Subset Sum Problem

Problem Statement
You have a collection of non-negative values, representing available options, and a non-negative target value. Your task is to determine whether there exists a subset within the collection whose sum equals the given target value.
Example
Example1:
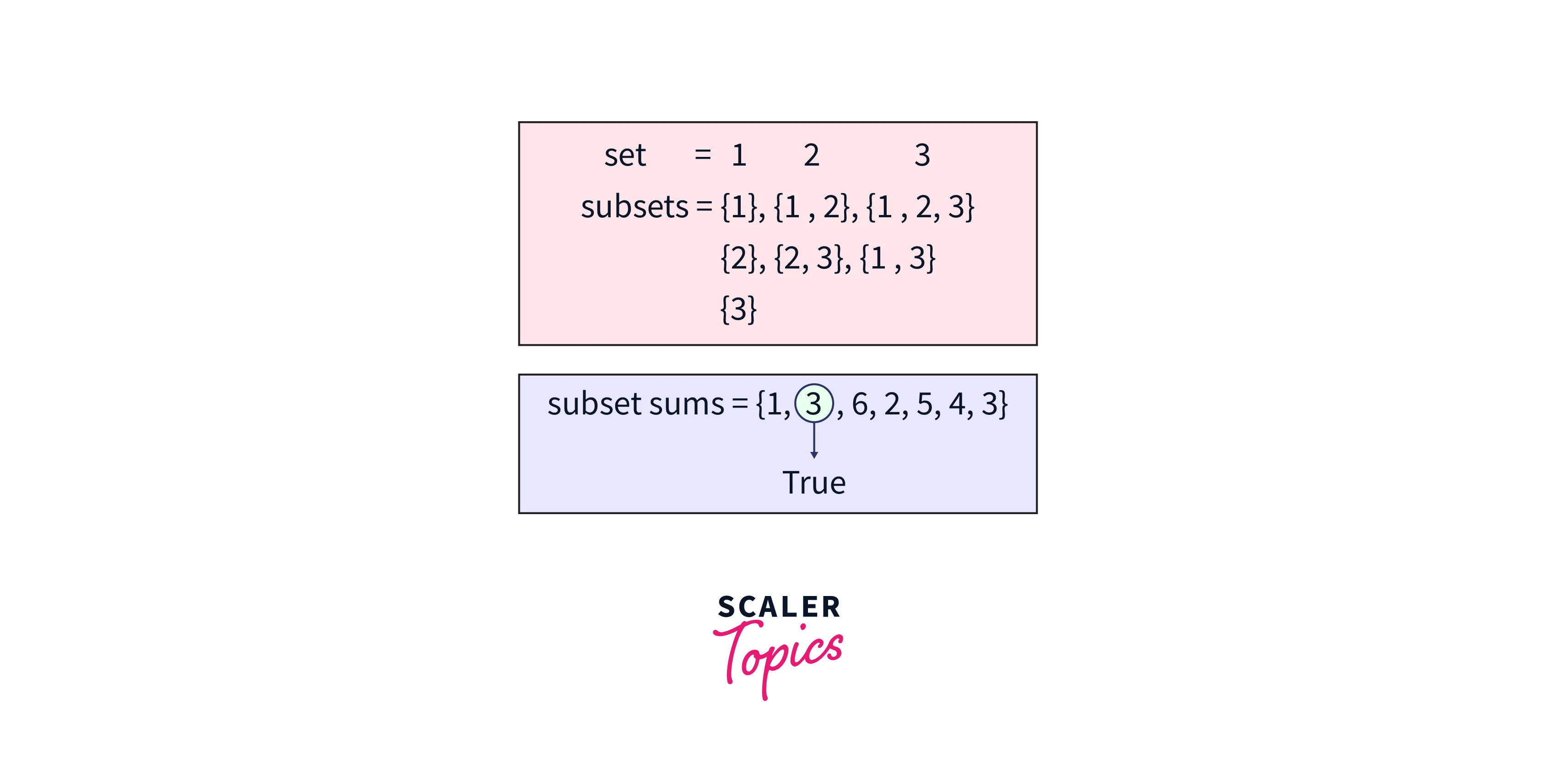 Example2:
Example2:
Approach 1: Using Recursion
We can approach the Subset Sum Problem recursively by considering two cases for each element in the set:
- Case 1: Include the current element in the subset. In this case, reduce the target sum by the value of the current element, and consider the remaining elements in the set.
- Case 2: Exclude the current element from the subset. In this case, keep the target sum unchanged and consider the remaining elements in the set.
The recursion continues until we either find a subset that satisfies the target sum or exhaust all elements in the set.
Following is the recursion tree:
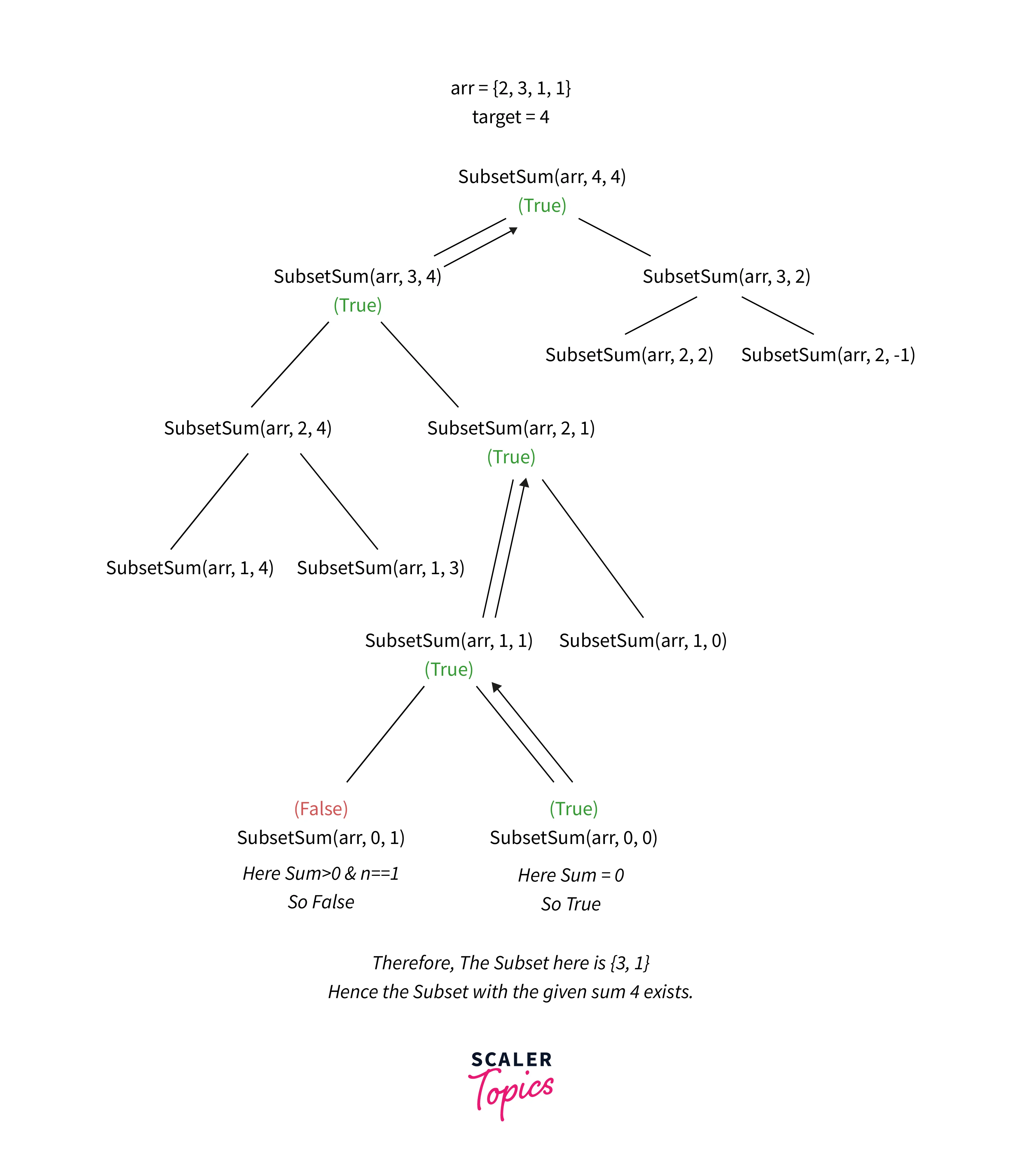
Algorithm:
- Define a recursive function that takes the current index of the set and the remaining sum to be achieved.
- For each index, check the base cases:
- If the remaining sum is zero, return true (subset found).
- If there are no elements left to consider (index becomes zero) and the remaining sum is still positive, return false (no subset found).
- Recur by considering two cases:
- Case 1: Include the current element and reduce the remaining sum by the value of the current element.
- Case 2: Exclude the current element and keep the remaining sum unchanged.
- If any of the recursive calls return true, then there exists a subset that satisfies the target sum; otherwise, no such subset exists.
Code Implementation
C++
Python
Java
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The time complexity of recursive solution for the Subset Sum Problem is exponential, O(2^n), as it may need to explore all possible subsets of the given set to find the solution. This problem is classified as NP-Complete, indicating that there is no known polynomial-time solution for it.
Space Complexity: The auxiliary space complexity of the recursive solution is O(n), where n represents the recursion stack space required for the recursive calls.
Approach 2: Using Memoization
- Utilize dynamic programming by creating a 2D array to store the results of subproblems.
- Each state in the solution can be uniquely identified by two variables: the index and the remaining sum.
- Compute and store the value of each state in the 2D array to avoid recalculation of the same state.
By memoizing the results, we can significantly reduce the time complexity of the algorithm, making it more efficient compared to the naive recursive approach.
Code Implementation
C++
Python
Java
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: The time complexity is O(sum * n) because we iterate through each element in the set and for each element, we iterate through the target sum.
Space Complexity: The auxiliary space complexity is also O(sum * n) because of the 2D array used for memoization and the recursion stack space.
Approach 3: Using Dynamic Programming
To solve the sum of subset problem efficiently using dynamic programming:
- Initialization: Create a 2D boolean array of size (n + 1) * (sum + 1), where n is the size of the given array and sum is the target sum. Initialize the array with appropriate base cases.
- Dynamic Programming Iteration:
- Iterate through each element of the set (i) and each possible sum value (j).
- Use the dynamic programming relation:
- If the current element (A[i-1]) is greater than the current sum value (j), copy the value from the previous row: dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j].
- Otherwise, update dp[i][j] to true if either dp[i-1][j] is true or dp[i-1][j-set[i-1]] is true.
- Result Check: After completing the iteration, check if dp[n][sum] is true. If true, there exists a subset with the target sum.
This approach effectively identifies whether there exists a subset of elements from the given set that sums up to the target sum, accomplishing the task in pseudo-polynomial time.
Example :
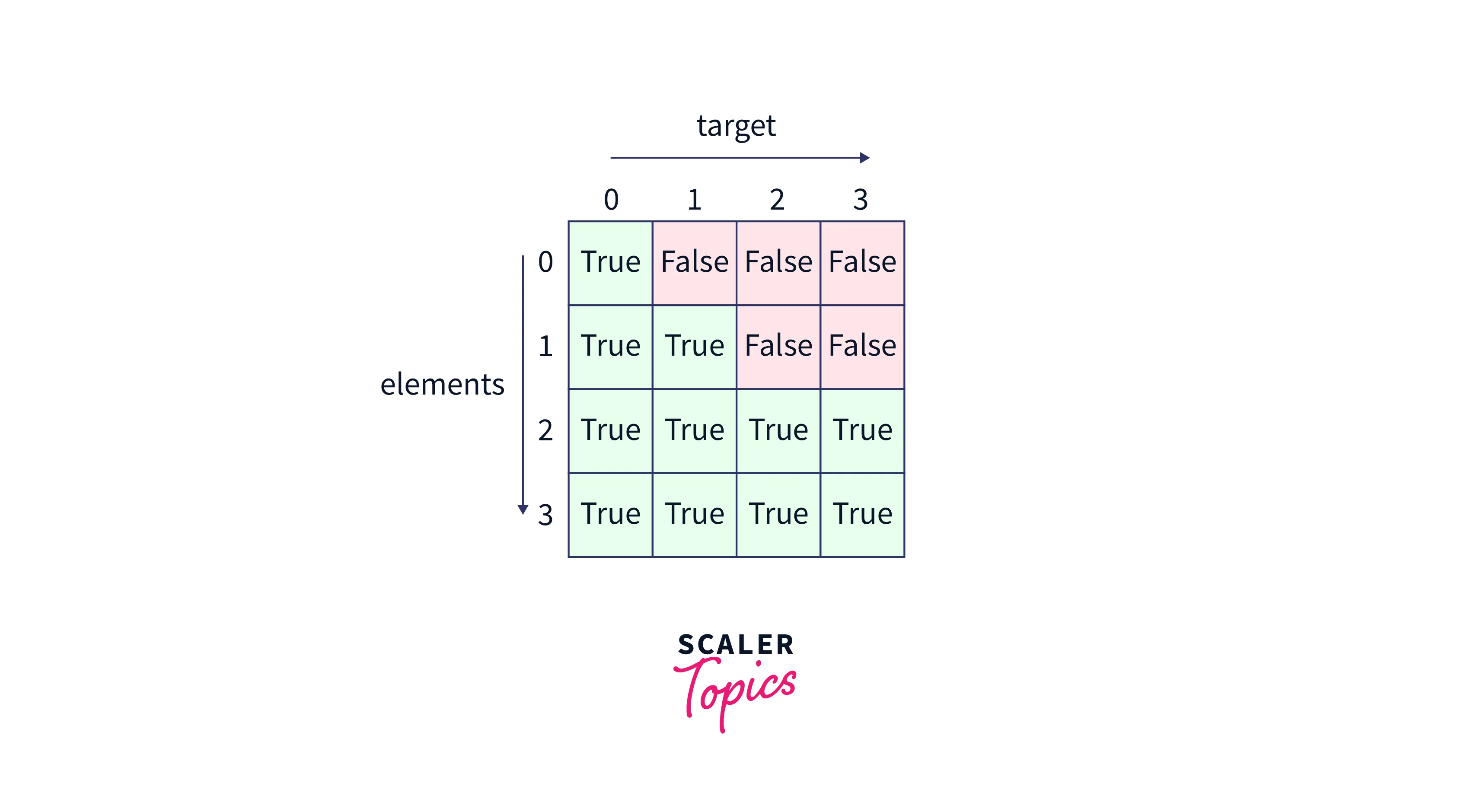
Code Implementation
C++
Python
Java
Output
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(sum * n) - We iterate through each element in the array and each possible sum value.
Space Complexity: O(sum * n) - The space complexity arises from the 2D array used for dynamic programming, which has a size proportional to the product of the array size and the target sum.
Approach 4: Using Dynamic Programming With Space Optimization to Linear
Instead of storing the entire 2D array for dynamic programming, we only need to store the results for the previous row (prev) and the current row (curr).
Approach:
- Define two arrays: prev and curr, both of size (sum + 1), to store the results of the just previous row and the current row, respectively.
- Iterate through each element in the given array and each possible sum value, updating the curr array based on the dynamic programming relation.
- Once the curr array is calculated, swap it with the prev array to prepare for the next iteration.
- After processing all rows, the answer is stored in the prev array.
By only storing the results for the previous and current rows, we achieve space optimization while still efficiently solving the Subset Sum Problem.
Code Implementation
C++
Java
Python
Output:
Complexity Analysis
Time Complexity: O(sum * n) - We iterate through each element in the array and each possible sum value.
Space Complexity: O(sum) - The space complexity arises from the 1D array used for dynamic programming, which has a size proportional to the target sum plus one.
Conclusion
- Problem Overview: Subset Sum problem involves finding whether a subset of non-negative values equals a given target sum.
- Approaches: Explored recursive, memoization, dynamic programming, and space-optimized dynamic programming methods.
- Recursion: Simple but exponential time complexity.
- Memoization: Reduces time complexity to O(sum * n) but has high space complexity.
- Dynamic Programming: Efficiently solves the problem with time and space complexity of O(sum * n).
- Space-Optimization: Maintains linear space complexity while achieving the same time complexity as dynamic programming.
