What is a Puppet in DevOps?
As DevOps methodologies keep getting traction in the field of software development, more and more software and tools are starting to get inculcated into the software development workflow. Here's the answer to 'What is Puppet DevOps', because you guessed it, puppet is one of these tools.
Puppet in DevOps is a tool that deals with system and state management. Its main core is streamlining and automating the configuration management process. Puppet is one of the most popular tools in DevOps when it comes to deploying applications and, managing and configuring states of servers.
There are two main versions of Puppet available in the market
Open Source Puppet
This version of Puppet comprises the basic fundamentals and elements of Puppet. With an Apache 2.0 License, it can be downloaded and used from Puppet's website without any prevailing costs. This is the way to go for individual developers and small businesses.
Puppet Enterprise
Puppet Enterprise comes with the full package, with all the functionalities and perks of Puppet being available to users. It is paid, but with Puppet Enterprise, businesses will be able to effectively use all features of Puppet without any complications.
The Current Landscape for Puppet in DevOps
To take a deep dive into What is Puppet DevOps, let's discuss how Puppet fits into the DevOps ecosystem.
Puppet is a powerful configuration management tool that enables IT teams to automate the deployment and management of software and infrastructure. Its open-source version, Open Source Puppet, is widely used by companies of all sizes, while Puppet Enterprise offers additional features and support options for larger enterprises.
One of Puppet's key features is its declarative language, which enables IT teams to define the desired state of their infrastructure and software in code. This makes it easy to automate repetitive tasks and maintain consistency across multiple servers and environments.
Puppet also provides a number of modules and templates that enable IT teams to quickly set up and manage common services like Apache, MySQL, and Nginx. These modules can be easily customized and extended to meet the specific needs of an organization.
In addition to its current features, Puppet is poised to continue evolving and adapting to the changing needs of DevOps. For example, Puppet is increasingly being used in containerized environments, where it can automate the deployment and management of container clusters.
Looking ahead, Puppet is well-positioned to continue playing a key role in DevOps environments. As the demand for automation and infrastructure as code continues to grow, Puppet's powerful features and flexible architecture make it an attractive solution for IT teams of all sizes.
The current landscape for Puppet in DevOps is dynamic and evolving. With its powerful features, growing community, and ability to adapt to new technologies and trends, Puppet is well-positioned to help IT teams automate their infrastructure and software for years to come.
Understanding Puppet Architecture
Puppet uses a client-server architecture to manage infrastructure and automate software deployment. The Puppet agent runs on client machines, while the Puppet server stores configuration data and manages the deployment of software and infrastructure changes.
Puppet architecture is composed of several key components, including:
Manifests
Manifests are the core building blocks of Puppet configuration. They define the desired state of the infrastructure and software, including packages, files, services, and users. Manifests are written in the Puppet configuration language and are executed by the Puppet agent.
Templates
Templates are reusable configuration files that can be customized based on the needs of different nodes. They are written in the Embedded Ruby (ERB) template language and allow for dynamic content generation based on variables defined in the Puppet manifest.
Files
Files are static resources that can be deployed to client machines by the Puppet agent. They can include any type of file, including configuration files, scripts, and binaries.
Modules
Modules are collections of Puppet code that provide pre-built functionality for managing specific services or applications. Modules can be shared across different nodes and can be customized as needed
Certificate authority
Puppet uses a public key infrastructure (PKI) to authenticate clients and servers and secure communication between them. The Puppet master acts as a certificate authority (CA) and generates and signs SSL certificates for both the Puppet server and the client.
How Does Puppet Work?
Puppet in DevOps works with a client-server architecture. Plus, it has nodes: master and agents. Master nodes are nodes which manage the subsequent agent nodes.
The agent nodes check the status of the master node every 30 minutes to determine if any changes need to be executed. If the master node shows an update, that's when the agent nodes download the necessary files and carry them out.
Let's use some illustrations to understand this concept better:
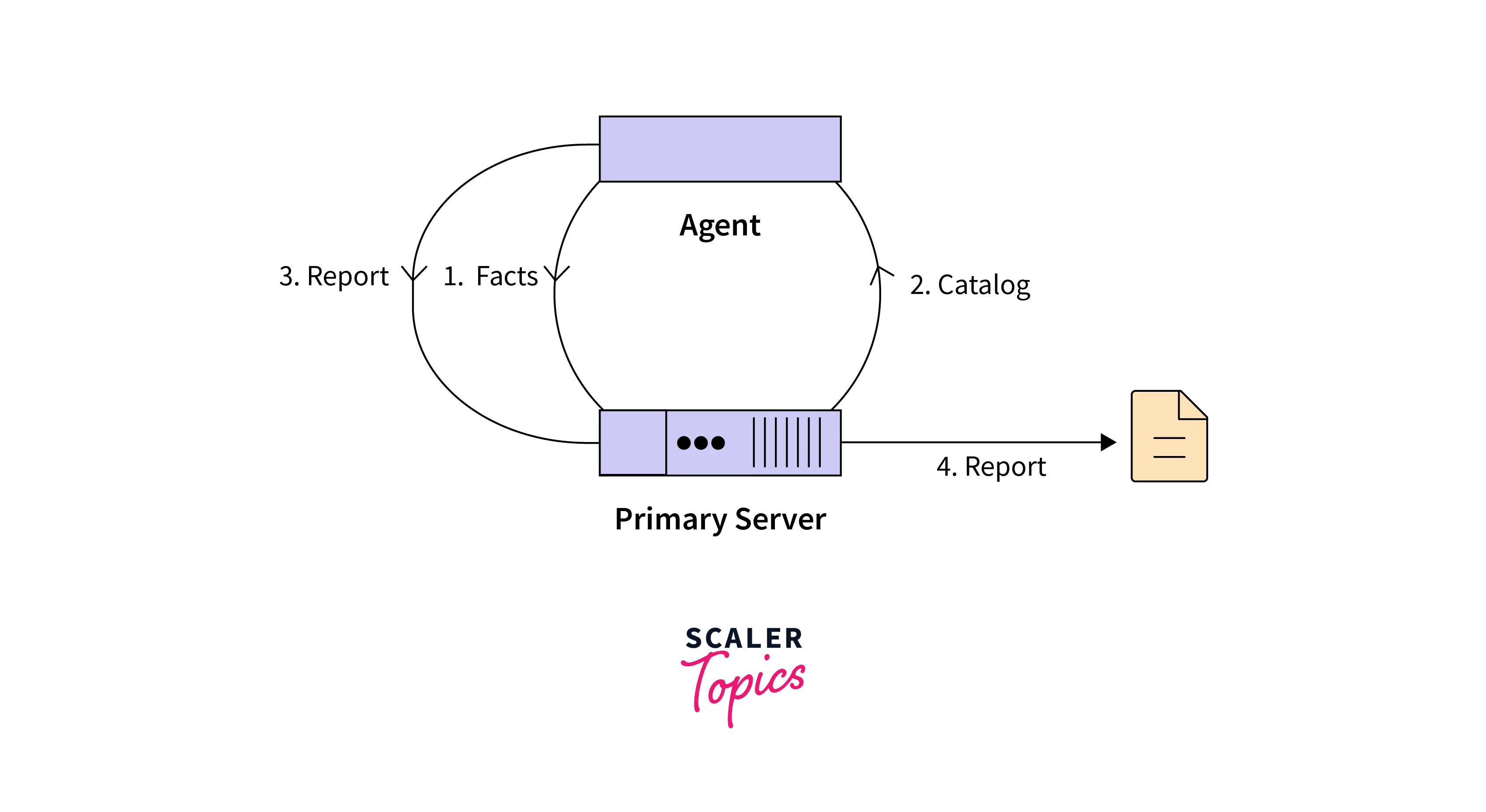
- We have a master node and 3 agent nodes.
- Each agent node signifies our servers or any type of infrastructure we want to manage using Puppet.
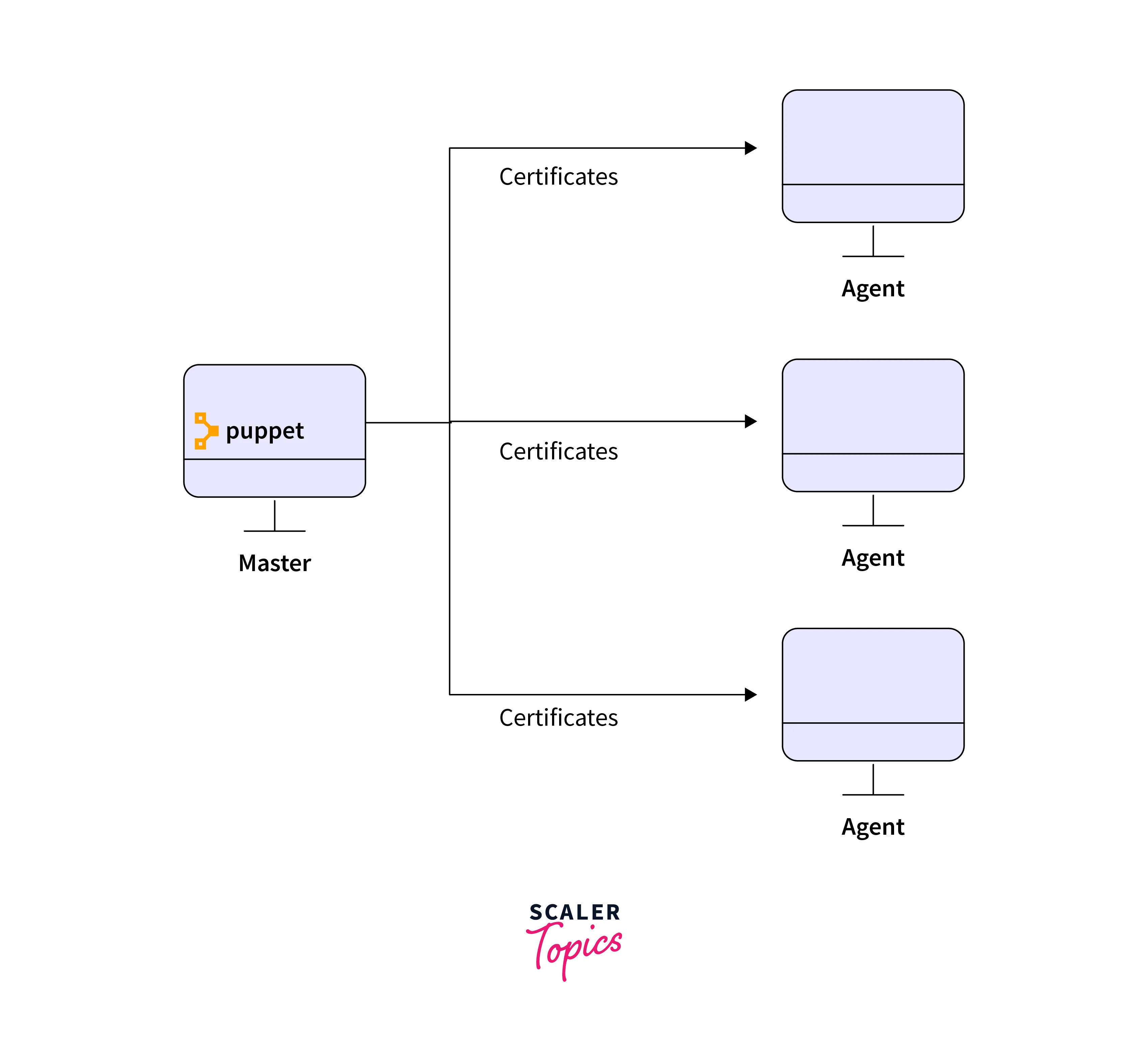
- The communication between master and agent nodes is handled via secure certificates.
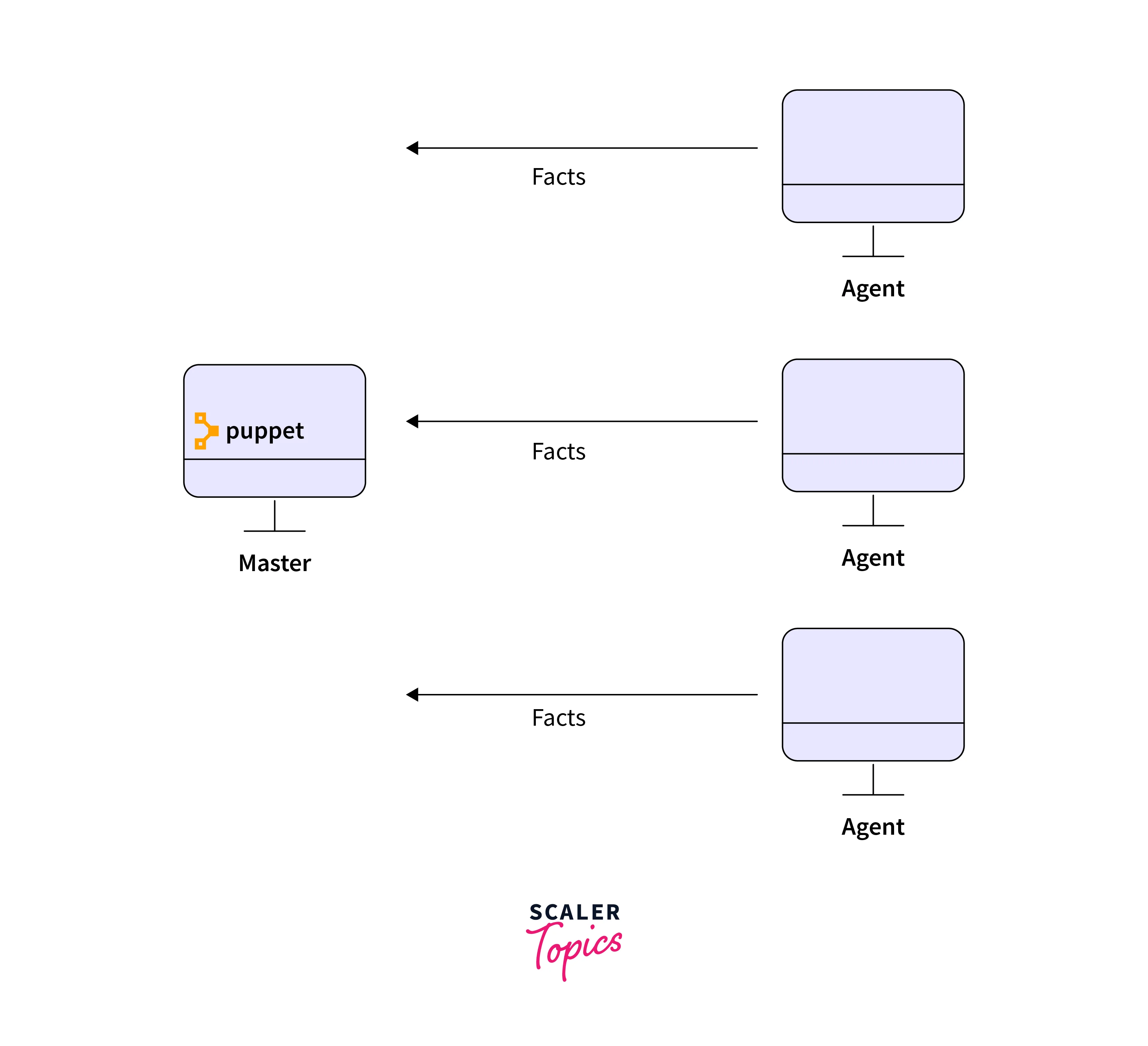
- Upon successful establishment of the connection, the agent nodes send facts to the master node. These facts comprise things like IP address, hostname, etc.
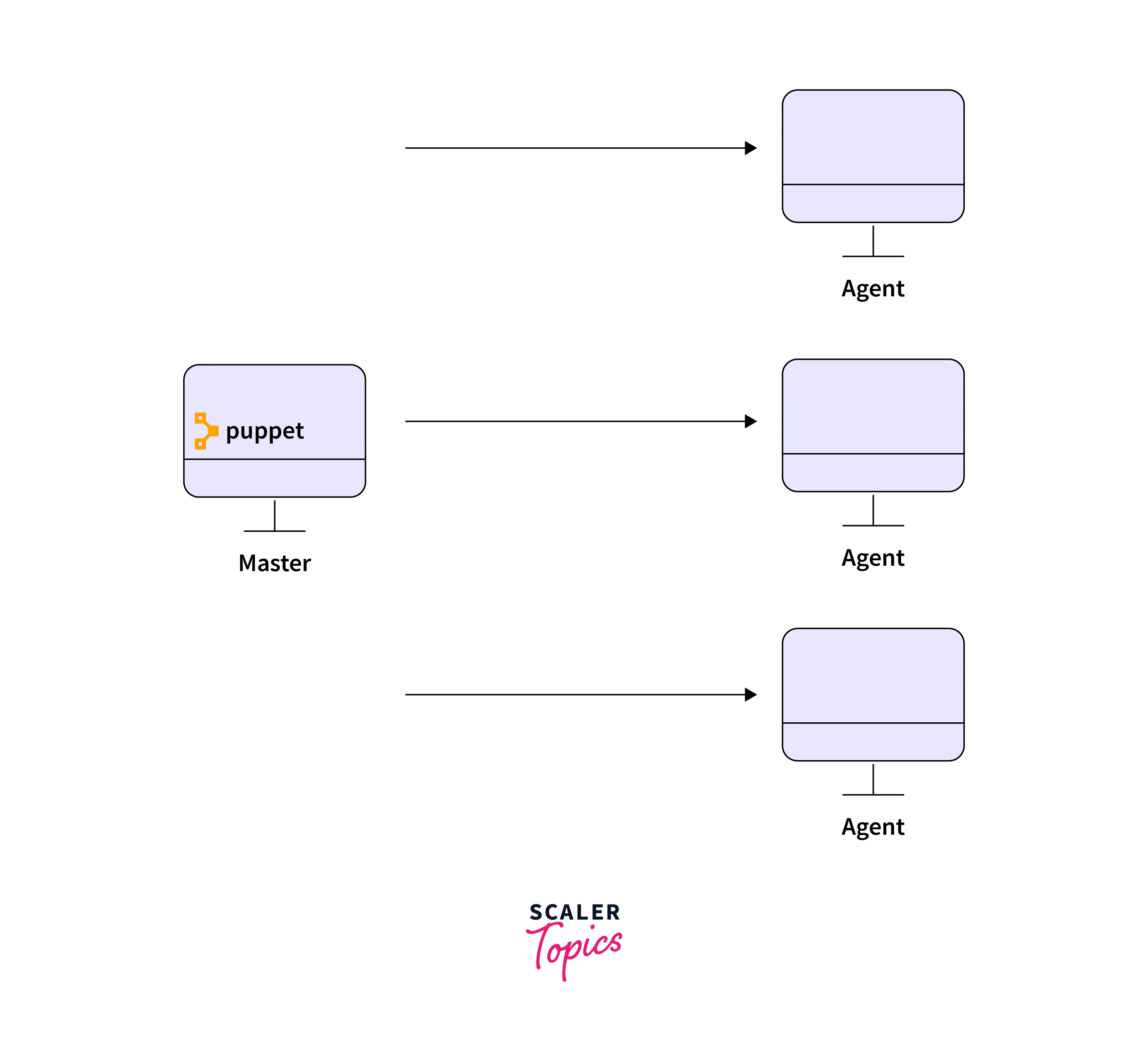
- The agent receives a catalog file. It checks to see if its current state is the same as the configuration given in the catalog file. If they're the same, the agent doesn't make any changes, but if they are different, the agent makes the required changes and acknowledges the changes to the master node.
For example, if we want to install a tool, let's say Apache, on each of our agent nodes, we can use this manifest file:
In this example, we define a class called "apache" that installs the Apache web server package, ensures the service is running and enabled, and creates a simple "Hello World from the Puppet Master!" index.html file in the web server's document root.
Then, the code includes the "apache" class in the configuration for each agent node ('agent1.example.com', 'agent2.example.com', and 'agent3.example.com').
When the agents check in with the Puppet master and receive their catalog, they will apply the Apache configuration specified in the "apache" class.
Why consider Puppet for DevOps?
Puppet in DevOps has become a popular choice among businesses due to its many benefits. In this section, we will discuss some of the key benefits of using Puppet for DevOps, and get even closer to the answer of What is Puppet DevOps.
Benefits
Efficiency
One of the main benefits of using Puppet is that it allows IT teams to automate routine tasks, such as software installation and configuration management. By automating these tasks, IT teams can reduce the amount of time and effort required to manage IT infrastructure. This allows them to focus on higher-value tasks, such as improving the performance and security of their systems.
Puppet also allows IT teams to use code to define and manage infrastructure and software configurations. This makes it easier to manage large and complex environments, as changes can be made more easily and consistently. This can lead to significant time and cost savings for IT teams.
Consistency
Another key benefit of using Puppet is that it helps ensure consistency across the IT environment. Puppet uses declarative language to define the desired state of infrastructure and software configurations. This ensures that configurations are consistent across all nodes in the environment.
This consistency reduces the risk of configuration drift, which can occur when manual changes are made to configurations. Configuration drift can lead to errors and inconsistencies in the environment, which can cause downtime and other issues.
Scalability
Puppet is designed to scale to meet the needs of large and complex IT environments. It can easily manage hundreds or thousands of nodes, making it an ideal choice for organizations with a large and distributed infrastructure. Puppet also supports cloud-based environments, making it easy to manage resources across multiple cloud providers.
Flexibility
Puppet allows IT teams to define infrastructure and software configurations in a flexible and dynamic way. This makes it easy to customize configurations based on the needs of specific nodes or groups of nodes. Puppet also supports multiple operating systems, making it a versatile tool for IT teams working with heterogeneous environments.
Puppet also supports various deployment models, including agent-based and agentless deployment. This flexibility allows IT teams to choose the deployment model that best fits their environment.
Security
Puppet provides several security features that help protect IT environments from security threats. Puppet's certificate-based authentication and encryption help to secure communication between the Puppet server and the agent. This ensures that configuration data and software deployments are protected from unauthorized access and tampering.
Puppet also supports RBAC (role-based access control) and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) integration, allowing IT teams to control access to infrastructure and software configurations.
Overall, using Puppet for DevOps can help IT teams improve the efficiency, consistency, scalability, flexibility, and security of their infrastructure and software deployment processes. By automating routine tasks and ensuring consistency, IT teams can focus on more strategic initiatives and drive greater value for their organization.
Best Practices
While Puppet can provide many benefits to IT teams, it's important to follow best practices to ensure a successful implementation. Here are some best practices to consider when using Puppet for DevOps:
- Start Small When starting with Puppet, it's important to start small and gradually build up your environment. Begin by configuring a few nodes, and then gradually add more nodes and complexity as you become more comfortable with Puppet. This approach can help you identify and address any issues early on, and avoid overwhelming yourself with too much complexity at once.
- Use Source Control Using source control can help you manage changes to your Puppet code and configurations. Source control allows you to track changes, collaborate with other team members, and revert to previous versions if needed. Consider using a tool such as Git to manage your Puppet code.
- Use Idempotent Code Idempotent code is code that can be run multiple times without changing the outcome. This is an important principle to follow in Puppet, as it ensures that your infrastructure and software configurations remain consistent and predictable. Make sure that your Puppet code is designed to be idempotent, and test it thoroughly to ensure that it behaves as expected.
- Use Roles and Profiles Roles and profiles are a common design pattern used in Puppet. Roles represent a specific node type, such as a web server or database server, while profiles represent a specific set of functionality that can be applied to multiple roles. Using roles and profiles can help simplify your Puppet code and make it more modular and reusable.
- Test Your Code Testing your Puppet code is essential to ensure that it behaves as expected. Puppet provides several testing frameworks, including rspec-puppet and beaker, that you can use to test your code. Make sure that you test your code thoroughly before deploying it to production, and consider using continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines to automate your testing and deployment processes.
- Take Measures for Security When using Puppet for DevOps, it's important to follow security best practices. This includes securing communication between the Puppet server and agents using certificates, encrypting sensitive data, and using RBAC to control access to Puppet resources. You should also regularly monitor and audit your Puppet environment to ensure that it remains secure.
By following these best practices, you can help ensure a successful implementation of Puppet for DevOps. These practices can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure that your Puppet environment is secure, reliable, and scalable.
Conclusion
- Puppet is a powerful tool that can automate the management of infrastructure at scale.
- The open-source version of Puppet offers a flexible and cost-effective solution for small to medium-sized businesses.
- Puppet's client-server architecture provides a secure and efficient way to manage nodes in a network.
- Puppet's modular design allows for easy customization and adaptation to different environments.
- Following best practices can help ensure that Puppet is used effectively and efficiently in a DevOps environment.
- As businesses continue to adopt DevOps practices, Puppet is poised to play an increasingly important role in managing infrastructure.
