What is Blockchain?
A Blockchain is a continuously growing list of linked and secured blocks using cryptography. Blockchain is a cryptographically secure transactional singleton machine with a shared state. Blockchain aims to take control from a single company/organization and distribute it to all its members. This way, everyone, not just one person/organization, will be involved in the decision.
Let’s break this down:
- Cryptographically secure means that it is secured by complex mathematical algorithms that are very hard to break.
- Transactional Singleton machine means that there is only one instance(single occurrence) of the machine responsible for creating all the transactions in the system.
- Shared state means that the machine's latest state(state is simply the condition of something at a specific time) is shared and open to everyone.
How Does Blockchain Work?
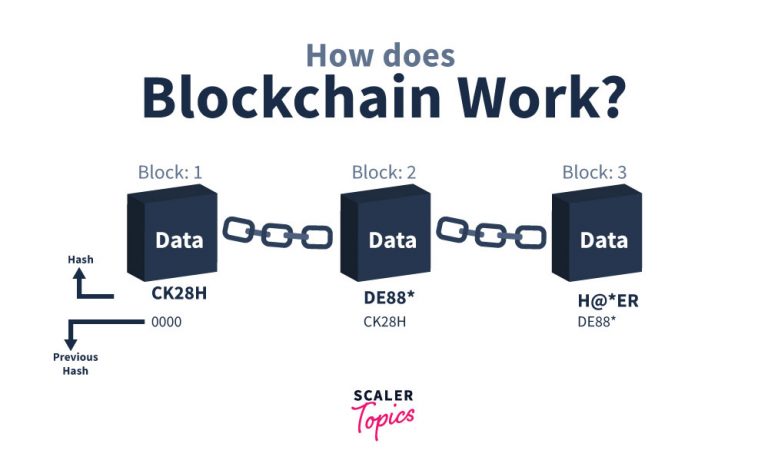 Blockchain, as the name suggests, is just a chain made up of individual data blocks.
Blockchain, as the name suggests, is just a chain made up of individual data blocks.
The working process is simple: a new block is created and attached to the chain whenever fresh data needs to be added. After it has been attached, all the computers connected to the blockchain network update their cloned copy of the Blockchain. This is because it is decentralized and distributed to everyone in the network, so everyone needs to have an identical copy of the Blockchain.
This process looks simple, let’s dive a little deeper and understand how the creation and addition of blocks to the chain happens.
There are three main concepts: Nodes, Blocks, and Miners.
1. Nodes
Blockchain is a distributed ledger(a database that stores all the information in the Blockchain) via the nodes connected to the network. Any electronic item that maintains a copy of the Blockchain can be considered a Node.
There is a copy of the Blockchain to every node. Whenever a new block needs to be added, the network algorithmically approves any newly mined blocks for the chain. Blockchain is open so that every action can be viewed and checked.
Nodes are responsible for accepting or rejecting a transaction, as they check whether a transaction is valid. They are the heart of Blockchain.
2. Blocks
Blocks are the building blocks of the Blockchain.
There are three essential elements in a block.
- Data
- 32-bit number called nonce. It is randomly generated when a block is created.
- Hash: It is a 256-bit number that is generated with the help of nonce.
Blocks can be considered as files where the network data is permanently recorded. Once written, it cannot be altered.
3. Miners
Miners are the people/computers responsible for everything, like creating new blocks and solving complex math problems.
Miners create new blocks, and the process of creating new blocks is called mining. Every block in the Blockchain has a unique nonce and hash, and it also stores a link to the previous and next block with the help of the hash of each block.
The main job of a miner is to solve highly complex math problems. It involves finding a nonce value that generates an accepted hash. Well, a nonce is a 32-bit number, and a hash is a 256-bit number, so roughly, there are 4 billion possible nonce-hash combinations (232).
When a block is created and added successfully, the miner is rewarded financially. This is why so many people are getting into mining with large and expensive setups.
Because of this complexity, it is said that Blockchain is immutable(unchangeable). If anyone wants to change any block, it requires re-mining, not just the block with the change but also all the blocks that come after that block.
Types of Blockchain Networks
There are four different types of Blockchain
1. Public Blockchain
Public or permissionless blockchains are the ones that are open to everyone. Anyone can take part and use them. Every node in the public Blockchain is authorized to access the Blockchain (single shared state).
In a public blockchain, the history of changes is visible to everyone in the network. In this, the speed of transactions can be slow as there are many people, and to ensure security, the addition of blocks takes time.
Some famous examples of this are Bitcoin, Ethereum, etc.
2. Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are like the reverse of public blockchains. They are authorized. These operate in a closed network.
Many organizations use Blockchain for their internal purpose. It is not safe to share any sensitive information on a public network. So, for their purpose, many organizations have created their internal blockchains whose access is given to the people the owner organization allows to.
These can be helpful in the scenario of Elections, asset management, health care, real estate, government services, and insurance.
Due to their small size and the fact that only authorized people can access a private blockchain, they can be faster than public Blockchain in many cases.
Some examples are Hyperledger, Ripple, etc.
3. Hybrid Blockchain
A hybrid blockchain is a blockchain that tries to use the best parts of both private and public blockchains.
In this, the members can decide who can participate in the Blockchain and which transactions are made public.
Companies can use both private and public blockchains to create their hybrid system.
For example, XinFin has developed a Ramco System system for managing Supply Chain logistics, which uses Ethereum (public Blockchain) and Quorum (private Blockchain).
4. Consortium Blockchain
Consortium or Federated Blockchain is a blockchain technology where multiple organizations govern the platform. This is a permissioned network.
This may look very similar to a private blockchain, but one important difference exists. In a private blockchain, there is only one organization on the platform, but there are multiple organizations in the consortium. This ensures the decentralized nature of blockchain technology.
Use cases of consortium blockchain can be Banking and payments, food tracking(IBM food trust), and shipping.
Blockchain Use Cases and Applications
Many people and organizations consider Blockchain to be a revolutionary technology. Hence, over the years, Blockchain has been used in several applications.
1. Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies are digital currencies that use blockchain technology to record and secure every transaction. Cryptocurrency is an application of Blockchain. Many people think that Cryptocurrency is Blockchain, but that is wrong!
Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Dogecoin are all cryptocurrencies, and if both parties agree, these can be used to buy or sell goods and services just like we do with Dollars, Rupees, Euros, etc.
Cryptocurrencies use a public blockchain, so the transactions are secure and transparent.
Many people and organizations believe that in the coming years, cryptocurrencies will replace our current money (fiat money).
2. Banking
Blockchain is being used to carry out transactions in fiat currency (dollars, rupee, euro, etc). Transactions with a blockchain are faster than financial institutions and can be carried out during non-business hours. The verification of transactions in the case of Blockchain is also faster.
Other than transactions, it can help in fraud detection as every individual on a blockchain network has a unique identification number, and cryptocurrencies operate on public blockchains.
3. Asset Transfers
Not only the transfer of money but Blockchain can also be used to transfer ownership of various types of assets, if not all. Recently, this idea has become popular with the rise in popularity of NFTs(Non-Fungible Tokens), which represent ownership of digital arts and videos.
Organizations are working on implementing blockchain technology to include the transaction of assets like real estate, vehicles, etc., which will reduce the paperwork involved while buying these assets. In such a scenario, both parties will use Blockchain to verify if the seller owns the asset and if the buyer has enough money to buy the asset. If the conditions match, then the transaction can be carried out.
This method will eliminate brokers and increase the rate at which these transactions occur, making the transaction paperless.
4. Smart Contracts
An excellent analogy to understand smart contracts is the Vending Machine. When certain conditions (money and drink choice) are met, the contract gets executed (you get the drink!).
A smart contract is a script that, when called with specific parameters, performs some action or computation if certain conditions are satisfied.
Smart contracts are beneficial because they are secure and trustworthy. With smart contracts, two or more parties making the deal do not have to involve an intermediary; a smart contract works as a reliable mediator to execute the transaction.
Smart contracts can be used in asset deals. If someone wants to sell a house, then a smart contract can be written that will receive the payment from the buyer and transfer it to the seller once the ownership of the asset is transferred.
5. Supply Chain Monitoring
A supply chain is a complex system which involves several external intermediaries. Blockchain can have many benefits in supply chain monitoring.
It can reduce the cost of transactions and make them transparent. In a supply chain, many transactions need to be made overseas, and these can be made faster and less expensive to execute with the help of a blockchain.
It helps to reduce fraud in the chain and thus makes the supply chain more reliable.
It helps in auditability as data cannot be changed once entered into the Blockchain. So the authorities’ work and a lot of paperwork are reduced.
Walmart has been working with IBM since 2016 to create a blockchain for its food supply chain.
6. Elections
Elections are a field with the potential for a lot of fraud. There have been incidents in the past where people were found guilty of modification of votes. Votes are changed in the ballot boxes, and so on.
Blockchain has great potential to be used in voting as it will be impossible for any party to change the information on a blockchain. Several countries are working with companies to create a blockchain solution that will be implemented shortly.
Blockchain Decentralization
Decentralization means there is no single point of control. The decisions are made collectively with the help of consensus by all the nodes on the network.
Decentralization comes with a drawback of speed. Transactions take more time as they need to be verified by multiple nodes; hence, there is a decrease in speed.
Blockchain Security
Blockchain is considered secure as there needs to be a consensus if anyone needs to add something to the blockchain database.
In the past, however, some source codes have been hacked. These mainly include the code written by the smart contract creator.
Blockchain Scalability
Scalability is the ability of a system to handle the growing number of transactions. Blockchain solutions need to be scalable because more and more people will join and use the network.
Current blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum are capable of handling much much lower number of transactions per second compared to centralized solutions like VISA.
Pros and Cons of Blockchain
Pros
- Establishes trust among the parties involved in transactions
- Higher security
- Removes the need for third-party intermediaries.
- Allows participants to check the authenticity
- Transparency
- Create a tamper-proof record
- Greater transparency
- Automation
Cons
- Limit the number of transactions per second
- High energy costs
- Can be used for illegal purposes
- Risk of asset loss (You need to remember the key of your wallet)
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain
Bitcoin and Blockchain are intertwined technologies, but they serve distinct purposes. Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency, a form of cryptocurrency, enabling secure, peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries like banks. It operates on a blockchain, a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. The latter is a broader concept—a decentralized, tamper-resistant ledger technology. Blockchain finds applications beyond currency, offering transparent and secure records in supply chain, finance, and healthcare industries. In essence, Bitcoin represents a use case, illustrating the potential of blockchain technology in creating transparent, secure, and decentralized systems for various applications.
Blockchain vs. Banks
Blockchain challenges the traditional banking model by providing a decentralized, transparent, and secure ledger for financial transactions. Unlike banks, which rely on central authorities, Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, reducing the need for intermediaries. This fosters faster, more accessible, and cost-effective transactions. Blockchain's transparency, achieved through cryptographic verification, contrasts with the privacy banks maintain. At the same time, banks remain integral to traditional finance.
How is Blockchain Different from the Cloud?
Blockchain and the cloud are distinct technologies. The cloud is a centralized data storage and processing system managed by third-party providers. In contrast, Blockchain is a decentralized, tamper-resistant ledger technology for secure and transparent transactions. While the cloud relies on a central authority, Blockchain operates on a distributed network without intermediaries, ensuring transparency and trust through consensus mechanisms. Blockchain concerns decentralized trust and data integrity, while the cloud focuses on centralized, scalable computing resources. Both have unique applications, with the cloud excelling in data storage and computation, while Blockchain revolutionizes trust in transactions without a central point of control.
Investing in Blockchain
Blockchain is not an asset but a technology, meaning you cannot directly invest in it. There are several other ways to invest in Blockchain, the easiest being cryptocurrency. This has become a popular choice nowadays, and many people are getting involved in buying, selling, and mining crypto.
Another way to get involved in the Blockchain is by buying digital assets as NFTs(Non-Fungible Tokens). Buying an NFT is purchasing the ownership of an asset.
From a business point of view, you can buy the stocks of the companies that are creating their blockchain solutions or using Blockchain for their use. You can also work for these companies as a software developer and make smart contracts or d-apps.
Conclusion
- Blockchain is a new technology that aims at solving many real-world problems.
- It is a decentralized solution that adds data in the form of blocks, which are linked to each other to form a chain with the help of cryptography(math).
- In Today's scenario, Blockchain is a demanding technology in Software Engineering. Click here to learn how to become a blockchain developer.
