Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)
Overview
SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) is a standardized form of protocol that is used in digital communication between the sender and the receiver. It uses a fiber optic medium to transmit a huge amount of data across a large distance. SONET helps us to transmit data over larger distances with greater data transmission rates. We have another protocol i.e. Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH). SONET and SDH are quite similar and they are developed for the same reason. SDH standard can work with the SONET lines as well.
What is Synchronous Optical Network (SONET)?
The synchronous optical network or SONET is a standardized form of protocol that is used in digital communication between the sender and the receiver. SONET protocol uses fiber optic medium (optical fibers) to transmit a huge amount of data across a large distance. One of the main advantages that a synchronous optical network provides is that it can be used to transfer multiple streams of data simultaneously (at the same time) using optical fibers.
Some of the important points related to SONET are:
- SONET is used in the physical layer of the OSI model for broadband synchronized transmission of data such as voice, video, etc.
- It was developed by Bellcore in the mid-1980s and it was developed for the public telephone network.
- It is used in the North American region.
- SONET is standardized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
- SONET is efficient and costs low for a few channels because of higher transmission rates.
- SONET is somewhat similar to the SDH which is used in regions like Japan and Europe.
- At the higher capabilities, there is a problem with bandwidth efficiency.
- There is more overhead related to the SONET protocol as it is complex to implement and we have to work with multiple channels.
- There is no standard compatible with the SONET protocol.
- Tributary services are used for transporting and switching payloads and for the tributary services, the mux services of SONET are necessary.
Why SONET is Called a Synchronous Network?
Let us now try to understand why SONET is a synchronous network.
In SONET, we have a single Primary Reference Clock (PRC) which handles the transmission timing of signals and the equipment used across the entire network. A typical PRC provides the reference signal for the timing or synchronization of other clocks within a network or section of a network. In particular, the PRC can also provide the reference signal to the slave clock
Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) are together used to provide the capability for telecommunication to provide high-speed services for both voice and data over the same network.
SONET Network Elements
Let us now learn about the various SONET network elements.
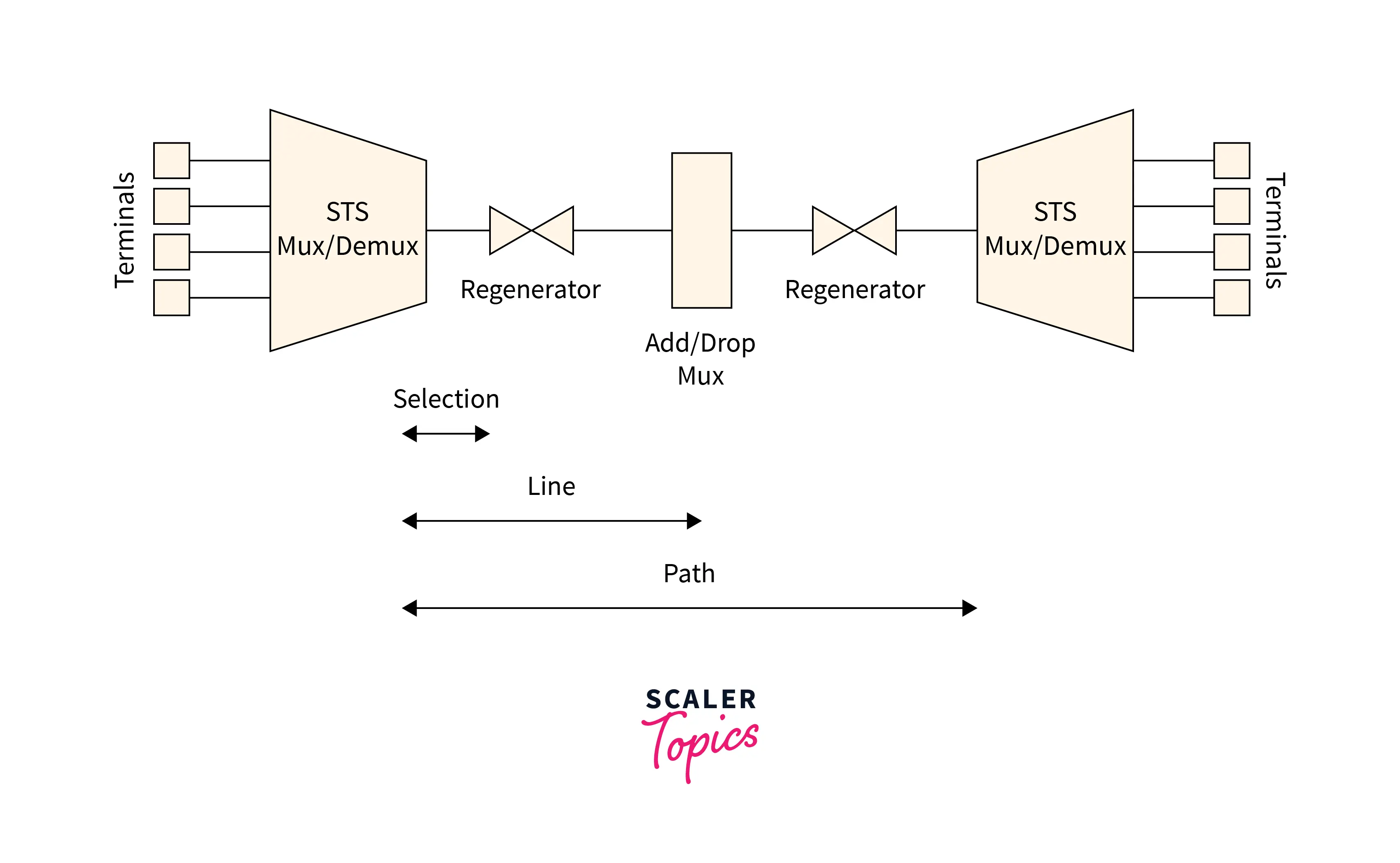
- STS Multiplexer: It is used to perform multiplexing of the digital signals (combine all the different frequencies into a strengthened single signal at the sender's end so that transmission can take place easily) and it converts the electrical signals to optical signals. What are multiplexers? Well, a device that can combine all the different frequencies into a single signal (composite signal) at the sender's end so that transmission can take place easily is called a multiplexer.
- STS Demultiplexer: The STS Demultiplexer is just opposite to the multiplexer, it performs the de-multiplexing of the digital signals. Along with de-multiplexing, it converts the optical signals back into electrical signals. What are demultiplexers? Similar to the multiplexers, at the receiver's end, we use a device that can do the reverse work which is to extract the individual frequency. Theoretically, we can say that the device that combines the various frequencies into a single composite signal at the sender's end is termed a multiplexer (MUX) and the device that extracts the various frequencies from the composite signal at the receiver's end is termed a de-multiplexer (DEMUX).
- Regenerator: A regenerator is nothing but a repeater that strengthens the provided optical signals. Hence, a regenerator is a device that increases the incoming optical signal and allows them to travel farther than it would have traveled without the regeneration of the signal.
- Add/ Drop Multiplexer: It is a multiplexer that enables the signal to be added or removed from a source. The add or drop multiplexer adds the signals (to be sent to the receiver to create a strong single signal) from several sources to a particular path or removes the unuseful signal from the specified path so that the transmission of signals can take place more smoothly.
Refer to the image provided below for more clarity.
Why SONET is Used?
SONET consists of multiplexers and demultiplexers. In the previous section, we learned about them and other network-related elements used in the SONET protocol communication. Using SONET, we can make the network carry voice, video, and data simultaneously.
A SONET is a protocol that is used to change the electrical signal into an optical signal and allows it to travel farther. In today's world, SONET acts as a standard that is used by other digital networks for interconnection. It uses the already existing conventional transmission systems like an optical medium through tributary attachments for data transmission. The data transmission speed is Gigabit, which is similar to Ethernet speed.
SONET Standards
For the line rates ranging up to 10 Gbps (gigabits) per second, we have the SONET standards. So, the line rates of the signals that are approaching the 30 gigabits per second range are possible to deal with SONET protocol.
The optical carrier levels such as level-1, or OC-1. OC-1 are base units of SONET and they support up to 51.84 Mbps (megabytes) per second. On the other hand, the OC-3 level supports the triple bandwidth.
ANSI T1.105 and T1.117 specify the ANSI standards.
Let us look at the speed table of the SONET network.
| Electrical Signal | Optical Carrier | Speed |
|---|---|---|
| STS-1 | OC-1 | 51.48 Mbps |
| STS-3 | OC-3 | 155.52 Mbps |
| STS-12 | OC-12 | 622.08 Mbps |
| STS-24 | OC-24 | 1.24 Gbps |
| STS-48 | OC-48 | 2.48 Gbps |
| STS-192 | OC-192 | 9.95 Gbps |
SONET Connections
Let us now look at the connections involved in the SONET connection.
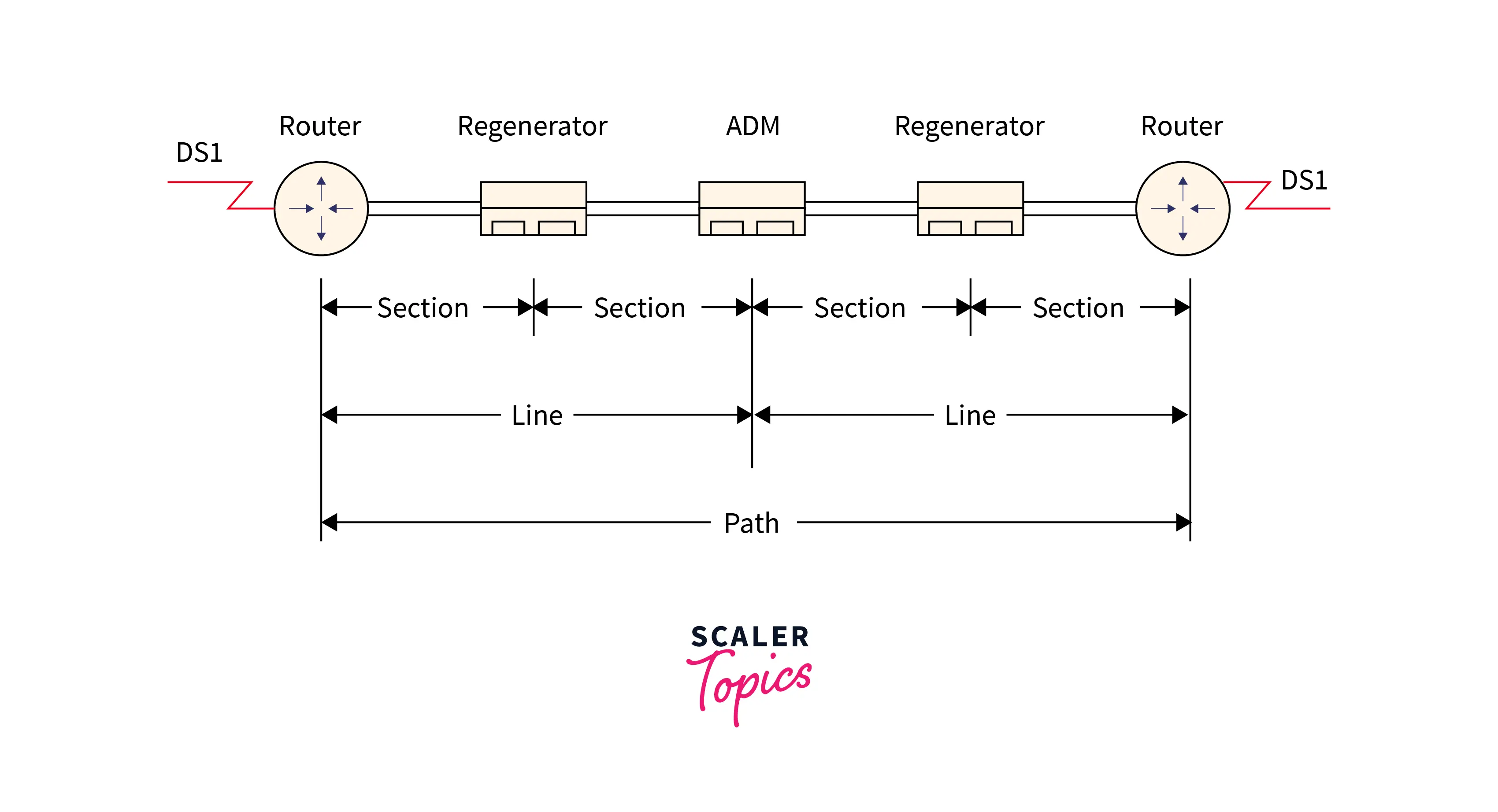
- Section: It is the portion of the network that connects the two neighboring devices of the network.
- Line: It is the portion of the network that connects the two neighboring multiplexers of the network.
- Path: The end-to-end section in the network.
Refer to the image provided below for more clarity.
SONET Layers
Let us now learn about the various layers involved in the SONET protocol.
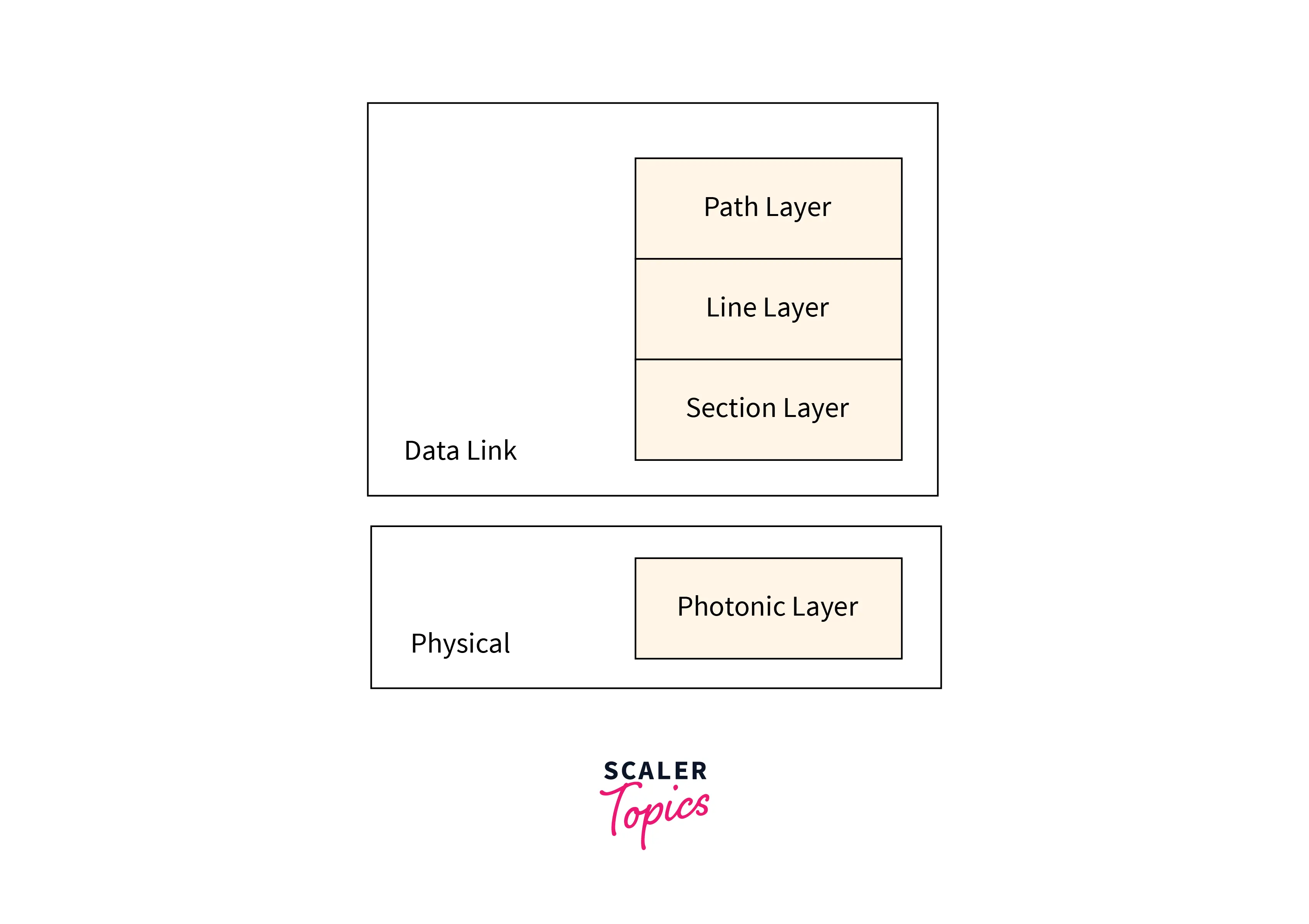
- Path Layer: It is the first layer of SONET present in the Data Link Layer of the OSI model and it allows the movement of the signals from the optical source to the optical destination of the signal or data. We have STS Mux/Demux in the Path layer that is responsible for providing the path layer functions.
- Line Layer: It is the second layer of SONET present in the Data Link Layer of the OSI model and it allows movement of the signals across the physical line. We have STS Mux/Demux as well as the Add/Drop Mux in the Line Layer that is responsible for providing the line layer functions.
- Section Layer: It is the third layer of SONET present in the Data Link Layer of the OSI model and it allows movement of the signals across the physical section in the form of signals. Each device present on the network provides the section layer functions in SONET.
- Photonic Layer: It is the fourth layer of SONET present in the Physical Layer of the OSI model and it is similar to the Physical layer of the OSI model. The photonic layer provides physical signification for the fiber optic cables.
Refer to the image provided below for clarity.
To learn more about the OSI model, please refer to here.
Advantages of SONET
Some of the major advantages that the SONET protocol provides are:
- SONET helps us to transmit the data over larger distances.
- SONET can provide greater data transmission rates as it used the physical and data link layer of the OSI model and can transmit numerous signals at a single time.
- SONET provides broader bandwidth than other protocols due to its feature of multiple signal transmission.
- In the case of the SONET protocol, there is very less electromagnetic interference.
- SONET protocol provides multiple data types like data, voice, and video for transmission.
- SONET can also carry high-level protocols like Internet Protocol (IP) because SONET also uses the framing concept that is used in the OSI model for data transmission.
- SONET also defines the interoperability standards for the organizations.
However, SONET utilization is costlier.
SONET Configuration Issues
Let us now see some of the configuration issues present in the synchronous optical network.
- Clocking: It is used for deriving the clocking from the network. For more details, you can refer to Configuring Clock Settings on POS Router Interfaces.
- Loopback: The loopback is internal line value of DTE.
- Framing: Framing tells us the type of protocol that is being used for transmission. SONET and SDH are supported by most of the Cisco framers.
- Payload Scrambling: The payload scrambling value is set to ON and it is used to specify the payload.
- S1S0 flag: The S1S0 flag value lies between 0 and 3 while its default value is 0. It is used for alarm indication signals. With SONET, S1S0 must be set to 0, and with SDH it must be set to 2. Value 3 corresponds to the received Alarm Indication Signal (AIS).
- J0 flag (0-255): J0 flag setting is present in the trace identifier section of SONET and it is used for the tracing. By tracing we mean the traceroute, traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track in real-time the pathway taken by a packet on an IP network from source to destination, reporting the IP addresses of all the routers it pinged in between.
- C2 flag (0-255): C2 flag is used to set the STS path signal label. We can configure the C2 flag using the pos flag command. This setting specifies the STS path signal label (5 to 7 are configured with the pos flag command).
- Alarm reporting: It allows us to specify the alarm that is used for reporting. Some of the permitted values of the alarm are b1-TCA, b2-TCA, sf-ber, sd-ber, los, lof, ais-l, and rdi-l. We can configure the alarm using the pos report command.
- Alarm thresholds: The alarm thresholds allow us to specify the BER or bit error rate threshold of the alarm signal. We can configure the alarm threshold using the pos threshold command.
Debugging Synchronous Optical Network
We can debug the synchronous optical network. If the link of the SONET is down/down, we should check the active alarms and other defects associated with SONET.
Now for the troubleshooting, we can check the SONET controller which provides us various L1 and SONET information regarding the troubleshooting. To view the current state of the POS controller, we can use the active defects and the active alarms fields of SONET.
The number present under the section, Line, and Path tells us the number of times the error has occurred. This number does not indicate the current error.
We have a BIP (Bit Interleaved Parity) error corresponding to the specific SONET layer. The layer-wise BIP error is:
- BIP (B1): Line layer.
- BIP (B2): Section layer.
- BIP (B3): Path layer.
We can use the show controllers pos x/y command to display all the statuses of the SONET controller.
Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)
We have another digital communication protocol i.e. SDH (Synchronous Digital Hierarchy) which is a multiplex technology that is usually used in telecommunications. Synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) is the international equivalent of SONET. SDH is comparatively cheaper and faster than the PDH (Plesiochronous Digital Hierarchy). SONET and SDH are quite similar and they are developed for the same reason. SDH standard can work with the SONET lines as well. SDH provides high-order multiplexing.
Difference between Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) and Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SDH)
As we know the Synchronous Digital Hierarchy and Synchronous Optical Network are quite similar to each other. Let us now look at the differences between both protocols.
| SONET | SDH |
|---|---|
| SONET stands for Synchronous Optical Network. | SDH stands for Synchronous Digital Hierarchy. |
| SONET is developed by ANSI (American National Standards Institute). | SDH is developed by ITU-T (International Telecommunication Union – Telecommunication Standardization Sector). |
| SONET has 27 (i.e. 9x3) bytes of total transport overheads. | SDH has 81 (i.e. 9×9) bytes of a total number of transport overheads. |
| SONET can only transmit data synchronously. | SDH can only transmit data both synchronously and asynchronously. |
| SONET provides lesser transmission rates than SDH because SONET does not use high-order multiplexing to transfer signals. | SDH provides better transmission rates than SONET because SDH uses the high-order multiplexing technique to transfer signals. |
| SONET is a kind of digital hierarchy interface. | SDH is a user network interface and U reference-point interface. |
| The frame of SONET is made up of 6,480 bytes and it uses the STM i.e. Synchronous Transport Module. | The frame of SDH is made up of 2,430 bytes and it uses the STS i.e. Synchronous Transport Signal. |
| The basic unit of SONET is called the Optical Carrier level. | The basic unit of SDH is known as the synchronous transmission module level-1(STM-1). |
Additional Resources
We have a lot more content on the server, client, their connection, OSI model, TCP/IP model, and whatnot. Please refer to the links provided below to learn more content related to computer networking on Scaler Topics!
Conclusion
- SONET (Synchronous Optical Network) is a standardized form of protocol that is used in digital communication. It uses a fiber optic medium to transmit a huge amount of data across a large distance.
- SONET is used in the physical layer for broadband synchronized transmission of data such as voice, video, etc.
- It was developed by Bellcore in the mid-1980s and it was developed for public telephone networks. It was standardized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI).
- We have a single Primary Reference Clock (PRC) in the SONET protocol which handles the transmission timing of signals and the equipment used across the entire network.
- Path Layer is the first layer of SONET that allows the movement of the signals from the optical source to the optical destination of the signal or data. The path Layer is the first layer of SONET that allows the movement of the signals from the optical source to the optical destination of the signal or data.
- Line Layer is the second layer of SONET that allows movement of the signals across the physical line. Section Layer is the third layer of SONET that allows movement of the signals across the physical section.
- Photonic Layer is the fourth layer of SONET that provides physical signification for the fiber optic cables. It is similar to the Physical layer of the OSI model.
- SONET protocol provides multiple data types like data, voice, and video for transmission. It can also carry high-level protocols like Internet Protocol (IP).
- SONET can provide greater data transmission rates and provides broader bandwidth than other protocols.
