What Is GitHub?
GitHub is a web-based platform for version control and collaboration, enabling developers to manage and track changes in their code repositories. It supports Git, a distributed version control system, allowing multiple contributors to work on projects simultaneously. GitHub facilitates seamless collaboration through features like pull requests, issues, and branching. Developers can host and share code, contribute to open-source projects, and track issues. It serves as a hub for software development, fostering community collaboration and providing tools for project management. GitHub has become a central platform for code hosting, collaboration, and the open-source software development community.
What is GitHub?
The answer to What is Git hub is, GitHub is a cornerstone in the realm of software development, serving as a web-based platform that revolutionizes collaboration, version control, and project management. Founded in 2008, GitHub employs Git, a distributed version control system, allowing developers to efficiently track changes in their code repositories. It has become a central hub where individuals and teams can host, share, and work on software projects.

At the heart of GitHub is the concept of repositories, which are storage spaces for code and related assets. These repositories can be public or private, fostering both open-source collaboration and secure, proprietary development. GitHub's branching mechanism enables developers to work on different aspects of a project simultaneously, facilitating parallel development without conflicts.
- One of GitHub's pivotal features is the pull request system. This mechanism allows developers to propose changes to a project, which are then reviewed and discussed before being merged into the main codebase. This promotes a collaborative and transparent approach to code modifications.
- GitHub also integrates issue tracking, providing a structured way to manage tasks, bugs, and feature requests. This enhances project organization and helps teams stay focused on their goals.
- Beyond its technical functionalities, GitHub serves as a social platform for developers. User profiles allow individuals to showcase their work, contributions, and affiliations. This fosters a sense of community, enabling developers to connect, learn from each other, and collaborate on projects of mutual interest.
- GitHub's impact extends to the broader open-source ecosystem, hosting millions of projects that are freely accessible and modifiable by the global community.
- Its user-friendly interface and compatibility with various programming languages have contributed to its widespread adoption, making it a fundamental tool for software development teams and individuals alike.
How does GitHub work?
GitHub users undertake various actions such as setting up accounts, uploading files, and initiating coding projects. However, the true essence of GitHub unfolds when users engage in collaborative endeavors.
While coding independently is feasible, the construction of most development projects involves the collaborative efforts of teams. Although these teams may occasionally work in a shared physical space, more commonly, they operate asynchronously. The challenges of creating collaborative projects with distributed teams are numerous, but GitHub significantly simplifies this process through various means.
Firstly, GitHub serves as a centralized repository where all code and documentation reside. This centralization mitigates accessibility issues, providing a streamlined way for anyone to contribute to a project. Each repository also incorporates essential instructions and details that outline project goals and rules.
Coding, often perceived as a creative and abstract process, poses challenges, especially when multiple developers are working on different sections of code. Ensuring seamless integration becomes crucial, as one piece of code may inadvertently disrupt another. GitHub addresses these challenges by visually demonstrating how changes in both files will impact the main branch. This preemptive conflict detection enhances the efficiency of the coding process by identifying potential issues before changes are pushed.
Furthermore, GitHub facilitates the tracking of changes and reverting to previous project versions. To grasp this functionality, it is imperative to delve into the foundational technology of GitHub—Git—and delve into the concept of version control.
GitHub transcends being a mere platform for individual actions; it evolves into a collaborative space where diverse contributions converge. Through centralized organization, conflict detection mechanisms, and robust version control capabilities, GitHub plays a pivotal role in simplifying collaborative coding endeavors for teams, regardless of their geographical dispersion.
What is Git?
Git is a powerful and widely used open-source distributed version control system created by Linus Torvalds in 2005. At its core, Git is designed to manage and track changes in source code during software development, providing a structured and efficient way for multiple developers to collaborate on a project.

What sets Git apart is its distributed nature. In Git, each developer working on a project has a complete copy of the entire codebase and its history on their local machine. This decentralization enables developers to work independently and make changes without the need for a constant connection to a central server. The full history and code repository are available locally, allowing for quick and seamless branching and merging of code.
Branching is a key feature of Git, allowing developers to create separate lines of development for features, bug fixes, or experiments without affecting the main codebase. These branches can later be merged, preserving a coherent project history.
Git has become a fundamental tool in the software development workflow due to its efficiency, speed, and flexibility. It provides a reliable way to track changes, collaborate effectively, and manage complex projects with multiple contributors. The high adoption rate, with over 87% of developers using Git according to industry surveys, highlights its widespread importance in the modern software development landscape.
What is Version Control?
Version control is a systematic and organized approach to tracking changes in files, particularly in the context of collaborative work or software development. It serves as a critical tool for managing different versions of a project over time, offering a structured way to handle modifications, track history, and coordinate contributions from multiple individuals.
In essence, version control provides a snapshot of a project's state at different points in time. It allows developers, or any collaborators, to revisit and compare various versions of files or the entire project, facilitating collaboration, troubleshooting, and project management.
One of the key functionalities of version control is the ability to create branches. Branching enables developers to work on different features or bug fixes independently, maintaining a separation until changes are ready to be merged back into the main codebase. This approach ensures that ongoing development does not interfere with the stability of the existing project.
Moreover, version control systems help in detecting and resolving conflicts that may arise when multiple contributors make changes to the same file simultaneously. This prevents data loss and promotes a smooth collaboration process.
Advanced version control systems, such as Git, have become standard in the software development industry. They provide a distributed approach, enabling each developer to have a complete copy of the project's history and code on their local machine. This distributed nature enhances collaboration, allows for efficient branching and merging, and ensures a comprehensive and well-documented project history. Overall, version control is fundamental for maintaining order, consistency, and collaboration in projects undergoing continuous development or modification.
Why is Version Control helpful for Coding?
In the realm of software development, developers frequently and concurrently engage in updating code to introduce new features and rectify bugs. Directly implementing these changes to the source code poses potential issues that could adversely affect users. To mitigate this risk, developers operate on their individual copies of the code. After rigorous testing, the modified code is then seamlessly integrated into the main codebase.
Consider a scenario with multiple contributors; the process becomes intricate rapidly, especially without a mechanism to consolidate everyone's contributions into a cohesive codebase or discern individual contributors and their respective changes. It becomes imperative to systematically track and store each modification, aiding in troubleshooting and facilitating the restoration of previous versions when necessary.
This is where Git comes into play. When a developer aims to modify software, they follow a structured process:
- Download their copy of the source code from its central storage location, known as a repository, to their local system.
- Safely make modifications to their local copy.
- Merge the revised copy back with the source files in the repository.
- Add comments explaining the changes.
Git meticulously tracks all these modifications and preserves previous versions as backups. GitHub, in tandem with Git, enhances this process by providing visibility into changes made by developers as a group, streamlining troubleshooting efforts, particularly in complex projects. In essence, the combination of Git and GitHub systematically organizes collaborative development, ensuring transparency, organization, and effective version control in software projects.
What is GitHub used for?
GitHub enables software developers and engineers to establish free, remote, publicly accessible repositories in the cloud. Termed a "repo," a repository encompasses the files of a coding project and their revision history. After configuring a repository on GitHub, you can duplicate it to your local device, make local file additions or modifications, and subsequently "push" these alterations back to the repository, rendering your changes visible to the public.
Enhanced Collaboration
The most prominent feature that sets GitHub apart is its comprehensive set of project collaboration tools, encompassing version control and access control.
To illustrate the remarkable collaborative capabilities of GitHub, consider a scenario where you intend to develop an online game and decide to enlist the help of a friend. You initiate a repository on GitHub, serving as a centralized storage for all files, including current and past versions. Subsequently, you grant collaborator access to your friend, enabling them to contribute to this repository.
In this collaborative endeavor, you take charge of the main gameplay and screens, while your partner focuses on developing the game’s menu and settings screens. To ensure simultaneous development without interference, GitHub introduces the concept of branches, allowing for the creation of separate development areas. Consequently, your friend builds out their screens in their branch, while you continue your work in your designated branch.
Upon completion of your friend's work, they can initiate a pull request, proposing to merge their branch with yours. If you approve, the branches seamlessly merge, consolidating your collaborative code.
Imagine another developer discovering your game’s repository and envisioning the addition of a multiplayer mode. Using GitHub's forking feature, they create their own copy of your repository, integrating their new features.
Upon completion, this developer submits a pull request to you. With your approval, the forked repository merges with yours, enhancing your game with multiplayer functionality.
It's essential to note that while anyone can fork a public repository, the decision to accept or reject pull requests rests with the repository owners.
Recognizing that perfection is elusive in the initial stages of software development, GitHub incorporates an "Issues" section in your repository. This section serves as a dynamic space for listing to-dos, reporting problems with your game, engaging in discussions, and ultimately marking issues as resolved. In times of troubleshooting, consulting a file’s changelog becomes a valuable practice, providing insights into when and where issues occurred.
GitHub functions as a centralized hub where developers, ranging from a few individuals to extensive teams, can seamlessly contribute to a project. The platform eliminates concerns about overriding someone else’s work or losing track of changes, offering an efficient and organized collaborative environment.
Easy File Management
Employing GitHub eliminates the constraint of being confined to a specific device or environment. GitHub enhances the Git experience by introducing a sleek graphical user interface (GUI) layer, augmenting Git's command-line functionality. While developers are adept at utilizing the command line, it may not always be the most efficient means of interacting with files for many. GitHub's interface offers a streamlined and user-friendly alternative for executing Git actions and reviewing file history. This proves especially convenient for developers and facilitates accessibility for beginners navigating Git.
GitHub's accessibility is further amplified by its cloud-based infrastructure. Users can seamlessly access their repository from any location and device, facilitating the download of the repository and enabling the effortless push of their changes. In essence, GitHub's combination of a user-friendly interface and cloud-based functionality contributes to a more efficient and accessible experience for developers at varying skill levels.
Social Networking
For any user familiar with GitHub, it's evident that the platform extends beyond a mere workspace for coding. Each GitHub user possesses a profile showcasing their projects, contributions, and site activity. Moreover, users can explore the public-facing profiles and repositories of others. The social network aspect of GitHub is pivotal to its success, fostering an environment that encourages developers to delve into diverse open-source projects.
In the past, collaboration required aspiring contributors to reach out personally to project owners, seeking permission. GitHub has revolutionized this process, making it as simple as forking a project and initiating a pull request. Project owners can then review a contributor's profile and past contributions before approving their request. GitHub serves not only as a collaborative platform but also as a showcase for projects, acting as a portfolio for users. Recruiters leverage GitHub for talent scouting, capitalizing on the availability of prospects' code for comprehensive review and evaluation. This multifaceted social and professional dimension elevates GitHub beyond a conventional coding platform, contributing significantly to its widespread adoption and success.
Open-Source Projects
GitHub, propelled by the advantages we've explored, has ignited a surge in open-source collaboration, giving rise to numerous widely adopted software technologies. From CSS frameworks to data visualization libraries and engaging games, the realm of impressive accomplishments owes much to the existence of open GitHub repositories. Reflecting the trends of Web 2.0, GitHub has democratized software development, providing an inclusive platform for anyone keen on learning programming. This has led to the establishment of a vibrant, innovative, and productive community, where individuals from diverse backgrounds contribute to and benefit from the wealth of knowledge and projects hosted on the platform.
Private Repositories
Certainly, the question arises: how does GitHub generate revenue when everything is freely accessible and open-source? GitHub's financial model includes offering paid services, notably private repositories. Through a paid plan, teams gain the ability to collaborate on GitHub while maintaining the privacy of their code behind closed virtual doors. GitHub extends its revenue streams by providing enterprise solutions, furnishing organizations with comprehensive internal collaboration tools tailored to meet the specific needs and scale of large enterprises. In essence, while GitHub supports an expansive open-source ecosystem, its sustainability is ensured through the provision of premium services, enhancing collaboration and security for teams and organizations.
How to Get Started Using GitHub?
Before delving into GitHub, it's advisable to familiarize yourself with the command line since Git employs the terminal as its interface.
Install GIT
Ensure your device has the most recent Git version installed, a crucial step for GitHub repository collaboration. Having Git on your system is a prerequisite for effective interaction with your GitHub repository. Multiple installation methods exist, so it's advisable to adhere to the guidelines outlined on the official Git website . Importantly, the Git software comes without any cost, allowing users to access its features freely.
Sign up for GitHub
Upon successfully installing Git, navigate to GitHub's website and initiate the creation of an account using your email address.
Start a Repository
Upon the completion of setting up your GitHub account, you will be directed to your dashboard. To initiate your inaugural repository, click on "Create repository." This action allows you to centralize all the code associated with your new GitHub project in a unified location.
Name Your Project
In the "Create a new repository" interface, input your desired repository name and provide an optional description (modifiable later if needed).
Add Project Details
Within the same interface, include essential elements such as a README file, providing a text description of your project (considered a best practice in development), a .gitignore file to exclude irrelevant files like .DS_Store, and a license for your project. These additions facilitate a clearer understanding for collaborators, outlining project details and guidelines to be adhered to.
Create Your Repository
Select "Create repository," and you will be redirected to your primary repository page, displaying a list of your files.
Create a Local Copy of our Repository
Now, initiate the creation of a local copy of your GitHub repository, commonly referred to as "cloning." This step allows for file editing and facilitates the implementation of changes through pushing. On your main repository page, select the green Code button and copy the HTTPS URL assigned to your repository.
Even though a copy of your project exists on your hard drive, the cloning process is considered a best practice. It simplifies the tracking of file additions or removals, offering transparency into collaborative contributions. Moreover, cloning enhances the resolution of merge conflicts, streamlining the collaborative development process on GitHub. By adhering to this practice, you ensure a comprehensive overview of modifications, contributing to an efficient and well-organized workflow within the GitHub environment.
Choose a Directory
Launch your terminal and direct it to the desired directory where you intend to store your repository copy.
Paste your Repository URL
Within the terminal, type 'git clone,' and proceed to paste the repository URL you copied earlier. Your command should take the following form:
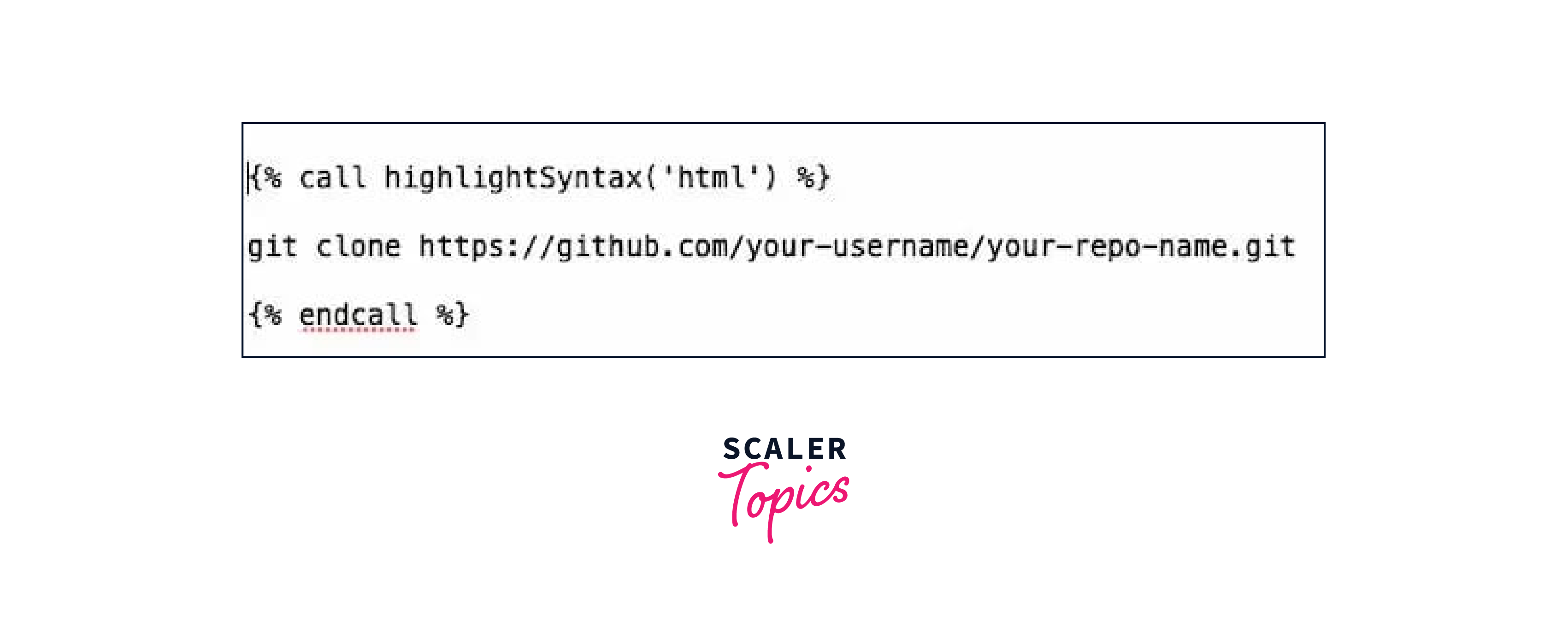
Clone And Check Your Copied Repository
Hit Enter to initiate the repository cloning. A new file, bearing your repository's name, will be added to your local filesystem. Upon opening this file, you'll observe it encompasses the files from your GitHub repository, serving as copied versions. These replicated files are editable, enabling you to make changes and subsequently push them back to your GitHub repository. This streamlined process allows for efficient local editing before implementing modifications on the central repository hosted on GitHub.
Create a New File in your New Repository
Conclude by generating a new file in your cloned repository and pushing it to GitHub. Within your local clone, generate a fresh text file named hello.txt. Insert the text "Hello, world!" into it and save the file. This process demonstrates how to locally create and modify files before pushing the changes to your GitHub repository, enhancing the collaborative and version-controlled development workflow.
Prepare to Push your Files
In the terminal, navigate to inside your cloned repository. Then, type git add . and press Enter. This prepares all files in your cloned repository to be pushed.
Commit Your Changes To The Changelog
Within the terminal, direct yourself to the interior of your cloned repository. Following this, input 'git add .' and press Enter. This command facilitates the preparation of all files within your cloned repository, ensuring they are ready for the subsequent push operation. This streamlined process is integral in the version control workflow, allowing for the systematic addition and synchronization of modifications made locally with the central repository on GitHub.
Push your Cloned Repository Files
Input 'git push origin main' into the terminal and press Enter. This command signifies the push operation to the 'main' branch of the origin repository, synchronizing your local changes with the central repository hosted on GitHub.
Check for your New File
Upon revisiting your GitHub repository, you will notice the addition of your new file. This marks the completion of the process, and you are now prepared to commence your work and initiate collaboration on your newly established project.
Conclusion
- GitHub is an online platform for version control and collaboration, allowing developers to manage, share, and work on software projects.
- GitHub provides a platform for hosting and collaborating on Git repositories, facilitating version control, collaboration, and project management in coding.
- Git is a distributed version control system for tracking changes in code, enhancing collaboration and managing project history efficiently.
- Version control is a system that tracks and manages changes to code or files, facilitating collaboration and maintaining project history.
- Version control in coding aids in tracking changes, managing collaboration, and reverting to previous states, ensuring organized and efficient development.
- GitHub is a platform for version control and collaboration in software development, enabling teams to manage and share code efficiently.
