React Native Track Player : Complete Tutorial
Overview
In every day of our lives, we must have used many song applications, like spotify, apple music and amazon music etc. We might have noticed that when we click on any music, it opens up the track player with a clean and interactive user interface.
The progress bar shows the current position of the song, and we can easily control the playback using the provided buttons. This is what Track Player describes.
In this article, we are going to make a track player control by building a music track player with the help of a library named react-native-track-player.
What is React Native Track Player?
Starting with React native track player, we might implement a track player from scratch. But it can be time-consuming and might not be reusable for others.
To simplify the use of Track Player with less configuration The react-native-track-player module makes our development easy.
a. Features
- Lightweight: It provides a robust and flexible API for playing audio tracks in your application. supports various audio formats, including MP3, AAC, FLAC, and more.
- Feels Native: In the case of Track player react native, the library strives to provide a native-like experience by adhering to the design patterns and user expectations of the respective iOS and Android platforms.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: React native track player abstracts the differences between the two platforms, providing a consistent API and behaviour.
- Media Controls support: react-native-track-player provides events for controlling the app from a Bluetooth device, the lockscreen, a notification, a smartwatch, or even a car.
- Offline Playback: Track player react native allows you to pre-download tracks and store them locally, enabling users to listen to their favourite content even without an internet connection.
- Adaptive bitrate streaming support: react-native-track-player with bit rate streaming support allows you to stream audio tracks with varying bit rates.
- Background support: React native track player supports background audio playback, which means the audio will continue playing even when the app is in the background or when the device is locked.
- Fully Customizable: Notification icons are customizable!
- Supports React Hooks: Includes React Hooks for common use cases so you don't have to write them.
- Casting support: Use in combination with react-native-track-casting (WIP) to seamlessly switch to any Google Cast-compatible device that supports custom media receivers.
b. Installation
To install the React native track player.
Create a new React Native;
Install the React native track player package by following the command:
We start our project by running
c. APIs
It provides several categories of APIs that you can use to control and manage audio playback in your React Native applications. Those are;
-
Event Handling APIs: We will discuss these events later in our article. Stay tuned!
-
Playback control APIs These APIs control the audio tracks in the React Native application. These are very common, as we discussed before.
| Player APIs | description | properties |
|---|---|---|
| setupPlayer(options) | Accepts a PlayerOptions object. | |
| updateOptions(options) | Accepts a MetadataOptions object. | |
| play() | Plays or resumes the current track. | |
| pause() | Pauses the current track. | |
| seekTo(seconds) | Seeks to a specified time position in the current track. | seconds |
| setVolume(volume) | Sets the volume of the player. | volume |
| getVolume() | Gets the volume of the player (a number between 0 and 1). | |
| setRate(rate) | Sets the playback rate | rate |
| getRate() | Gets the playback rate, where 1 is the regular speed. | |
| getDuration() | Gets the duration of the current track in seconds. | |
| getPosition() | Gets the position of the current track in seconds. | |
| getBufferedPosition() | Gets the buffered position of the current track in seconds. | |
| getState() | Gets the playback State of the player. |
-
Lifecycle APIs
- setupPlayer(options: PlayerOptions)
- registerPlaybackService(serviceProvider)
- useTrackPlayerEvents(events: Event[], handler: Handler)
-
Queue Management APIs:
| Queue APIs | description | properties |
|---|---|---|
| add(tracks, insertBeforeIndex) | Adds one or more tracks to the queue. | tracks [], insertBeforeIndex |
| remove(tracks) | Removes one or more tracks from the queue. | tracks [] |
| skip(index, initialPosition) | Skips to a track in the queue. | index, initialPosition |
| skipToNext(initialPosition) | Skips to the next track in the queue. | initialPosition |
| skipToPrevious(initialPosition) | Skips to the previous track in the queue. | initialPosition |
| reset() | Resets the player stopping the current track and clearing the queue. | |
| getTrack(index) | Gets a track object from the queue. | index |
| getCurrentTrack() | Gets the index of the current track | |
| getQueue() | Gets the whole queue | |
| removeUpcomingTracks() | Clears any upcoming tracks from the queue. | |
| updateMetadataForTrack(index, metadata) | Updates the metadata of a track in the queue. | index, metadata |
| setRepeatMode(mode) | Sets the repeat mode. | mode |
| getRepeatMode() | Gets the repeat mode. |
- Playback State APIs
- useTrackPlayerEvents
- useProgress
- usePlaybackState
Integrating react-native-track-player Library
Before implementing the Track player react native app, there are some steps to integrate your app with the react-native-track-player.
Step-1
create a playback service module named service.js.
The playback service module in react native track player is a crucial component responsible for managing audio playback operations in the background.
Step-2
We need to register the playback service that is service.js in our main component index.js.
Step-3
Create a file that can contain all the services and controls for Trackplayer.
After completing the controller part for the Track player react native, we can add those controller properties to the UI component.
Note: Registering the playback in React native track player involves setting up the necessary configurations and callbacks to establish a connection between the player instance and the audio playback functionality in your application.
Simple Track Player
Now we are going to create a simple music track player.
musicController.js
The setupPlayer() function is defined as an async function. It checks if the player is already set up by calling TrackPlayer.getCurrentTrack() in React native track player
Inside the catch block, the setupPlayer() function sets up the player by calling TrackPlayer.setupPlayer(). It then uses TrackPlayer.updateOptions() to configure various options related to playback behavior and capabilities.
Finally, the function returns the value of isSetup, indicating whether the setup process was successful.
The addTrack() function adds a single track object with properties such as id, url (the audio file URL), artwork, title, artist, and duration.
here in app.js adding the controllers with buttons to play and pause.
App.js
Output

How to Manage the Playlist
For creating a playlist, we required a collection of audio tracks that could be played in a specific sequence. It provides a convenient way to organize and manage a series of tracks for playback within a React native track player application.
musicController.js
In the above controller, we added multiple tracks, some of which are remote and some of which are local. With that, we added capabilities like skipToNext, skipToPrevious, SeekTo that control the playback in react-native-track-player.
a. Visualizing Manageable Playlist
To visualize a playlist, we are using Flatlist to represent our multiple tracks, which can be scrollable when they overflow the screen.
App.js
By using the TrackPlayer.getQueue method, we will retrieve the current playlist. This can be useful for displaying playlist information.
Playback and PlayerState Management
For handling the audio player track in a playlist, we need visual enhancement in our app. Here we are using react-native-vector-icons to show all the playback controls.
a. Visualization
In this section, we will improve our app functionality by adding playback duration, an audio track progress bar, and the current track name and singer in the header of our React native track player app.
App.js
Looping and Shuffling Playlist Items
Shuffling in the React native track player refers to the functionality of randomising the order of tracks in a playlist during playback.
By executing the handleShuffle() function, the current playlist is shuffled randomly.
Output:
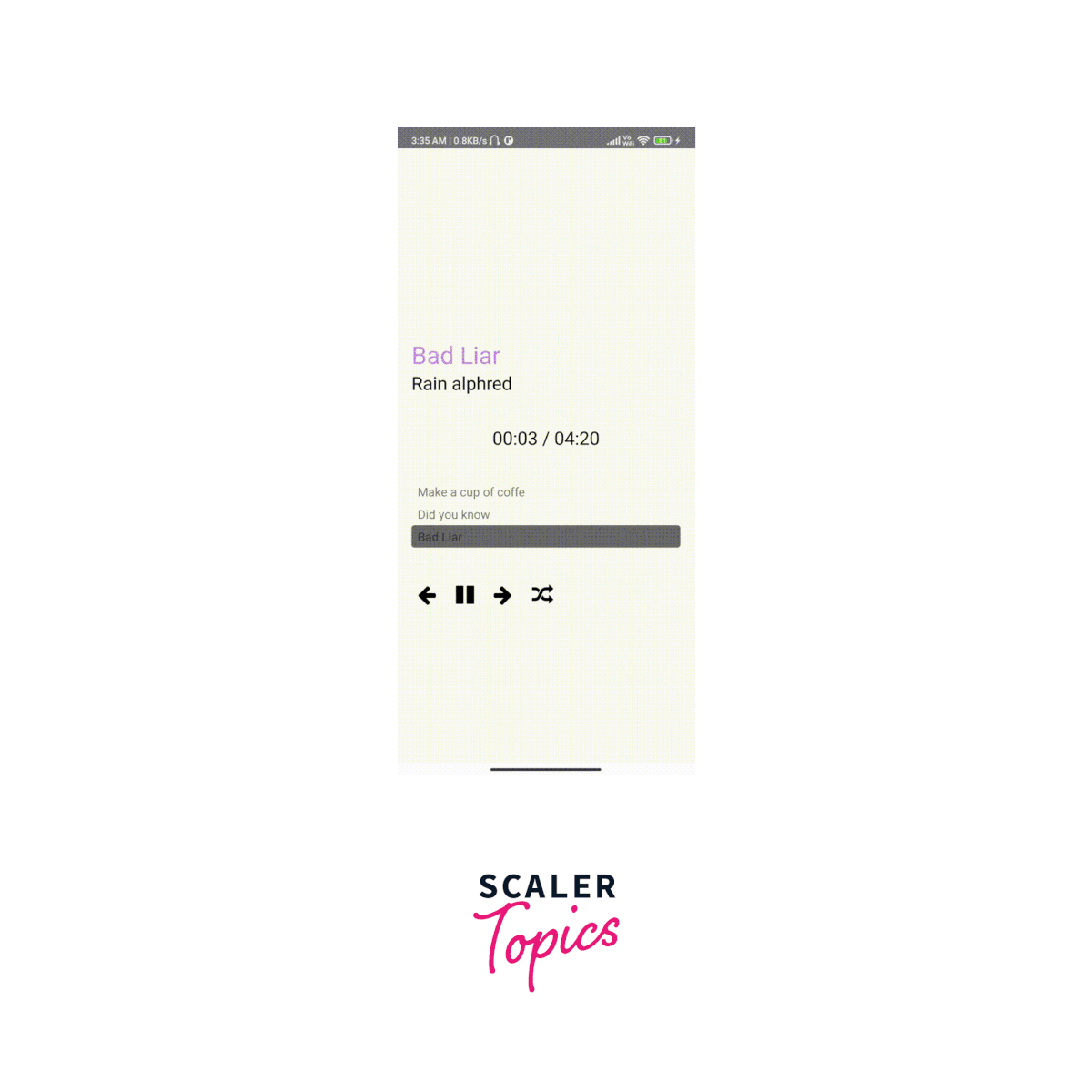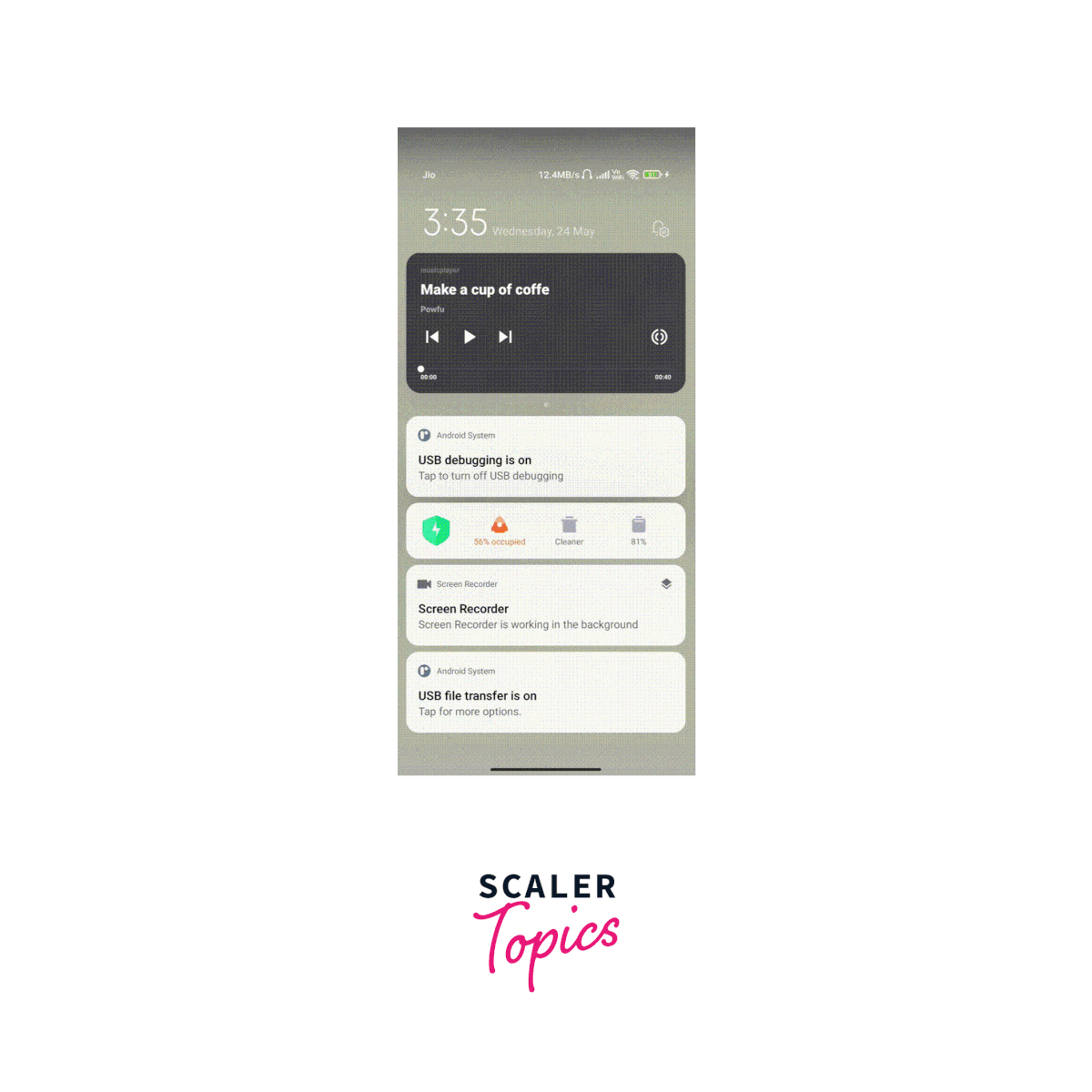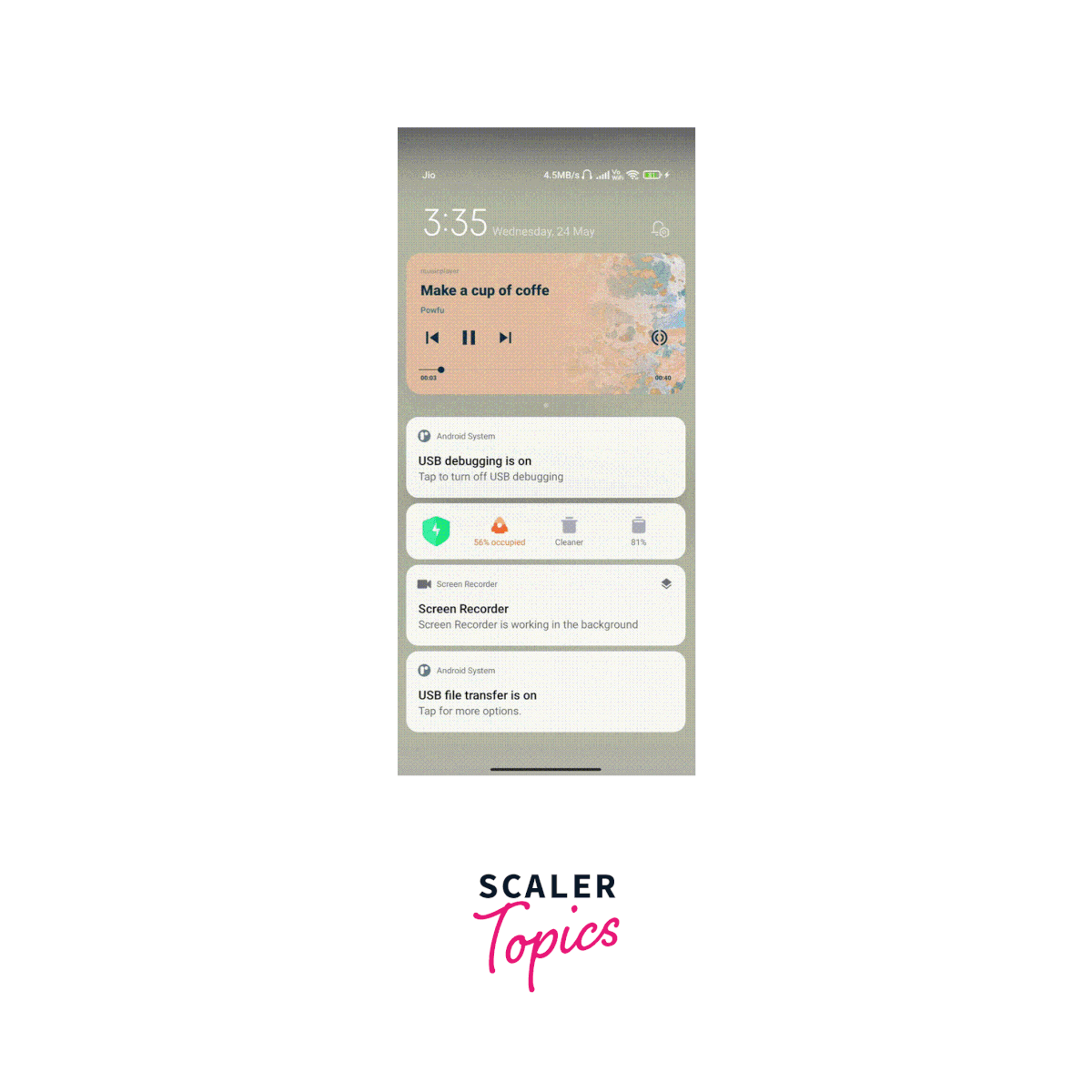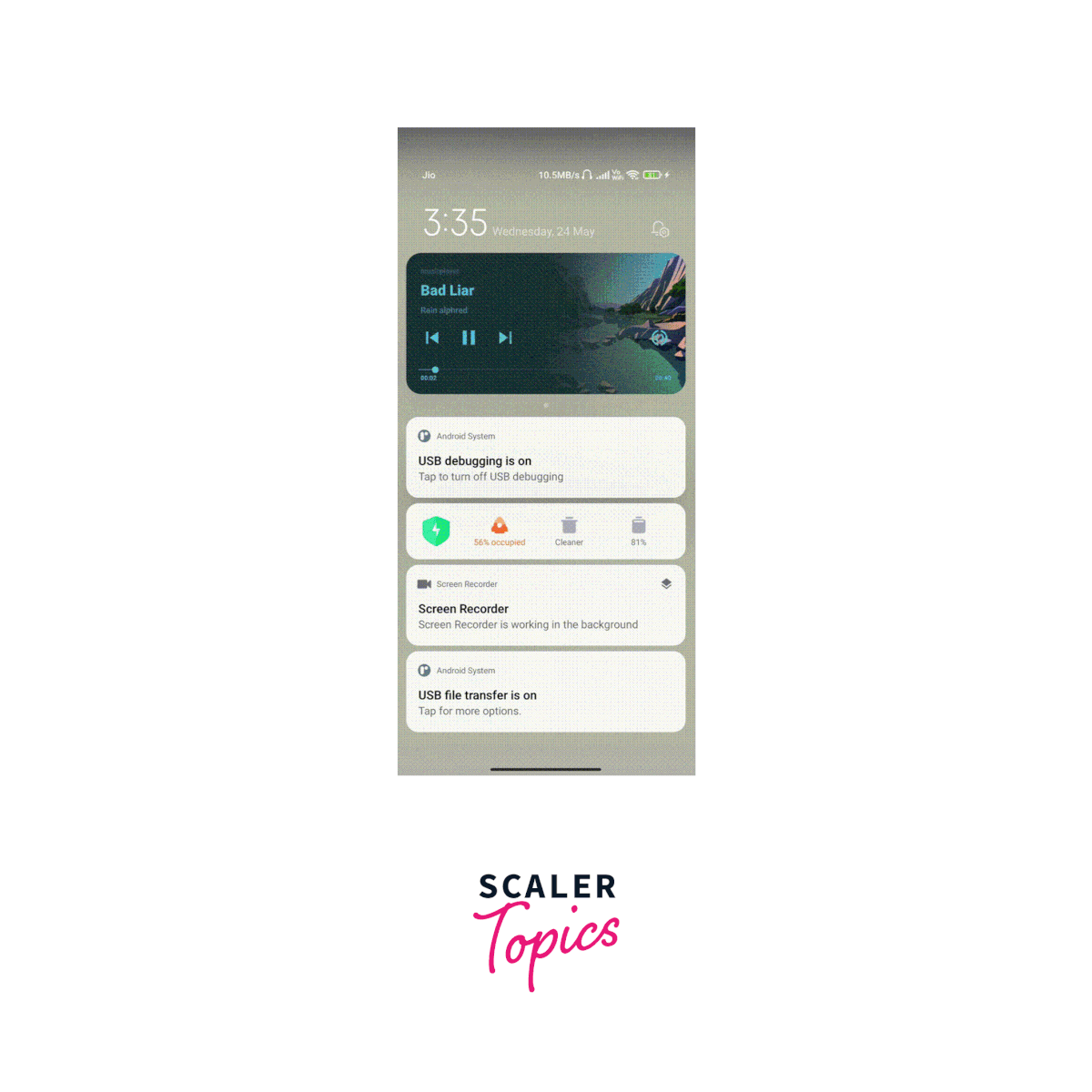
How to Use Track Player Events
Track player in react native provides different events to handle our background player and media controls.
We can use it by adding:
Player Events in react-native-track-player.
Media Control Events in react native track player. You can checkout the different media control events
Above properties support both ios and Android.
But some of the events exist that only support ios, not Android.
Those are RemoteLike, RemoteDislike, RemoteBookmark
How to Work with the Background Mode?
To work with the background mode in react-native-track-player, you need to configure the audio player to continue playing audio even when the app is in the background or the device is locked.
musicController.js
playbackService function that sets up event listeners for remote control events in react-native Track Player. Let's break down the code.
When the user pauses playback using a remote control or a headset, an Event.RemotePause event will be triggered. The event listener logs a message to the console and calls the pause() method of the react-native-track-player to pause the audio playback.
Like that, all events on PlaybackService will be triggered when any background or external event comes.
Playlist Storage
For storing the playlist, we have multiple options available. Those could be
React native File system: React Native FS provides the ability to create, write, and manage files within the device's file system. We can create a dedicated directory to store playlist files or use a specific file for each playlist. React Native FS can be used to support offline playback scenarios.
React native Async Storage: React Native Async Storage can be used to store playlists for track player by serializing the playlist data into a string format and persistently saving it.
The playlist data can be stored using a unique key in async storage, allowing easy retrieval and updating.
External File system:
Instead of storing playlist files locally on the device, you can leverage cloud storage services such as Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Firebase Storage.
These services provide scalable and secure storage solutions, and you can use appropriate SDKs or APIs to interact with them from your React Native app.
Note: React Native Fetch Blob is a third-party library that provides a way to perform file system operations, including file uploading and downloading, in React Native applications.
If you are using Expo to build your React Native application expo file system is a path to go
FAQs
Q1: How can you handle audio playback in the background using React native track player?
Answer: Create an asynchronous function with multiple events like RemotePlay(), RemotePause(), RemoteNext(), and RemotePrev(). And add that function to the root of the React Native project registry.
Q2: Can you customize the player interface in React native track player?
Answer: Yes, React native track player offers a flexible and customizable UI component called Player, which allows you to design and style your player interface. You can customize the look and feel of the player controls, track progress bar, play/pause buttons, and other elements to match the design of your application.
Conclusion
- If you are looking for a fully-featured audio module for your React Native application, then the react-native-track-player library is a great option.
- The library is highly performant and can be used to create production-ready applications.
- This library is a fully-fledged audio module created for music apps.
- Additionally, the library dispatches events to JavaScript for UI update usage, which makes it easy to integrate with React Native applications.
