Using Spring Data in MongoDB
Overview
Spring Data MongoDB is a powerful tool for managing and storing different types of Spring data. With the use of collections, documents, and fields, Spring data can be efficiently modeled and stored. Collections group related data while documents represent individual records, making it easy to manage and query data.
MongoDB's support for various data types like string, boolean, number, date, and object makes
it is a great choice for storing and managing Spring data. Spring data like planning data, task tracking data, and retrospective data can be efficiently managed using MongoDB. MongoDB's flexibility and support for unstructured data allow for a more dynamic approach to data modeling, making it easier to store and manage Spring data more efficiently.
In conclusion, Spring Data MongoDB is a powerful tool for managing and storing different types of Spring data. With MongoDB's flexibility and support for various data types, Spring data can be efficiently modeled and stored. The use of collections, documents, and fields also makes it easy to manage and query data. By utilizing MongoDB for Spring data management, businesses, and developers can optimize their data storage and management capabilities.
Introduction to Spring Data MongoDB
Spring Data MongoDB is a subproject of Spring Data that provides support for working with MongoDB, a widely-used document-oriented NoSQL database. One of the key benefits of Spring Data MongoDB is its ability to provide a high-level, object-oriented interface for working with MongoDB data. It enables developers to easily map Java objects to MongoDB documents using a simple set of annotations, allowing them to write Java code to interact with MongoDB data rather than having to work with the low-level MongoDB Java driver.
Another key feature of Spring Data MongoDB is its support for reactive programming. It provides support for reactive programming through the use of the Spring WebFlux module, allowing developers to write reactive MongoDB-based applications. Overall, Spring Data MongoDB provides a flexible way to interact with MongoDB using Java, with features including object mapping, powerful query capabilities, and reactive programming for efficient and scalable applications.
MongoTemplate
MongoTemplate is a powerful class offered by the Spring Data MongoDB module that makes it easy to interact with MongoDB using Java. It provides a high-level abstraction layer for performing common MongoDB operations, such as inserting, updating, deleting, and querying documents.
To use MongoTemplate in a Spring Data MongoDB application, developers can create an instance of the class by injecting it using Spring's dependency injection framework. Once they have an instance of MongoTemplate, developers can use its methods to perform a wide range of MongoDB operations. For instance, they can insert new documents using the insert() method, update existing documents using the updateFirst() or updateMulti() methods, and execute MongoDB queries using the find(), findOne(), or aggregate() methods.
Apart from its standard MongoDB operations, MongoTemplate also offers support for MongoDB GridFS, which is a specification for storing and retrieving large files in MongoDB. With MongoTemplate, developers can work with GridFS using the store(), find(), and delete() methods, allowing them to store and retrieve large files with ease. Overall, MongoTemplate is a versatile and powerful tool that simplifies the process of managing data stored in MongoDB. Its simple and intuitive API, combined with support for advanced MongoDB features, makes it a popular choice for building complex MongoDB-based applications.
Here's an example of how to use MongoTemplate to insert or update records in a MongoDB collection:
Configuration
XML Configuration
XML configuration is a way of configuring Spring Data MongoDB using an XML file. In this approach, we define beans that represent the different components of our application and specify their properties using XML tags and attributes. Spring framework uses these beans to create instances of our application components and to wire them together.
To configure Spring Data MongoDB using XML configuration, we need to define a MongoClient bean that represents the MongoDB client instance, and a MongoTemplate bean that uses the MongoClient to perform database operations.
Here's an example of how to configure Spring Data MongoDB using XML configuration:
In this example, we define three beans:
- mongoClient: This bean represents the MongoDB client instance. We specify the URI of the MongoDB instance to connect to in the value attribute of the constructor-arg tag.
- mongoDbFactory: This bean represents the database factory instance. We specify the mongoClient bean as a constructor argument, and set the databaseName property to the name of the database we want to use.
- mongoTemplate: This bean represents the MongoTemplate instance. We specify the mongoDbFactory bean as a constructor argument.
- PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor: This bean is a post-processor that translates any exceptions thrown by MongoDB into Spring's DataAccessException hierarchy.
With these beans defined, we can use the mongoTemplate bean to perform CRUD operations on MongoDB. For example, we can inject the mongoTemplate bean into a Spring bean annotated with @Repository, and use it to perform database operations.
Java Configuration
Certainly! Java configuration is another way to configure Spring Data MongoDB, using Java code instead of XML files. With this approach, we define a configuration class that contains methods annotated with @Bean annotations, which return instances of our application components.
Here's an example of how to configure Spring Data MongoDB using Java configuration:
In this example, we define a MongoConfig class annotated with @Configuration, which contains four methods:
- getDatabaseName(): This method overrides a method in AbstractMongoClientConfiguration to specify the name of the database we want to use.
- mongoClient(): This method creates and returns a MongoClient instance that connects to the MongoDB instance running on localhost:27017.
- mongoTemplate(): This method creates and returns a MongoTemplate instance, which is a wrapper around the MongoClient instance. It uses the mongoClient() method to get the MongoClient, and the getDatabaseName() method to get the name of the database.
- exceptionTranslation(): This method creates and returns a PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor, which is a post processor that translates any exceptions thrown by MongoDB into Spring's DataAccessException hierarchy.
We also use the @EnableMongoRepositories annotation to enable Spring Data MongoDB repositories in our application. We specify the base package for our repositories using the base packages attribute.
With this configuration in place, we can now use the mongoTemplate() method to perform CRUD operations on MongoDB. For example, we can inject the MongoTemplate instance into a Spring bean annotated with @Repository, and use it to perform database operations.
To use spring-data-MongoDB in your project, you need to add the following dependency to your Maven:
How to use mongo Template
To use MongoTemplate in Spring Data MongoDB, we first need to configure it in our application context. We can do this using either XML configuration or Java configuration, as explained in my previous responses.
Once we have the MongoTemplate bean defined in our application context, we can inject it into our Spring beans using the @Autowired annotation. Here's an example:
In this example, we define a UserRepositoryImpl class that implements a UserRepository interface. We inject the MongoTemplate instance using the @Autowired annotation.
We then use the mongoTemplate instance to perform CRUD operations on our MongoDB database. In the save() method, we save a User object to the database using the mongoTemplate.save() method. In the findById() method, we query the database using the Query and Criteria classes and retrieve a User object using the mongoTemplate.findOne() method.
We can also use the mongoTemplate instance to perform more complex database operations, such as aggregations, indexing, and map-reduce. The MongoTemplate class provides a wide range of methods for interacting with MongoDB, and we can use them to perform almost any operation that we can perform using the MongoDB shell.
Mongo Repository
In Spring Data MongoDB, we can use the MongoRepository interface to define a repository for our MongoDB documents. The MongoRepository interface provides a set of methods for performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations on our documents. We can extend the MongoRepository interface in our custom repository interfaces, and Spring Data MongoDB will provide us with a default implementation of these methods.
Configuration
XML Configuration
In Spring Data MongoDB, we can also configure our MongoDB repositories using XML configuration. Here's an example:
In this example, we first define a mongo-client bean that specifies the MongoDB host to connect to. We then define a db-factory bean that specifies the name of the database we want to use and references the mongo-client bean for the connection.
Next, we define a repositories tag with the base-package attribute set to the package where our MongoDB repositories are located. We also specify the mongo-template-ref attribute to reference the mongoTemplate bean that we will define next.
Finally, we define a mongoTemplate bean of type MongoTemplate that references the mongoDbFactory bean for the database connection.
With this configuration in place, we can define our MongoDB repositories using the MongoRepository interface, as explained in my previous answer. Spring Data MongoDB will automatically create an instance of the repository implementation and inject it wherever we use the repository interface.
Java Configuration
In Spring Data MongoDB, we can also configure our MongoDB repositories using Java configuration. Here's an example:
In this example, we define a MongoConfig class that extends the AbstractMongoClientConfiguration class. This class provides default implementations of some methods required for configuring MongoDB.
We use the @EnableMongoRepositories annotation to enable MongoDB repository support in our application. We specify the package where our repositories are located using the basePackages attribute.
We then override the getDatabaseName() method to specify the name of the MongoDB database that we want to use. In this example, we use the myDatabase database.
We override the mongoClient() method to provide a MongoClient instance for connecting to the MongoDB database. We use the mongoUri property to specify the MongoDB connection string. This property is read from the application.properties file using the @Value annotation.
Finally, we define a mongoTemplate bean using the @Bean annotation. We create a new MongoTemplate instance by passing in the mongoClient() and getDatabaseName() methods.
With this configuration in place, we can define our MongoDB repositories using the MongoRepository interface, as explained in my previous answer. Spring Data MongoDB will automatically create an instance of the repository implementation and inject it wherever we use the repository interface.
Create the Repository
Once you have configured your Spring application to work with MongoDB, you can create a repository by extending the MongoRepository interface. This interface provides a set of methods for performing CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on a MongoDB collection, and can be customized by adding your custom query methods. By extending this interface, you can quickly and easily create a repository that integrates with your MongoDB database:
After defining a UserRepository interface that extends MongoRepository, you can use Spring's dependency injection to auto-wire the repository into your application and start using the built-in CRUD operations provided by MongoRepository. In addition to the default CRUD methods, you can also define your custom query methods in the repository interface to perform more advanced database operations. This makes it easy to integrate MongoDB into your Spring application and work with your database flexibly and efficiently.
How to use Mongo Repository
To use MongoDB repositories in a Spring Data MongoDB project, we need to follow these steps:
-
Define a repository interface: First, we need to define a repository interface that extends one of the Spring Data MongoDB repository interfaces such as MongoRepository, ReactiveMongoRepository, or CrudRepository. Here's an example:
-
Annotate the repository interface: We need to annotate the repository interface with the @Repository annotation. This annotation is not required, but it's a good practice to use it to indicate that this interface is a repository.
- Use the repository: We can now use the repository in our application code. We can auto-wire the repository interface and call its methods to perform CRUD operations on the database.
In this example, we define a UserService class that autowires the UserRepository interface. We define methods to save a user and retrieve users by first name and last name.
Here is an example of how to use the save() method
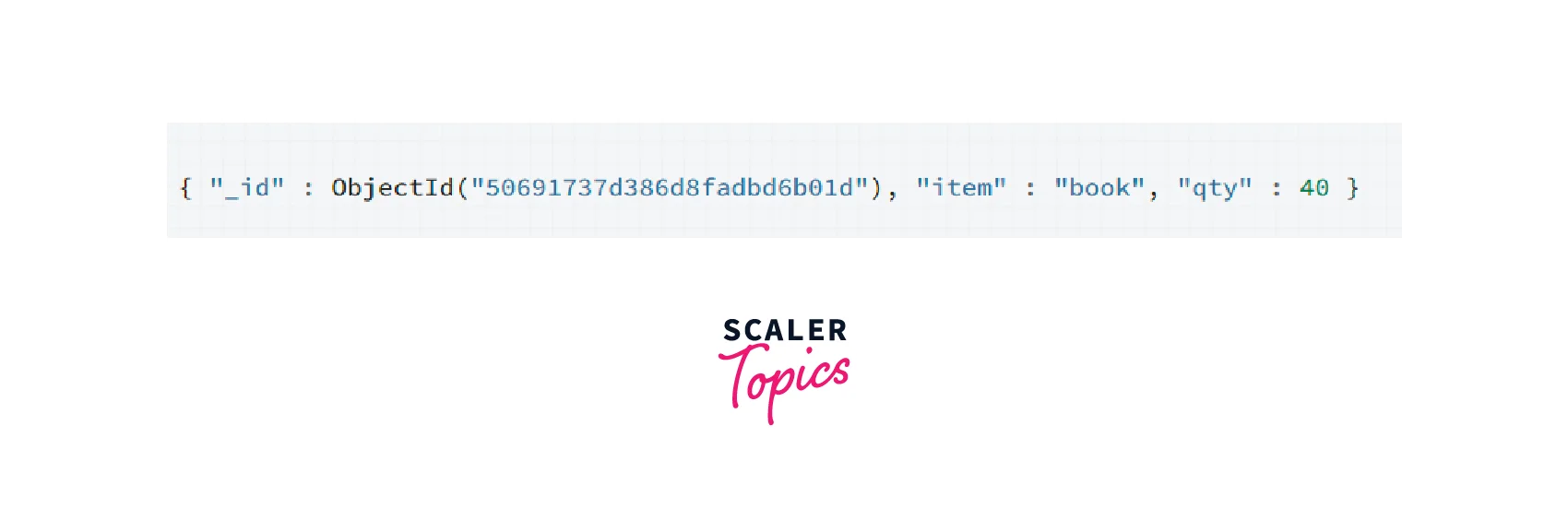

Important Annotations
There are several important annotations that are commonly used in Spring Data MongoDB to configure and use repositories. Here are some of the most important annotations and their purposes:
- @Document: This annotation is used to specify the MongoDB document that corresponds to a Java class. We can use this annotation to set the collection name, indexes, and other options for the MongoDB document.
- @Id: This annotation is used to mark a field as the primary key of a MongoDB document.
- @Indexed: This annotation is used to specify indexes on MongoDB fields. We can set options such as unique, sparse, and TTL (time-to-live) using this annotation.
- @Repository: This annotation is used to mark a class as a Spring Data MongoDB repository.
- @Autowired: This annotation is used to automatically wire a Spring bean into a class.
- @Qualifier: This annotation is used to specify which implementation of a bean to use when multiple implementations of the same bean interface are available.
- @Configuration: This annotation is used to mark a class as a configuration class for a Spring application context.
- @EnableMongoRepositories: This annotation is used to enable Spring Data MongoDB repositories in a Spring application context.
Building an Application to Store Data and Retrievee Using Spring Data MongoDB
To build an application that `stores and retrieves data using Spring Data MongoDB, we will need to follow these steps:
Prerequisites
-
Spring Initializer: We need to create a Spring Boot application using Spring Initializer. We will need to add the Spring Data MongoDB dependency in the pom.xml or build. gradle file.
-
Installing and Launching MongoDB: We need to install MongoDB on our local machine and start the MongoDB server.
Defining Simple Entity
-
We need to define a simple entity class with @Document annotation to specify the MongoDB collection and @Id annotation to specify the primary key field.
-
We can define other fields with appropriate data types and add @Indexed annotation on fields to create indexes.
For example, We will define a simple entity class named User with @Document annotation to specify the MongoDB collection and ``@Id` annotation to specify the primary key field:
Creating Simple Queries
-
We can define queries by creating repository interfaces that extend the MongoRepository interface.
-
We can define custom queries using @Query annotation on repository methods.
We will create a repository interface named UserRepository that extends the MongoRepository interface:
We have defined two query methods in our repository interface - findByEmail() and findByFirstName(). The findByEmail() method will return a User object based on the value of the email field. The findByFirstName() method will return a list of User objects based on the value of the first name field.
Application Class Creation
-
We need to create a Spring Boot application class and add a @SpringBootApplication annotation on it.
-
We need to autowire the MongoTemplate or MongoRepository objects in our application class to use them.
We will create a Spring Boot application class named MyApplication:

Executable Jar Construction
-
We can create an executable jar file of our Spring Boot application using Maven or Gradle build tools.
-
We can run the jar file using the command java -jar <jar-file-name>.jar.
We can build an executable jar file of our Spring Boot application using the following command:
This will create a jar file named my-application.jar in the target directory. We can run this jar file using the following command:
FAQS
Q. What is Spring Data MongoDB, and how is it different from other MongoDB libraries?
A. Spring Data MongoDB is a library that provides a set of abstractions and APIs for working with MongoDB in a Spring application. It offers a higher level of abstraction than the MongoDB Java driver, making it easier to work with MongoDB in a Spring-based application. Spring Data MongoDB offers features such as a query DSL, support for mapping entities to MongoDB documents, and automatic repository implementation based on method names.
Q. How do I configure Spring Data MongoDB to connect to my MongoDB instance?
A. To configure Spring Data MongoDB to connect to your MongoDB instance, you can use either XML or Java-based configuration. For XML configuration, you would typically define a MongoClient bean and a MongoTemplate bean, while for Java-based configuration, you can create a MongoClient bean and a MongoTemplate bean using the MongoClientFactoryBean and MongoTemplate classes, respectively.
Q. How can I define entities and repositories using Spring Data MongoDB annotations?
A. You can define entities and repositories using Spring Data MongoDB annotations. For example, you can annotate a POJO class with @Document to indicate that it should be mapped to a MongoDB document, and you can use annotations such as @Id and @Field to specify how the fields of the class should be mapped to the document. Similarly, you can annotate a repository interface with @Repository and extend the MongoRepository interface to inherit CRUD methods and other common operations.
Q. What are some best practices for using Spring Data MongoDB in my applications?
A. Some best practices for using Spring Data MongoDB in your applications include using the appropriate indexes for your queries, using projections and limiting results to improve query performance, and carefully defining your entities and repository interfaces to take advantage of Spring Data MongoDB's automatic query generation features. Additionally, you should make sure to handle exceptions correctly and consider using caching mechanisms such as Redis or Ehcache to reduce database load.
Conclusion
- Spring Data MongoDB is a library that provides a set of abstractions and APIs for working with MongoDB in a Spring application.
- It offers features such as a query DSL, support for mapping entities to MongoDB documents, and automatic repository implementation based on method names.
- You can configure Spring Data MongoDB using either XML or Java-based configuration, and define entities and repositories using Spring Data MongoDB annotations.
- Best practices for using Spring Data MongoDB include using appropriate indexes, projections, and limiting results to improve query performance, carefully defining entities and repository interfaces, and handling exceptions correctly.
- Overall, Spring Data MongoDB is a powerful and easy-to-use tool that can help you build scalable, maintainable applications with MongoDB and Spring.
