Types of Business Analytics
Overview
Business analytics is the systematic approach to interpreting, understanding, and deriving insights from vast sets of business data using statistical analysis, data mining, and quantitative techniques. Organizations use the derived data for effective and strategic decision-making. The diversity in types of business analytics is due to the different nature of business challenges and the varied insights sought by different stakeholders. Let us explore the various types of business analytics to extract meaningful information from their data.
Types of Business Analytics
Business analytics includes a wide range of analytical techniques, each having distinct purposes in the data-driven decision-making process. These can be broadly categorized into Descriptive Analytics, Diagnostic Analytics, Predictive Analytics, Prescriptive Analytics, and Cognitive Analytics.
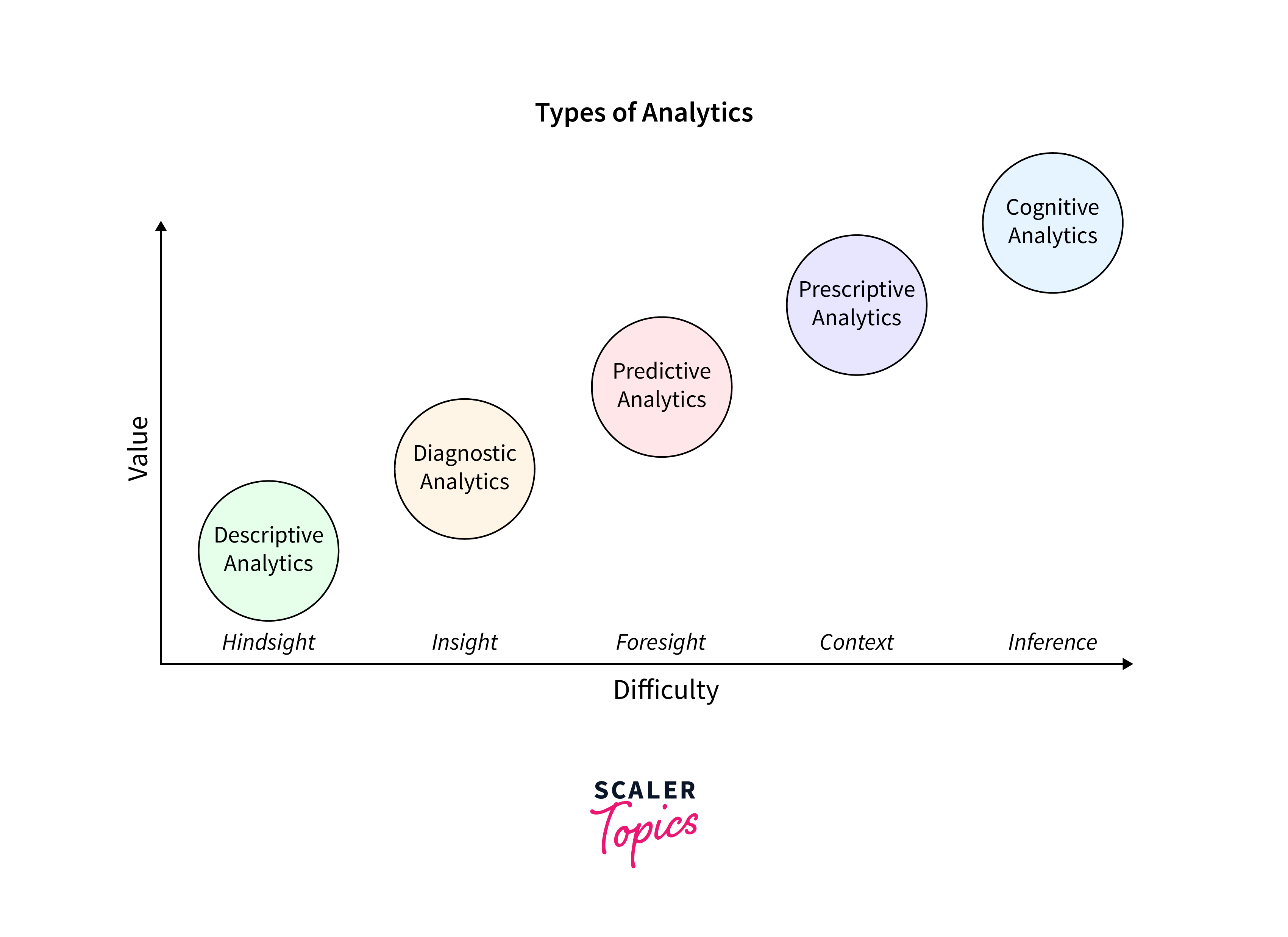
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive analytics is the examination and summarization of historical data to provide an overview of past events. It provides analytics of everything that happened, by presenting data in a meaningful and understandable way. Descriptive analytics uses key performance indicators(KPI) as metrics to provide an overview of an organization's historical performance. Common KPIs include sales revenue, customer acquisition cost, conversion rates, and average order value.
Outcomes:
Descriptive analytics is used to generate reports, dashboards, and visualizations that show historical data trends. By analyzing KPIs and relevant metrics, organizations can identify areas of success, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions.
Tools:
Common tools for descriptive analytics are:
- Spreadsheet software (e.g., Microsoft Excel)
- Tools for Data visualization (e.g., Tableau, Qlik, Power BI).
- Statistical software (e.g., R, Python).
Example Situation:
In e-commerce, descriptive analytics can be employed to analyze sales data over the past year. By creating visualizations, such as monthly sales trends and product performance charts, the business can identify peak sales periods, popular products, and areas that require improvement. This information helps in inventory planning, marketing strategy adjustments, and overall business optimization based on historical performance.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics explores deeper into data to identify the root causes behind specific outcomes or events by analyzing historical data patterns of certain business scenarios.
Outcomes:
The primary outcome of diagnostic analytics is a complete understanding of the factors influencing specific outcomes. It helps in the identification of correlations, patterns, and anomalies within datasets by exploring relationships between variables,
Tools Used:
Common tools for diagnostic analytics are:
- Correlation and Regression Analysis tools to understand the relationship between various factors
- Statistical software for data discovery and mining.
- Time Series Analysis tools for trend identification
Example Situation:
In healthcare, diagnostic analytics can be applied to understand the factors influencing patient readmission rates. By analyzing patient data, including medical history, treatment adherence, and post-discharge care, healthcare providers can identify patterns leading to readmissions. This insight can help in the improvement of post-discharge instructions or personalized care plans, to reduce unnecessary hospital returns.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics involves utilizing statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future trends and outcomes based on historical and current data. It works by identifying patterns and making informed predictions.
Outcomes:
The primary outcome of predictive analytics is the ability to anticipate future trends, behaviors, or events. Predictive analytics is used to build models that forecast future scenarios. Through historical data, it identifies patterns and applies algorithms to make predictions which are used to optimize strategies, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive advantage.
Tools Used:
Common tools for predictive analytics are:
- Packages for Machine learning (e.g., TensorFlow, Scikit-Learn).
- Predictive analytics Dashboard tools (e.g., RapidMiner, IBM Watson Studio, H2O).
- Data science and Data mining tools.
Example Situation:
In finance, predictive analytics can be applied to forecast stock prices. By analyzing historical stock data, market trends, and relevant economic indicators, predictive models can be developed to anticipate future stock movements. This information assists investors in making informed decisions about buying, selling, or holding stocks, enhancing their ability to navigate the volatile financial market.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics focuses on recommending actions to optimize outcomes. It goes beyond predicting future scenarios by suggesting the best course of action based on the analysis of potential impacts and benefits.
Outcomes:
The primary outcome of prescriptive analytics is actionable insights that guide decision-making to achieve desired outcomes. It is used to model various scenarios and evaluate the potential outcomes of different decisions., which organizations determine the most effective strategies or interventions to maximize benefits or minimize risks.
Tools Used:
Common tools for prescriptive analytics are:
- Optimization software(e.g., Google Analytics, APMonitor)
- Simulation tools(e.g., Alteryx, Spotfire)
- Decision analysis tools(e.g., KNIME) .
These tools are often integrated with advanced analytics platforms or business intelligence solutions.
Example Situation:
In supply chain management, prescriptive analytics can be employed to optimize inventory levels. By considering factors such as demand fluctuations, lead times, and storage costs, prescriptive models can recommend optimal inventory levels to minimize holding costs while ensuring product availability. This enables organizations to make strategic decisions that balance efficiency and customer satisfaction in their supply chain operations.
Cognitive Analytics
Cognitive analytics involves the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to simulate human thought processes. It enables systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously, enhancing the depth and speed of data analysis. Cognitive analytics aims to answer complex questions and solve problems by using cognitive functions.
Outcomes:
- The primary outcome of cognitive analytics is the generation of advanced insights and the ability to handle unstructured data effectively.
- Cognitive analytics is used to process unstructured data, such as text, images, and voice, to derive insights.
- Natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and deep learning techniques are applied to understand context, sentiment, and patterns in data, enabling systems to provide intelligent responses and recommendations.
- It allows automated decision-making and the identification of patterns in large datasets that may be challenging for traditional analytics methods.
Tools Used:
Common tools for cognitive analytics are:
- Machine learning frameworks (e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch)
- Natural language processing libraries (e.g., NLTK, spaCy)
- Cognitive computing platforms (e.g., IBM Watson).
Example Situation:
In customer service, cognitive analytics can be applied to analyze customer interactions. By processing customer queries, feedback, and sentiments expressed in various channels, cognitive analytics can identify patterns to improve response accuracy and automate the resolution of common issues. This enhances the overall customer experience by providing quicker and more personalized support.
Top Companies Choose Different Types of Business Analytics
Leading companies across industries recognize the importance of integrating various types of business analytics into their operations. Let us explore some of those companies.
Amazon
- Amazon utilizes business analytics extensively for dynamic pricing, demand forecasting, and customer personalization.
- Tools like Amazon Web Services (AWS), along with machine learning algorithms, analyze customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history to optimize product recommendations and pricing.
- Business analytics also aids in inventory management and supply chain optimization, ensuring efficient operations.
Uber
- Uber leverages business analytics to optimize the pricing algorithms based on demand, traffic conditions, and user patterns.
- Additionally, analytics is applied for route optimization, predicting rider demand, and improving driver allocation.
- This enables Uber to provide a seamless and efficient transportation service.
Microsoft
- Microsoft utilizes business analytics for product development, customer relationship management, and marketing strategies.
- Tools like Power BI assist in visualizing and interpreting data for decision-makers.
- Business analytics helps Microsoft understand user behavior in their software products, allowing them to make data-driven improvements, optimize marketing campaigns, and enhance customer experiences.
Starbucks
- Starbucks utilizes business analytics for customer engagement and operational efficiency.
- The company's mobile app gathers customer data, preferences, and purchasing habits.
- Analytics tools help Starbucks understand consumer trends, optimize store locations, and tailor marketing promotions. This data-driven approach enhances the overall customer experience and drives loyalty.
Apple
- Apple applies business analytics in various aspects, from supply chain management to marketing.
- The company uses analytics to understand customer preferences, forecast demand for new products, and optimize inventory levels.
- In marketing, Apple analyzes user data to personalize advertising and promotions. Tools like Tableau enable Apple to extract insights that inform strategic decisions.
What Types of Business Analytics Should You Choose?
Choosing the right types of business analytics depends on the specific needs and goals of an organization. Here are key considerations including the advantages and disadvantages of each role:
Descriptive Analytics
- Advantage: Provides a historical overview, aiding in understanding past performance and trends.
- Disadvantage: Limited to retrospective insights, may not offer actionable foresight.
Diagnostic Analytics
- Advantage: Identifies root causes behind specific outcomes, facilitating targeted interventions.
- Disadvantage: Time-consuming, requires in-depth analysis, and may not be suitable for real-time decision-making.
Predictive Analytics
- Advantage: Forecasts future trends, enabling proactive decision-making and risk mitigation.
- Disadvantage: Relies heavily on historical data and assumptions, outcomes may vary in rapidly changing environments.
Prescriptive Analytics
- Advantages: Recommends optimal actions for desired outcomes, guiding decision-making.
- Disadvantage: Complex implementation, reliance on accurate data, and potential resistance to automated decision recommendations.
Cognitive Analytics
- Advantages: Using AI for advanced pattern recognition and autonomous decision-making.
- Disadvantage: Requires sophisticated tools, potential ethical concerns, and high initial investment.
FAQs
Q. How do business analytics differ from business intelligence?
A. Business analytics focuses on analyzing data to gain insights and make informed decisions, while business intelligence is more about collecting, reporting, and visualizing data.
Q. What is the difference between cognitive analytics, predictive, and prescriptive analytics?
A. Cognitive analytics involves simulating human thought using AI, predictive analytics forecasts future outcomes based on historical data, and prescriptive analytics recommends optimal actions by analyzing potential impacts, guiding decision-making for desired outcomes or risk minimization through advanced data modeling and optimization techniques
Q. Can small businesses benefit from business analytics?
A. Yes, businesses of all sizes can benefit from analytics. Smaller enterprises can use analytics to optimize operations, understand customer behavior, and make strategic decisions.
Conclusion
- Business analytics involves the systematic application of statistical analysis, data mining, and quantitative techniques to interpret, understand, and derive actionable insights from business data. Organizations use business analytics to make informed decisions for strategic planning based on data-driven insights.
- Descriptive analytics focuses on examining historical data to provide an overview of past events, summarizing and interpreting data to understand what has happened in a business. Diagnostic analytics delves deeper into data to uncover the reasons behind specific outcomes or events, aiming to identify root causes by analyzing historical data patterns.
- Predictive analytics utilizes statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future trends and outcomes based on historical and current data. Prescriptive analytics recommends optimal actions by analyzing potential impacts and benefits, guiding decision-making to achieve desired outcomes or minimize risks.
- Cognitive analytics involves the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to simulate human thought processes. It enables systems to learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously, enhancing the depth and speed of data analysis.
- Companies like Amazon, Uber, Microsoft, Starbucks, and Apple employ business analytics for pricing, operations, marketing, and customer insights. Choosing the right analytics job type depends on your goals, demand, and resources.
