What is Show Index Statement In MySQL?
What is SHOW INDEX Statement in MySQL?
The MySQL SHOW INDEX statement is used for displaying data or information about the keys or indexes that we have defined within any particular table in our MySQL database. The MySQL SHOW INDEX statement can be used for retrieving data that provides the names of the indexes within the table, the columns within them, the type of index, the cardinality of indexes within the table (i.e., the number of distinct values in the index), and if the indexes are visible to the query optimizer or not.
Syntax of MySQL SHOW INDEX
The following is the syntax of MySQL SHOW INDEX statement:
Parameters
- table_name: The table_name refers to the table within the MySQL database whose index information is being retrieved.
The SHOW INDEX Query Returns the Following Fields/Information
The MySQL SHOW INDEX statement returns a set of results that include one row for each index on the table, with columns for the index name, column name, index type, cardinality, and other relevant details.
In this section, we will go through the insights of the return value of MySQL SHOW INDEX statement.
table
- The table column consists of the name of the table whose index is being accessed.
non_unique
- The non_unique column checks if the retrieved index consists of duplicates or not. If it contains duplicates then it returns 1 otherwise, it returns 0.
key_name
- The key_name column consists of an index's name. The index name within the table becomes PRIMARY if the table consists of a primary key.
seq_in_index
- The seq_in_index column consists of the sequence number of the column in the index. The seq_in_index column, by default, begins from 1.
column_name
- The column_name consists of the name of a column within the return value.
collation
- The collation column name consists of data on the sorting of columns within our index.
- The collation column consists of three types of values:
- A: It is used to represent ascending values.
- D: It is used to represent descending values.
- Null: It is used to represent values that are not sorted.
cardinality
- The cardinality column consists of an estimate of the total count of unique values within our index table.
- If the value of cardinality is higher, it signifies a substantial chance that the index is being used.
sub_part
- The sub_part column is basically therefix
- The sub_part column consists a NULL value when the table's every column is indexed.
- The sub_part column returns a the number of indexed characters When the column is partially indexed.
packed
- The packed column is used to display the way the key has been packed. If the data is not available it displays NULL.
null
- The null column checks whether the column has a blank value or not.
- It returns a blank value if the column doesn't have a NULL value.
- It returns YES if the column does have a NULL value.
index_type
- The index_type column consists of the index method's name, for example, HASH, FULLTEXT, BTREE, RTREE, FULLTEXT, etc.
comment
- The comment column consists of the information of the index that has not been described in their column.
index_comment
- The index_comment column consists of comment that has been made for any specific index whenever an index with comment attributes is created.
visible
- The visible column consists of YES or NO values.
- YES: It refers that the index being visible to the query optimizer.
- NO: It refers that the index is not visible to the query optimizer.
expression
- The expression column consists of an expression for the key part, and column_name represents NULL for the functional parts.
- The expression column consists of NULL, and column_name represents the column indexed by the key part for non-functional parts.
Filter Index Information
The information that we obtain from MySQL SHOW INDEX statement can be further filtered. As we saw in the previous section the MySQL SHOW INDEX returns a set of columns. Now what if we need any particular data among that information?
We can use the WHERE clause and MySQL SHOW INDEX to filter the information obtained.
Suppose we have a table USERS which has the following structure:
Now suppose we use the MySQL SHOW INDEX statement in the above table:
Thus the output will be the following:
Now suppose we need to filter data of indexes where the collation value is A. In this case, we will use the WHERE clause:
Thus we will get the rows for the indexes where the collation is "A". The output will look like the following:
MySQL SHOW INDEXES Examples
In this section, we will go through some examples to have a better understanding of MySQL SHOW INDEX statement. This section will use a USER table with two indexes age and gender. We will create the table using the following query:
Code:
Now we will create the indexes.
Code:
For the rest of the section, we will be using this table to go through different examples of MySQL SHOW INDEX statement.
Example 1: Displaying INDEXES of a Table
In this example, we will display the indexes of the table using the MySQL SHOW INDEX statement.
Code:
Output:
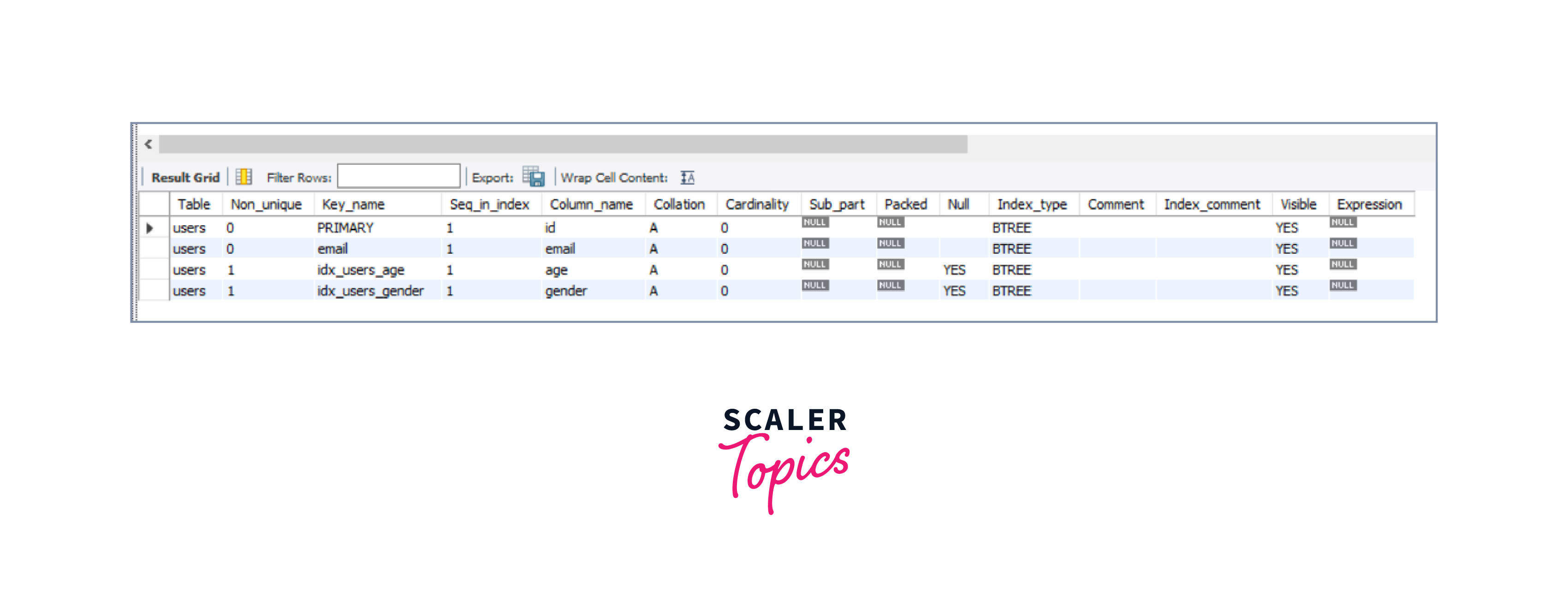
Explanation of the example:
In the above example, we have already created a table USERS with indexes within it. Now, we are supposed to display all the in our Users table. Thus we will query SHOW INDEXES FROM users which will display all the indexes in the Users table thus we will get our desired result.
Example 2: Displaying Information About a Certain Index on the Users Table:
In this example, we will display information about a certain index among indexes of the table using the MySQL SHOW INDEX statement.
Code:
Output:
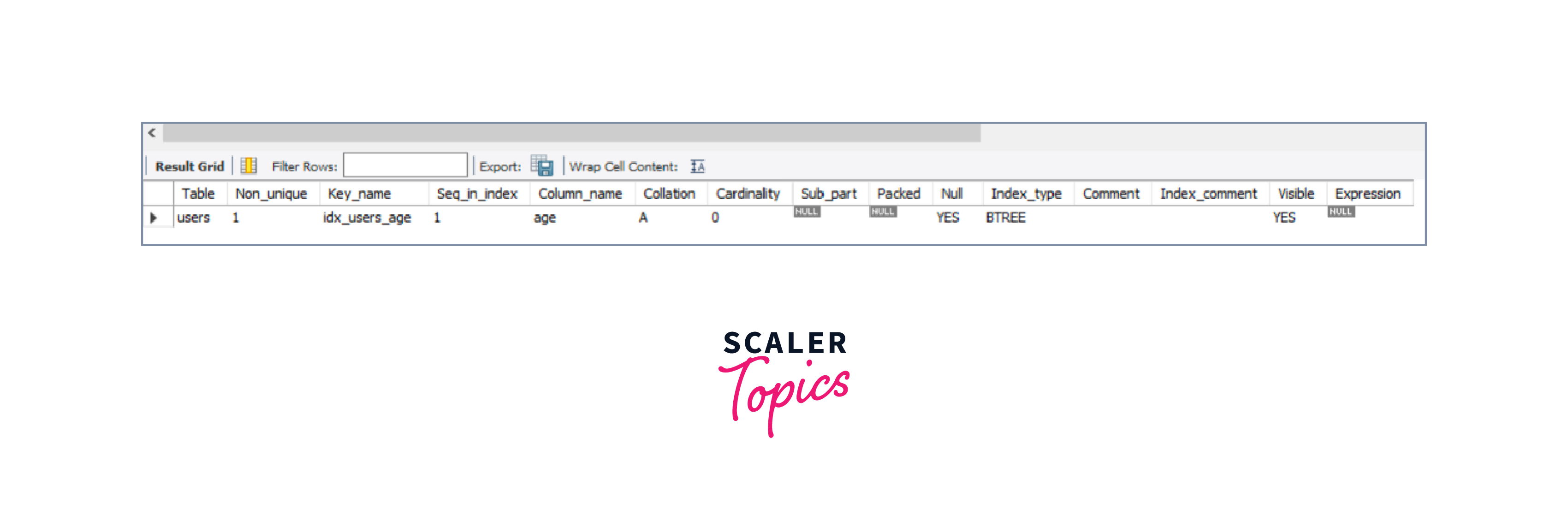
Explanation of the example:
In the above example, we have already created a table USERS with indexes within it. Now, we are supposed to display the data about a certain index within our Users table. Thus we will query SHOW INDEXES FROM users WHERE Key_name = 'idx_users_age' which will display all the data about a certain index with key_name being 'idx_users_age' in the Users table thus we will get our desired result.
Example 3: Displaying Information About the Size of All Indexes on the Users Table:
Code:
Output:
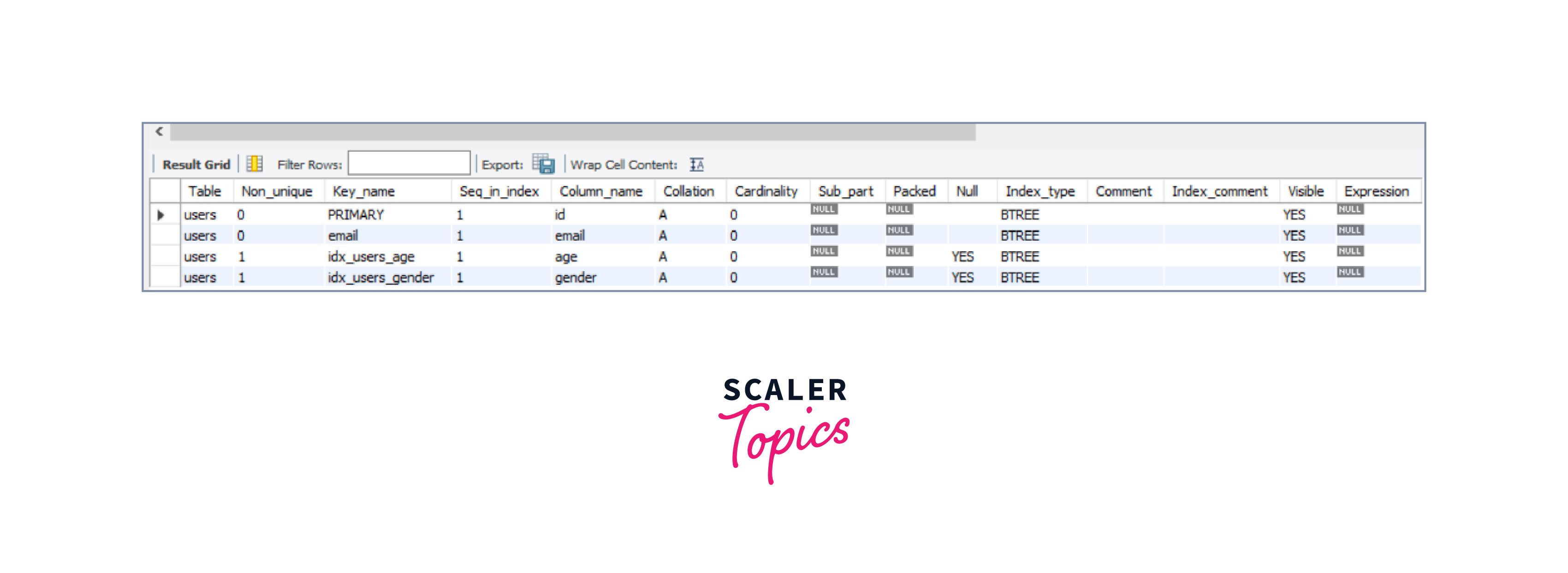
Explanation of the example:
In the above example, we have already created a table USERS with indexes within it. Now, we are supposed to display the data about the size of all indexes on the user's table. Thus we will query SHOW INDEXES FROM users WHERE Seq_in_index = 1; which will display all the data about the size of all indexes on the user's table thus we will get our desired result.
Conclusion
- The MySQL SHOW INDEX displays information on indexes within any particular table in our MySQL database.
- The MySQL SHOW INDEX statement can be used for retrieving data.
- The MySQL SHOW INDEX takes tablename as a parameter that refers to the table within the MySQL database whose index information is being retrieved.
- The MySQL SHOW INDEX statement returns a set of results that include one row for each index on the table, with different columns.
- We can use the WHERE clause and the MySQL SHOW INDEX to filter the information obtained.
