Rownum in PostgreSQL to Get Row Number
Overview
In the world of relational databases, PostgreSQL stands tall as a powerful and versatile option. One of the fundamental requirements in database querying is to retrieve rows with a unique identifier, often referred to as row numbers. PostgreSQL provides a convenient way to obtain row numbers using the ROW_NUMBER function, commonly known as Rownum. This article will delve into the mechanics of Rownum in PostgreSQL, its syntax, and provide illustrative examples to help you harness its capabilities efficiently.
PostgreSQL ROW_NUMBER Function
The ROW_NUMBER function in PostgreSQL is an analytical window function that assigns a unique integer value to each row returned by a query. The assigned values are based on the specified column ordering, providing a sequential numbering of the result set.
Getting Row Number in PostgreSQL
To utilize the ROW_NUMBER function, you need to understand the window function concept. A window function allows you to perform calculations across a set of rows related to the current row. The ROW_NUMBER function, in particular, returns the row's sequential number within the specified window frame.
When using the ROW_NUMBER function, you must define the partitioning and ordering criteria for the window frame. The partitioning clause separates the result set into partitions, and the ordering clause determines the sequence in which the row numbers are assigned within each partition.
For example, suppose you have a table named "employees" with columns employee_id, first_name, and salary. You can use the ROW_NUMBER function to get the row numbers based on ascending salary within each department as follows:
In this example, the ROW_NUMBER function partitions the result set by the department column and orders the rows within each partition by salary. The row_num column will display the corresponding row numbers.
Syntax
The syntax for utilizing Rownum in PostgreSQL is straightforward and involves the use of the ROW_NUMBER function, a powerful analytical window function.
To employ Rownum in PostgreSQL, you need to understand the fundamental structure of the ROW_NUMBER function. The syntax is as follows:
Let's break down the components of the syntax:
- ROW_NUMBER(): This is the core function that generates row numbers for each row returned by the query. It does not require any parameters inside the parentheses.
- OVER: This keyword indicates that the ROW_NUMBER function is used as a window function. Window functions perform calculations across a set of rows related to the current row.
- PARTITION BY partition_expression: The PARTITION BY clause is optional but very useful. It divides the result set into partitions based on the specified column(s). The partition_expression is used to define the grouping criteria for the partitions. Rows with the same values in the specified column(s) will be treated as belonging to the same partition.
- ORDER BY sort_expression: The ORDER BY clause is also optional, but it determines the order in which the row numbers are assigned within each partition. The sort_expression specifies the column(s) based on which the rows are sorted to calculate the row numbers.
The ROW_NUMBER function does not change the actual order of the result set. Instead, it assigns a unique row number to each row according to the specified order and partitioning. This makes it an ideal tool for various analytical and reporting tasks.
Examples
Let's consider a sample table named employees with the following structure:
| employee_id | first_name | last_name | department | salary |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | Smith | HR | 45000 |
| 2 | Jane | Doe | IT | 55000 |
| 3 | Bob | Johnson | IT | 60000 |
| 4 | Alice | Williams | Finance | 48000 |
| 5 | James | Brown | HR | 52000 |
Example 1: Simple ROW_NUMBER Usage
Suppose we want to retrieve the employee details along with their respective row numbers based on their salaries in descending order. We can achieve this using the ROW_NUMBER function with the ORDER BY clause:
Output:
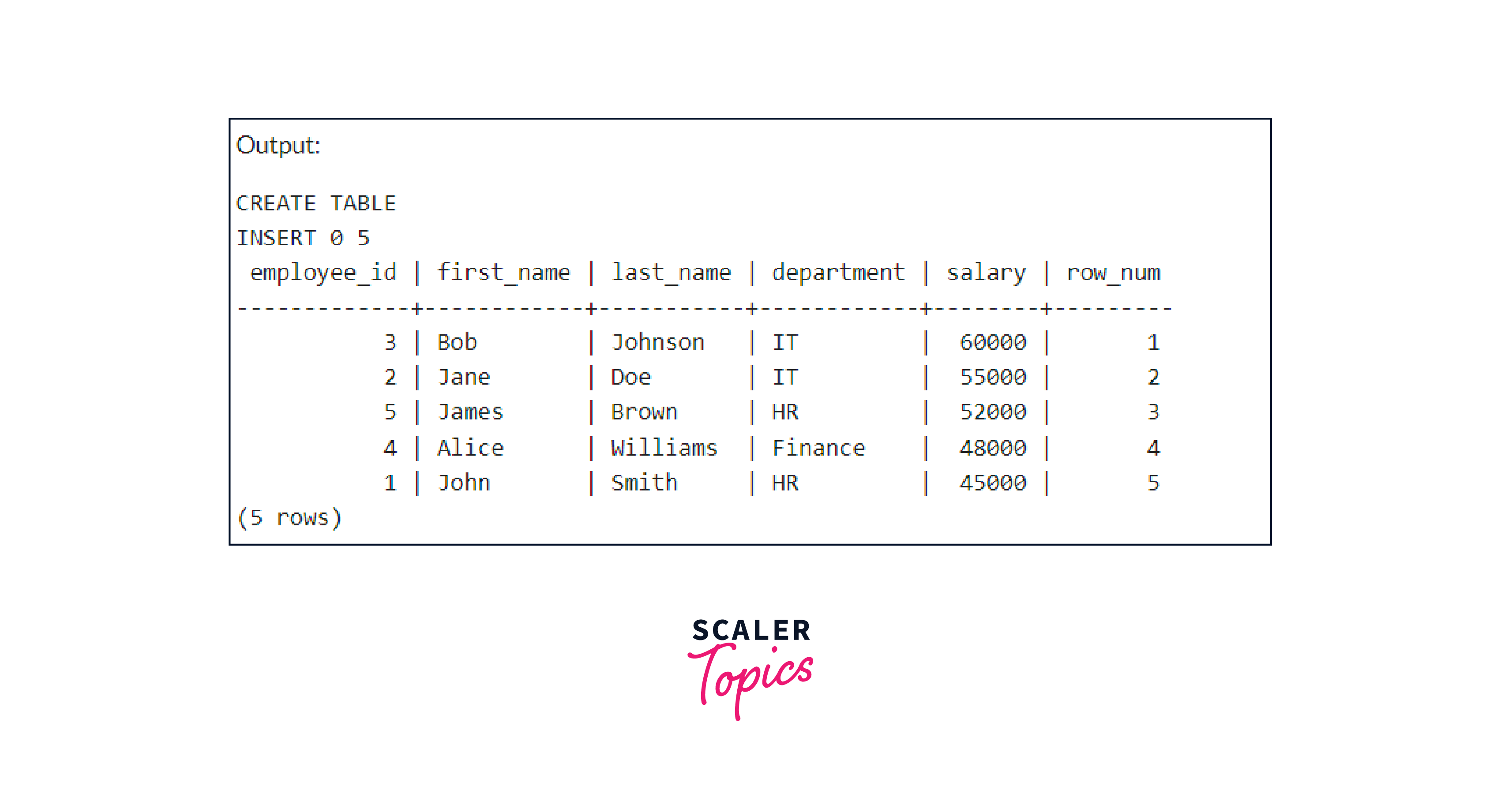
The output displays the employee details with an additional column row_num, representing their row number based on descending salary order.
Example 2: ROW_NUMBER with PARTITION BY
Now, let's use the PARTITION BY clause to divide the employees into partitions based on their departments and order them by salary within each department:
Output:
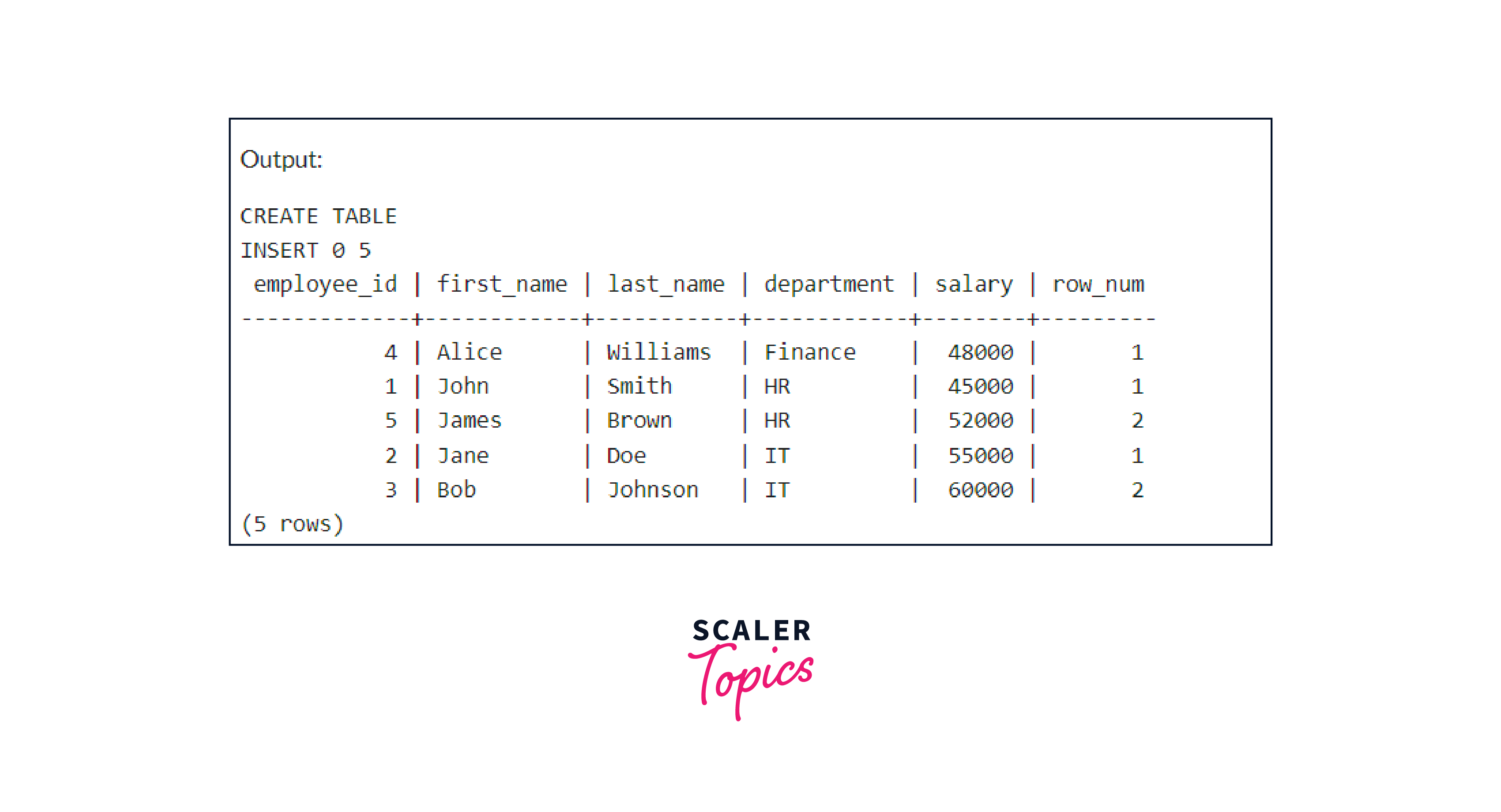
In this output, the employees within each department are assigned row numbers based on their salary in ascending order within their respective partitions.
FAQs
Q. Can the ROW_NUMBER function be used with other window functions in PostgreSQL?
A. Yes, the ROW_NUMBER function can be used in conjunction with other window functions like RANK, DENSE_RANK, and NTILE to perform more complex analytical operations.
Q. Is there a limit to the number of partitions when using ROW_NUMBER in PostgreSQL?
A. There is no inherent limit to the number of partitions. However, the performance of the query may be affected if you create an excessive number of partitions.
Q. Can I use multiple ORDER BY columns within the ROW_NUMBER function?
A. Absolutely! You can specify multiple columns within the ORDER BY clause to determine the row number based on multiple sorting criteria.
Conclusion
- Rownum, facilitated by the ROW_NUMBER function, serves as an analytical window function in PostgreSQL. It efficiently assigns unique row numbers to each row returned by a query based on the specified ordering and partitioning.
- The syntax for using Rownum in PostgreSQL is clear and straightforward. By incorporating the PARTITION BY and ORDER BY clauses, you can control the grouping and sorting of row numbers according to your specific requirements.
- Rownum in PostgreSQL allows you to organize and analyze your data effectively. It is useful for various applications, such as ranking data, filtering unique rows, and facilitating pagination in query results.
- By leveraging Rownum in PostgreSQL, you can gain valuable insights from your data for better decision-making, reporting, and performance optimization.
