Merge K Sorted Linked Lists

How to merge K sorted linked lists
Given K sorted linked lists, merge them in a sorted manner and return the head of the linked list.
- Example 1:
- Output:
- Example 2:
- Output:
Explanation:
All elements from the sorted lists are merged in a sorted manner and the head of the sorted list is returned.
Constraints :
- k == lists.length
- 0 <= k <= 10^4^
- 0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
- -10^4^ <= lists[i][j] <= 10^4^
- lists[i] is sorted in ascending order.
- The sum of lists[i].length will not exceed 10^4^.
Approach 1(Simple):
- Approach: A straightforward solution is to merge two lists at a time. Merge the 1^st^ list with the 2^nd^ and store the result. While merging we select the smallest of both elements at each step. Next merge the result with the 3^rd^ list and so on. This can be better explained using the below notation:
KaTeX parse error: $ within math mode
- Implemenation:
Python implementation for merging k sorted linked lists:
- Output:
Java implementation for merging k sorted linked lists:
- Output:
C++ implementation for merging k sorted linked lists:
- Output:
- Explanation :
Merged lists in a sorted order where every element is greater than the previous element.
Complexity Analysis:
-
Time Complexity : O(N*k) where N is the number of elements to be merged. (total number of elements from all k lists given)
- Traversing every list for merging it with previously merged list and also every node is traversed for atleast once. So to sum up the time complexity would be N times the number of lists given.
-
Space Complexity : O(1) No extra space needed (as inplace merging is done)
Approach 2(Using merge sort)
- Approach:
- Traverse all the linked lists and collect the values of the nodes into an array.
- Sort and iterate over this array to get the proper value of nodes in a sorted manner.
- Create a new sorted linked list and extend it with the new nodes.
For example:
Now collect all the values of all nodes into array :
Apply merge sort over the array arr , which takes about O(N logN).
Create a new linked list and extend it with new nodes from the sorted array arr and return the head of the merge sorted linkedlist.
Output:
- Implementation: Below is the implementation of above approach
Python implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using merge sort:
- Output
Complexity Analysis
- Time complexity : O(N log N) where N is the total number of nodes.
- Collecting all the values costs O(N) time.
- A stable sorting algorithm costs O(Nlog N time.
- Iterating for creating the linked list costs O(N) time.
- Space complexity : O(N)
- Sorting cost O(N) space (depends on the algorithm you choose).
- Creating a new linked list costs O(N) space.
Also, this approach does not take advantage of the fact that each list is already in a sorted manner.
Approach 3(Using min-heap):
Min Heap : A Min-Heap is a complete binary tree in which each internal node's value is less than or equal to the values of the node's children. Heaps can be represented using arrays. When stored as array they follow the below property:
- if a node is saved at index k, its left child is stored at index 2k + 1.
- the right child is stored at index 2k + 2.
-
Approach:
- The idea is to construct a min-heap of size k and insert each list’s first node into it.
- Then pop the root node (having minimum value) from the heap add it to the output list and insert the next node from the sam list as the popped node.
- We repeat this process until the min-heap is exhausted.
- We return the head of sorted merged output.
-
Algorithm :
- Create a min-heap and insert the first element of all the ‘k’ linked lists (Min-heap size is always less than or equal to k).
- As long as the min-heap is not empty, perform the following steps:
- Remove the top element of the min-heap (which is the current minimum among all the elements in the min-heap) and add it to the result list.
- If there exists an element (in the same linked list) next to the element that popped out in the previous step, insert it into the min-heap.
- Return the head node (result list) of the merged list.
- Implementation: Below is the implementation of above approach:
Python implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using min-heap:
In python implementation we have heap as heapq, where all heap pop, heapify, and heap push all methods are available in the heapq package.
- Output
Java implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using min-heap :
- Output
C++ implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using min-heap:
- Output
- Explanation: All elements from the sorted lists are merged in a sorted manner and the head of the sorted list is returned. Merged lists in a sorted order where every element is greater than the previous element.
Complexity Analysis:
-
Time Complexity:O(N * log k) , where, ‘N’ is the total number of elements among all the linked lists, ‘k’ is the total number of lists given for merging.
- Insertion and deletion operation will be performed in min-heap for all N nodes from all lists.
- Insertion and deletion in a min-heap/priority queue require log ktime(this is the main advantage of why we use min-heap) where k is the length of min-heap
-
Space Complexity:O(k)
- The priority queue/min-heap will have at most ‘k’ number of elements at any point of time, hence the additional space required for our algorithm is O(k).
Approach 5: (Divide and Conquer)
This approach doesn’t require extra space for heap and works in O(n log k).This approach is the modification of the previous approach to reduce the space complexity and make it more efficient for merging the given k sorted linked lists.
- Approach:
First step includes the divide step
- Divide step:
- Send all k/2 lists to merge function at a time
- Merge step:
To consider smaller values and add them to create a new list/ can be done by manipulating the list itself.
- Create a pointer to return the combined list
- Add the smaller value by comparing the both lists.
- Increment pointer of the list from which value has been taken to add it to the result list.
- Return merged and sorted linked list from taken two lists.
- For all levels there are N number of nodes present
- Divide step:
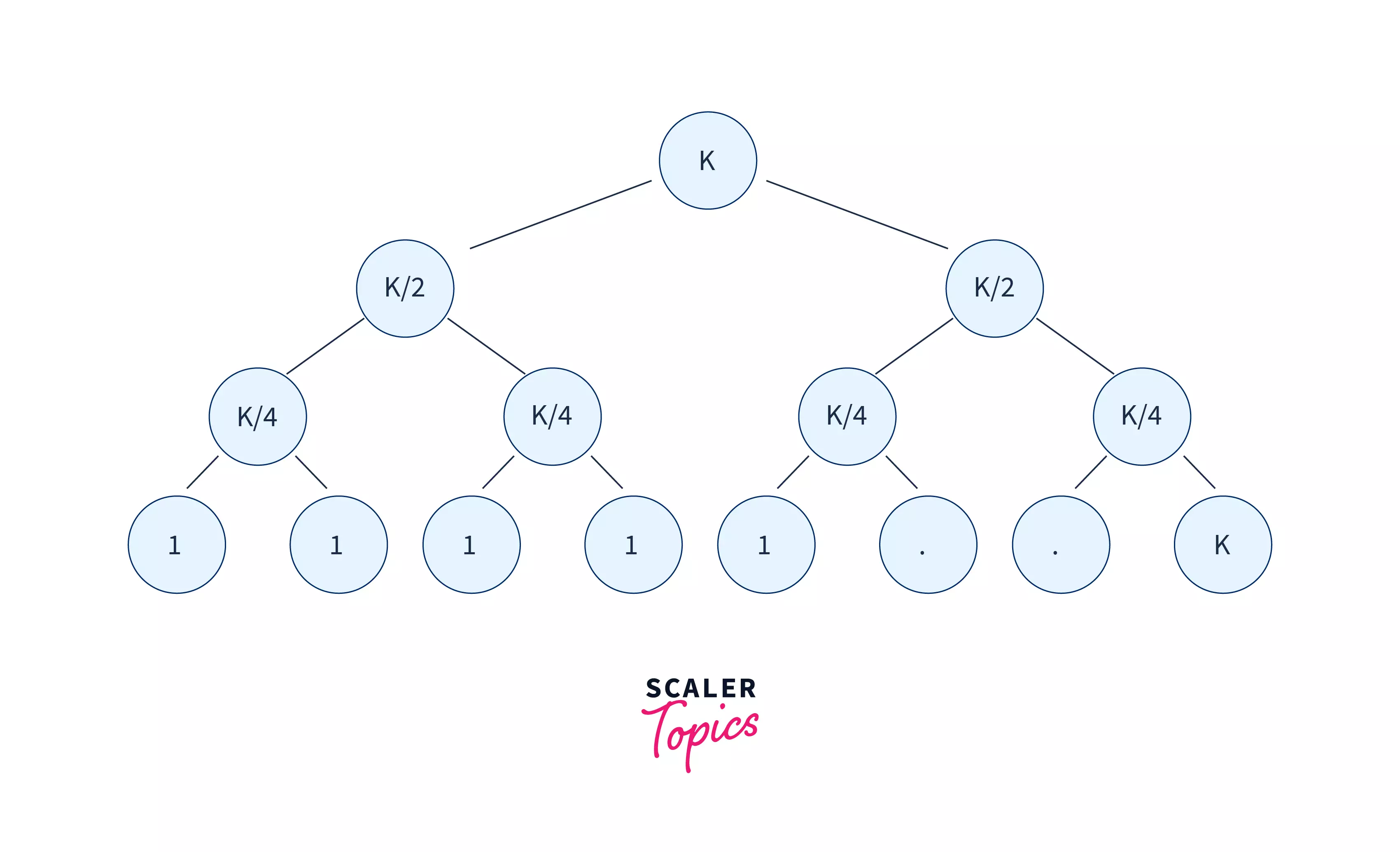
To merge the k linked lists here, we need to know how to merge two sorted linked lists.
- Algorithm:
- Pair up k lists and merge each pair.
- After the first pairing, k lists are merged into k/2 lists with an average 2N/k length, then k/4, k/8, and so on.
- Repeat this procedure until we get the final sorted linked list.
- Implementation: Below is the implementation of this approach.
Python implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using divide and conquer technique:
- Output:
Java implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using divide and conquer technique:
- Output:
C++ implementation for merging k sorted linked lists using divide and conquer technique:
- Output:
- Explanation: All elements from the sorted lists are merged in a sorted manner and the head of the sorted list is returned. Merged lists in a sorted order where every element is greater than the previous element.
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(Nlogk) where k is the number of linked lists and "N" is the total number of elements among all the linked lists.
- We can merge two sorted linked list in O(N) time where N is the total number of nodes in two lists.
- Sum up the merge process and we can get: (As outer while loop in function mergeKLists() runs log k times and every time it processes n*k elements.)
- Space Complexity: O(1)
- Auxiliary space is needed to merge the final 2 linked lists of size N/2.
- We can merge two sorted linked lists in O(1) space by appling in-place merging technique( we can manipulate the pointers itself)
Conclusion:
- We have discussed various approaches to merge K sorted linked lists in a sorted manner.
- The first approach includes merging two lists at a time and the resultant list is merged with the next list and so on, this takes a time complexity of O(N*K) and space complexity of O(1)(in-place merging is done).
- The second approach uses merge sort where all the elements are added in the array and merge sort is applied on it then a new linked list is formed this approach takes a time complexity of O(N logN) and a space complexity of O(N) which is used during merging and for creating new linked list.
- The third approach uses min-heap where the first element from all the k lists is inserted into the min-heap and the root is popped out, now the next element of the list is inserted, and so on till the size of the min-heap becomes zero, the time complexity O(N logK) and the size of min-heap is always K, so space complexity is O(K).
- Final approach uses the divide and conquer technique, in which k-lists are divided into pairs and merged, now the resultant merged list is merged with the another merged list, and so on. This is considered to be more efficient than other approaches with the time complexity O(N logN) and the space complexity O(N), it can also be done in O(1) by manipulating the pointers(in-place).
- Every approach discussed here can be done using in-place merging i.e, by manipulating the existing links, or else a new list can be created which takes an extra space of O(N) where N is the total numbers to be merged from all linked lists.
