MongoDB Repository
Overview
In the world of modern application development, data management plays a crucial role. When working with MongoDB, a popular NoSQL database, implementing a MongoDB repository can bring structure and efficiency to your data operations. A MongoDB repository is a design pattern or layer that acts as an intermediary between your application code and the MongoDB database. It encapsulates the CRUD operations. In this article, we will explore the concept of a MongoDB repository, its benefits, and how it simplifies data management.
What is MongoRepository?
An interface called MongoRepository is offered by Spring Data in the org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository package. The CrudRepository interface is further extended by the QueryByExampleExecutor and PagingAndSortingRepository interfaces. Mongodb repository offers all the tools required to build CRUD applications, and it also enables derived custom query methods.
Syntax
Description of the parameters used in the above command :
- T : Type of domain that the repository control (Typically, the name of the Entity/Model class)
- ID : The entity type of the repository's entity id (Typically, the Entity/Model class's wrapper class for your @Id is built there.)
Illustrative Example
public interface BookRepo extends MongoRepository<Book, Integer> {}
This represents the generic type parameters used by the MongoRepository interface. In this case, Book represents the entity class that defines the structure of a book, and Integer represents the type of the book's identifier.
By extending the MongoRepository interface with Book as the entity type and Integer as the identifier type, the BookRepo interface inherits various CRUD operations and additional querying capabilities from the MongoRepository. These operations include saving, updating, deleting, and finding books based on their identifiers or specific criteria.
MongoRepository Configuration
-
XML Configuration : We must carry out the settings from section 3.1 and set up the repositories in order to use custom repositories (extending the Mongodb repository):
<mongo:repositories base-package="com.baeldung.repository" mongo-template-ref="mongoTemplate"/>
-
Java Configuration : In a similar terms, we'll extend the setup we already developed in section 3.2 and include a fresh annotation:
@EnableMongoRepositories(basePackages = "com.baeldung.repository")
-
Create the Repository : After setup, we must extend the current Mongodb repository interface to establish a repository:
public interface UserRepository extends MongoRepository<User, String> { // }
Now that this UserRepository has been automatically wired, we may use Mongodb repository operations or add our own.
How to Use MongoRepository?
Insert
Let's begin with an empty database and the insert operation :
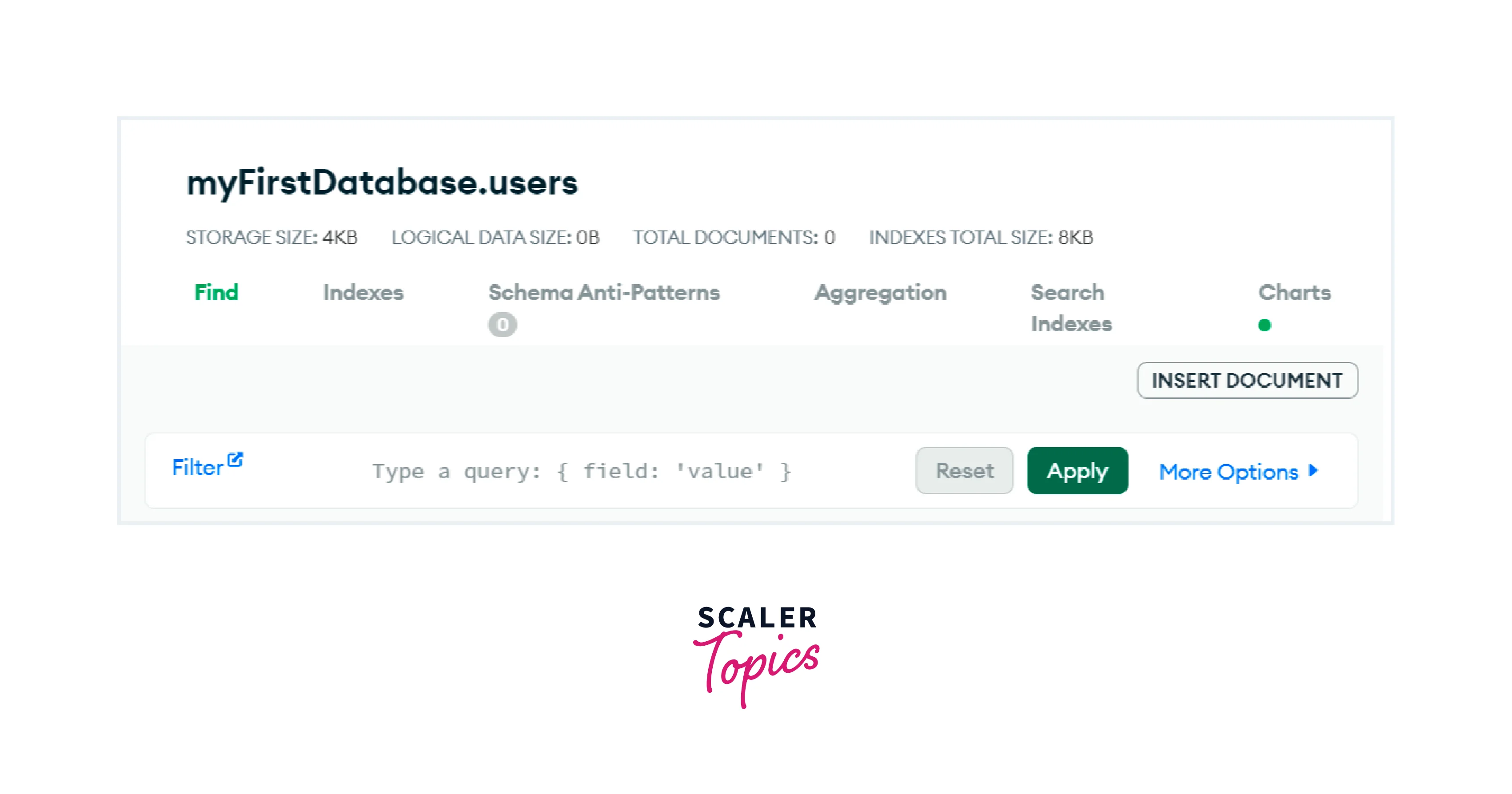
Now let us insert one user in the above database :
User Class :
UserService class :
UserRepository class :
The database will appear as follows :
Save- Insert
The save action has save-or-update semantics, meaning that it either does an update if an id is present or an insert if it is not.
Let's examine the insert, the first semantic, initially database in empty.
Now, when a new user is saved :
The database will appear as follows :
The identical action, save, will then be examined with update semantics.
Save- Update
Now let's examine save with update semantics applied to a preexisting entity :
We will update the existing user when we save it :
The database will appear as follows :
Because we utilise an object with a known _id, we can see that in this specific case, save employs the semantics of update.
Delete
The database was in the following condition before calling delete :
Now we will use the delete operation :
The database will appear as follows :
{}
FindOne
The database is in the following condition when findOne is called :
Now let's run the findOne command :
And the outcome will return the following information :
Exists
Before calling, the database is in the following condition :
Let's execute the existing command, which will naturally return true :
FindAll with Sort
Before using findAll, the database was in this condition :
Now we will use the function findAll with sort :
The outcome will be arranged in a sorted order by name :
FindAll with Pageable
Before using findAll, the database was in this condition :
Let's run findAll now while using a pagination request :
There will be just one person on the resultant users list :
Different Methods
The following list includes some of the most significant methods found inside the JpaRepository.
-
saveAll() : Every specified entity is saved using this method.
- Syntax : <S extends T> List<S> saveAll(Iterable<S> entities)
- Parameters : Entities cannot be null, nor can they contain null.
- Return Type : The stored entities are never going to be empty. The iterable that is returned will be the exact same size as the one that was supplied as an input.
- Exception Thrown : If one of the specified entities, or all of them, are null, an IllegalArgumentException is thrown.
-
insert() : Inserts the specified entity. Assumes the instance is brand-new so that insertion optimizations can be used. Use the returned instance for subsequent actions as the entity instance may have undergone substantial modification as a result of the save operation.
- Syntax : <S extends T> S insert(S entity)
- Parameters : Entities must not be null.
- Return Type : The saved entity is returned.
-
findAll() : gives back every instance of that type.
- Syntax : Iterable<T> findAll()
- Return Type : All the entities are returned.
MongoRepository Implementation
We'll create a Spring Boot application that uses a Mongodb repository to handle a Book instance. The MongoDB database is used to store the data. A RESTful controller is employed.
- Step 1 : Create a spring boot application using the IntelliJ IDEA.

-
Step 2 : Include the following dependency in your project.
- DevTools
- MongoDB
- Spring Web
- Lombok
Now lets see how the pom.xml file looks after adding the dependencies.
- Step 3 : Create three packages, and then add some classes and interfaces to each of them as shown in the figure below.
- model
- repository
- controller
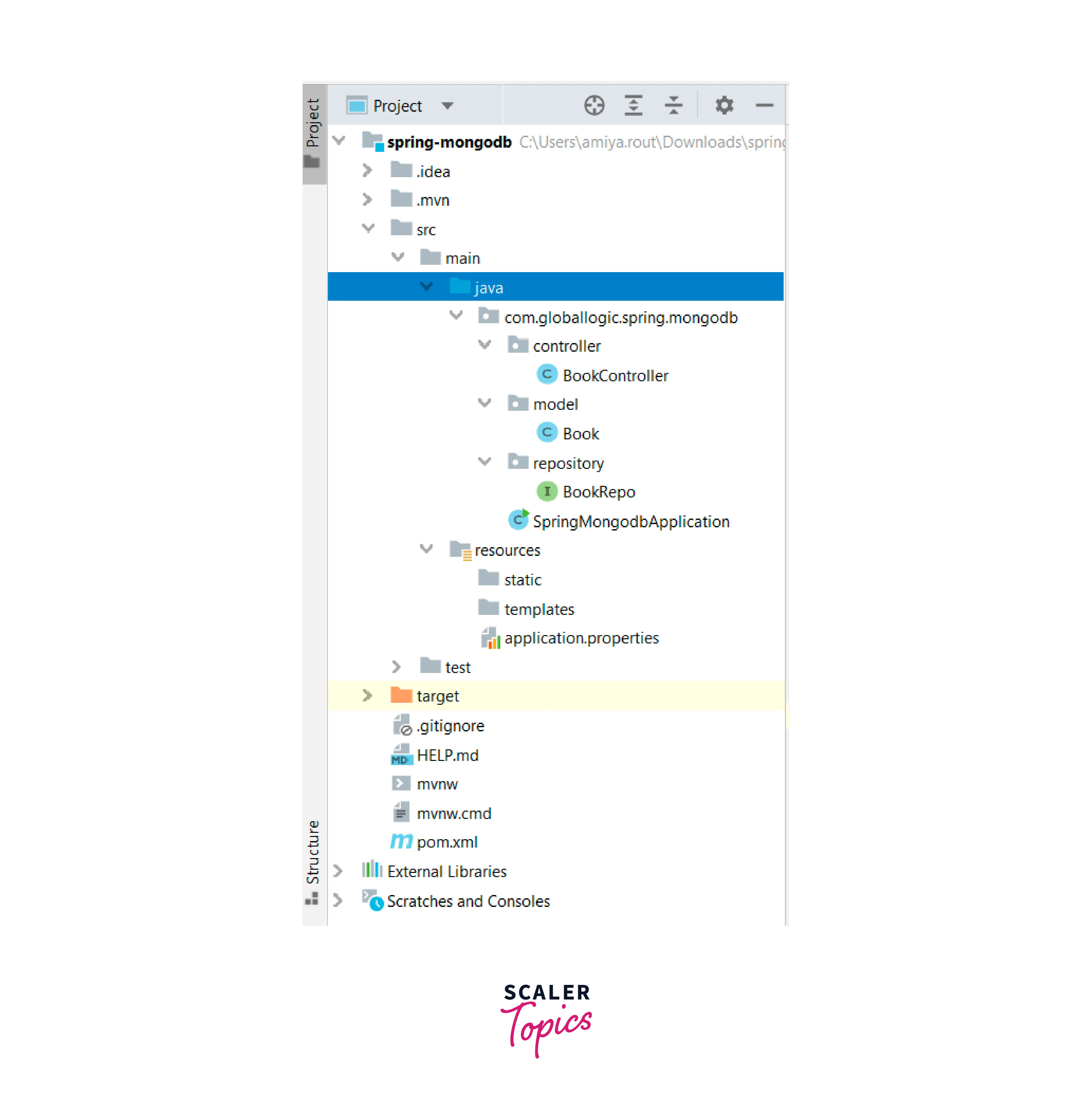
Note : Interface : Green Rounded Icon 'I' Buttons. Classes : Blue Rounded Icon 'C' Buttons.
- Step 4 : Adding a straightforward POJO class to the Book.java file. (which is inside the entity package)
- Step 5 : Make a straightforward user interface and give it the name BookRepo. As mentioned previously, this interface will extend the Mongodb repository. (inside the repository package)
- Step 6 : Create the class BookController inside the package. (inside the controller package)
- Steo 7 : The application.aattribute code can be seen below :
- Step 8 : construct a database called BookStore in your MongoDB Compass, and within of it, construct a collection called Book, as shown in the accompanying image. (inside mongoDB compass)

Run your application now, and while doing so, check out our MongoDB Compass and Postman to test the APIs.
Endpoint Testing in Postman
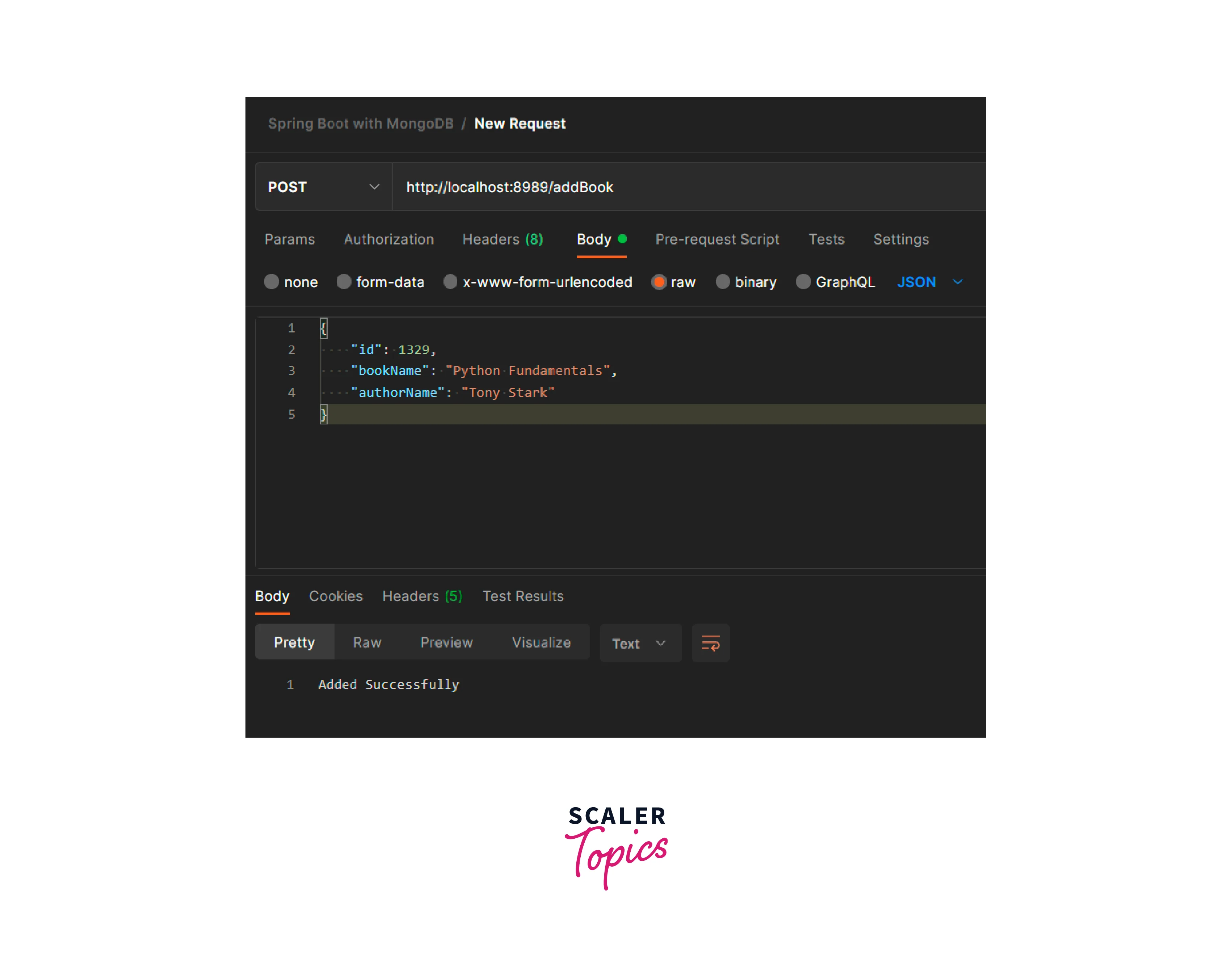
- Endpoint 1 : POST – http://localhost:8989/addBook I am sending a post request with the keys id, bookName, and authorName.
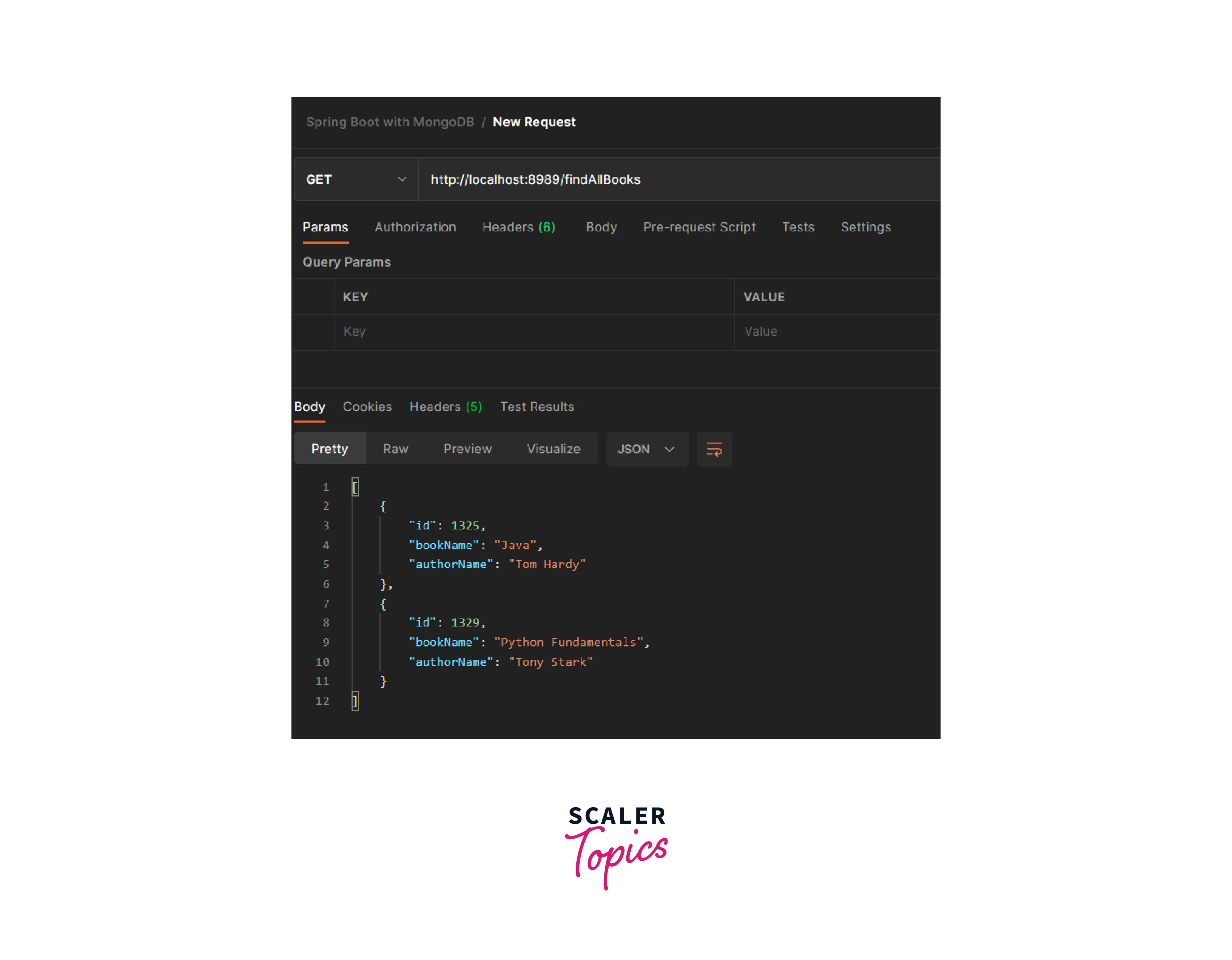
- Endpoint 2 : GET – http://localhost:8989/findAllBooks Sending a get request with 2 entries : id, bookName, authorName.
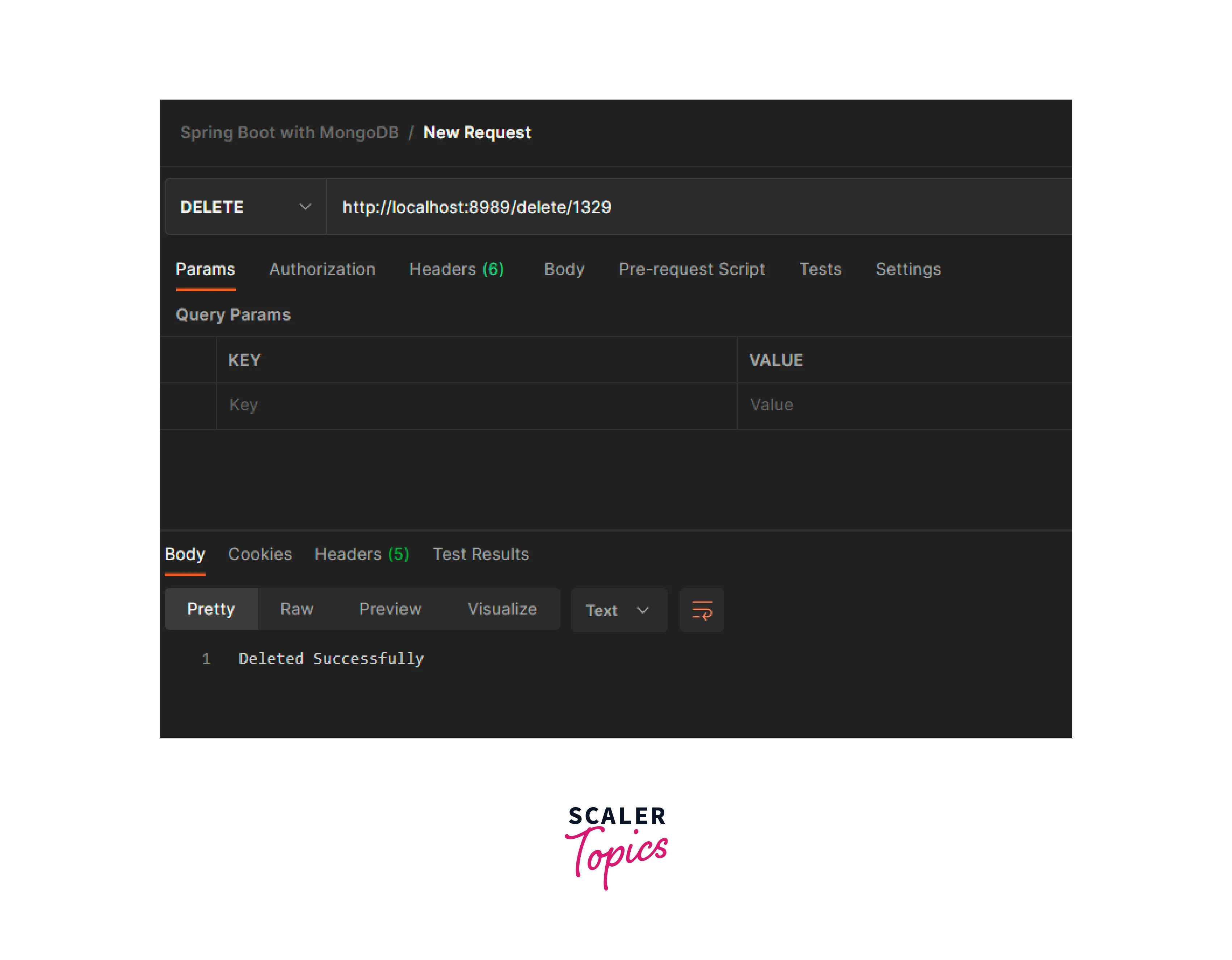
- Endpoint 3 : Delete – http://localhost:8989/findAllBooks Sending a get request with the id.
Last but not least, MongoDB Compass is represented as follows in the graphic below :

FAQs
Q. How does Spring Boot Connect to MongoDB?
A. Both the MongoTemplate class and Mongodb repository interface allow MongoDB to connect to Spring Boot. The CrudRepository interface, which has methods to carry out fundamental CRUD operations, is extended by the Mongodb repository. The MongoTemplate class may be used to create unique searches and aggregations as well as to have more precise control over query filters. The MongoTemplate class implements interfaces to facilitate aggregate, search, update, upsert, index, removal, and other actions.
Q. Which database is Best for Spring Boot?
A. The Spring Boot framework works well with both NoSQL and SQL databases. However, because of its inherent document-based structure, a NoSQL database like MongoDB provides several advantages. A more natural method to define and navigate across data is through document structure. Data that is perceived collectively remains collective. For all database operations in MongoDB, Spring additionally offers connectors like Mongodb repository and MongoTemplate.
Q. What is Spring Boot Used For?
A. The Spring Boot framework is used to build web apps that are production-ready and preconfigured. Developers are not required to develop lengthy code. The development time is greatly decreased with Spring Boot. It automatically includes widely used web application libraries like:
- spring-webmvc
- tomcat
- validation-api
Additionally, Spring Boot supports integrated servlet containers. By including the spring-boot-starter-web dependency in the pom.xml file, Java programs may be executed independently of other applications.
Conclusion
- An interface called Mongodb repository is offered by Spring Data in the org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository package.
- Mongodb repository offers all the tools required to build CRUD applications, and it also enables derived custom query methods.
- MongoDB repository syntax public interface MongoRepository<T,ID> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T,ID>, QueryByExampleExecutor<T>
- The CrudRepository interface is further extended by the QueryByExampleExecutor and PagingAndSortingRepository interfaces.
- The most significant methods found inside the JpaRepository are saveAll(), insert(), findAll().
