What is IoT?
Overview
Internet of Things refers to the concept of connecting a device to other devices through the Internet. Such devices are capable of processing and are equipped with hardware and software suitable to a specific purpose, which the device fulfills.
What is IoT?
An IoT ecosystem consists of electronic devices, users, and at the center, the Internet. IoT aims to create interconnections of flexibly scalable sizes. In an IoT network, there are a number of digital devices connected to the internet.
Each device would ideally serve a specific purpose of its own. To be able to use internet access and perform various tasks, an IoT device is equipped with a microchip for processing.
Why is Internet of Things (IoT) so Important?
With technological advancements, increasing internet users, and more devices being evolved to more digital and responsive forms, IoT has greatly gained momentum. It has become an important tool in reducing the gap between a device and the user.
- IoT has helped eliminate barriers such as linguistic differences, physical disabilities, distant communication, etc.
- A.I. has become more accessible and portable than ever with the uprising of IoT in the form of A.I. SoCs (system on chip) and connection to A.I. on the cloud.
- Devices become more responsive, featureful and interactive. An IoT based clock for an instance does more than just showtime.
- IoT has enabled new advancements such as remote sensing, technological medical equipment, satellite technology components, etc.
- IoT devices help in more effective and efficient data collection.
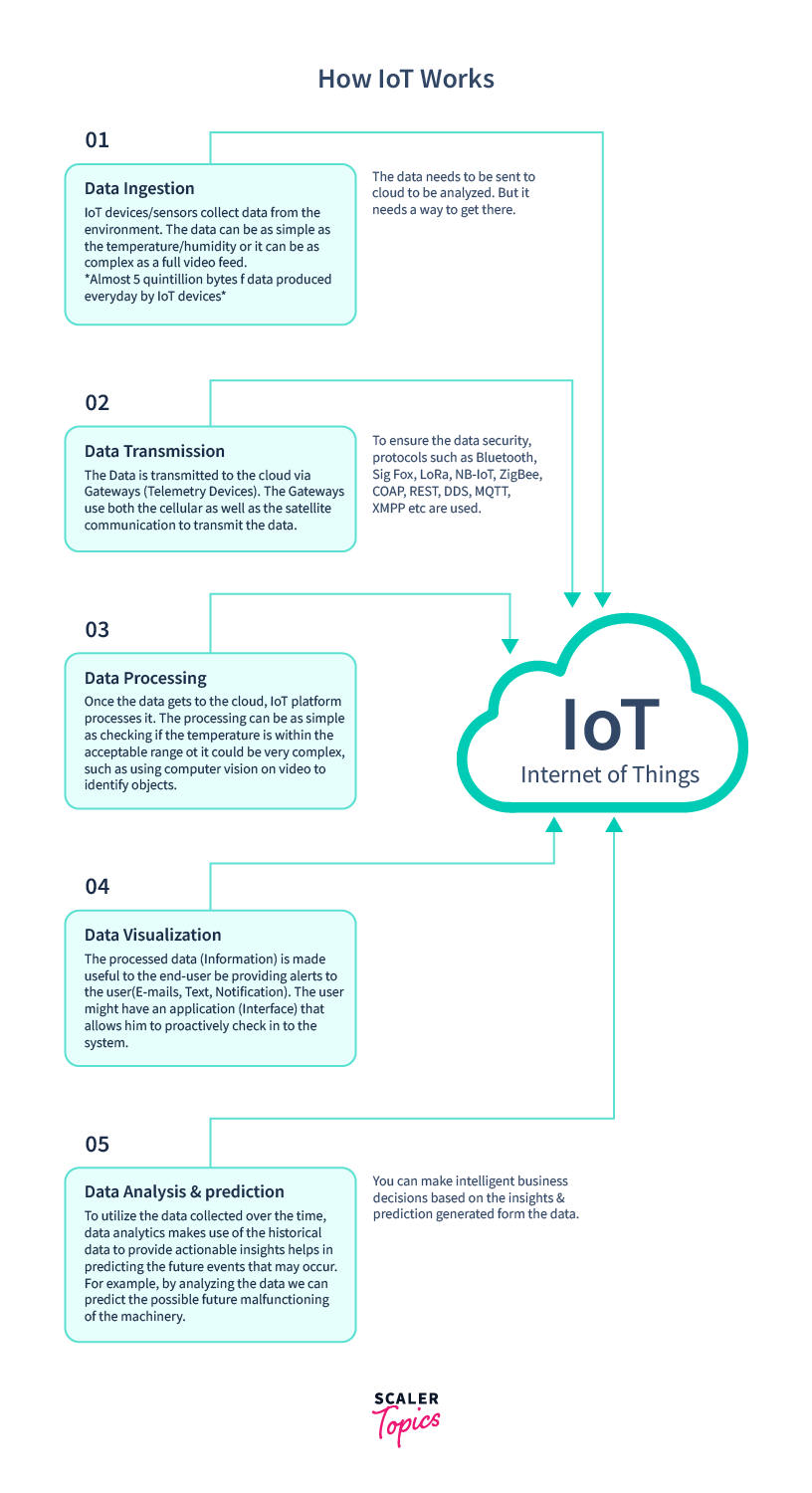
How Does IoT Work?
An IoT network consists of devices that have built-in sensors. Such devices are connected to a platform that stores data from them. The relevant data is then utilized for performing tasks that fulfill the requirements of users.
Data is stored on the IoT platforms, but not all of it would be useful. IoT devices select only certain data pieces that are significant to perform some task. These pieces of data are able to identify patterns, make recommendations, predict problems beforehand. Following are the four major components of an IoT ecosystem:
1. Sensors
sensors are embedded within the devices of an IoT network. A sensor obtains all the details from an environment that can have many complexities. Sensors detect even the most sensitive changes. this heavily improves security. These sensors collect all the data. Ex, a smartphone can detect a user's location.
2. Connectivity
After being collected, data is sent to the cloud infrastructure. It is also called an IoT platform. To transfer the data, the devices will need a medium. Connections like WAN, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, mobile networks, etc act as that medium. These media are different from one another and provide varying results and security effects.
3. Data Processing
On the IoT platform (cloud infrastructure) the data is analyzed. This process of analysis is one of the biggest obstacles in IoT application development. The analysis can be as simple as checking the speed of a fan or as complicated as using hybrid AI/software tech for identifying security intrusions using hardware such as infrared cameras. An IoT application should be developed in a manner such that it can process all the data efficiently and in real-time.
4. User Interface
In this step, the user is informed about the actions by making use of a notifier service or an alert system to the IoT application. This way the user will be informed that their commands have been executed in the systems.
Technologies That Have Made IoT Possible
Following three technological advancements have made it possible for IoT to come this far:
1. Increase in Processing Capability of Embedded Platforms
Microcontrollers have been replaced by general-purpose processors in computational devices because of ever-reducing cost, power requirements, and size in exchange for the same amount of processing potential.
This shift to modern CPUs is crucial because CPUs can run operating systems with support for major programming languages and complete networking stacks, something microcontrollers can not do.
2. Development of Small-footprint OSs and Protocols
With an increase in the performance of embedded platforms, the hardware demands of lightweight operating systems either reduce or remain unaltered.
On the protocol side, such a dynamic occurred as lightweight TCP/IP stacks were written for embedded platforms. And also new protocols were written keeping in mind the limited processing bandwidth and capability of these devices.
3. Development of Wireless Communications
Choices in connectivity methods for low power and small devices have been increasing in the consumer and industrial markets. Popular options include Xbee, Zigbee, cellular communications, mesh networking, Bluetooth, WiFi, etc.
Wired network connections are not always feasible to be used with IoT devices. Wireless network connections solve this problem.
Applications of IoT
- Smart Home setups such as Google nest, Amazon Alexa, etc. They consist of several gadgets such as screens, microphones, speakers, etc.
- Wearable equipment such as smartwatches, medical devices, personal health monitors, etc
- Smart city is a big innovation and spans over a variety of use cases such, as implementing which IoT plays a vital role.
- Smart grids promise to obtain data on the behaviors of consumers and electricity suppliers in an automated manner so as to improve efficiency and economy.
- Industrial usage such as connecting machines and devices in industries such as power generation, oil, gas, and healthcare.
- Smart cars are absolutely dependent on IoT technology.
- IoT has several applications in healthcare, such as remote monitoring equipment, smart sensors, equipment integration.
- Retailers have begun adopting IoT products and services across a number of applications that improve store operations.
- Through IoT physical retailers can compete against online challengers more strongly. They can regain their lost market share and attract consumers into the store, thus making it easier for them to buy more while saving money.
- Supply chains have been using IoT for some years now. IoT provides solutions to issues such as tracking goods while they are in transit, helping suppliers exchange inventory information, etc.
IoT Deployment
The initial planning does not have much to do with the technology of IoT. Rather, it is much related to what the business aims to achieve. The next step after setting business goals is to design a compliant network that will accomplish these goals.
A network design and specification must cover the schema of the network, the choice of components, their locations and measurement of their performance.
As soon as wireless technology is added to any project, the project's complexity is also increased. Not only must the correct system architecture be created, but also tackling the other challenges such as signal strength, etc is required. Mobile-based IoT deployments may also require a certification stage.
No deployment goes live without a fairly long period of intense testing. Technology is not the only aspect of testing. It is vital to also do checks against the original business goals.
After this, IoT deployment undergoes a digital transformation that improves efficiency, reduces costs, increases revenue, etc.
Industries Which Can Use IoT
1. Healthcare
IoT is used in creating a variety of medical equipment such as surgical instruments, monitors, etc.
2. Manufacturing Industry
IoT is used in various machines and robots that are deployed in manufacturing factories for interconnectivity.
3. Transportation and Logistics
IoT devices make transportation organizations smarter and more successful. They ensure cost-reducing, emissions-reducing, more efficient travel, better vehicles, improved security, and more strategic traffic management.
4. Retail
Smart retail stores enable retailers to run their business more effectively and increase profits by improving customer experience using data collection and digital connectivity. Common uses are online payments, surveillance, etc.
5. Municipal
Building managers globally are looking for IoT solutions for improving buildings’ quality as well as reducing costs.
6. Agriculture
IoT in farming enables monitoring fields using sensors, automating irrigation systems, weather forecasting.
7. Finance
IoT enables banks to assess their economic situation and offer customers services as per their requests which ensures building a healthy relationship. IoT technology ensures that customers’ financial data is kept secure.
8. Robotics
IoT is tremendously useful in robotics. It helps gather remote data, execute distant jobs, transmit information, etc.
9. Automobile
Self-driving cars are heavily dependent on IoT technology. Components such as screens, GPS, etc are used in vehicles of all types and are based on IoT.
10. Defense
The defense industry can use IoT to digitalize weaponry. This could boost military efficiency, expand the region of operability by using modern IoT gear such as drones, etc, use IoT-driven guided weapons such as missiles, UAVs, etc.
11. Space firms/tech
IoT is used in space industries for communication, data exchanging, and research purposes.
Conclusion
- Internet of Things refers to the concept of connecting a device to other devices through the Internet.
- With technological advancements, increasing internet users, and more devices being evolved to more digital and responsive forms, IoT has greatly gained momentum.
- Following are the four major components of an IoT ecosystem: sensors, connectivity, data processing, and user interface.
- Several industries such as defense, healthcare, space, finance, agriculture, and much more extensively.
