numpy.argmax() in Python
The numpy.argmax() is a function in Python's Numpy library that returns the index of the maximum value from a 1D array. It can also be used with multiple-dimensional arrays. With 2D arrays and axis specified it can return an array of indices of maximum value in each column or row. It is mainly used in scientific computing, data analysis, and machine learning.
Syntax:
The Syntax for numpy.argmax() function is as follows:
Parameters
It takes 3 parameters out of which the input array is a mandatory parameter. By default axis and out are set to None.
- input_array - Input array from which we wish to find the index of the maximum element.
- axis - It is an optional parameter, it specifies the axis along which the maximum values are computed.
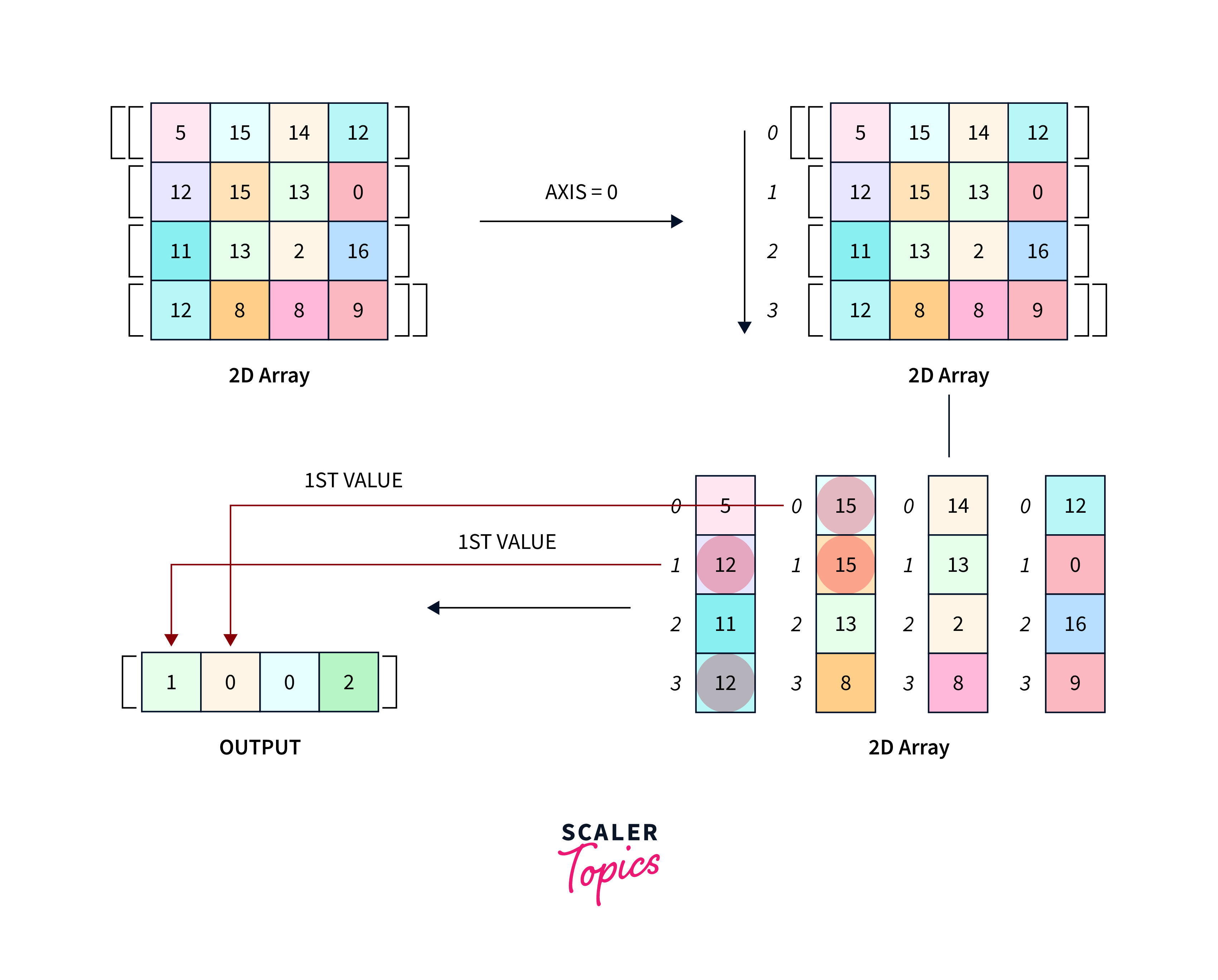
- When axis = 0 then the function finds the index of the max element in the vertical direction in a multidimensional array. When the axis = 1 then the function finds the index in the horizontal direction.
- out - In case we already have an array and we wish to store the result in the same array then we pass this array as an argument in out.

Return
The return value of the numpy.argmax() in Python is an array of indices of the maximum values along the specified axis. The shape of the returned array depends on the input array and the axis along which the operation is performed. For a 1D array, it returns a single value, for a 2D array, it returns a 1D array, and so on.
Note: Alternatively, the functions max() and np.where() can also be used to find the maximum element. If the index is not required and we only want the maximum element then we can use the max() function in Python. In case we want an index then we can give the desired condition in np.where() which will then return the index of the max element.
Code and Output
Let us look at an example of numpy.argmax() in Python. We will be taking two arrays a 1D array and a 2D array. We will apply the function and look at the output.
Example:
Output:
Let us now see what happens when an empty array is passed to the argmax().
For example:
Output 1:
Output 2:
Thus, when the axis is 0 it returns an empty array but in case axis = 1 it throws an exception.
In practice, it's important to handle empty arrays appropriately based on the specific requirements of your code.
FAQs
Q. What does argmax do in NumPy?
A. It is used to find the maximum element indices along an array's specified axis.
Q. What is NumPy’s argmax function used for?
A. The primary purpose of the argmax function in NumPy is to find the indices of the maximum values along a specified axis in an array. It helps identify the position of the maximum element within the array.
Q. How does argmax work on a 1D array?
A. When applied to a 1D array, the argmax function returns the index of the maximum element in that array.
Q. Can argmax be applied to multi-dimensional arrays?
A. Yes, argmax can be applied to multi-dimensional arrays. When applied along a specific axis, it returns the indices of the maximum values along that axis. The shape of the output depends on the shape of the array.
Q. Is it possible to use argmax with other data types besides integers?
A. The argmax function in NumPy is generally designed for numerical data types. It may not work as expected with non-numeric data types. It is primarily used for finding the indices of maximum values in arrays of numbers.
Q. What happens if the input array is empty?
A. If the input array is empty (has zero elements), the behavior of argmax depends on the axis parameter. If axis is not specified, it returns an empty array. If axis is specified, it may raise an exception.
Conclusion
- The numpy.argmax() in Python takes an array of one or more dimensions and returns the indices of maximum elements along a row.
- It takes an input_array, axis, and out_array as parameters. The input_array contains the maximum element, the out_array can be used to store the indices, and the axis defines the axis of search.
- If the axis is given 0 operations are performed vertically, and 1 is for row search.
- The return type is a single value in the case of the 1D array and it can be a 1D or more than one-dimensional array based on the shape of the input array.
