New Technology in Computer Science in 2024
In 2024, Computer Science is witnessing groundbreaking advancements, including quantum computing reaching practical applications, enabling unprecedented processing speeds. Artificial Intelligence evolves with enhanced natural language understanding and context-aware systems. Edge computing has become more prevalent, facilitating real-time data processing at the source. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) experiences see substantial improvements, reshaping industries. Additionally, cybersecurity measures incorporate advanced machine learning algorithms for more robust threat detection and prevention.
Latest Computer Science Trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
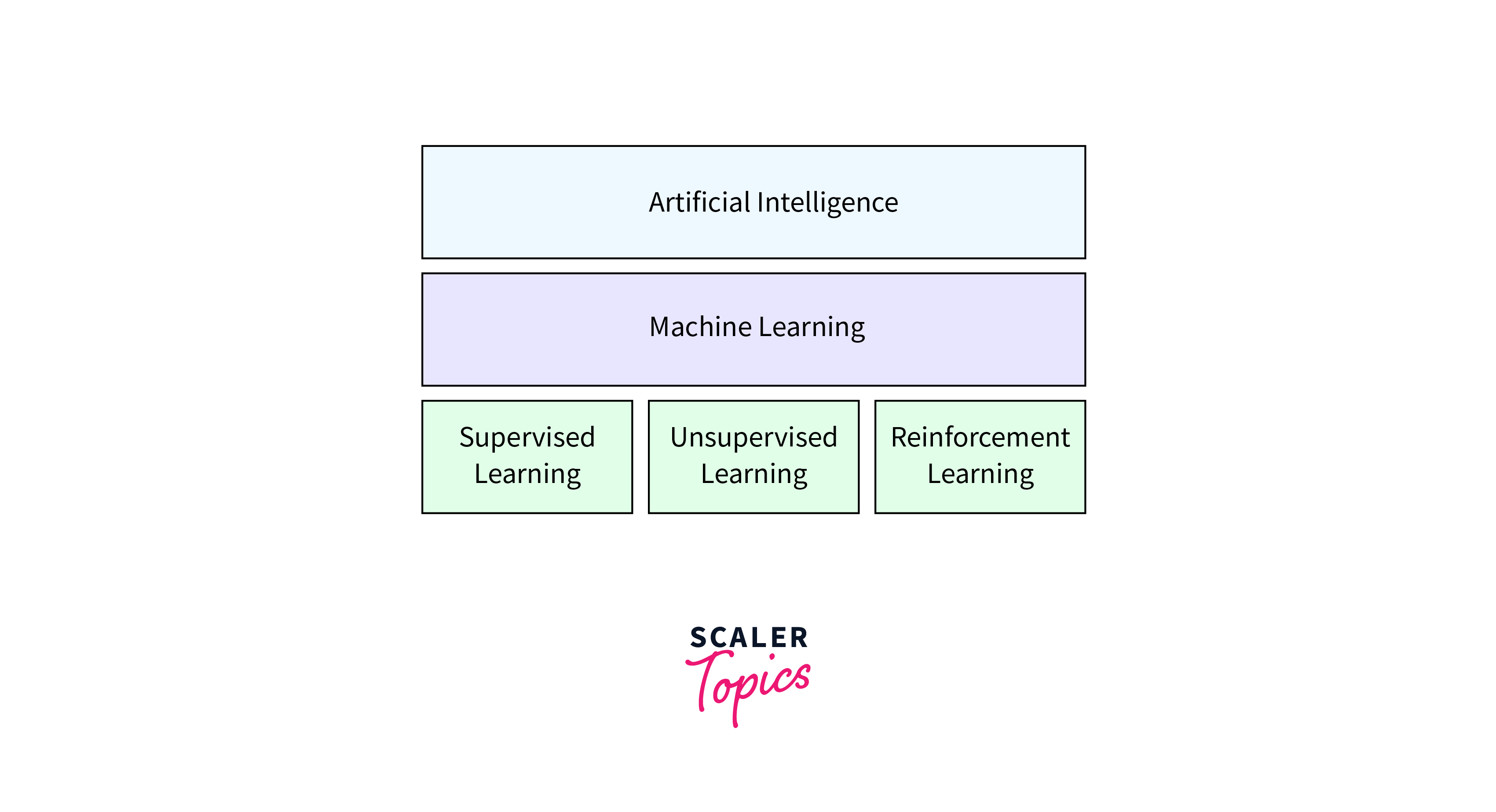
In the phase of new technology in computer science, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as a trailblazer, consistently leading computer science trends with remarkable progress in areas such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. AI's transformative impact extends across diverse sectors, including healthcare, finance, and the burgeoning field of autonomous vehicles. Striking a balance between innovation and responsibility, the industry places a strong emphasis on developing ethical AI, focusing on interpretability and robustness to ensure the conscientious deployment of AI technologies.
Initiatives such as the Fair AI Principles, which advocate for fairness, accountability, transparency, and explainability in AI systems, are gaining traction. Organizations are increasingly adopting frameworks like Ethical AI Guidelines and establishing policies that prioritize user privacy, data security, and the prevention of algorithmic bias. These measures aim to create a solid foundation for the ethical development and deployment of AI technologies.
The recent advancements in language understanding, exemplified by models such as GPT-4 and the evolution of transformer models, underscore the ever-expanding capabilities of AI in comprehending and generating human-like language. Additionally, the exploration of reinforcement learning is pushing the boundaries of AI applications, particularly in the realm of autonomous decision-making, contributing to the development of more sophisticated and adaptable systems.
Collaboration emerges as a pivotal trend, driving innovation and ethical considerations in the AI landscape. One notable example is the collaboration between tech companies, research institutions, and ethicists to develop a unified approach to ethical AI. Initiatives like the Partnership on AI bring together diverse stakeholders to address challenges associated with AI's societal impact. Such collaborations foster an exchange of ideas, promote transparency, and help in formulating guidelines that align with ethical principles.
In the healthcare sector, partnerships between AI developers and medical professionals are yielding ethical AI solutions that prioritize patient well-being, data privacy, and compliance with medical standards. Financial institutions are collaborating with AI experts to ensure the responsible use of algorithms in decision-making processes, preventing discriminatory outcomes.
As AI continues to evolve, its interdisciplinary nature fosters collaboration across fields, underlining its pivotal role in addressing intricate problems across various domains. Through specific ethical frameworks and collaborative efforts, the AI community can ensure that innovation is coupled with responsible practices, making a positive impact on society.
Edge Computing
Edge Computing has emerged prominently in response to the escalating demand for low-latency processing. This innovative paradigm strategically decentralizes computing power, relocating it closer to the data source. Edge devices, positioned at the periphery of the network, autonomously process information locally, significantly enhancing real-time data analysis for diverse applications such as IoT, AR/VR, and autonomous systems.
The ongoing drive towards efficient edge AI solutions is fundamentally reshaping the landscape of data handling. This transformative shift ensures not only faster response times but also diminishes reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure. As the adoption of edge computing accelerates, security concerns and resource optimization become pivotal aspects guiding the evolution of innovative edge computing architectures. Striking a delicate balance between performance and reliability, these architectures define the trajectory of a more responsive and decentralized computational future.
Quantum Computing
Quantum Computing stands on the cusp of a profound revolution, poised to reshape the landscape of computational power. Ongoing strides in quantum processors, advancements in qubit stability, and the pursuit of effective error correction signify significant progress towards the practical implementation of quantum computing applications. The milestone of achieving quantum supremacy demonstrates the potential to solve complex problems exponentially faster than classical computers, unlocking new frontiers in scientific and industrial capabilities.
Exploration of quantum algorithms, such as Shor's and Grover's, holds promise for transformative applications in areas like cryptography and tackling intricate optimization challenges. Despite formidable obstacles related to scaling and maintaining quantum coherence, the global commitment to research and development is intensifying, with substantial investments from both private companies and governments. The realization of quantum supremacy marks the dawn of a new era in computation, promising groundbreaking advancements with far-reaching implications across scientific and industrial domains.
Robotics
In the realm of new technology in computer science innovation, the strides in Robotics are not just transforming but revolutionizing industries. The breakthroughs encompass not only advancements in autonomous navigation and human-robot interaction but also delve into the intricate domain of swarm robotics. The integration of cutting-edge soft robotics and ingenious biomimicry techniques is propelling the development of robots endowed with unparalleled flexibility and adaptability.
This transformative journey extends further by incorporating the power of machine learning and computer vision into the robotics landscape. This integration empowers robots not just to operate but to thrive in dynamic environments by learning, perceiving their surroundings, and making intelligent decisions.
The applications of Robotics span a myriad of sectors, from revolutionizing manufacturing and optimizing logistics to enhancing healthcare services and contributing to the exploration of outer space. The versatility and transformative impact of Robotics underscore their role as indispensable in new technology in computer science, continuously shaping and advancing various industries.
Cybersecurity
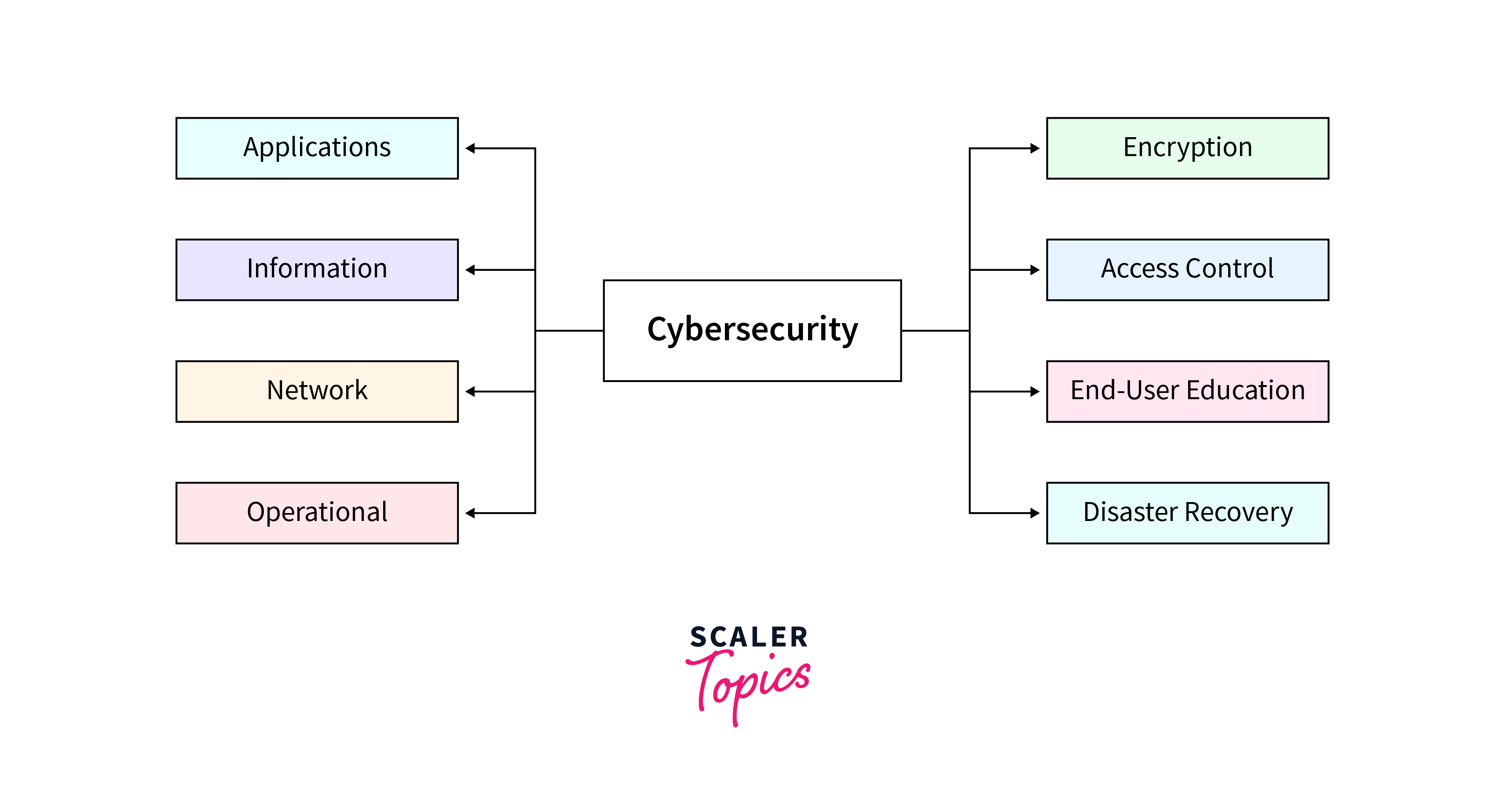
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, cybersecurity assumes a paramount role in safeguarding sensitive information and critical infrastructure. The emphasis on security is not just a necessity but an ongoing commitment to fortify defenses against evolving cyber threats. This commitment is reflected in the implementation of robust zero-trust architectures, strategically leveraging threat intelligence, and deploying cutting-edge AI-driven security measures.
Technological innovations play pivotal roles in enhancing data protection. End-to-end encryption and the secure and transparent nature of blockchain technologies are instrumental in fortifying the defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. As the digital ecosystem continues to expand with the proliferation of technologies like cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), securing interconnected systems becomes an increasingly complex challenge.
Organizations recognize the significance of proactive cybersecurity measures and invest significantly in rigorous approaches such as penetration testing and vulnerability assessments. These measures, coupled with continuous adaptation to emerging threats, form the cornerstone of a robust cybersecurity strategy. In an environment marked by sophisticated cyber threats, organizations must remain vigilant, adaptive, and proactive in ensuring the resilience of their digital infrastructure.
Bioinformatics
In the dynamic field of Bioinformatics, revolutionary technologies are orchestrating a profound transformation in biological research and healthcare. The fusion of computational biology, data analytics, and machine learning is not merely enhancing but reshaping the landscape of deciphering complex biological data. This transformative journey unfolds through groundbreaking advances in genomic sequencing, precise protein structure prediction, and the burgeoning realm of personalized medicine.
Bioinformatics is at the forefront of addressing critical challenges in understanding diseases, expediting drug discovery processes, and advancing precision medicine. The collaborative synergy between computer scientists and life scientists is instrumental in navigating the intricate intersection of computational analysis and biological insights. As the global demand for personalized healthcare continues to rise, Bioinformatics emerges as a pioneering force, consistently propelling innovations that seamlessly bridge the gap between computational prowess and profound biological understanding.
Data Science
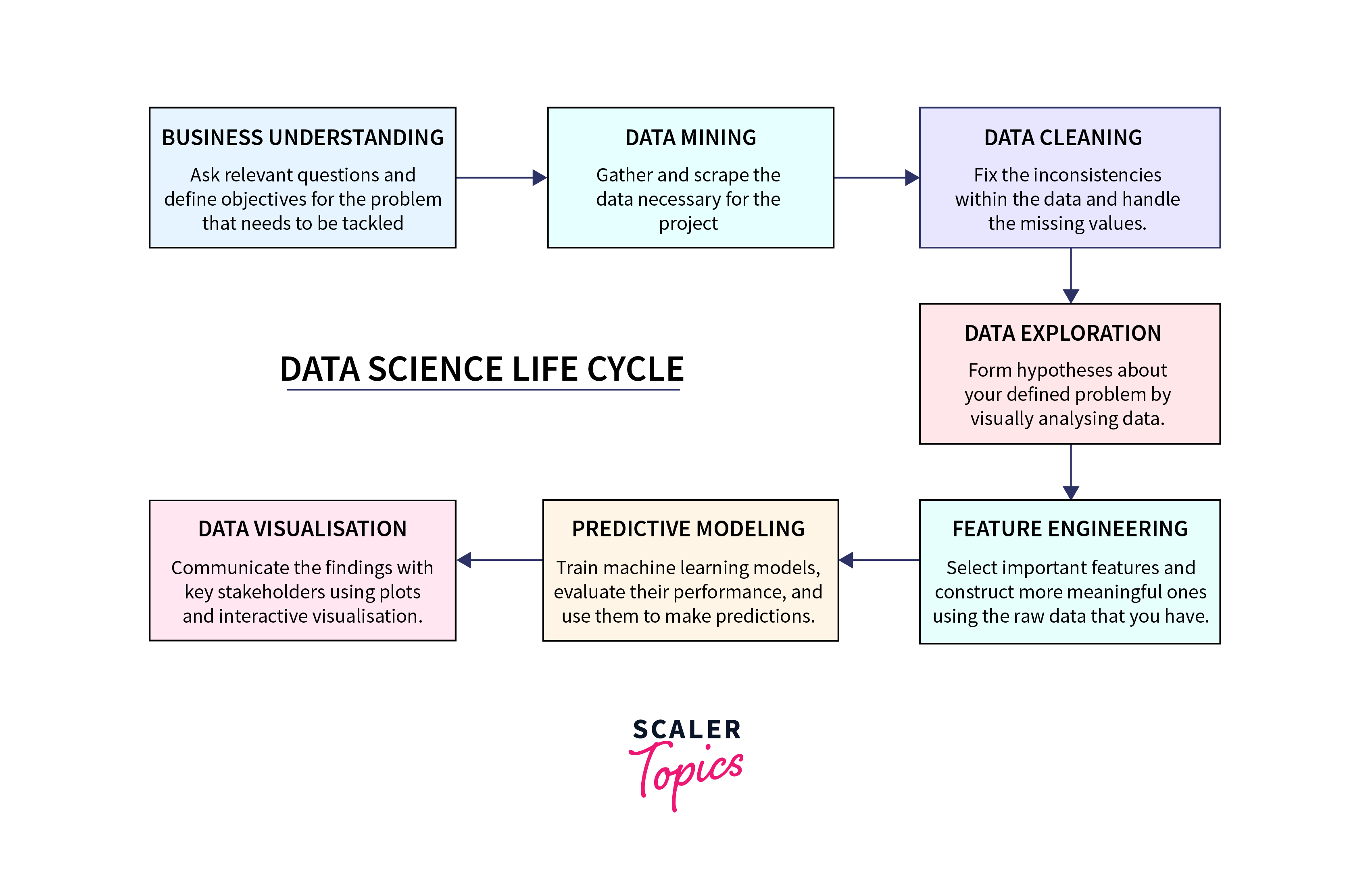
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, Data Science stands resolute as an indispensable cornerstone across various industries. Its impact is magnified through the adept utilization of advanced statistical techniques, machine learning, and the profound capabilities of big data analytics. Organizations, recognizing the transformative power of data, increasingly lean on data scientists to not only extract valuable insights but also to serve as architects of informed decision-making and drivers of innovation.
The expansive scope of Data Science encompasses the entire data lifecycle—from meticulous data collection to precise data cleaning and insightful data analysis. A crucial emphasis is placed on the art of storytelling through data visualization, enabling effective communication of complex findings. The integration of artificial intelligence and automation further amplifies the discipline's capabilities, fostering advancements in predictive modelling** and pattern recognition.
As businesses embark on the journey to become more data-driven, Data Science assumes a pivotal role, dynamically evolving to meet the growing demands of the digital era. Its multifaceted contributions continue to shape the future of information discovery and utilization across diverse sectors, perpetuating a data-driven paradigm that propels innovation and excellence.
Full Stack Development
Full Stack Development remains a dynamic and highly sought-after skill set, requiring proficiency in both frontend and backend technologies. Adept full-stack developers command expertise in various programming languages, frameworks, and databases, empowering them to construct end-to-end web applications. This trend expands beyond traditional web development, encompassing proficiency in emerging areas such as cloud computing, containerization, and microservices architecture.
In the pursuit of comprehensive solutions, full-stack developers play a pivotal role in crafting seamless, interactive, and scalable applications that meet evolving business needs. The ever-changing landscape of technology frameworks and tools necessitates full-stack developers to maintain adaptability, with continuous learning serving as an integral aspect of mastering this versatile and multifaceted discipline.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
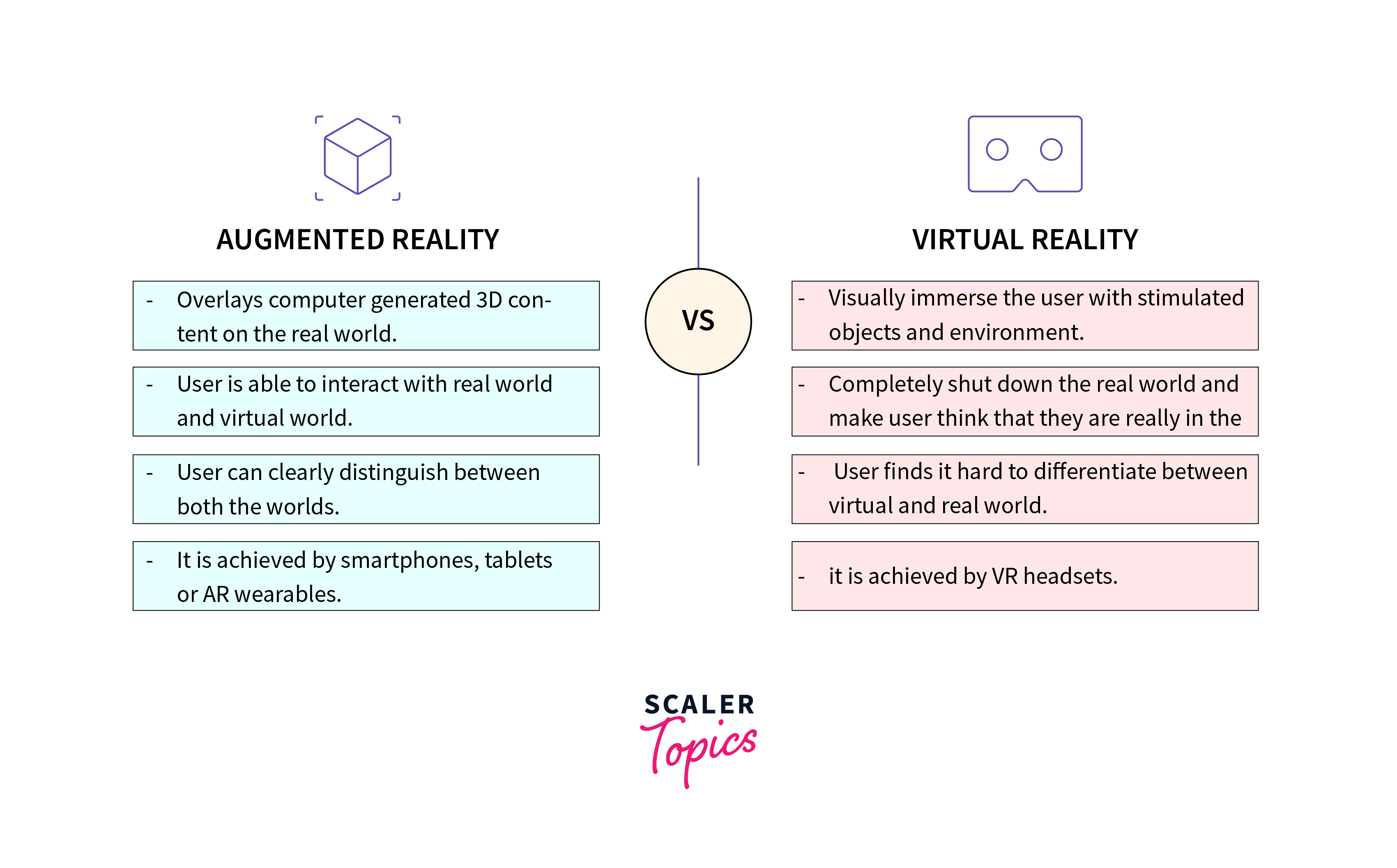
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) have emerged as transformative forces, reshaping how we look at and interact with the digital and physical worlds. VR immerses users in entirely virtual environments, providing a heightened sense of presence and engagement. On the other hand, AR overlays digital elements in the real world, improving the user's perception by blending virtual and physical information seamlessly. Applications of VR and AR span diverse sectors, from entertainment and gaming to education, healthcare, and enterprise. The ongoing evolution of hardware, software, and content creation tools is enhancing the realism and accessibility of these technologies, making them integral for interactive simulations, immersive storytelling, and practical applications that redefine user experiences.
5G
The advent of 5G technology represents a monumental leap in the evolution of wireless communication. Beyond its role in delivering faster mobile internet, 5G introduces unparalleled speed, low latency, and the capability for massive device connectivity. This transformative technology empowers a diverse array of applications, extending from enhanced mobile broadband to the vast realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), smart cities, and industrial automation.
The remarkable combination of high bandwidth and low latency inherent in 5G facilitates real-time communication, paving the way for groundbreaking innovations. These include immersive augmented reality experiences, the seamless addition of autonomous vehicles into our daily lives, and the delivery of remote healthcare services with unprecedented efficiency. As 5G networks continue their expansive global deployment, they stand as the backbone for the next generation of technological advancements, ushering in a new era characterized by enhanced connectivity and boundless possibilities.
Automation
Automation stands as a trailblazer in technological advancement, harnessing cutting-edge tools to revolutionize traditional processes across various industries. From robotic process automation (RPA) to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), organizations are fervently adopting automated solutions to optimize workflows and elevate operational efficiency. The seamless integration of smart sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) devices enables real-time monitoring and control, orchestrating transformative changes in sectors such as manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare.
As industries increasingly embrace automation, a paramount focus is directed towards upskilling the workforce. This ensures effective collaboration with automated systems, fostering a harmonious blend of human expertise and the continuous evolution of technological advancements.
Blockchain
In the realm of digital innovation, blockchain technology stands out as a decentralized and secure system for managing and verifying transactions. Recognized for its distributed ledger and immutable nature, blockchain introduces a paradigm shift by fostering transparency and trust in various domains. While initially associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, blockchain's applications extend far beyond finance.
It finds utility in supply chain management, healthcare, and more. The concept of smart contracts automates and enforces agreements, reducing reliance on intermediaries. As blockchain matures, ongoing developments focus on addressing scalability challenges and exploring new consensus mechanisms, paving the way for innovative solutions that redefine how data is stored, verified, and transacted.
Voice Technology
Voice Technology has evolved into a pervasive and transformative force, reshaping the way we interact with digital systems. With advancements in speech recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and voice synthesis, this technology enables seamless communication between humans and machines.
From virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to voice-enabled applications, voice interfaces are becoming integral in smart homes, automobiles, and consumer electronics. The focus on improving accuracy, context awareness, and multilingual capabilities drives ongoing research, making voice technology a cornerstone in the quest for more intuitive and accessible human-computer interaction.
IoT (Internet of Things)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a revolutionary paradigm that connects physical devices, allowing them to communicate and share data. IoT encompasses a vast ecosystem of devices, from sensors and actuators to everyday objects, creating a network of interconnected entities. This technology has far-reaching implications, influencing sectors such as healthcare, agriculture, and smart cities.
Sensor networks, data analytics, and machine learning algorithms play crucial roles in extracting valuable insights from the massive amounts of data generated by IoT devices. Security remains a paramount concern, leading to the development of robust IoT security protocols and frameworks to safeguard privacy and data integrity.
Serverless Computing
Serverless Computing represents a paradigm shift in cloud computing, eliminating the need for managing infrastructure. In a serverless architecture, developers focus solely on code, and the cloud provider handles the underlying infrastructure automatically. This model offers benefits such as cost efficiency, scalability, and rapid deployment.
Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) platforms, like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions, exemplify serverless computing, enabling developers to build and deploy applications without the complexities of server management. As organizations increasingly embrace serverless computing, it fosters a more agile and cost-effective approach to application development, driving innovation in the cloud computing landscape.
Drones
Drones, once predominantly associated with military applications, have evolved into indispensable tools across diverse industries, driven by advancements in technology. Equipped with sophisticated components like GPS technology, sensors, and high-resolution cameras, drones are transforming various sectors. In agriculture, drones enable precision farming, providing farmers with real-time data for crop health monitoring, yield optimization, and precise pesticide distribution. In logistics, automated drone deliveries are streamlining supply chain operations, enhancing efficiency and reducing delivery times. Additionally, drones play a pivotal role in disaster response, conducting aerial surveys, and aiding search and rescue missions.
As technology progresses, the autonomy of drones is increasing through the integration of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered features. AI-driven navigation and obstacle avoidance enhance their capabilities, making them more adaptable to complex environments. The applications of drones extend beyond traditional industries, finding utility in filmmaking, infrastructure inspection, and environmental monitoring. The continuous innovation in drone technology positions them as versatile tools with profound implications for various sectors.
Intelligent Apps
The emergence of Intelligent Apps signifies a paradigm shift in software development, leveraging advanced technologies to create applications that learn and adapt based on user interactions and data insights. These apps integrate cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to enhance functionality and provide personalized experiences.
Personalization is a hallmark of intelligent apps, influencing recommendations in e-commerce, content curation, and user interactions with virtual assistants. Through sophisticated algorithms, these apps analyze user behaviour, preferences, and patterns to offer tailored and context-aware services. The integration of voice recognition and natural language processing (NLP) further enhances user interactions, making the user experience more intuitive and responsive.
Continuous refinement of algorithms ensures that intelligent apps evolve, delivering increasingly accurate predictions and insights. This adaptability positions them as dynamic tools that cater to the evolving needs and preferences of users, contributing to a more efficient and personalized digital experience across various domains.
NFT (Non-Fungible Token)
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, have emerged as a transformative force in the digital economy, utilizing the secure and transparent nature of blockchain technology. NFTs represent unique, indivisible digital assets, providing a tangible form of ownership and authenticity for digital content. Each NFT is uniquely identifiable, and its ownership history is immutably recorded on the blockchain, ensuring digital scarcity. This innovation has disrupted traditional concepts of ownership in the virtual space.
NFTs find applications across various domains, from digital art and music to virtual real estate and in-game items. Artists and creators tokenize their work, enabling direct engagement with global audiences and unlocking new revenue streams through mechanisms like smart contracts that automate royalties. Buyers, in turn, gain provable ownership and a direct stake in the digital content they acquire. The NFT ecosystem is dynamic, fostering creativity, collaboration, and the exploration of novel business models.
Big Data Analytics
In the era of data abundance, Big Data Analytics plays a pivotal role in extracting meaningful insights from large and complex datasets. Businesses leverage advanced analytics tools, encompassing techniques such as data warehousing, machine learning algorithms, and predictive modelling, to transform raw data into actionable intelligence. This process enables organizations to identify patterns, trends, and correlations, empowering data-driven decision-making.
Big data analytics has profound implications across industries. In healthcare, it aids in disease prediction and personalized medicine. In finance, it enhances risk management and fraud detection. The insights derived from big data analytics optimize supply chains, improve customer experiences, and inform strategic planning. As data volumes continue to skyrocket, the demand for skilled professionals versed in big data analytics remains high, driving ongoing innovation and efficiency improvements in diverse sectors.
Computer Network
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, computer networks play a foundational role, serving as the backbone for communication and connectivity. A computer network is a complex system of interconnected devices, facilitate the seamless exchange of data and resources. These networks can range from local area networks (LANs) within a confined space to expansive global systems like the Internet. Key components of a computer network include routers, switches, and protocols that govern data transmission. The advent of 5G technology further enhances network capabilities, offering unprecedented speed and low latency. The concept of network security is paramount, involving measures such as firewalls and encryption to protect against cyber threats.
As new technology in computer science advances, the implementation of cloud computing transforms traditional network architectures, enabling scalable and flexible infrastructure. The emergence of edge computing brings computing resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time processing. In the context of emerging technologies, the deployment of IPv6 addresses the limitations of IPv4, ensuring continued growth in the number of connected devices. The evolution of software-defined networking (SDN) introduces programmability and automation, revolutionizing network management and configuration.
Navigating a Career in Advanced Technologies
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Education: Acquire a strong foundation in mathematics, programming, and machine learning concepts through formal education or online courses.
- Projects: Build a robust portfolio showcasing AI projects, demonstrating practical skills in areas like natural language processing or computer vision.
- Specialization: Explore specific AI domains such as robotics, healthcare, or financ to develop expertise in niche areas.
-
Edge Computing:
- Learn Cloud Technologies: Acquire proficiency in cloud computing platforms, as edge computing often complements cloud services.
- Networking Knowledge: Develop a solid understanding of networking principles to optimize low-latency processing.
- Hands-On Experience: Engage in projects that involve deploying applications at the edge, utilizing frameworks like TensorFlow Lite or AWS Greengrass.
-
Quantum Computing:
- Mathematics Proficiency: Strengthen your foundation in linear algebra, calculus, and complex numbers.
- Quantum Programming: Learn languages like Qiskit or Cirq for quantum programming and experiment with quantum algorithms.
- Stay Updated: Given the rapid evolution, stay informed about advancements through academic research and industry developments.
-
Robotics:
- Educational Background: Pursue degrees in robotics, mechatronics, or related fields to build a strong theoretical foundation.
- Programming Skills: Develop proficiency in programming languages like Python and C++ for robot control.
- Hands-On Experience: Engage in hands-on projects, participate in robotics competitions, and contribute to open-source robotics projects.
-
Cybersecurity:
- Cybersecurity Certifications: Obtain certifications like CISSP, CEH, or CompTIA Security+ to validate your expertise.
- Networking: Build a network within the cybersecurity community through conferences, online forums, and networking events.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated on the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and security solutions through ongoing education.
-
Bioinformatics:
- Biological Sciences Foundation: A background in biology, biochemistry, or related fields is beneficial.
- Computational Skills: Develop proficiency in programming languages like Python and R for data analysis.
- Collaboration: Engage in interdisciplinary collaboration, bridging biological insights with computational expertise.
-
Data Science:
- Educational Background: Pursue degrees in data science, statistics, or related fields.
- Technical Skills: Master tools and languages like Python, R, SQL, and popular data science libraries.
- Real-World Projects: Showcase your skills through practical projects, emphasizing the ability to derive actionable insights.
-
Full Stack Development:
- Learn Frontend and Backend Technologies: Acquire proficiency in frontend technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and backend technologies (Node.js, Python, Ruby).
- Frameworks and Libraries: Familiarize yourself with popular frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue for frontend, and Express, Django, or Ruby on Rails for backend.
- Version Control: Learn version control systems like Git and collaborate on projects hosted on platforms like GitHub.
-
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality:
- Education: Pursue degrees or certifications in computer graphics, game development, or related fields.
- Programming Skills: Learn languages like C#, Unity, or Unreal Engine for VR/AR application development.
- Portfolio Development: Create a portfolio showcasing VR/AR projects, emphasizing creativity and user experience.
-
5G:
- Telecommunications Background: A background in telecommunications, electrical engineering, or related fields is advantageous.
- Certifications: Obtain certifications in 5G technologies to validate your expertise.
- Keep Abreast of Standards: Stay updated on evolving 5G standards and participate in industry forums and conferences.
-
Automation:
- Engineering or IT Background: Pursue degrees in engineering or IT disciplines with a focus on automation and control systems.
- Programming Skills: Acquire proficiency in languages like Python, Java, or C++ for automation scripting.
- Hands-On Projects: Engage in real-world automation projects to demonstrate practical skills.
-
Blockchain:
- Educational Background: A background in computer science, cryptography, or finance is beneficial.
- Blockchain Certifications: Obtain certifications in blockchain technologies to showcase expertise.
- Contributions to Open Source: Contribute to open-source blockchain projects and build a strong online presence.
-
Voice Technology:
- Natural Language Processing Knowledge: Develop expertise in natural language processing and speech recognition.
- Programming Skills: Learn languages like Python or Java for voice technology application development.
- Participate in Voice-Related Communities: Engage with communities focused on voice technology, staying updated on industry trends.
-
IoT (Internet of Things):
- Networking and Embedded Systems: Build a foundation in networking protocols and embedded systems.
- Programming Skills: Acquire proficiency in languages like C, Python, or Java for IoT device programming.
- Security Knowledge: Understand IoT security principles and implement secure communication protocols.
-
Serverless Computing:
- Cloud Platform Proficiency: Master serverless offerings on cloud platforms like AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, or Google Cloud Functions.
- Application Architecture: Understand serverless application architecture and design principles.
- Continuous Learning: Stay updated on evolving serverless technologies and explore new frameworks and tools.
FAQs
Q. What is the best technology to learn in 2024?
A. The best technology to learn in 2024 depends on individual interests and career goals. In-demand technologies include Artificial Intelligence (AI), Data Science, Edge Computing, and Cybersecurity. It's essential to align your learning path with your specific industry or field of interest.
Q. What are the trending technologies in the IT Industry in 2024?
A.The IT industry in 2024 is witnessing trends in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Quantum Computing, 5G Technology**, **Automation, and Virtual Reality/Augmented Reality (VR/AR). Staying updated with these trends can offer exciting opportunities for professionals.
Q. What is the difference between Machine Learning and Data Science?
A. Machine Learning is a subset of Data science. While Data Science involves extracting insights from data through various methods, including statistics and data analysis, Machine Learning specifically focuses on developing algorithms that enable machines to learn patterns and make predictions.
Q. What is the scope of Machine Learning?
A. The scope of Machine Learning is vast, covering industries like healthcare, finance, marketing, and more. It enables predictive analysis, pattern recognition, and automation, making it integral for organizations seeking data-driven decision-making.
Q. What does edge computing mean?
A. Edge Computing involves processing data closer to the source of generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This paradigm reduces latency and enhances real-time data analysis, making it crucial for applications like Internet of Things (IoT) devices and augmented reality.
Conclusion
- A dynamic mix of technologies, from AI to Quantum Computing and Edge Computing, characterizes the computer science landscape, showcasing a vibrant industry.
- The intersection of AI and Data Science with various fields highlights a trend toward interdisciplinary collaboration, fostering innovative solutions.
- Technologies like AI are making tangible impacts in healthcare, manufacturing, and cybersecurity, transforming processes and decision-making.
- Ongoing innovations, especially in Quantum Computing and 5G applications, underscore the rapid pace of technological evolution.
- The prominence of AI brings ethical considerations to the forefront, emphasizing responsible deployment for societal benefit.
- The maturation of technologies fuels a growing demand for skilled professionals in areas like Machine Learning, Cybersecurity, and IoT, highlighting the need for continuous skill development.
