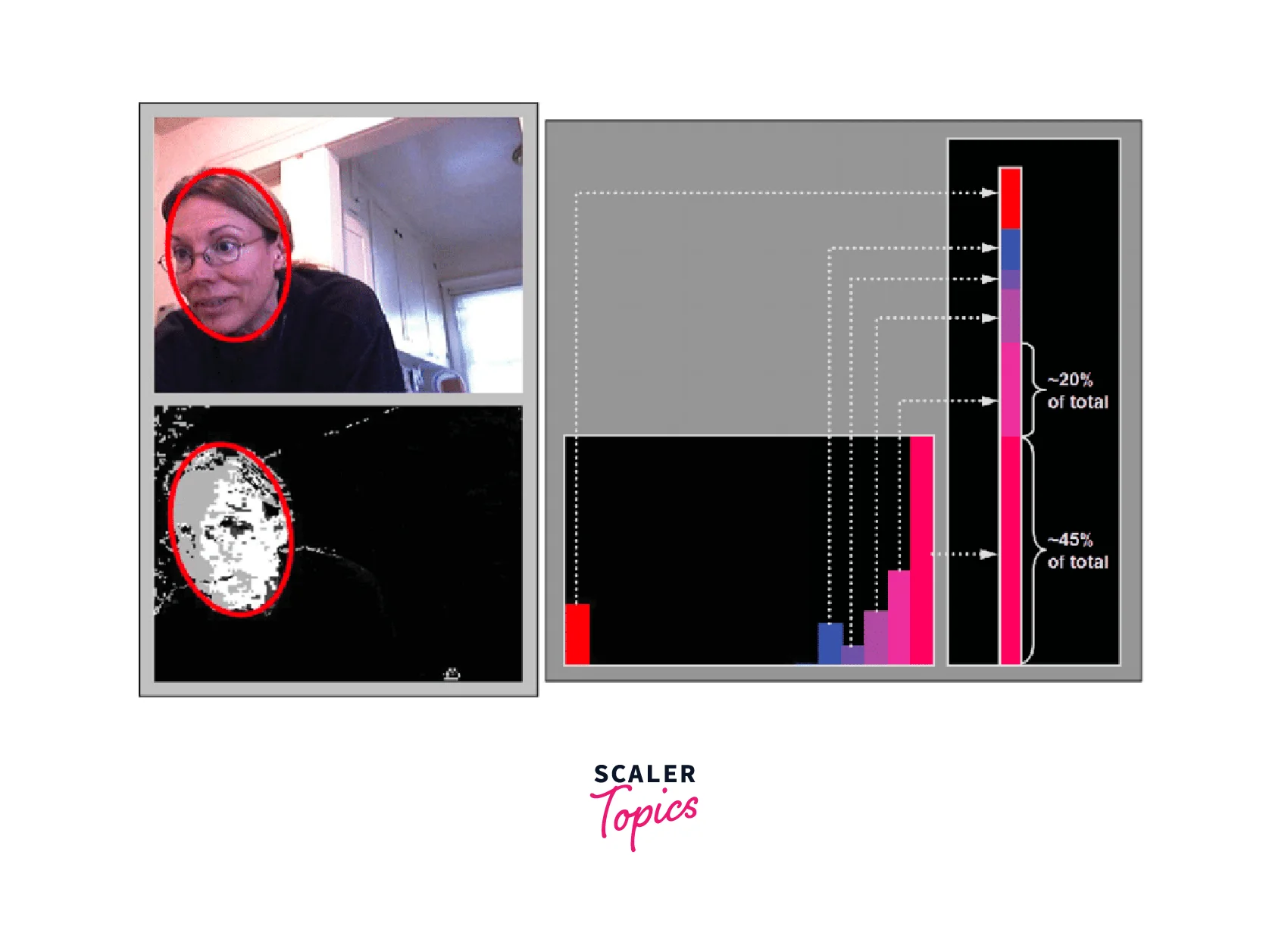
CamShift is a versatile technique for object tracking in computer vision that has been used in various applications. However, its performance may degrade in the presence of changes in lighting, background, occlusions, or objects with complex shapes. Researchers have proposed modifications and extensions to address these limitations.
Explanation of CamShift Algorithm
The CamShift algorithm works by first creating a color histogram of the object being tracked in the first frame of the video sequence. This histogram represents the color distribution of the object and is used to model the object in subsequent frames.
In each frame, the CamShift algorithm searches for the object by iteratively applying MeanShift to a search window that is initially placed around the object's estimated location.
Once the search window converges to a stable location, the algorithm computes the mode of the probability distribution to obtain the object's location in the current frame. This location is then used to initialize the search window in the next frame, and the process is repeated.
Mathematical Formulae and Equations
The CamShift algorithm can be mathematically represented as follows:
-
Calculation of color probability distribution for the object in the search window:
where:
- is the pixel coordinate
- is the search window
- is the Gaussian function
- is the center of the search window
- is the bandwidth
- is the color channel density function
- is the intensity value of pixel (x,y)
- is the normalization factor
-
Calculation of the object location and size:
-
Calculation of the orientation angle:
Steps Involved in Camshift Algorithm
The steps involved in the CamShift algorithm are:
- Load the video or image sequence and initialize the video writer if needed.
- Select the object to be tracked by drawing a bounding box around it.
- Convert the selected region to the HSV color space.
- Calculate the histogram of the selected region in the Hue channel.
- Normalize the histogram to a range of 0 to 255.
- Backproject the histogram over the entire frame to obtain a probability distribution.
- Apply the Mean Shift algorithm to the probability distribution to obtain the new location of the object.
- Draw a rectangle around the new location of the object.
- Repeat steps 3 to 8 for each frame in the video or image sequence.

Implementation of CamShift Algorithm Algorithm Using OpenCV
This is the core section where we will implement the CamShift algorithm using OpenCV. We will go through the step-by-step process of applying the CamShift tracking algorithm to update the position, size, and orientation of the tracked object in each frame of the video or image sequence. This will involve performing color space conversion, histogram backprojection, and adaptive mean shift iterations.
The step-by-step instructions to implement the CamShift algorithm using OpenCV is given below:
We start by importing the OpenCV module to implement the camshift algorithm.
Step 1: Load the video or image sequence and initialize the video writer if needed.
Step 2: Select the object to be tracked by drawing a bounding box around it.
Step 3: Convert the selected region to the HSV color space.
Step 4: Calculate the histogram of the selected region in the Hue channel.
Step 5: Normalize the histogram to a range of 0 to 255.
Step 6: Backproject the histogram over the entire frame to obtain a probability distribution.
Step 7: Apply the CAMshift algorithm to the probability distribution to obtain the new location of the object.
Step 8: Draw a rectangle around the new location of the object.
Step 9: Display the frame
Step 10: Close all the windows
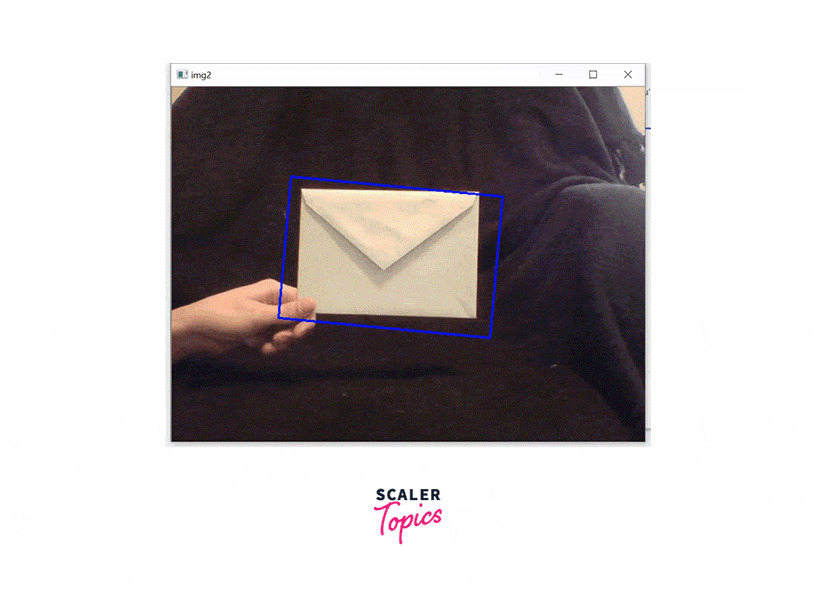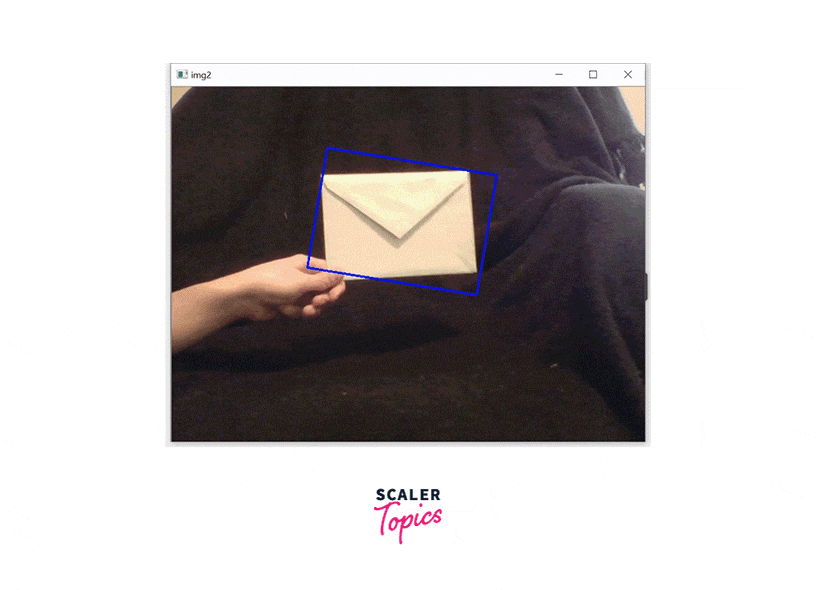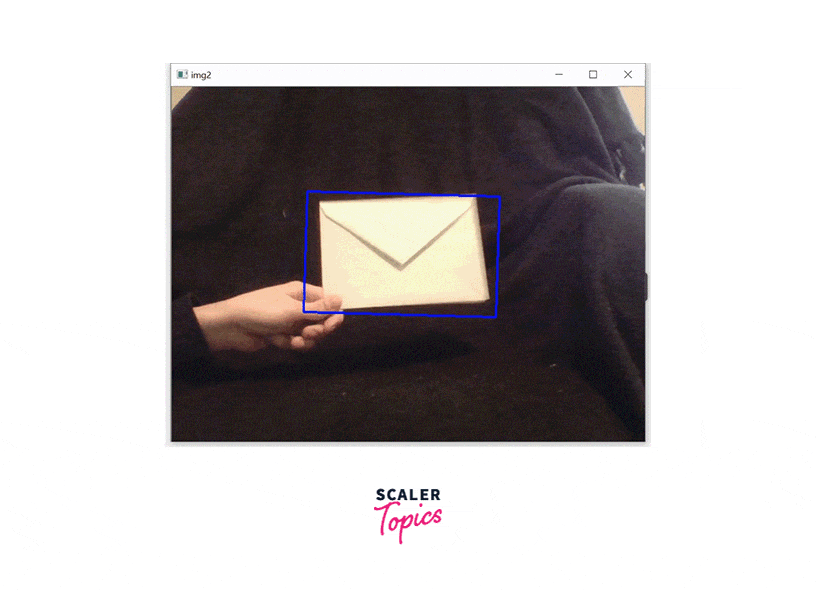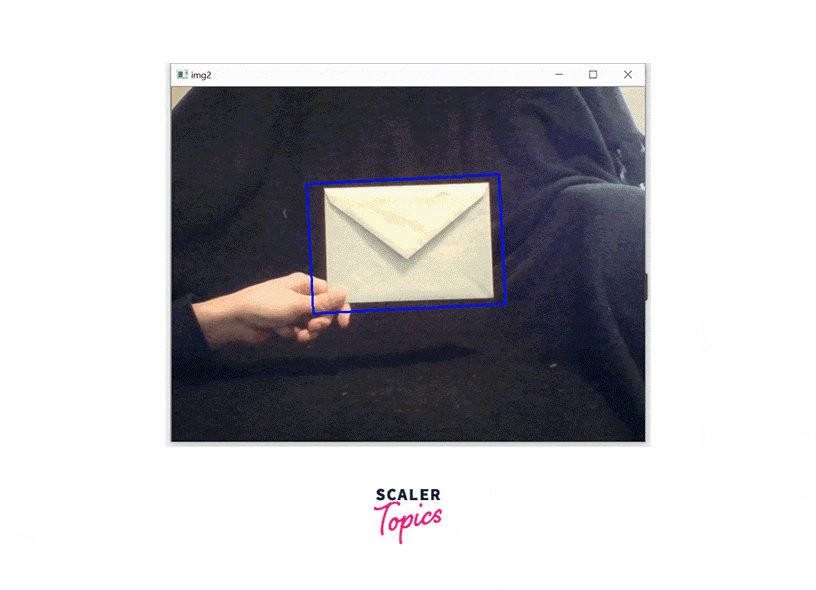
That's it! With these steps, you can implement the CamShift algorithm using OpenCV.
Comparison Between MeanShift and CamShift Algorithms
Here is a comparison between the algorithms of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV :
- Object tracking:
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are used for object tracking in computer vision. - Search window:
MeanShift uses a fixed-size search window, while CamShift uses a dynamically adjusting search window that can adapt to changes in object size and shape. - Histogram:
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV uses color histograms to model the object being tracked. - Convergence:
MeanShift can converge to local maxima, while CamShift uses a more robust algorithm that converges to the global maximum. - Complexity:
CamShift is a more complex algorithm than MeanShift, as it involves additional steps such as calculating the orientation of the search window and updating its size and shape. - Performance:
CamShift is generally more accurate than MeanShift when tracking objects with complex shapes or dealing with occlusions, but it can be more sensitive to changes in lighting and background.

In summary, algorithms of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV have their strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which algorithm to use depends on the specific requirements of the application. MeanShift is a simpler and faster algorithm that works well for tracking objects with simple shapes and clear boundaries, while CamShift is a more powerful algorithm that can handle more complex objects but requires more computation.
Differences Between Meanshift and Camshift in OpenCV
| Difference | MeanShift | CamShift |
|---|---|---|
| Search window | Uses a fixed-size search window | Uses a dynamically adjusting search window that can adapt to changes in object size and shape |
| Convergence | Can converge to local maxima | Converges to the global maximum |
| Complexity | A simpler and faster algorithm | A more complex algorithm that involves additional steps such as calculating the orientation of the search window and updating its size and shape |
| Performance | Works well for tracking objects with simple shapes and clear boundaries | Generally more accurate when tracking objects with complex shapes or dealing with occlusions, but can be more sensitive to changes in lighting and background |
The main differences between algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are the search window, convergence, complexity, and performance. MeanShift uses a fixed-size search window while CamShift uses a dynamically adjusting search window. MeanShift can converge to local maxima while CamShift converges to the global maximum.
CamShift is a more complex algorithm that involves additional steps such as calculating the orientation of the search window and updating its size and shape. Finally, MeanShift works well for tracking objects with simple shapes and clear boundaries, while CamShift is generally more accurate when tracking objects with complex shapes or dealing with occlusions, but it can be more sensitive to changes in lighting and background.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Algorithm
The advantages and disadvantages of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are discussed below:
Advantages of MeanShift:
- Simpler and faster algorithm compared to CamShift
- Works well for tracking objects with simple shapes and clear boundaries
- Less sensitive to changes in lighting and background
Disadvantages of MeanShift:
- It Can converge to local maxima instead of the global maximum, leading to inaccurate tracking results
- May not work well for tracking objects with complex shapes or dealing with occlusions
Advantages of CamShift:
- Generally more accurate when tracking objects with complex shapes or dealing with occlusions
- Uses a dynamically adjusting search window that can adapt to changes in object size and shape
- Converges to the global maximum
Disadvantages of CamShift:
- More complex algorithm that involves additional steps such as calculating the orientation of the search window and updating its size and shape
- It Can be more sensitive to changes in lighting and background compared to MeanShift
- May be slower compared to MeanShift due to the additional steps involved
Use Cases Where One Algorithm May Be Preferred Over the Other
There are several use cases where one algorithm may be preferred over the other:
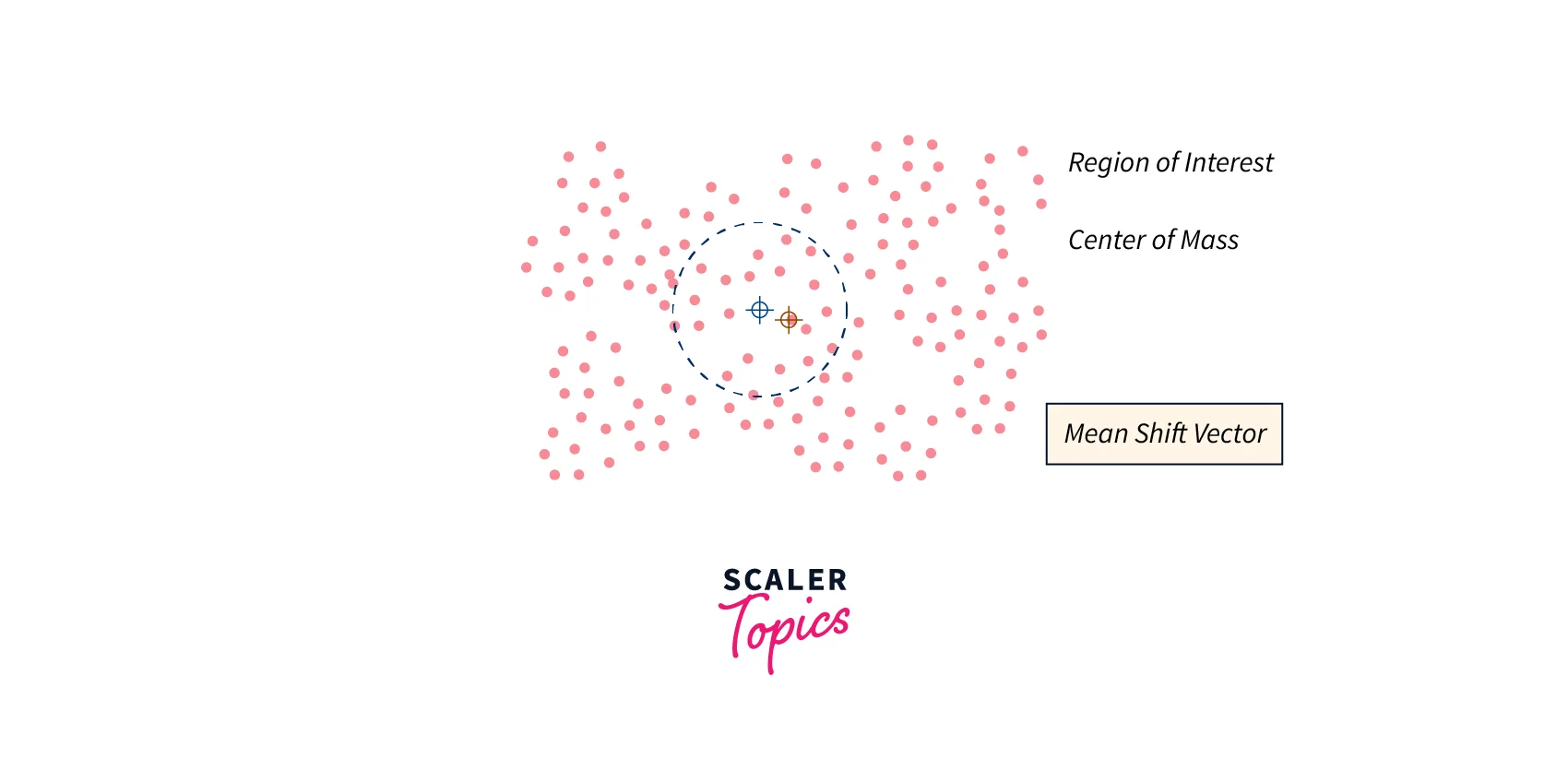
- MeanShift may be preferred when tracking objects with simple shapes and clear boundaries, and when speed is a critical factor. For example, in a real-time video surveillance system that needs to track objects in real-time, MeanShift may be the better option.
- CamShift may be preferred when tracking objects with more complex shapes or when dealing with occlusions. For example, in an augmented reality application where a user is interacting with virtual objects that can have arbitrary shapes and sizes, CamShift may be the better option.
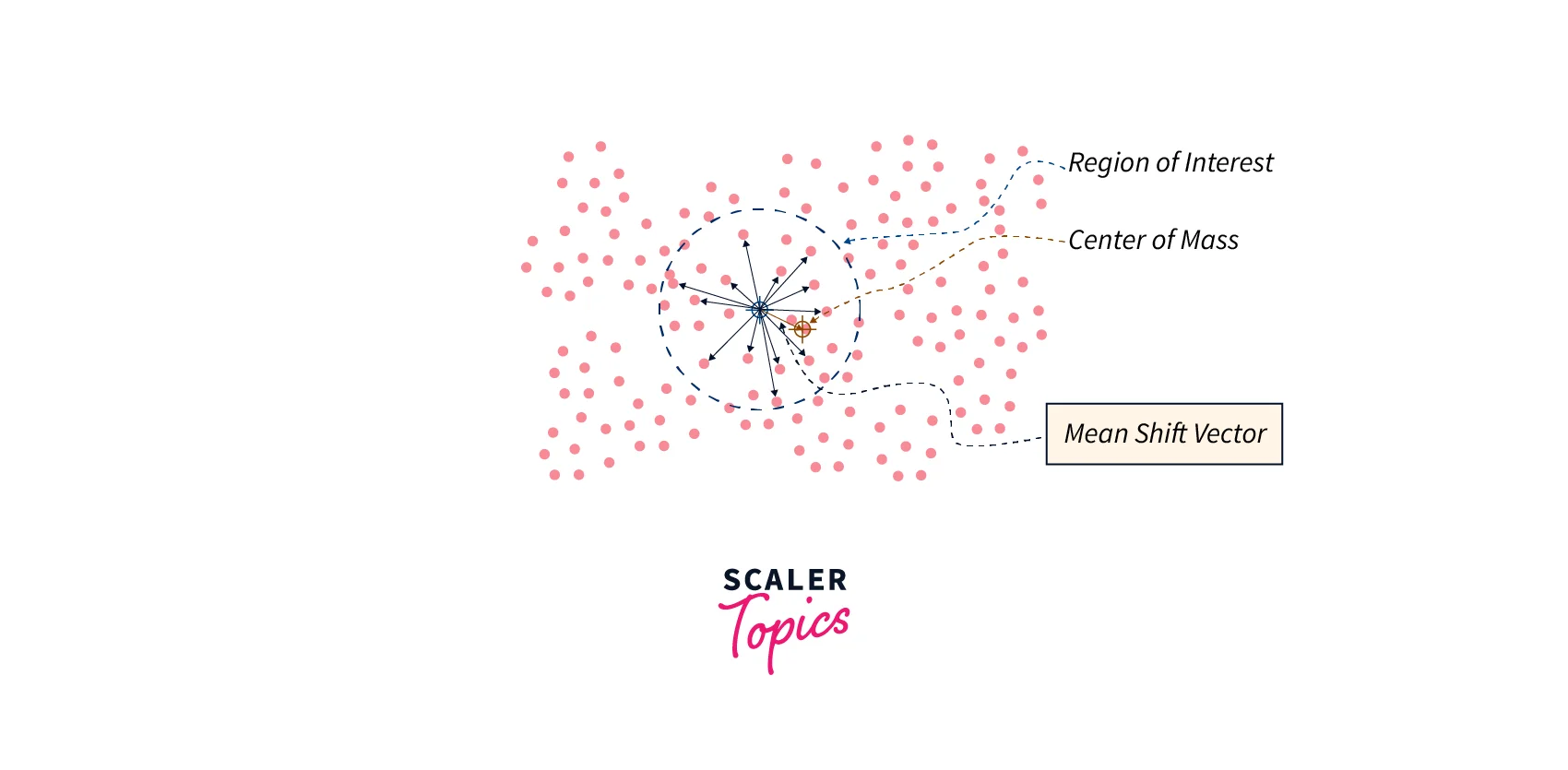
- CamShift may also be preferred when tracking objects that can change size or shape over time, such as a person walking towards or away from the camera. CamShift's ability to dynamically adjust the search window makes it better suited for tracking such objects.
Overall, the choice between MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including the complexity of the objects being tracked, the desired tracking accuracy, the processing power available, and the real-time performance requirements.
Applications of MeanShift and CamShift
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV have a wide range of applications in computer vision and related fields.
Some of the applications of MeanShift algorithm include:
- Object tracking in video surveillance systems:
Object tracking in video surveillance systems is the process of automatically detecting and following objects of interest in a video stream. It involves analyzing frames in real time, identifying and tracking objects based on their appearance and motion. Object tracking enables tasks such as anomaly detection, object recognition, and behavior analysis, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of video surveillance systems. - Image segmentation and object recognition:
Image segmentation is the process of dividing an image into meaningful regions or segments. It aims to separate objects or areas of interest from the background. Object recognition, on the other hand, involves identifying and classifying specific objects within an image or a video stream. It enables automated understanding and analysis of visual content, contributing to tasks like object detection, classification, and scene understanding.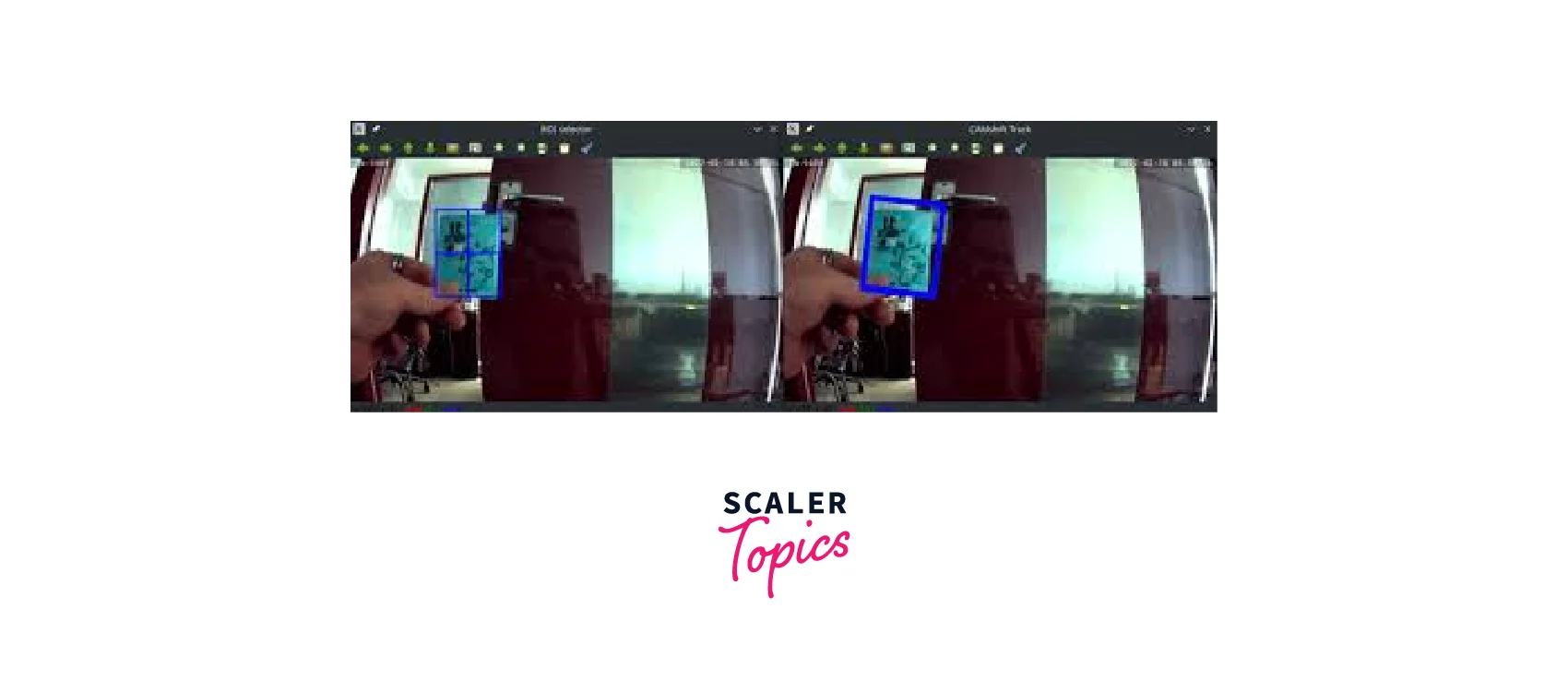
- Face tracking and detection in real-time video:
Face tracking and detection in real-time video involves automatically detecting and tracking human faces in a video stream. It utilizes computer vision techniques to locate faces, extract facial features, and track their movements over consecutive frames. This enables applications such as face recognition, emotion analysis, and gaze tracking. Real-time processing ensures swift and accurate face tracking, enabling various interactive and surveillance-based systems. - Gesture recognition in human-computer interaction:
Gesture recognition in human-computer interaction involves interpreting human gestures and movements to enable interaction with digital systems. It utilizes computer vision and machine learning techniques to analyze and classify hand or body gestures. Gesture recognition enables natural and intuitive interaction, allowing users to control and manipulate digital interfaces through gestures, enhancing applications such as virtual reality, gaming, robotics, and interactive displays.
Some of the applications of the CamShift algorithm include:
The CamShift algorithm has diverse applications in computer vision. One prominent area is video surveillance systems, where CamShift enables real-time object tracking, facilitating automated analysis, and enhancing security measures. Moreover, CamShift can be employed in robotics for object tracking and manipulation tasks, enhancing autonomous systems' capabilities. Overall, the versatility of the CamShift algorithm makes it applicable across various domains, revolutionizing object tracking and interaction in different fields.
- Object tracking in complex scenes with occlusions and changing backgrounds:
Object tracking in complex scenes with occlusions and changing backgrounds poses significant challenges. It involves continuously monitoring and following objects of interest despite occlusions and varying backgrounds. Robust object-tracking algorithms, such as those based on deep learning or adaptive models, are employed to handle these complexities. These algorithms utilize techniques such as motion estimation, appearance modeling, and occlusion handling to track objects accurately in dynamic and challenging environments.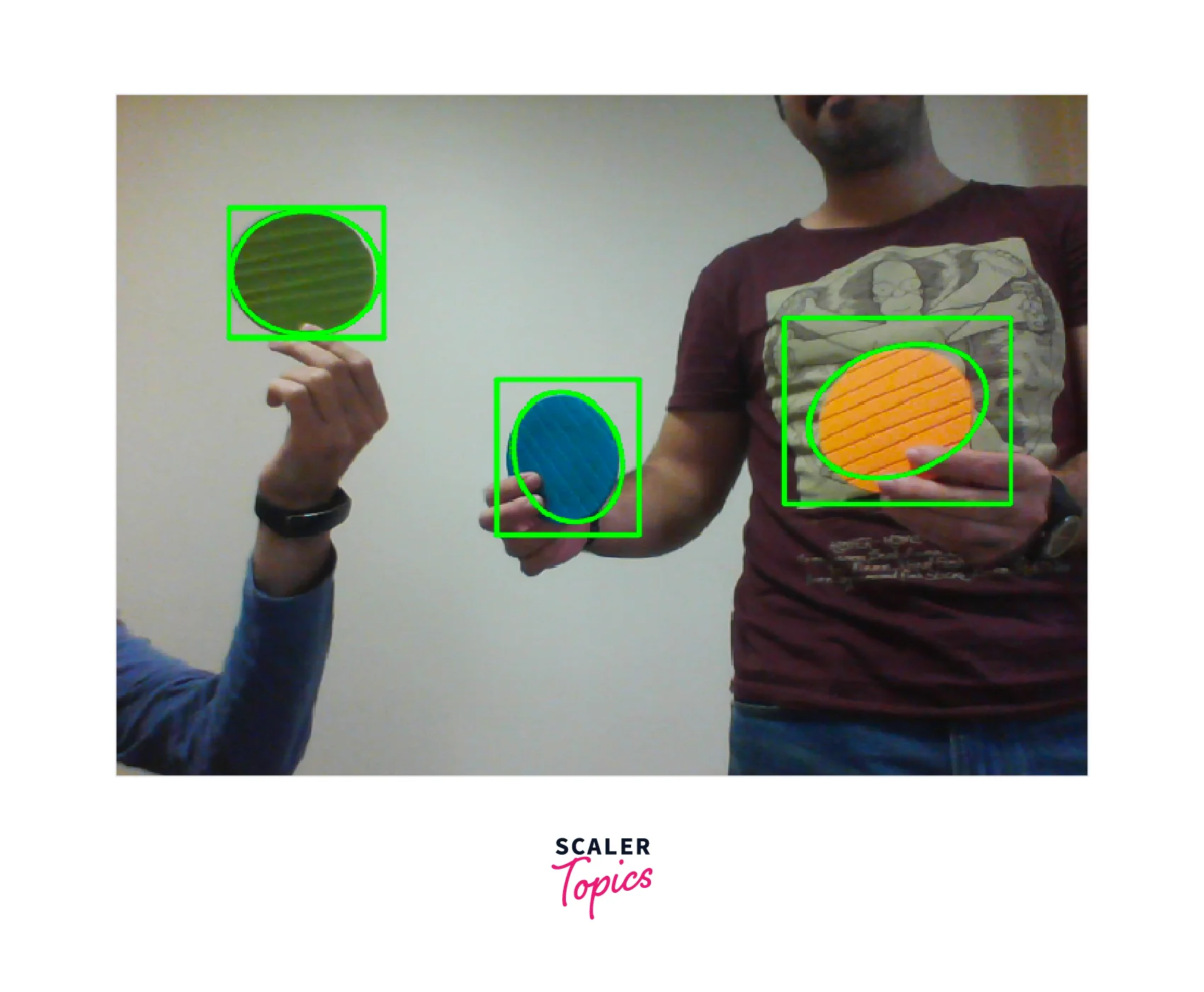
- Hand tracking and gesture recognition in augmented reality applications:
Hand tracking and gesture recognition are crucial components of augmented reality (AR) applications. They involve accurately detecting and tracking hand movements in real-time to enable intuitive interaction with virtual objects. Computer vision techniques, such as depth sensing and machine learning, are employed to recognize hand gestures and gestures for actions like grabbing, swiping, or rotating virtual objects. This enhances the user experience and enables seamless integration of virtual and real-world elements in AR environments. - Facial feature tracking and emotion recognition in video analysis:
Facial feature tracking and emotion recognition play a vital role in video analysis. Facial feature tracking involves accurately detecting and tracking facial landmarks, such as eyes, nose, and mouth, over time. Emotion recognition utilizes these tracked features to analyze facial expressions and infer emotions. This technology finds applications in areas such as human-computer interaction, user experience research, and sentiment analysis for personalized and empathetic interactions.
Overall, Algorithms of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV have proven to be powerful tools for object tracking and analysis in a wide range of applications.
Real-world Applications of the Algorithms
Real-world applications of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV can be found in various fields such as computer vision, robotics, autonomous systems, and image processing.
Real-world Applications of MeanShift Algorithm:
In computer vision and image processing, it is extensively used for object tracking in surveillance systems, enabling the automated monitoring of people or objects of interest in video streams. MeanShift also plays a crucial role in video analysis and motion detection, assisting in tasks like anomaly detection, activity recognition, and behavior analysis.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Real-time Object Tracking for Robotics and Autonomous Systems | MeanShift algorithm is applied for real-time object tracking in robotics and autonomous systems, enabling tasks such as navigation and manipulation. |
| Face Tracking and Feature Detection for Emotion Recognition | Meanshift is utilized for face tracking and feature detection in video analysis, facilitating emotion recognition and analysis in various applications. |
| Microscopy Image Analysis for Cell and Bacteria Tracking | Meanshift is used for tracking cells and bacteria in microscopy images, aiding in research and analysis in the field of biology and microbiology. |
| Visual Tracking of Aircraft and Missile Targets | Meanshift algorithm finds application in visual tracking of aircraft and missile targets for military purposes, providing valuable information for defense systems. |

Real-world Applications of Camshift Algorithm:
The versatility and effectiveness of the CamShift algorithm make it a valuable tool in different domains, revolutionizing object tracking and interaction in various real-world scenarios.
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Security and Surveillance Systems | CamShift algorithm is used for real-time object tracking in video surveillance systems, enhancing automated analysis. |
| Pedestrian Detection and Tracking | CamShift aids in detecting and tracking pedestrians in autonomous vehicles, ensuring safe navigation and interaction. |
| Real-time Face Tracking and Recognition | CamShift algorithm enables accurate face tracking and recognition in video conferencing systems, enhancing user experience. |
| Medical Image Analysis for Tumor Detection and Tracking | CamShift can be utilized in medical image analysis for tumor detection and tracking, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning. |
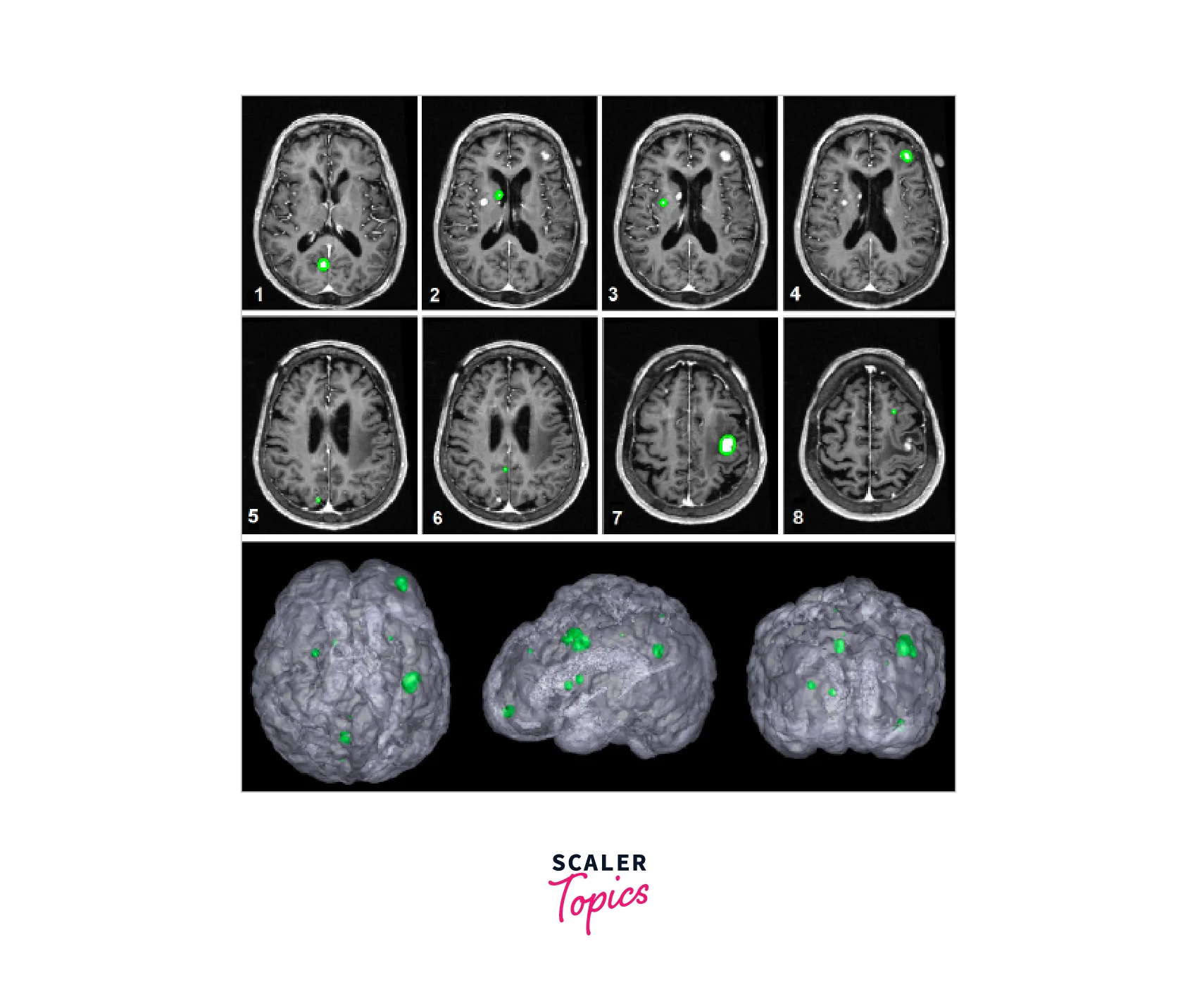
The algorithms of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV have proven to be effective in various applications and continue to be an active area of research and development in the field of computer vision and related areas.
Examples of These Algorithms Used in Computer Vision
The algorithms of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are widely used in computer vision for various applications. Here are some examples of how these algorithms are used in computer vision:
- Object tracking:
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are used for tracking objects in videos and live streams. These algorithms can be used to track moving objects such as cars, people, and animals in real time. - Pedestrian detection:
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are used to detect and track pedestrians in real time. This application is widely used in autonomous vehicles and intelligent transportation systems. - Medical image analysis:
These algorithms can be used to detect and track tumors in medical images such as MRI and CT scans. This application can assist doctors in the early detection of cancer and improve patient outcomes. - Robotics:
Both Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are used in robotics for object tracking and localization. These algorithms can be used to locate and track objects in the robot's environment, allowing the robot to interact with its surroundings. - Face detection and recognition:
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV can be used to detect and recognize faces in images and videos. This application is widely used in security and surveillance systems and can also be used for video conferencing and other applications.
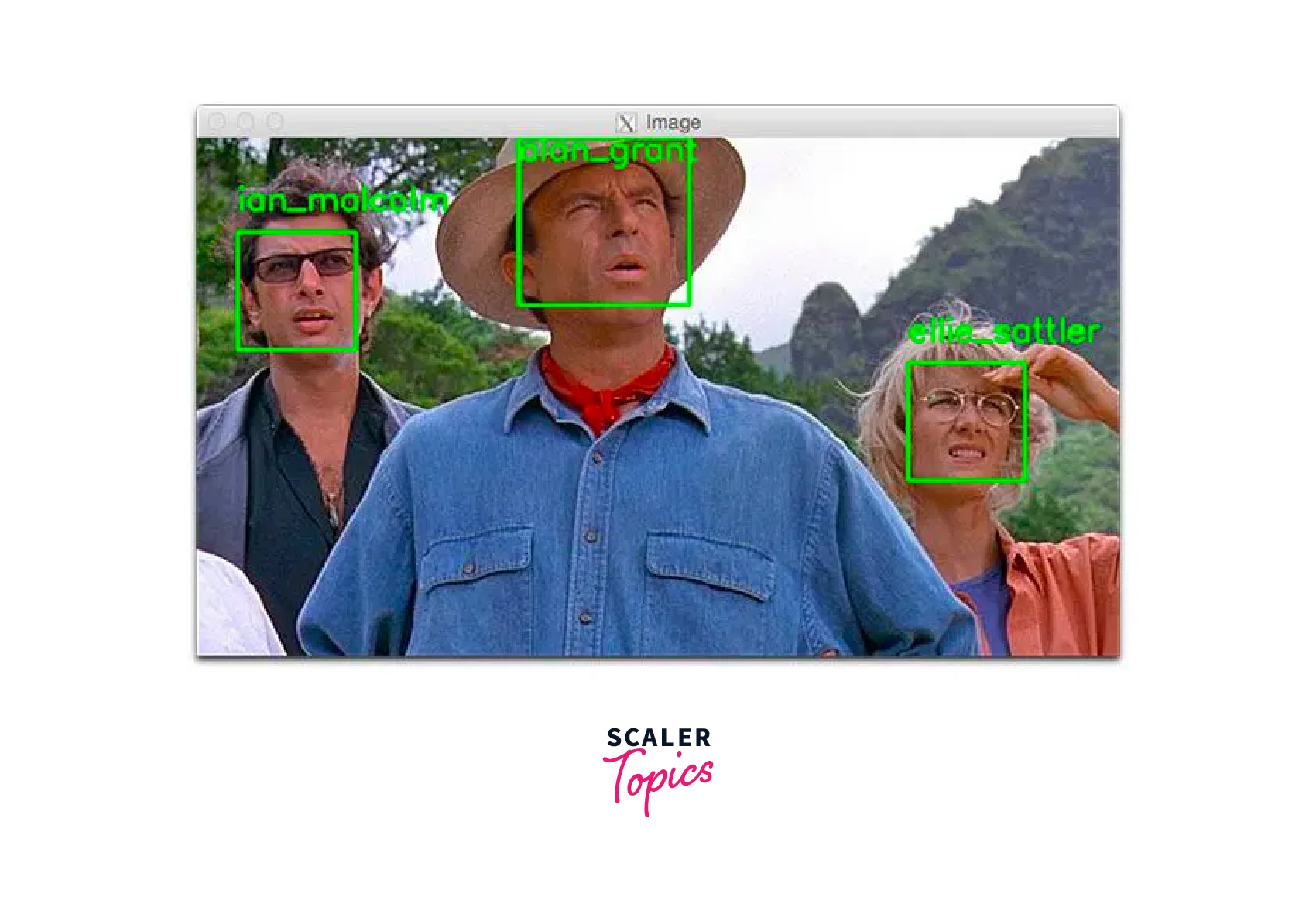
Overall, these algorithms are widely used in computer vision and have a wide range of applications in various field
Future Possibilities for The Use of These Algorithms
As computer vision continues to advance, there are many possibilities for the future use of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV. One area where these algorithms could be particularly useful is in the development of self-driving cars.
Algorithm of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV could be used to track other vehicles and objects on the road, allowing the car to avoid collisions and navigate through traffic.
Another potential application of these algorithms is in the field of robotics. MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV could be used to track objects in real-time, allowing robots to better understand their environment and interact with objects in a more intuitive way.

This could be particularly useful in manufacturing and assembly lines, where robots need to be able to locate and manipulate objects quickly and accurately.
Finally, MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV could be used in the development of augmented reality applications. By tracking objects in real-time, these algorithms could be used to create more immersive and interactive AR experiences. For example, they could be used to track a user's hand movements and allow them to interact with virtual objects in a more natural way.
Overall, the possibilities for the use of MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV algorithms in computer vision are wide-ranging and exciting. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that we will see many more applications of these algorithms in the years to come.
Conclusion
- In conclusion, MeanShift and CamShift in OpenCV are powerful algorithms that have made significant contributions to the field of computer vision.
- They have been widely used in a variety of applications, including object tracking, video surveillance, robotics, and augmented reality.
- MeanShift is a simple and effective algorithm for object tracking, but it can struggle with complex object shapes and occlusions.
- CamShift is a more sophisticated algorithm that builds on MeanShift's strengths while addressing some of its weaknesses. It can handle non-rigid object shapes and changing sizes, but it may be sensitive to changes in lighting and background.
