SQL if Statement

How to Use SQL IF Statement?
Syntax
The syntax of the IF statement in SQL is as follows:
Parameters
- Expression: The condition or expression to be evaluated. It can be a comparison, logical operation, or any valid SQL expression.
Return Type:
The IF statement does not have a direct return type. Its purpose is to control the flow of execution based on the evaluation of the specified condition. The statements within the BEGIN block will be executed if the condition is true, and the statements within the ELSE block will be executed if the condition is false.
How to Use IF Statements in SQL?
The SQL IF statement works in the following way:
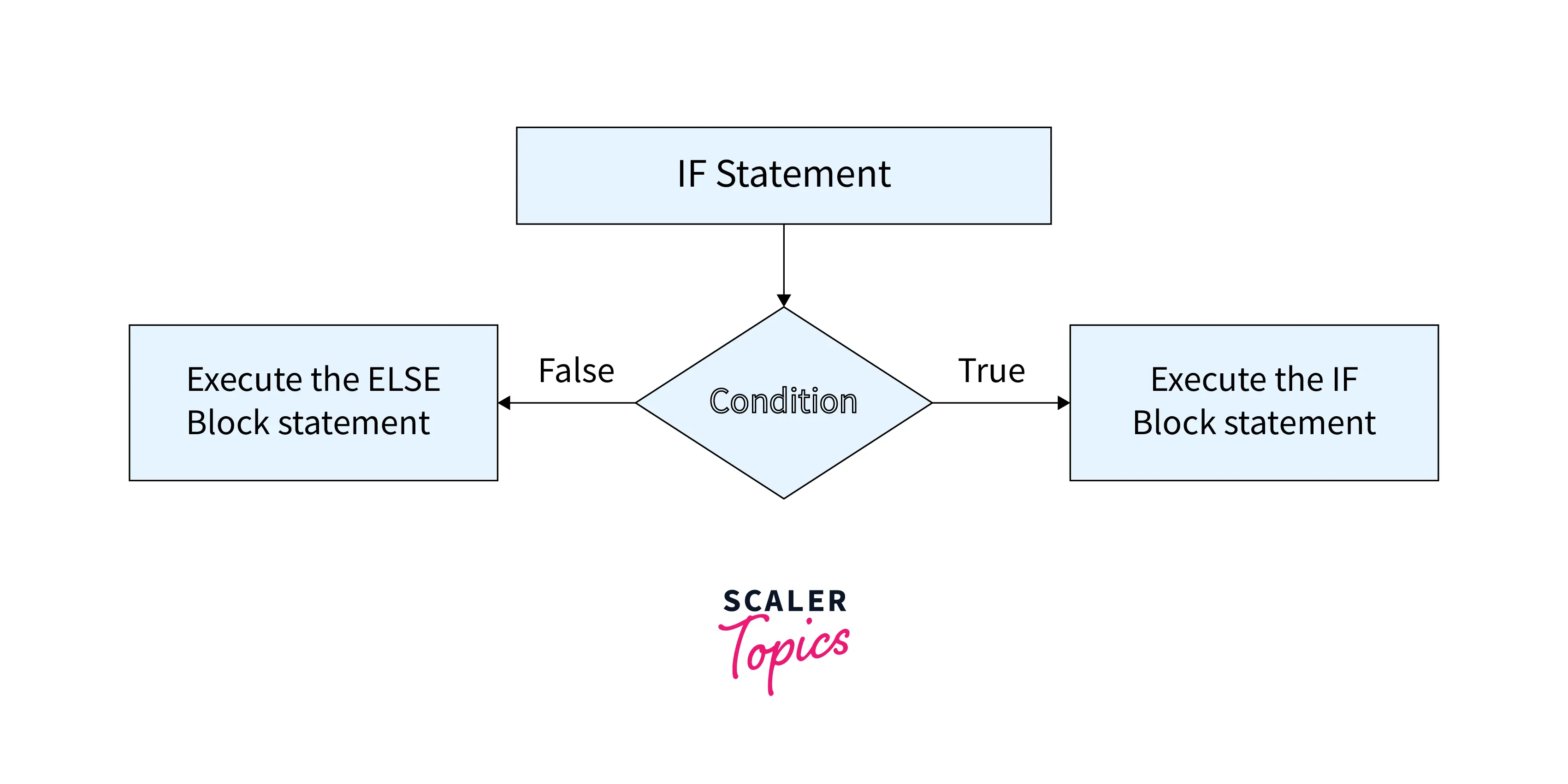
- We specify conditions in the SQL if statement and it verifies whether the condition is true or not.
- If the condition specified in the SQL query is true then the statements inside the IF block are executed
- Else the conditions in ELSE block are executed
The flow chart of the SQL IF statement is shown below:
Examples for SQL IF Statement
Example 1: Boolean Expression Containing Numerical Values in IF Statements
Here's an example of a Boolean expression with a numeric value that's always true. Because the condition is true, it prints the statement present inside the if block.
Code:
Output:
If the condition becomes false the statements inside the else block will get executed as follows:
Code:
Output:
Example 2: Boolean Expression Containing a Variable in IF Statement
A variable is used in the Boolean expression in the following example to execute the statement based on the condition. For example, if an employee has less than 50 days of attendance he is eligible for a bonus of 50%, otherwise he would be eligible for 30% bonus
Output:
Example 3: Combining a Variable in a Boolean Expression with Multiple IF Statements to Execute Queries
A SQL IF statement can incorporate multiple conditions to determine the appropriate execution path. Consider the following example:
- If an employee's leave days are less than , a message specified in the first IF statement will be displayed.
- If an employee's leave days exceed , a message from the second IF statement will be shown.
- Otherwise, the message provided in the ELSE statement will be printed.
Code:
Output:
Example 4: Use of IF Statements Without the ELSE Statement
Using the ELSE statement is not mandatory it is optional and can be decided by us whether we need it or not. SQL IF statements can also be executed without the ELSE block
The following expression evaluates to TRUE; thus, the message is printed.
Code:
Output:
Example 5: Here we Execute Scripts Based on an IF Statement
In the examples discussed till now, depending on whether a condition is true or false, messages are printed. However, in certain cases, we may also need to execute scripts based on specific requirements.
For instance, if the sales quantity is less than 100,000, the script should select records from the JuniorEmployeeSalary table. On the other hand, if an employee's salary exceeds 100,000, the script should select records from the SeniorEmployeeSalary table.
This demonstrates the flexibility of the IF statement in SQL, allowing us to choose different actions based on specific conditions.
Code:
Example 6: BEGIN and END Blocks in an IF Statement
It is possible to use the BEGIN and END statement blocks within an SQL IF statement. Whenever a condition is met, the code within the BEGIN and END blocks is executed.
Code:
Output:
The SQL IF statement and BEGIN END block allows us to specify multiple statements as well. Using the following query, we can execute two print statements if the condition specified in the if statement turns out to be false.
Output:
Conclusion
- The SQL IF statement provides the ability to include logic in queries.
- When a condition is met, the IF statement triggers specific logic based on the condition's status.
- IF statements can be considered as logically equivalent to CASE statements with searched-case-statement clauses.
- In the IF statement, optional ELSE IF clauses can be used, along with a default ELSE clause. The statement must end with an END IF clause to complete the block.
