Push-relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm
Overview
Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is an algorithm used for finding the maximum flows in a flow network. Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is more efficient in comparison to the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm. Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm and Ford-Fulkerson both use residual graphs of flow networks.
Introduction
Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is an algorithm used for calculating the flow network maximum flows. It uses a residual graph of the flow network.
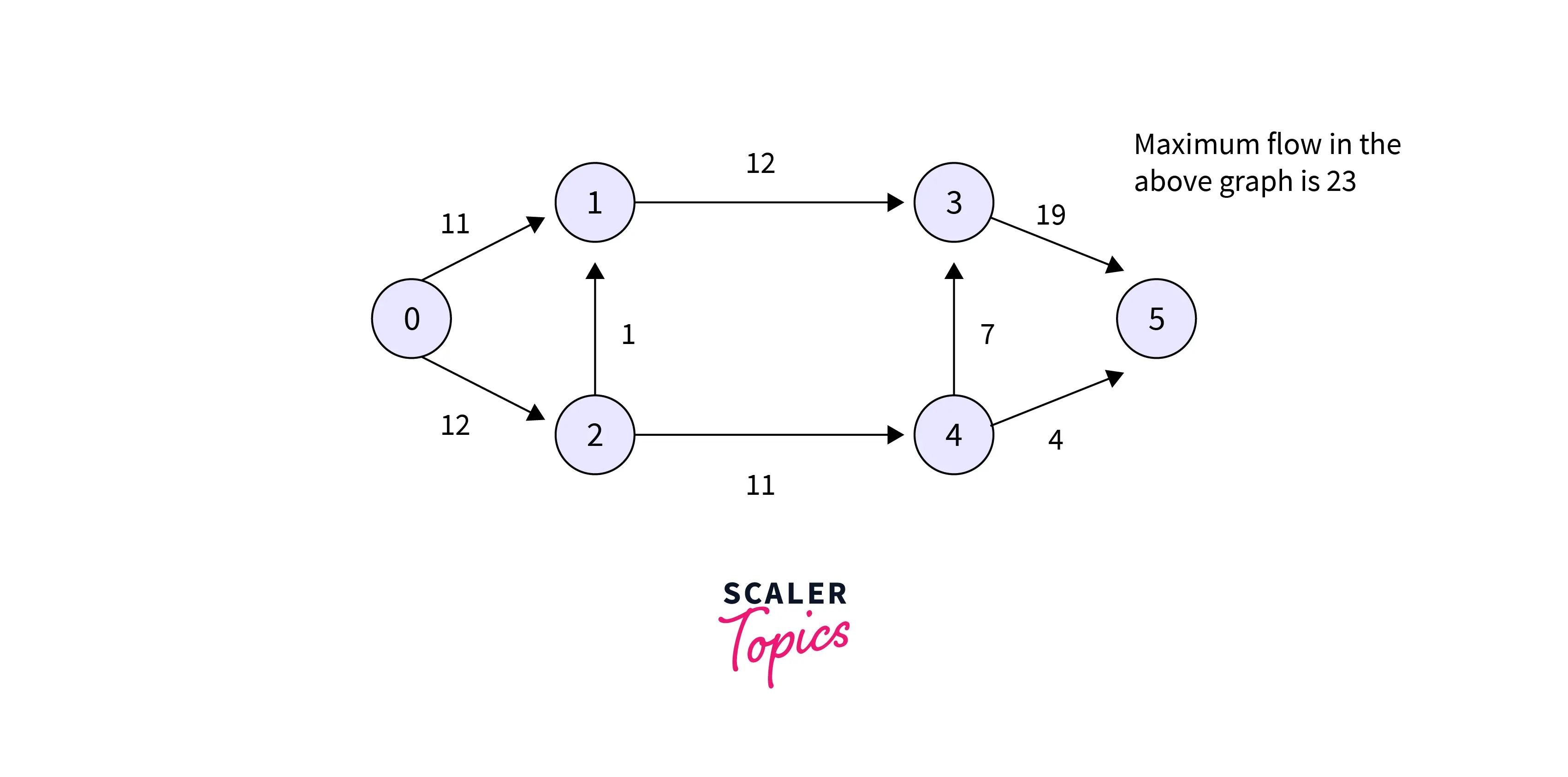
There is a flow network shown in the below-given graph below in which all edges have a capacity. In this graph, there are two vertices source 's' and 't' as a sink. Using the below-defined constraints, determine the maximum possible flow from s to t:
- The capacity of the given edge must be greater than the flow of the edge.
- Except for s and t, the incoming and outgoing flow of every edge in the graph should be equal. Below is an example of a graph (taken from the CLRS book).
Refer to the below for the example of the flow network of the graph

In the given graph, the maximum possible flow is 23. Refer to the below to show the maximum flow of the graph
Push-Relabel Algorithm
If we talk in terms of the efficiency of the approach then the approach used in Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is more efficient in comparison to the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm. Goldberg’s “generic” maximum-flow algorithm(Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm) is an algorithm whose time complexity time. It has a time complexity better than the complexity of the Edmond-Karp algorithm (Ford-Fulkerson's algorithm implementation based on the BFS) as the complexity of the Edmond-Karp algorithm is where 'E' represents edges of the graph and 'V' represents vertices of the graph. The algorithm based on the approach Push Relabel Maximum Flow has time complexity and it even works finer than the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm.
Similarities with Ford Fulkerson:
Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm and Ford-Fulkerson both use residual graphs of flow networks. The residual graph is a type of graph that is used to show the additional flow i.e. possible. There is a possibility of adding flow if a path exists from the source vertex to the sink vertex.
Differences with Ford Fulkerson
Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is an algorithm that uses a localized approach. For finding an augmenting path at a time it works on one vertex instead of examining the whole residual network. If we compare both algorithms in terms of the net difference between the inflow and outflow of the vertices then the zero value is maintained for the net difference between the total inflow and total outflow of every vertex except the source vertex and sink vertex in the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm. And now if we talk about the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm then it allows the value of the inflow to exceed the outflow until we do not reach the final destination. The net difference between the inflow and outflow of every vertex except the source and sink in the final flow is 0.
In the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm, we suppose nodes as joints and take edges as water pipes. Also, consider the source is at the highest level and the work of sending water to each adjacent node is done by it. When the water in any node reaches its excess point, then this particular node pushes the water to the node of a smaller height. Suppose at the vertex, if the water is locally trapped then the relabeled operation is performed at the vertex due to which there is an increment in its height. Before proceeding with the algorithm, we need to consider some of the given facts:
Height variable and an excess flow are some terms that every vertex has associated with. Height is used to find if the vertex can push the flow to an adjacent or not. A vertex is only allowed to push the flow to a vertex of a smaller height. The difference between the total outgoing and incoming flow in the vertex is considered excess time.
Excess Flow of u = Total Inflow to u - Total Outflow from u
Just like Ford Fulkerson, in the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm also flow and capacity are associated with every edge.
Complete Algorithm (step-wise)
Mainly there are 3 operations in the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm:
- PreFlow() Initialization Flows and heights of all the vertices are initialized by it.
-
Push() For creating the flow from the node having excess flow, the push() operation is used. Suppose in a residual graph, a condition occurs when there is excessive flow in a vertex and an adjacent of smaller height is there, then the push() operation is used to push the flow from the vertex to the adjacent having lower height. The value of the pushed flowing from the pipe (edge) is equivalent to the minimum of two values i.e. a minimum of capacity and excess flow of the edge.
-
Relabel() When there is excess flow in the vertex and there is no adjacent at the lower height, then in this condition relabel() operation is used. For performing push(), we generally increase the height of the vertex. So for increasing the height of the vertex, we need to choose the adjacent in the residual graph having minimum height. And after this, we add 1 to this particular adjacent.
Step-wise Example
Generally, residual graphs are not similar to normal graphs, they both are different. So first before proceeding with the example of the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm, we will learn about the residual graph.
Additional possible flow is indicated by the residual graph of the flow network. In a residual graph adding flow is possible if there exists a path from source to sink. In the residual graph, every edge is associated with the value called residual capacity and its value is equal to the difference between the current flow and original capacity. Residual capacity is generally represented by the edge's current capacity.
We need to do the following updates if we add or push flow from vertex u to v:
- We find the difference of flow and the capacity of the edge from u to v. And if the edge capacity is zero, then the particular edge is not allowed to stay in the residual graph, it will no longer exist.
- Addition of flow capacity of the edge from v to u.
Let us take an example, suppose there are two vertices x and y. And in the original graph 3/10 x ---------> y current flow from x to y is 3 and edge capacity from x to y is 10.
And there are two edges in the residual graph for the above-shown edge. 7 x ---------> y 3 x <--------- y
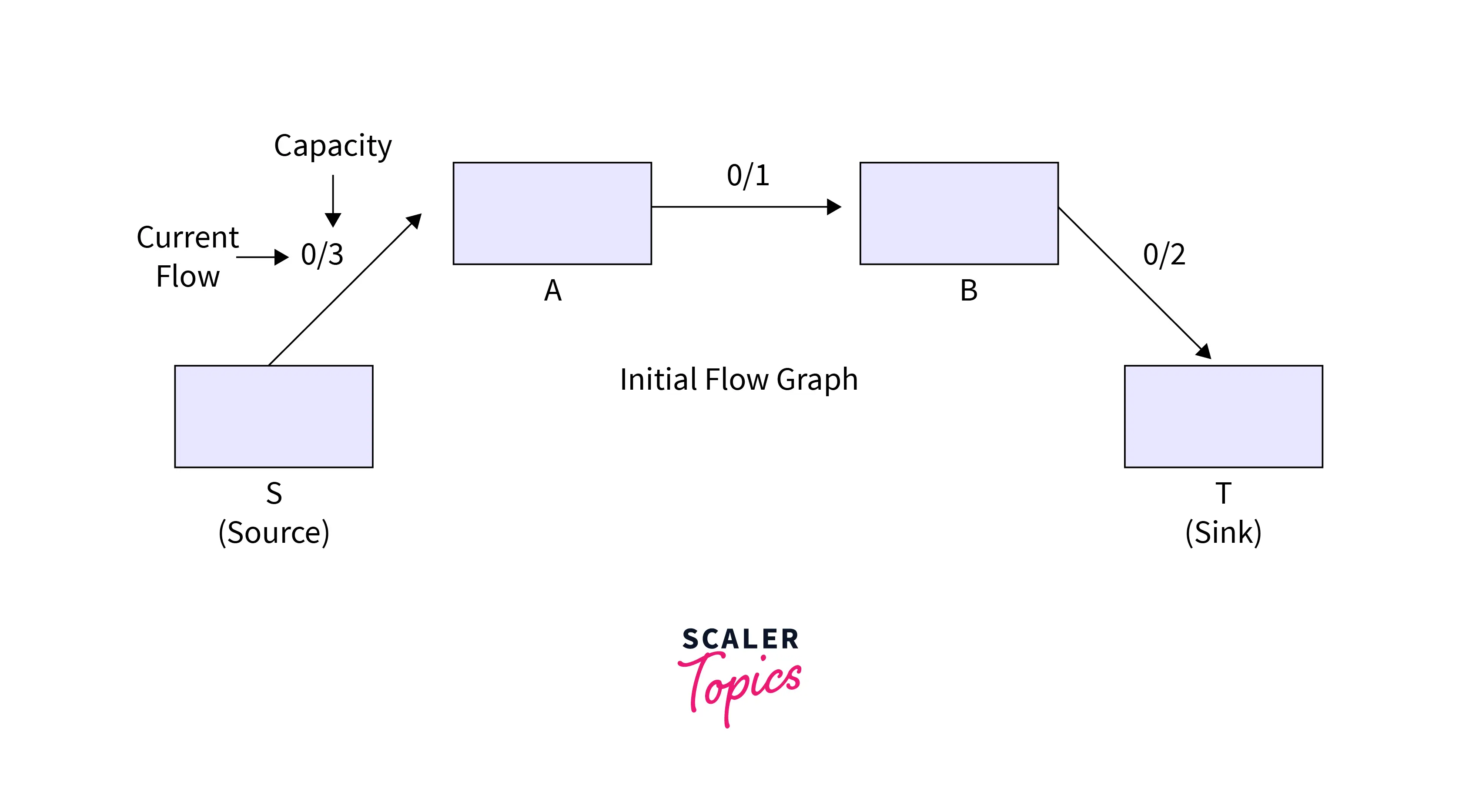
- The flow graph needs to be initialized.
Refer to the below for step1 of the example.
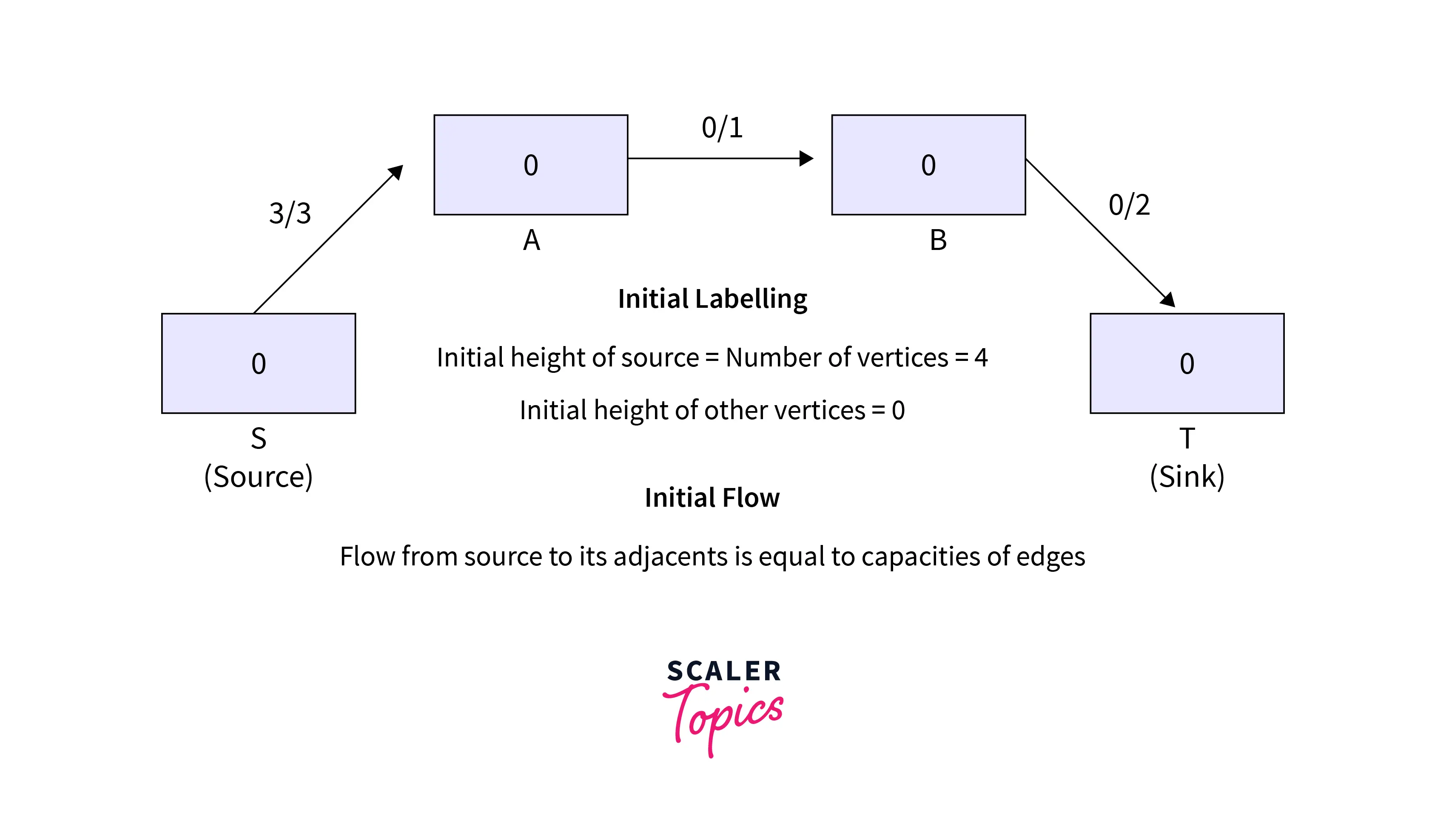
- There is a formation of an edge having capacity 3 from A to S and there is no edge from S to A after performing the PreFlow operation in the given residual graph.
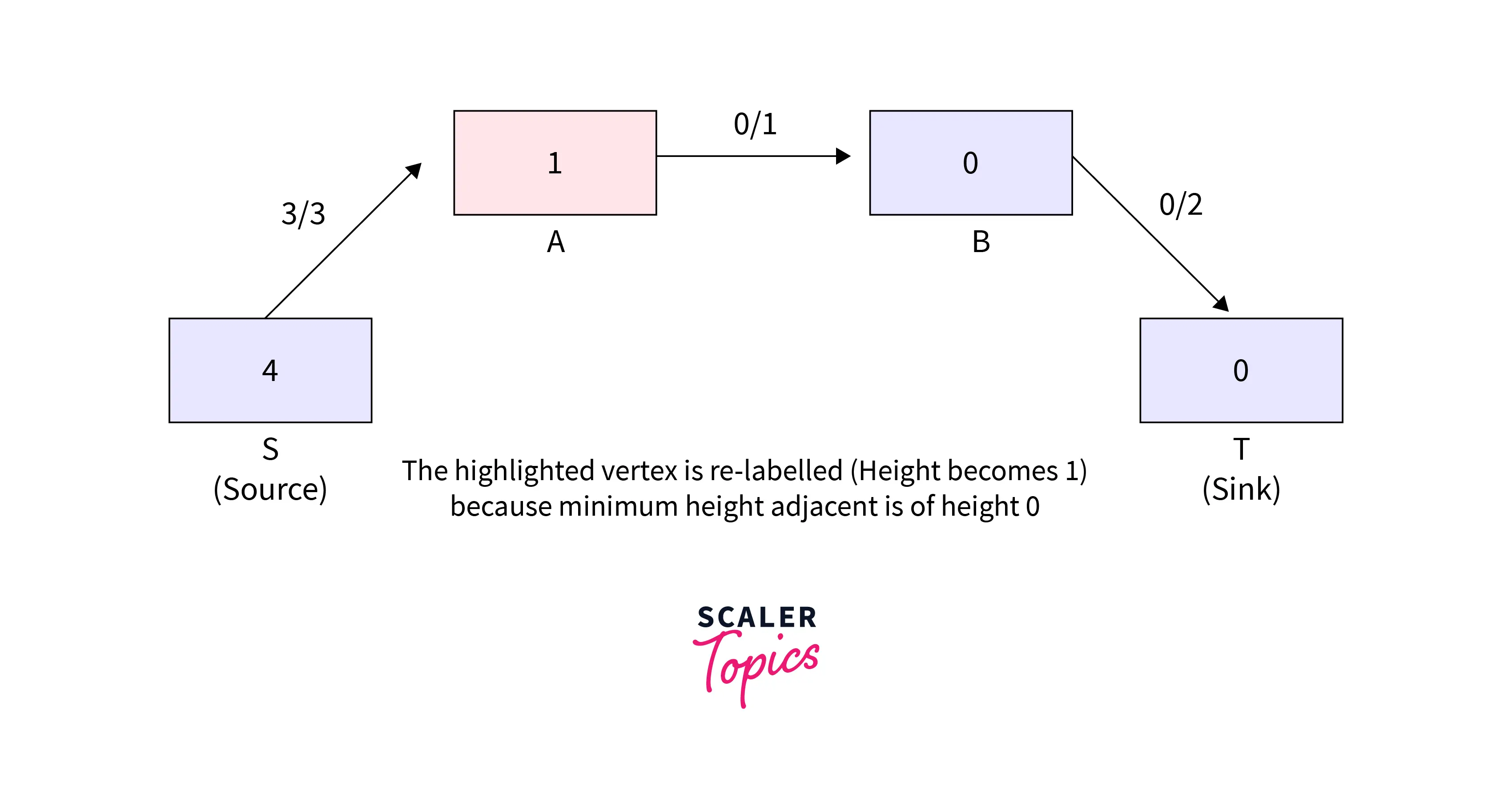
Refer to the below for step2 of the example.
- Relabel the vertex that is highlighted (now length becomes 1) as there is an excess flow and no adjacent of smaller height. Now the new value of the height is equal to the minimum heights of residual + 1. Vertex S and B are two adjacent vertices for A in the residual graph. And if we compare the height of both and then we get the minimum height of B i.e. 0 as the height of S is 4 and the height of B is 0. So we take 0 and add one into it and it becomes 1.
Refer to the below for step 13 of the example.
- Push() operation takes place as there is an excessive flow in the highlighted vertex and there is an adjacent having a lower height. At vertex A, the excess flow is 2 and there is an edge (A, B) with a capacity of 1. 2 is the minimum of two values and that is the amount of flow that is pushed.
Refer to the below for step 4 of the example.
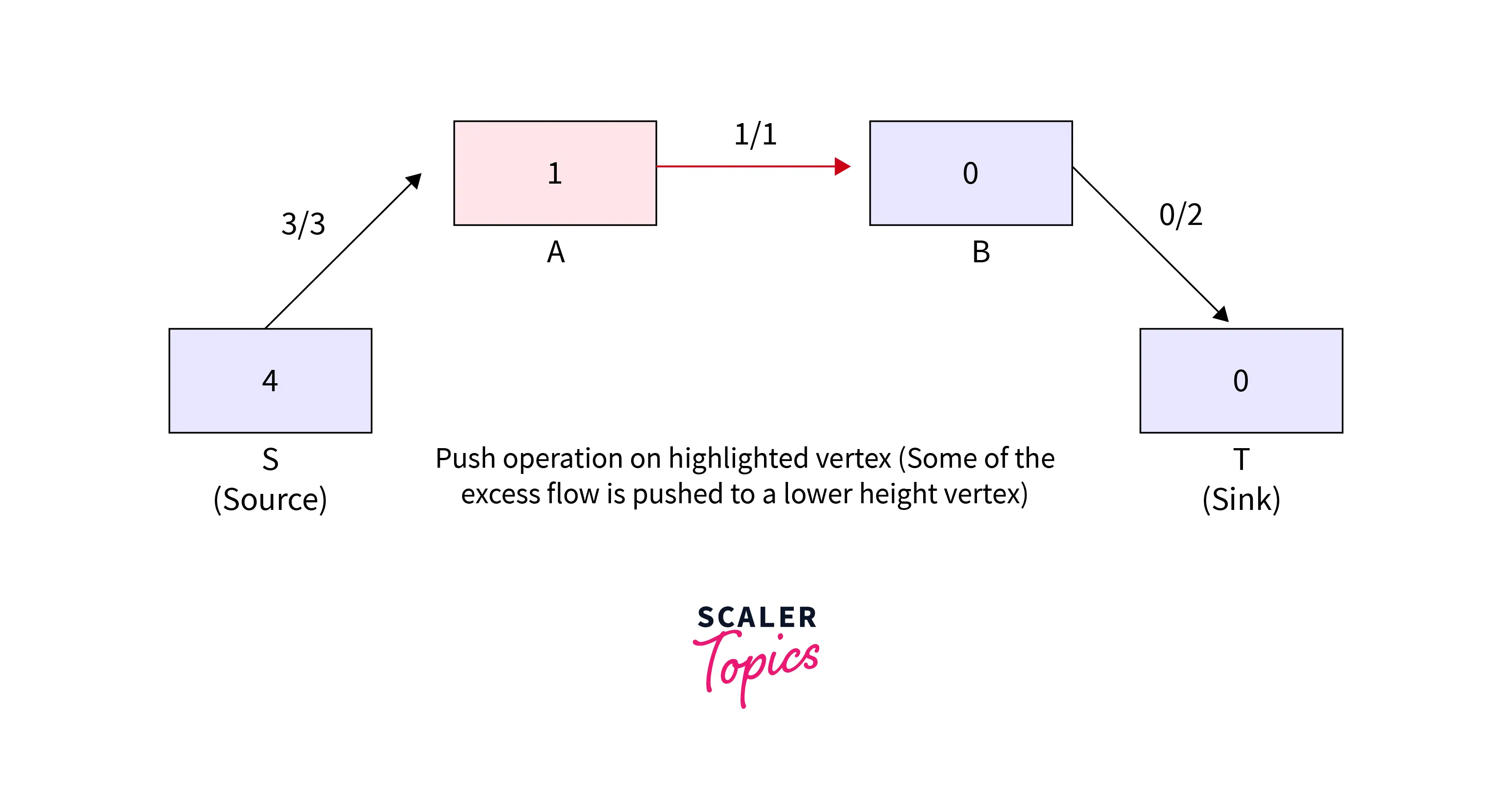
- Relabel the vertex that is highlighted ( now length becomes 1) as an excess flow and no adjacent having the smaller height is there.
Refer to the below for step 5 of the example.
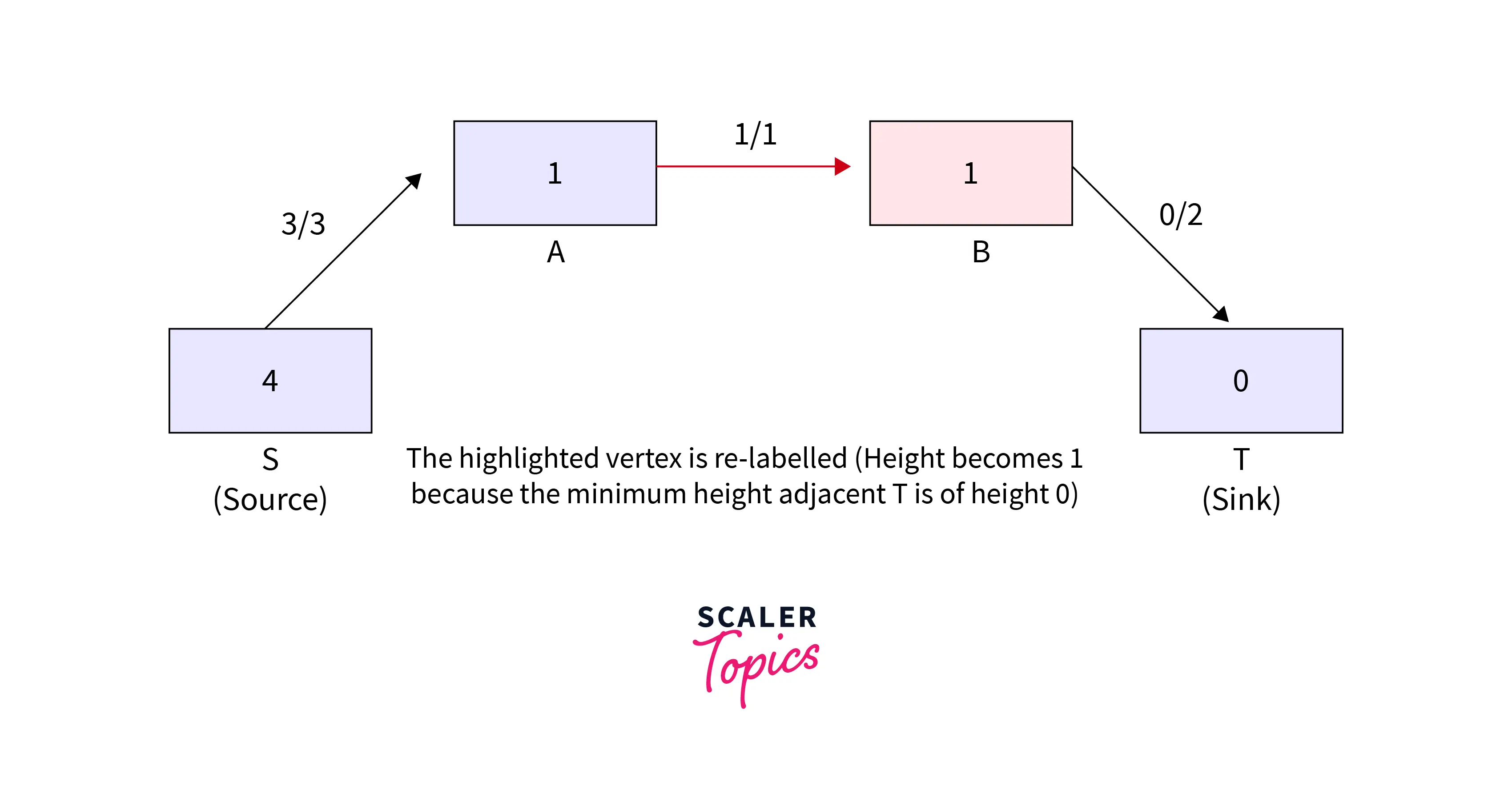
- Flow () operation from B to T takes place as there is an excess flow in the highlighted vertex and an adjacent having a lower height is there. Refer to the below for step 6 of the example.
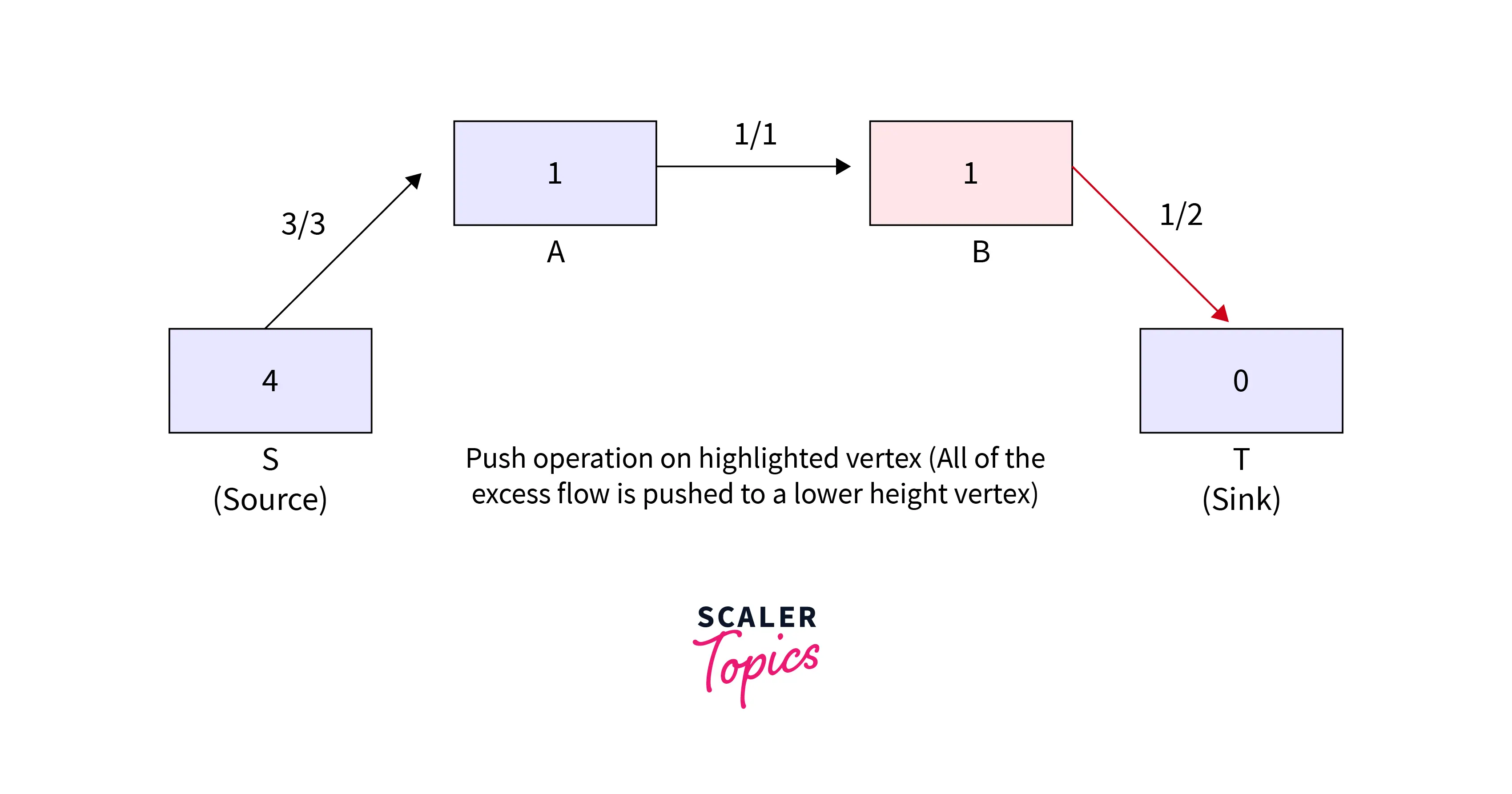
- Relabel the vertex that is highlighted ( now length becomes 5 ) as an excess flow and no adjacent having a smaller height is there.
Refer to the below for step 7 of the example.

- Push () operation takes place as there is an excess flow in the highlighted vertex and an adjacent having a lower height is also there.
Refer to the below for step 8 of the example.
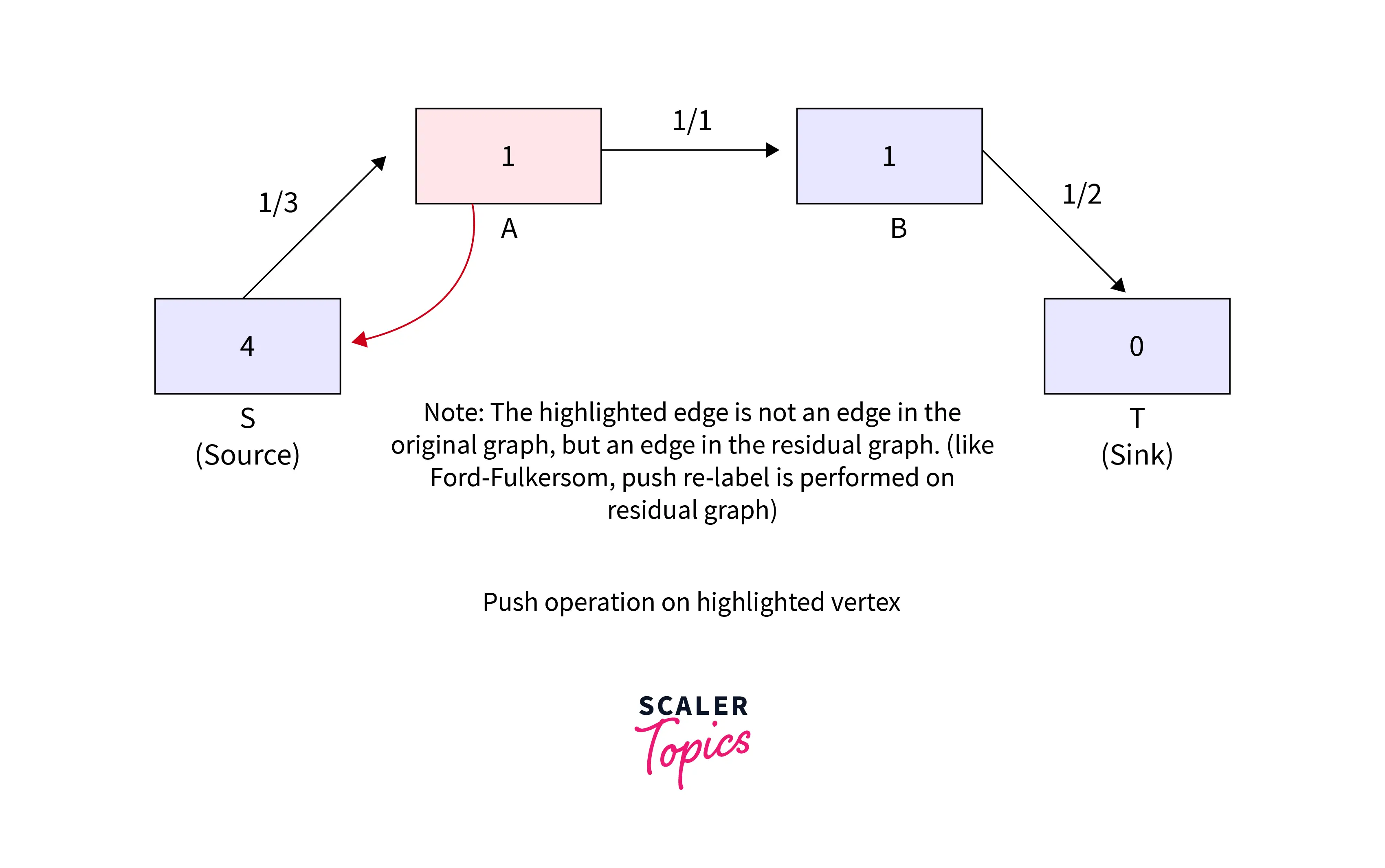
- Relabel the vertex that is highlighted ( there is an increment in height by 1) as there is an excess flow and no adjacent of smaller height.
Refer to the below for step 9 of the example.

Conclusion
- Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm is an algorithm used for calculating the flow network maximum flows.
- It is more efficient in comparison to the Ford-Fulkerson algorithm.
- Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm and Ford-Fulkerson both use residual graphs of flow networks.
- For finding an augmenting path this works on one vertex at a time instead of examining the whole residual network.
- Additional possible flow is indicated by the residual graph of the flow network.
- preFlow(), push(), and relabel() are the three main operations of the Push Relabel Maximum Flow Algorithm.
